Unit1 Medical Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
Diunggah oleh
Gokul RajanHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Unit1 Medical Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
Diunggah oleh
Gokul RajanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR, sed rate or Biernacki reaction) is a nonspecific measure of inflammation that is commonly used as a medical in vitro screening
test. The test was invented in 1897 by the Polish physician Edmund Biernacki and published
in Polish. In 1918 Swedish pathologist Robert Fhrus declared the same and along with Alf
Vilhelm Westergren published in English.
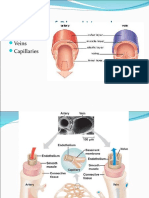
Anticoagulated whole blood in tube separates into an upper layer of plasma and lower
layer of blood cells because of gravity. Erythrocytes are heavier (their specific density-weight
is about 1.090kg/L and suspended in lighter plasma (which specific density-weight is about
1.027kg/L). The distance that cells fall (sedimentate) within a specified time interval (usually
1 hour) is defined as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). The rate of sedimentation of a
single erythrocyte is 0.2 mm/h but in vivo the sedimentation rate is higher, usually 1-2 mm/h.
In normal conditions erythrocytes settle faster because they aggregate (they form
stacks called rouleaux). ESR depends on the rate of aggregation (groups of 10 erythrocytes
settle 1 mm/h, groups of 50,000 erythrocytes settle 75 mm/h.
What factors elevates erythrocytes aggregation (and ESR)?:
Erythrocyte size,
Erythrocyte count,
Concentration of globulins (lipoproteins, glycoproteins, immunoglobulins),
Viscosity of plasma,
Concentration of albumin (after physical exercise, prolonged hunger).
However, the main factor in vivo is a ratio [albumin]/[globulins]. Elevation of globulin
concentration and decrease in albumin concentration reduces the electrical load of
erythrocytes and increase aggregating ability. ESR is an easy, fast and non-expensive
diagnostic method for observation of changes in plasma proteins.
Physiological states of increased ESR:
After meals,
After hot baths,
During menstruation,
After physical exercises,
Increases with age.
Pathological states of increased ESR:
Infectious diseases,
Neoplasmatic, invasive tumours,
Anaemias,
Chronic and acute diseases of liver,
Diseases of connective tissues.
Evaluation of ESR.
Elements of ESR set:
1. Plastic tubes with stoppers containing 0.25 mL of 3.1% solution of sodium citrate in
transport stand.
2. Glass multiple-use Westergren tubes with a scale ranging from 0 to 160, 180 or 200 mm.
Internal diameter is 2.5 mm (+/- 0.1 mm).
3. Sedimentation multiple-use vertical stand with 10 sockets.
4. Sedimentation multiple-use inclined (oblique) stand with 10 sockets (for fast ESR
evaluation).
Procedure:
1. Collect approximately 1.2 mL of the venous blood and open the citrate tube.
2. Fill the tube with blood up to the level of 1.25 mL, close the tube firmly and mix.
3. Introduce Westergren tube into opened citrate tube. The blood meniscus should reach
0 mm level Air bubbles should not be observed.
4. Place Westergren tube into the vertical stand (for an hour) or into the inclined (oblique)
stand (for 7 and 10 minutes) and then record the number of mm to which erythrocytes
have settled.
Reference values for of ESR:
Infants, children Adult males Adult females -
1 - 2 mm/h.
2 - 6 mm/h (0 10 mm/h).
3 - 10 mm/h (0 15 mm/h).
