Resources and Development PDF
Diunggah oleh
vssainiDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Resources and Development PDF
Diunggah oleh
vssainiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ch
hapter 1
Reesources and
a Development
R
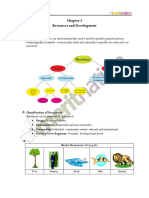
Resources
Suubstances available in ourr environment that can be
b used for sppecific purpooses and are
teechnologicallly accessible,, economicallly viable andd culturally acceptable
a
aree referred too as
reesources.
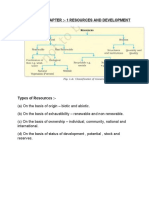
Classificatio
C
on of Resou
urces
Resources cann be classifiedd on the basis of
R
Orig
gin: Biotic annd abiotic
Exhaaustibility: Renewable and non-rennewable
Own
nership: Inddividual, com
mmunity-ownned, nationall and internaational
Statu
us of Devellopment: Potential, devveloped and stock
s
Biotic Resourcess: Having lifee
Tree
Humaan
Birds
Fish
Animaal
Abioticc Resourcees: Non-livinng
Stonnes
W
Water
Mounntains
Renewab
ble Resourrces: Can bee reproducedd or replenishhed
Solar energy
Wind energgy
Forest
Water
Non-renew
wable Reso
ources: Cannnot be reprooduced or reeplenished. They
T take milllions
of years to form.
f
E.g. Metalls, fossils fueels, minerals etc.
Coaal
Petroll
IIndividual Resourcess
Privattely owned by
b individualss
E.g. Inndividual ow
wnership of laand in the forrm of housess and agriculttural fields
Community
C
y-Owned Resources
R
Accesssible to all members
m
of a communityy
E.g. Village
V
pondss, public parkks, burial groounds etc.
National
N
Reesources
Thosee resources thhat exist withhin the territtory of a nation.
All miinerals, wateer bodies, forrests, wildlife
fe etc. withinn the countryy and within 12
nauticcal miles from
m the sea coaast are called national resources.
Internation
I
nal Resourcces
Thosee oceanic ressources that do
d not lie within the Excllusive Econoomic Zone off any
nationn.
They are managedd by international instituttions and eacch country haas an equal riight
to acccess these ressources.
Potential
P
Resources
R
Thouggh they are inn existence, they
t are not being complletely utilized.
E.g. Potential
P
of wind
w and solaar energy in Rajasthan
R
Developed
D
d Resourcess
Thosee resources thhat have beenn surveyed annd are readyy for utilizatioon.
Stock
S
n been utilized owing to
t lack of techhnical expertise.
Resouurces that exiist but have not
E.g. Making
M
hydroogen and oxyygen from waater
Reserves
R
a those ressources for whose
w
utilizattion man has the technicaal know-how
w but
They are
has noot started usinng them.
E.g. Use
U of river water
w
for gennerating electtricity
Problems
P
Related to Resources
R
Depleetion of resouurces due to over-utilizattion.
Accum
mulation in feew hands.
Indiscrriminate expploitation of resources
r
resulting in ecoological imbaalances.
Su
ustainable Developm
ment
Itt refers to thaat developmeent which is lasting enough to be usedd by the futuure generatioons.
D
Development
t should be suuch that it dooes not comppromise withh the needs of
o the comingg
geenerations.
Rio
R de Janeiro Earth Summit, 19992
NCED)
Unitedd Nations Coonference onn Environmennt and Devellopment (UN
Held at
a Rio de Janneiro in Braziil.
First ever
e Internattional Earth Summit.
S
Aimedd at addressinng the probleem of enviroonmental deggradation andd finding wayys of
proteccting the envvironment.
The declaration onn global clim
matic change and
a biodiverssity was signed.
G
Forestt Principles were
w adoptedd.
The Global
AGEN
NDA 21 wass formulated.
Aims at achhieving globaal sustainablee developmeent.
For combaating environnmental damaage, povertyy and diseasess through gloobal
cooperatioon.
Every counntry is suppoosed to formuulate its ownn Agenda 21.
Resource
R
Pllanning
It is neecessary for making
m
maxiimum utilizaation of the available resoources.
