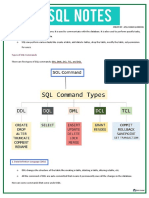
List of SQL Commands
Diunggah oleh
txungoDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
List of SQL Commands
Diunggah oleh
txungoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
List of SQL commands
1 of 7
about:reader?url=https://www.codecademy.com/articles/sql-commands...
codecademy.com
List of SQL commands
Background
SQL, 'Structured Query Language', is a programming language
designed to manage data stored in relational databases. SQL
operates through simple, declarative statements. This keeps data
accurate and secure, and helps maintain the integrity of databases,
regardless of size.
Here's an appendix of commonly used commands.
Commands
ALTER TABLE
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column datatype;
ALTER TABLE lets you add columns to a table in a database.
AND
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_1 = value_1
AND column_2 = value_2;
AND is an operator that combines two conditions. Both conditions
must be true for the row to be included in the result set.
25/12/2015 0:54
List of SQL commands
2 of 7
about:reader?url=https://www.codecademy.com/articles/sql-commands...
AS
SELECT column_name AS 'Alias'
FROM table_name;
AS is a keyword in SQL that allows you to rename a column or table
using an alias.
AVG
SELECT AVG(column_name)
FROM table_name;
AVG() is an aggregate function that returns the average value for a
numeric column.
BETWEEN
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name BETWEEN value_1 AND value_2;
The BETWEEN operator is used to filter the result set within a certain
range. The values can be numbers, text or dates.
COUNT
SELECT COUNT(column_name)
FROM table_name;
COUNT() is a function that takes the name of a column as an
argument and counts the number of rows where the column is not
NULL.
25/12/2015 0:54
List of SQL commands
3 of 7
about:reader?url=https://www.codecademy.com/articles/sql-commands...
CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE table_name (column_1 datatype,
column_2 datatype, column_3 datatype);
CREATE TABLE creates a new table in the database. It allows you to
specify the name of the table and the name of each column in the
table.
DELETE
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE some_column =
some_value;
DELETE statements are used to remove rows from a table.
GROUP BY
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column_name;
GROUP BY is a clause in SQL that is only used with aggregate
functions. It is used in collaboration with the SELECT statement to
arrange identical data into groups.
INNER JOIN
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_1
JOIN table_2
ON table_1.column_name = table_2.column_name;
An inner join will combine rows from different tables if the join
25/12/2015 0:54
List of SQL commands
4 of 7
about:reader?url=https://www.codecademy.com/articles/sql-commands...
condition is true.
INSERT
INSERT INTO table_name (column_1, column_2,
column_3) VALUES (value_1, 'value_2', value_3);
INSERT statements are used to add a new row to a table.
LIKE
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name LIKE pattern;
LIKE is a special operator used with the WHERE clause to search for
a specific pattern in a column.
LIMIT
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
LIMIT number;
LIMIT is a clause that lets you specify the maximum number of
rows the result set will have.
MAX
SELECT MAX(column_name)
FROM table_name;
MAX() is a function that takes the name of a column as an argument
25/12/2015 0:54
List of SQL commands
5 of 7
about:reader?url=https://www.codecademy.com/articles/sql-commands...
and returns the largest value in that column.
MIN
SELECT MIN(column_name)
FROM table_name;
MIN() is a function that takes the name of a column as an argument
and returns the smallest value in that column.
OR
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name = value_1
OR column_name = value_2;
OR is an operator that filters the result set to only include rows where
either condition is true.
ORDER BY
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
ORDER BY column_name ASC|DESC;
ORDER BY is a clause that indicates you want to sort the result set
by a particular column either alphabetically or numerically.
OUTER JOIN
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_1
LEFT JOIN table_2
25/12/2015 0:54
List of SQL commands
6 of 7
about:reader?url=https://www.codecademy.com/articles/sql-commands...
ON table_1.column_name = table_2.column_name;
An outer join will combine rows from different tables even if the the
join condition is not met. Every row in the left table is returned in the
result set, and if the join condition is not met, then NULL values are
used to fill in the columns from the right table.
ROUND
SELECT ROUND(column_name, integer)
FROM table_name;
ROUND() is a function that takes a column name and an integer as
an argument. It rounds the values in the column to the number of
decimal places specified by the integer.
SELECT
SELECT column_name FROM table_name;
SELECT statements are used to fetch data from a database. Every
query will begin with SELECT.
SELECT DISTINCT
SELECT DISTINCT column_name FROM table_name;
SELECT DISTINCT specifies that the statement is going to be a
query that returns unique values in the specified column(s).
SUM
SELECT SUM(column_name)
25/12/2015 0:54
List of SQL commands
7 of 7
about:reader?url=https://www.codecademy.com/articles/sql-commands...
FROM table_name;
SUM() is a function that takes the name of a column as an argument
and returns the sum of all the values in that column.
UPDATE
UPDATE table_name
SET some_column = some_value
WHERE some_column = some_value;
UPDATE statments allow you to edit rows in a table.
WHERE
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name operator value;
WHERE is a clause that indicates you want to filter the result set to
include only rows where the following condition is true.