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hematology Chap 12Dokumen30 halamanHematology Chap 12Eyasu demsewBelum ada peringkat
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)Dokumen15 halamanErythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)Ramadan PhysiologyBelum ada peringkat
- PCV and EsrDokumen40 halamanPCV and EsrArslan Arshad100% (2)
- Hema I Chapter 12 - ESRDokumen30 halamanHema I Chapter 12 - ESRTesfaBelum ada peringkat
- Esr BML391Dokumen4 halamanEsr BML391Sinchan GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDokumen21 halamanErythrocyte Sedimentation RateKarshey Alagad ObutBelum ada peringkat
- Hema I Chapter 12 - ESRDokumen27 halamanHema I Chapter 12 - ESRSitra ZekeriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Hema I Chapter 12 - ESRDokumen29 halamanHema I Chapter 12 - ESRdileca1448Belum ada peringkat
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate: Stages of EsrDokumen2 halamanErythrocyte Sedimentation Rate: Stages of EsrErika Joille PatayonBelum ada peringkat
- ESR TestDokumen3 halamanESR TestTop SportsBelum ada peringkat
- Blood ComponentDokumen14 halamanBlood ComponentanandaronaBelum ada peringkat
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate: Definition DeterminationDokumen3 halamanErythrocyte Sedimentation Rate: Definition DeterminationAnusuya SBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Course 1Dokumen49 halamanLab Course 1lubna aloshibiBelum ada peringkat
- Packed Cell VolumeDokumen5 halamanPacked Cell VolumeMotasem Sirag Mohmmed othmanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 Blood As A Transport MediumDokumen43 halamanUnit 3 Blood As A Transport MediumKemoy FrancisBelum ada peringkat
- (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate: FemalesDokumen4 halaman(Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate: FemalesAhmed GaberBelum ada peringkat
- Aim: To Determine Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)Dokumen13 halamanAim: To Determine Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)Farhat jabeenBelum ada peringkat
- Water Dysbalance. EdemaDokumen8 halamanWater Dysbalance. EdemaIvan YeohBelum ada peringkat
- Shrutietalpublishedin IJPBSDokumen5 halamanShrutietalpublishedin IJPBSmiBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 08Dokumen9 halamanLesson 08asyafujisaki100% (2)
- RRMechatronics WhitePaper ESRDokumen20 halamanRRMechatronics WhitePaper ESRSri IriantiBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate & Osmotic FragilityDokumen3 halamanDetermination of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate & Osmotic FragilityPRASANTH KRISHNABelum ada peringkat
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDokumen3 halamanErythrocyte Sedimentation RateGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Clinical HematologyDokumen42 halamanIntroduction To Clinical HematologyBishoy GalalBelum ada peringkat
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)Dokumen7 halamanErythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)Mrym DestinyBelum ada peringkat
- Wintrobe Test PDFDokumen9 halamanWintrobe Test PDFMaria Chacón CarbajalBelum ada peringkat
- Esr and CRP: By: Saurabh Gupta Moderator: Dr. Rumpa DasDokumen44 halamanEsr and CRP: By: Saurabh Gupta Moderator: Dr. Rumpa DasMandavi HindBelum ada peringkat
- Capp&Dwe TomeldenfinalDokumen74 halamanCapp&Dwe Tomeldenfinaltomeldenalyssa13Belum ada peringkat
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDokumen7 halamanFluids and ElectrolytesNeweeJoonYowBelum ada peringkat
- Hema311 Lab - Week 10 - Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, Smear Preparation, and Osmotic Fragility TestingDokumen4 halamanHema311 Lab - Week 10 - Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, Smear Preparation, and Osmotic Fragility TestingJayvhie Gulane LayanBelum ada peringkat
- Teste ImunologiceDokumen20 halamanTeste ImunologiceuscatuscribBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid and Electrolytes Assignment 1. What Are The Different Processes of Body Fluid and Solutes Movement? and Give at Least 2 Examples EachDokumen8 halamanFluid and Electrolytes Assignment 1. What Are The Different Processes of Body Fluid and Solutes Movement? and Give at Least 2 Examples EachAngelicaBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid and Electrolytes Assignment 1. What Are The Different Processes of Body Fluid and Solutes Movement? and Give at Least 2 Examples EachDokumen8 halamanFluid and Electrolytes Assignment 1. What Are The Different Processes of Body Fluid and Solutes Movement? and Give at Least 2 Examples EachAngelicaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3 - CIrculation Part 1 - BLOODDokumen28 halamanTopic 3 - CIrculation Part 1 - BLOODSANA ZAMANBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Phase ReactantsDokumen9 halamanAcute Phase ReactantsSuresh KumawatBelum ada peringkat