It invoolves
Identificatiion of resourrces through surveys, mapping and measurement.
m
.
Evolving a structure foor utilizing reesources by means
m
of appropriate
technologyy and skills.
Synchronizzing the resoource developpment plans with the national
developmeent goals.
d
throughh the Five Year Plans.
Resouurce planningg in India is done
Conservatio
C
on of Resou
urces
Resouurces need too be conserveed as they aree vital for development.
Over--utilization annd irrational consumption of resourcees creates eccological
imbalaance.
Brun
ndtland Com
mmission Report
R
of 19987 introducced the conceept of Sustaiinable
Develoopment that focused
fo
on thhe conservatiion of resourrces for the fuuture.
Land
L
Resou
urces
Land is
i the basic natural
n
resourrce on whichh all other resources existt.
Indiass total land area:
a
3.28 miillion sq. km
m.
Plains: 43%
%
Mountainss: 30%
2
Plateaus: 27%
Uses of Land
Forests
Net sown area
a
Pastures
Housing
Roads
Barren andd waste land
Culturablee waste land
Fallow landd
Area underr miscellaneoous trees, croops and grovves
Natio
onal Forest Policy (19332) envisages 33% of thee land area unnder forests in
i
India. However, itt is only 22%
%.
Land Degradation
L
Causees
Deforestattion
Over-graziing
Mining andd quarrying
Over-irriggation
Mineral prrocessing
Industrial effluents
e
Jharkhhand, Chhatttisgarh, Madhhya Pradesh and Orissa arre the states where
deforeestation, owiing to miningg activities, has
h resulted in
i the degraddation of landd.
In Rajasthan, Gujaarat and Maharashtra, thee main cause of land degraadation is ovvergrazinng.
Meth
hods for Sto
opping Lan
nd Degradaation
Afforestatiion
Proper maanagement off grazing
Stabilizatioon of sand duunes
Control off mining activvities
Proper discharge of inddustrial efflueents
Soil
Soil is a renewablee natural resoource.
It takees millions off years to forrm.
It is foormed by thee action of temperature, running
r
wateer, wind andd glaciers.
n
SSoil Erosion
T washing away of the top layer of soil by the action of windd and water is called soil
The
e
erosion.
Soil foormation andd soil erosionn are simultanneous processses and a ballance exists
betweeen the two.
Activiities such as
Deforestattion
Over-graziing
Mining
Constructiion
o soil erosionn and disturbb the natural balance.
Increaase the rate of
Gully
y Erosion an
nd Badland
ds
Deep channnels called gullies
g
are forrmed when fast
f running water
w
cuts
through thhe soft clayeyy soil making deep ravines.
o land becom
mes unfit forr cultivation and
a is called badland.
This type of
mbal basin in Madhya
M
Praddesh
E.g. Cham
w
water fllows as a sheet down a sloope and washhes Sheett Erosion: Itt is caused when
off thee top layer off soil. Windss can also bloow-off the toop layer of sooil.
Methods
M
off Soil Conseervation
Ploughhing along thhe contour lines of slopess
Terracce farming
Plantinng strips of grass
g
between crops restrricts the flow
w of water annd breaks winnd
speed. This is calleed strip cro
opping.
m the fast mooving winds and
a preventss
Plantinng lines of trrees creates a shelter from
erosioon. These aree called sheltter beds.
Studeents Con
ntributio
on to Reevision Notes
N
Land
d Degradatiion
Land degradation is a human induced
i
or natural processs which neggatively affectts the land
to funnction effectiively with in an ecosystem
m, by acceptting, storing and recyclinng water,
energgy and nutrieents.
Conntributed by:
Garim
ma Dhirayan
Contrribute to this Revision No
ote:
If you find
f anything of
o importance missing
m
from thhis note, email it to us at revission-notes@meritnation.com
m, and
well add
a it to this noote under your name!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Natural Resources: Unit - 2Dokumen51 halamanNatural Resources: Unit - 2Sharmila BalanBelum ada peringkat
- Evs Unit2Dokumen62 halamanEvs Unit2prajjwalrajput2507Belum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources ConservationDokumen15 halamanNatural Resources ConservationLegend MuhiiBelum ada peringkat
- LECTURE 6: Managing Soil and Food ResourcesDokumen107 halamanLECTURE 6: Managing Soil and Food ResourcesDương Hà Trúc TâmBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources GuideDokumen55 halamanNatural Resources GuideRoshin VargheseBelum ada peringkat
- Wasteland ReclamationDokumen20 halamanWasteland ReclamationRekha YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources: Prepared By, Mr. Snehal Patel Assistant Professor, Sumandeep Vidyapeeth, Vadodara, Gujarat, IndiaDokumen52 halamanNatural Resources: Prepared By, Mr. Snehal Patel Assistant Professor, Sumandeep Vidyapeeth, Vadodara, Gujarat, IndiaJagesh RanjanBelum ada peringkat
- Natural ResouceDokumen127 halamanNatural ResouceSaket KumarBelum ada peringkat
- CH 1 Resources and DevelopmentDokumen11 halamanCH 1 Resources and DevelopmentSK ABDUR REHMAN (SK)Belum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources Lecture on Renewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesDokumen11 halamanNatural Resources Lecture on Renewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesransinghBelum ada peringkat
- Geography: Adiance Ractice AnualDokumen11 halamanGeography: Adiance Ractice AnualOm ShrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- ResourcesDokumen6 halamanResourcesAyushiBelum ada peringkat
- Enviornmnet Components and RelationshipDokumen23 halamanEnviornmnet Components and Relationshipsehrish iqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources Lecture on Renewable, Non-Renewable Land and WaterDokumen11 halamanNatural Resources Lecture on Renewable, Non-Renewable Land and WaterMayurdhvajsinh JadejaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 - Natural ResourcesDokumen75 halamanUnit 3 - Natural ResourcesFranz JosephBelum ada peringkat
- 3.NATURAL RESOURCES - NotesDokumen229 halaman3.NATURAL RESOURCES - NotesSHIREEN TEKADEBelum ada peringkat
- CH 2 NotesDokumen11 halamanCH 2 NotesKritika VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Resources and DevelopmentDokumen10 halamanResources and DevelopmentSouL FanBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Soc Sci Geo Revision Notes ch2-1Dokumen6 halaman8 Soc Sci Geo Revision Notes ch2-1KamranBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3, Natural Resources Lec 1Dokumen12 halamanUnit 3, Natural Resources Lec 1Arsha TanejaBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources8Dokumen25 halamanNatural Resources8rahulBelum ada peringkat
- Resources and Its DevelopmentDokumen4 halamanResources and Its DevelopmentShams AlamBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 - Natural Resources LectureDokumen60 halamanUnit 2 - Natural Resources LectureSamrudhi PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources Notes Ch 2Dokumen11 halamanNatural Resources Notes Ch 2Kritika VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Fish Mineral Fuels PetroleumDokumen14 halamanFish Mineral Fuels PetroleumAshlesha MardhekarBelum ada peringkat
- Math Science and TechnologyDokumen29 halamanMath Science and TechnologyDonna Claire BayaniBelum ada peringkat
- Environment Seminar 1Dokumen11 halamanEnvironment Seminar 1cyrusBelum ada peringkat
- AECC-Natural Resources and Land ResourceDokumen48 halamanAECC-Natural Resources and Land Resourcekillerjaat305Belum ada peringkat
- Resources Classification DevelopmentDokumen7 halamanResources Classification DevelopmentMkjBelum ada peringkat
- Classifying Resources and Factors in Soil FormationDokumen6 halamanClassifying Resources and Factors in Soil FormationNisha PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 1 Resources and DevelopmentDokumen36 halamanCh. 1 Resources and DevelopmentAnin BertBelum ada peringkat