- 9) (Lab) ESR (C. Patho)Dokumen15 halaman9) (Lab) ESR (C. Patho)Haider AliBelum ada peringkat
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Solution and ProcedureDokumen13 halamanErythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Solution and ProcedureCherenet TomaBelum ada peringkat
- A Comparative Study of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (Esr) UsingDokumen5 halamanA Comparative Study of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (Esr) UsingRaffaharianggaraBelum ada peringkat
- ReferenceDokumen7 halamanReferenceShaker MUhammedBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of Estimation, Clinical Use and Corrected Esr: Moderator: DR Mohd. Faheemuddin Speaker: Dr. Chandra ShekharDokumen57 halamanMethods of Estimation, Clinical Use and Corrected Esr: Moderator: DR Mohd. Faheemuddin Speaker: Dr. Chandra ShekharChandra ShekharBelum ada peringkat
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDokumen9 halamanErythrocyte Sedimentation RateNitesh Kumar KarnaBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology NotesdocxDokumen11 halamanHematology NotesdocxdmclmllBelum ada peringkat
- Definition of ShockDokumen29 halamanDefinition of Shockrazan asadBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Pathophys SGD 1Dokumen6 halamanRenal Pathophys SGD 1ReptarBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Diagnostic TestsDokumen14 halamanCardiac Diagnostic TestsSimran Josan100% (5)
- Istinye University Medical Faculty Physiology Lab Notes Blood Sampling Capillary Blood SamplingDokumen7 halamanIstinye University Medical Faculty Physiology Lab Notes Blood Sampling Capillary Blood Samplingazouz jaboobiBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial ReportDokumen24 halamanTutorial ReportindraniptrBelum ada peringkat
- Post Lab 01-09Dokumen7 halamanPost Lab 01-09Patrick ParconBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids and Electrolytes: Presented byDokumen17 halamanFluids and Electrolytes: Presented byJohn Henry ValenciaBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids & ElectrolytesDokumen15 halamanFluids & Electrolytesarvinnnn100% (2)
- Hematopoiesis Is The Complex Process of The Formation and Maturation of Blood CellsDokumen35 halamanHematopoiesis Is The Complex Process of The Formation and Maturation of Blood CellsYary MayorBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem Lab 1Dokumen8 halamanBiochem Lab 1Kristine PangahinBelum ada peringkat
- LABORATORY WORK 1 (RBCs) 1 семестрDokumen10 halamanLABORATORY WORK 1 (RBCs) 1 семестрCastleKGBelum ada peringkat
- L 5.1 Fixation and Fixatives UpdatedhDokumen19 halamanL 5.1 Fixation and Fixatives UpdatedhshaikhaboausaibaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hematologic DisordersDokumen124 halamanAssessment and Management of Patients With Hematologic DisordersAngelicaMarieRafananBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology Finals SallybusDokumen18 halamanHematology Finals Sallybusmomin.laangBelum ada peringkat
- Rudaina Alelyani MEV Assignment3.Dokumen15 halamanRudaina Alelyani MEV Assignment3.Rudaina AlelyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Haemodynamic Disorders SMS 313 2021Dokumen87 halamanHaemodynamic Disorders SMS 313 2021Dei BenjaminBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology and Etiology of Edema - IDokumen9 halamanPathophysiology and Etiology of Edema - IBrandy MaddoxBelum ada peringkat
- Method B This Method Uses A Numerical Designation From The Table As Listed BelowDokumen1 halamanMethod B This Method Uses A Numerical Designation From The Table As Listed BelowGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Method A This Method Uses An Alpha/numerical Designation From The Tables As Listed BelowDokumen1 halamanMethod A This Method Uses An Alpha/numerical Designation From The Tables As Listed BelowGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- ExpenceDokumen2 halamanExpenceGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Investing in Teacher: Investing For The FutureDokumen2 halamanInvesting in Teacher: Investing For The FutureGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- 4.1 Features of The Weld PreparationDokumen1 halaman4.1 Features of The Weld PreparationGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Crater Cracking: Rev 1 January 2009 TIG Welding © TWI LTD 2009Dokumen1 halaman5 Crater Cracking: Rev 1 January 2009 TIG Welding © TWI LTD 2009Gokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- JtdegtrtDokumen1 halamanJtdegtrtGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- 6 ErtryfgygfDokumen1 halaman6 ErtryfgygfGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Induced Cold Cracking (HICC) But It Is Often Referred To by OtherDokumen1 halamanHydrogen Induced Cold Cracking (HICC) But It Is Often Referred To by OtherGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen Induced Cold Cracking (HICC) But It Is Often Referred To by OtherDokumen1 halamanHydrogen Induced Cold Cracking (HICC) But It Is Often Referred To by OtherGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Constant Current Power Source: CharacteristicDokumen1 halamanConstant Current Power Source: CharacteristicGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Harvard Yard Tour MapnhDokumen1 halamanHarvard Yard Tour MapnhGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Globular Transfer Key CharacteristicsDokumen1 halamanGlobular Transfer Key CharacteristicsGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDokumen3 halamanErythrocyte Sedimentation RateGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- SR - No Description Drgno Elevation No. GriedDokumen6 halamanSR - No Description Drgno Elevation No. GriedGokul RajanBelum ada peringkat
- SiadhDokumen16 halamanSiadhGokul Rajan100% (1)
- Cat Hydo 10wDokumen4 halamanCat Hydo 10wWilbort Encomenderos RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Dye-Sensitized Solar CellDokumen7 halamanDye-Sensitized Solar CellFaez Ahammad MazumderBelum ada peringkat
- ANNAPURNA Sanitary Work 3 FinalDokumen34 halamanANNAPURNA Sanitary Work 3 FinalLaxu KhanalBelum ada peringkat
- Spice Processing UnitDokumen3 halamanSpice Processing UnitKSHETRIMAYUM MONIKA DEVIBelum ada peringkat
- Lifeline® Specialty: Fire Resistant QFCI Cable: Fire Resistant, Flame Retardant Halogen-Free Loose Tube - QFCI/O/RM-JMDokumen2 halamanLifeline® Specialty: Fire Resistant QFCI Cable: Fire Resistant, Flame Retardant Halogen-Free Loose Tube - QFCI/O/RM-JMkevinwz1989Belum ada peringkat
- Peter Honigh Indian Wine BookDokumen14 halamanPeter Honigh Indian Wine BookVinay JohnBelum ada peringkat
- TNEA Participating College - Cut Out 2017Dokumen18 halamanTNEA Participating College - Cut Out 2017Ajith KumarBelum ada peringkat
- (IME) (Starfinder) (Acc) Wildstorm IndustriesDokumen51 halaman(IME) (Starfinder) (Acc) Wildstorm IndustriesFilipe Galiza79% (14)
- Proposal For Real Estate Asset Management and Brokerage ServicesDokumen2 halamanProposal For Real Estate Asset Management and Brokerage ServicesTed McKinnonBelum ada peringkat
- LR 7833Dokumen11 halamanLR 7833Trung ĐinhBelum ada peringkat
- FAMILYDokumen3 halamanFAMILYJenecel ZanoriaBelum ada peringkat
- 30rap 8pd PDFDokumen76 halaman30rap 8pd PDFmaquinagmcBelum ada peringkat
- Information: Republic of The Philippines Regional Trial Court 8 Judicial Region Branch VIDokumen2 halamanInformation: Republic of The Philippines Regional Trial Court 8 Judicial Region Branch VIlossesaboundBelum ada peringkat
- Type of MorphologyDokumen22 halamanType of MorphologyIntan DwiBelum ada peringkat
- Packing List Night at Starlodge Adventure SuitesDokumen2 halamanPacking List Night at Starlodge Adventure SuitesArturo PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Anxxx PDFDokumen13 halamanAnxxx PDFDamion HaleBelum ada peringkat
- PLSQL Day 1Dokumen12 halamanPLSQL Day 1rambabuBelum ada peringkat
- Img - Oriental Magic by Idries Shah ImageDokumen119 halamanImg - Oriental Magic by Idries Shah ImageCarolos Strangeness Eaves100% (2)
- Jurnal Perdata K 1Dokumen3 halamanJurnal Perdata K 1Edi nur HandokoBelum ada peringkat
- Cover Letter For Lettings Negotiator JobDokumen9 halamanCover Letter For Lettings Negotiator Jobsun1g0gujyp2100% (1)
- OptiX OSN 8800 6800 3800 Configuration Guide (V100R007)Dokumen924 halamanOptiX OSN 8800 6800 3800 Configuration Guide (V100R007)vladBelum ada peringkat
- Holophane Denver Elite Bollard - Spec Sheet - AUG2022Dokumen3 halamanHolophane Denver Elite Bollard - Spec Sheet - AUG2022anamarieBelum ada peringkat
- Review Questions & Answers For Midterm1: BA 203 - Financial Accounting Fall 2019-2020Dokumen11 halamanReview Questions & Answers For Midterm1: BA 203 - Financial Accounting Fall 2019-2020Ulaş GüllenoğluBelum ada peringkat
- MGT 601-Smes Management MCQ For Final Term Preparation: ProductionDokumen80 halamanMGT 601-Smes Management MCQ For Final Term Preparation: ProductionSajidmehsudBelum ada peringkat
- 978-1119504306 Financial Accounting - 4thDokumen4 halaman978-1119504306 Financial Accounting - 4thtaupaypayBelum ada peringkat
- Eradication, Control and Monitoring Programmes To Contain Animal DiseasesDokumen52 halamanEradication, Control and Monitoring Programmes To Contain Animal DiseasesMegersaBelum ada peringkat
- 401 Lourdes School Quezon City Inc. v. GarciaDokumen2 halaman401 Lourdes School Quezon City Inc. v. GarciaIldefonso HernaezBelum ada peringkat
- NI 43-101 Technical Report - Lithium Mineral Resource Estimate Zeus Project, Clayton Valley, USADokumen71 halamanNI 43-101 Technical Report - Lithium Mineral Resource Estimate Zeus Project, Clayton Valley, USAGuillaume De SouzaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 Bone Tissue 2304Dokumen37 halamanChapter 6 Bone Tissue 2304Sav Oli100% (1)
- Pilapil v. CADokumen2 halamanPilapil v. CAIris Gallardo100% (2)