- SSTDokumen189 halamanSSTHariesh MuraliBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources PDFDokumen25 halamanNatural Resources PDFNIPER BNGBelum ada peringkat
- 8.2 Enviornment Components and RelationshipDokumen13 halaman8.2 Enviornment Components and RelationshipAyesha YounisBelum ada peringkat
- Threats to urban landscape resources and remediesDokumen5 halamanThreats to urban landscape resources and remediesMidhat FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- ESDM Unit I BSC Indvdl Consrvng Natur Sustn Lyfstyl0001Dokumen30 halamanESDM Unit I BSC Indvdl Consrvng Natur Sustn Lyfstyl0001Muthuraman ArBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Environmental Studies and Natural ResourcesDokumen17 halamanIntroduction to Environmental Studies and Natural ResourcesSilvinus Clisson PragashBelum ada peringkat
- CL - 8 - CH 2 - Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources - NOTES - 2022-23Dokumen6 halamanCL - 8 - CH 2 - Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources - NOTES - 2022-23sumedhasaha09Belum ada peringkat
- Natural ResourcesDokumen13 halamanNatural ResourcesAjaya Kumar MohapatraBelum ada peringkat
- Reading MaterialDokumen3 halamanReading MaterialAeishmeet kaurBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyDokumen18 halamanClassification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyMANISH JOSHIBelum ada peringkat
- ESDMDokumen64 halamanESDMJyothis T SBelum ada peringkat
- Geography (chp-1) NotesDokumen6 halamanGeography (chp-1) NotesParleen tannaBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources OverviewDokumen108 halamanNatural Resources OverviewDhruv SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Science & Disaster ManagementDokumen105 halamanEnvironmental Science & Disaster ManagementJyothis T SBelum ada peringkat
- Env StudiesDokumen29 halamanEnv StudiesRaiyan Zaman AdreyBelum ada peringkat
- MOD 1 Environmental StudiesDokumen36 halamanMOD 1 Environmental Studiesnihal9479Belum ada peringkat
- Resources and Devolopment NotesDokumen20 halamanResources and Devolopment NotesDanyaBelum ada peringkat
- MOD 1 Environmental StudiesDokumen36 halamanMOD 1 Environmental Studiesnihal9479Belum ada peringkat
- Evs Unit 2 - Natural Resources Part1Dokumen34 halamanEvs Unit 2 - Natural Resources Part1RajBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 8 Geography CH 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation & Wildlife ResourcesDokumen5 halamanCBSE Class 8 Geography CH 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation & Wildlife ResourcesPrathamesh BansodBelum ada peringkat
- The Treats To Urban LandscapeDokumen5 halamanThe Treats To Urban LandscapeMidhat FatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Overexplotaition: Msc. Chiara GuidinoDokumen56 halamanOverexplotaition: Msc. Chiara GuidinoDariel Ferro JuarezBelum ada peringkat
- Resources and DevelopmentDokumen53 halamanResources and DevelopmentAtoshili YepthoBelum ada peringkat
- Richmond Public School Assignment on Sustainable Management of Natural ResourcesDokumen10 halamanRichmond Public School Assignment on Sustainable Management of Natural ResourcesKalaivaniBelum ada peringkat
- Geography Notes For Class: X (Social Science) : Chapter 1: Resources and Development Remember These PointsDokumen4 halamanGeography Notes For Class: X (Social Science) : Chapter 1: Resources and Development Remember These PointsAkshit SethiBelum ada peringkat
- Class 10 Social Sciences Geography: Chapter 1 Notes Resources and Development 1. ResourcesDokumen8 halamanClass 10 Social Sciences Geography: Chapter 1 Notes Resources and Development 1. ResourcesSandhya SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resources (ASES 3101-Environmental Studies and Disaster Management)Dokumen28 halamanNatural Resources (ASES 3101-Environmental Studies and Disaster Management)Chandrasekhar SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Resource Management GuideDokumen37 halamanNatural Resource Management GuideRavi NegiBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Brownfield Regeneration: Cleanup, Design, and Reuse of Derelict LandDari EverandPrinciples of Brownfield Regeneration: Cleanup, Design, and Reuse of Derelict LandBelum ada peringkat
- Evoulution and GeneticsDokumen5 halamanEvoulution and GeneticsASUPREMEABelum ada peringkat
- NR 23 Strictly Anaerobic Beer Spoilage Bacteria With Special Emphasis On New and Emerging Species Riikka JuvonenDokumen37 halamanNR 23 Strictly Anaerobic Beer Spoilage Bacteria With Special Emphasis On New and Emerging Species Riikka JuvonenIvana NikolicBelum ada peringkat
- Proposed immunological mechanism of RTS,S malaria vaccine protectionDokumen2 halamanProposed immunological mechanism of RTS,S malaria vaccine protectionGhalapulla ReenaBelum ada peringkat
- Osmosis Lab AnalysisDokumen3 halamanOsmosis Lab AnalysisgBelum ada peringkat
- Communicable Disease Epidemiology: Causation, Transmission & PreventionDokumen32 halamanCommunicable Disease Epidemiology: Causation, Transmission & PreventionvolaaBelum ada peringkat
- Leslie Pray, Ph.D. 2008. Recombinant DNA Technology and Transgenic AnimalsDokumen5 halamanLeslie Pray, Ph.D. 2008. Recombinant DNA Technology and Transgenic AnimalsJosé Jhair Enrique IIIBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma On SkinDokumen9 halamanEffects of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma On SkinHamdika Yendri PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Mendelian Genetics - PPT Iiird SemDokumen70 halamanMendelian Genetics - PPT Iiird SemMousumi DasBelum ada peringkat
- Anaplastic meningioma diagnosisDokumen1 halamanAnaplastic meningioma diagnosisBhavik ChavdaBelum ada peringkat
- A Pi 20 Ne InstructionsDokumen4 halamanA Pi 20 Ne InstructionsNayely Diego de MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 119Dokumen29 halamanBiology 119a362626635Belum ada peringkat
- Video Recap of Multiple Alleles by Amoeba SistersDokumen2 halamanVideo Recap of Multiple Alleles by Amoeba Sistersapi-2331875660% (1)
- Patient HIV and Urine Test ResultsDokumen5 halamanPatient HIV and Urine Test ResultsPsyche's CupidoBelum ada peringkat
- NERO215 Handout 3Dokumen4 halamanNERO215 Handout 3Heena GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanism of Action of Penicillin & CephalosporinDokumen7 halamanMechanism of Action of Penicillin & CephalosporinshahabahmadBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of A PoisonDokumen6 halamanClassification of A PoisonCake ManBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To Plant Development: (Because Plants Are The Best)Dokumen40 halamanAn Introduction To Plant Development: (Because Plants Are The Best)jesusrgffBelum ada peringkat
- Trial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k2 Skema PDFDokumen13 halamanTrial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k2 Skema PDFhakimBelum ada peringkat
- Transmission Cycle of InfectionDokumen22 halamanTransmission Cycle of InfectionMikeBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 5 Type of Root SystemDokumen2 halamanActivity 5 Type of Root SystemPreiy Julian De GuiaBelum ada peringkat
- Chethan Pandarinath, PH.D.: Education and ResearchDokumen4 halamanChethan Pandarinath, PH.D.: Education and ResearchChethan PandarinathBelum ada peringkat
- Ch1 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science NotesDokumen8 halamanCh1 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science NotesONE CLICK COMPUTERBelum ada peringkat
- Threadfins of The World (Family Polynemidae)Dokumen8 halamanThreadfins of The World (Family Polynemidae)cavrisBelum ada peringkat
- Bioinformatics History of BioinformaticsDokumen10 halamanBioinformatics History of BioinformaticsSir RutherfordBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 22Dokumen91 halamanChapter 22YuoMatsukiBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation BTDokumen23 halamanPresentation BTTanvi JainBelum ada peringkat
- IronDokumen18 halamanIronAbeer BasharatBelum ada peringkat
- Toxoplasmosis: Zoonotic Disease Caused by Protozoan Parasite T. gondiiDokumen38 halamanToxoplasmosis: Zoonotic Disease Caused by Protozoan Parasite T. gondiiemmaBelum ada peringkat
- Summative test on understanding culture, society and politicsDokumen2 halamanSummative test on understanding culture, society and politicsRhaieyee ElBelum ada peringkat
- CH 15 NotesDokumen5 halamanCH 15 NotesCJBelum ada peringkat