25/12/2015 0:54
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Interview SQLDokumen22 halamanInterview SQLSandeep GantaBelum ada peringkat
- Perl 0411 PDFDokumen124 halamanPerl 0411 PDFGobara Dhan100% (1)
- Oop PHP With Mysql: Clifton S. AlegarmeDokumen32 halamanOop PHP With Mysql: Clifton S. Alegarmeapi-26932678Belum ada peringkat
- Perl - Part Iii: Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurDokumen24 halamanPerl - Part Iii: Indian Institute of Technology KharagpurAbdul Ghani KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Perl 4Dokumen112 halamanPerl 4AgnathavasiBelum ada peringkat
- What Is CGI?: Gateway Interface Is A Standard For InterfacingDokumen33 halamanWhat Is CGI?: Gateway Interface Is A Standard For InterfacingUmang Bhatt100% (1)
- Perl Dbi DpriestDokumen45 halamanPerl Dbi Dpriestmottur1984100% (1)
- Week 1: Perl BasicsDokumen5 halamanWeek 1: Perl Basicspeter11111988100% (3)
- Web Tech Solution (10 Marks Each) - 1Dokumen24 halamanWeb Tech Solution (10 Marks Each) - 1Narendra SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Oracle 11 G (SQL) : Quality Thought TechnologiesDokumen127 halamanOracle 11 G (SQL) : Quality Thought Technologiessirivella venkateshBelum ada peringkat
- Server Side ScriptingDokumen6 halamanServer Side ScriptingDr. MNV KiranbabuBelum ada peringkat
- JqueryDokumen18 halamanJqueryJadesh Chanda100% (1)
- Practical File: CO 202: Database Management SystemsDokumen42 halamanPractical File: CO 202: Database Management SystemsPranjalBelum ada peringkat
- Web Technologies MCQsDokumen53 halamanWeb Technologies MCQsRahul SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- WT Unit-5 NotesDokumen26 halamanWT Unit-5 NoteslavanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Server-Side Scripting OverviewDokumen35 halamanChapter 2 Server-Side Scripting OverviewAbdullaahi Ahmed AbdullahiBelum ada peringkat
- Static vs. Dynamic Websites: Introduction To PHPDokumen15 halamanStatic vs. Dynamic Websites: Introduction To PHPrummanzaidiBelum ada peringkat
- DBMS Lab ManualDokumen93 halamanDBMS Lab Manualdeepika_srivastav_1100% (1)
- Umesh Training PresentationDokumen15 halamanUmesh Training PresentationAvinabs SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Web Technology NotesDokumen72 halamanWeb Technology NotesjamieabeyBelum ada peringkat
- WSU - Jquery Reference CardDokumen13 halamanWSU - Jquery Reference Cardcheckmeout803Belum ada peringkat
- Writing SlidesDokumen10 halamanWriting SlidesMary CardBelum ada peringkat
- PHP FormDokumen11 halamanPHP FormImanBelum ada peringkat
- Short Perl Tutorial: Instructor: Rada Mihalcea University of AntwerpDokumen34 halamanShort Perl Tutorial: Instructor: Rada Mihalcea University of AntwerpBhaskar BabuBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To PerlDokumen62 halamanIntroduction To PerlParimal Dave100% (1)
- Lecture10 PHP2Dokumen16 halamanLecture10 PHP2Hanif Yuli AbdillahBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Sheet 2Dokumen21 halamanLab Sheet 2tariqshah457Belum ada peringkat
- Object Oriented Programming With PHPDokumen29 halamanObject Oriented Programming With PHPSenthil Kumar100% (1)
- Javascript Array Methods - Unshift, Shift, Push, and PopDokumen3 halamanJavascript Array Methods - Unshift, Shift, Push, and PopKrishna Murthy PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- PHP 5 Tutorial: Easy Learning With "Show PHP"Dokumen363 halamanPHP 5 Tutorial: Easy Learning With "Show PHP"Dave SedigoBelum ada peringkat
- PHP Tutorial - W3schools2 PDFDokumen88 halamanPHP Tutorial - W3schools2 PDFviru991Belum ada peringkat
- Cin 628 Week 2 TutorialDokumen6 halamanCin 628 Week 2 Tutorialsaneel kumar100% (1)
- Tips and Tricks PHPDokumen53 halamanTips and Tricks PHPYahya NursalimBelum ada peringkat
- Mail Server With Intranet and Live Chat A Java ProjectDokumen19 halamanMail Server With Intranet and Live Chat A Java ProjectKartikeyan Shukla100% (1)
- Client Side Scripting - 6thectureDokumen101 halamanClient Side Scripting - 6thecturesuyog lonsaneBelum ada peringkat
- Perl Quick Reference v1.0Dokumen8 halamanPerl Quick Reference v1.0mghuzurahmedBelum ada peringkat
- PERLDokumen86 halamanPERLanilBelum ada peringkat
- Web Technologies Notes: HTML Java Script CSS XML JDBC Servlets JSPDokumen98 halamanWeb Technologies Notes: HTML Java Script CSS XML JDBC Servlets JSPVikram ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- PHP SQL CommandDokumen14 halamanPHP SQL Commandmd jaberBelum ada peringkat
- MySQL Activity 1Dokumen7 halamanMySQL Activity 1Jeremias C. EsperanzaBelum ada peringkat
- PHP Lab ProgramsDokumen6 halamanPHP Lab Programsirfanahmed.dbaBelum ada peringkat
- VBAcourse Excel Code EasyDokumen92 halamanVBAcourse Excel Code EasyNaki oto100% (1)
- C Structures and UnionsDokumen61 halamanC Structures and UnionsRando BBelum ada peringkat
- Arrays in PHPDokumen40 halamanArrays in PHPSai Sangeetha RajiniBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Perl ProgrammingDokumen21 halamanIntroduction To Perl ProgrammingGeorge100% (10)
- Linux CommandsDokumen9 halamanLinux Commandsprat jariwala100% (1)
- Nota PHP PDFDokumen50 halamanNota PHP PDFShadowSky ZahirulBelum ada peringkat
- SQL LessonDokumen56 halamanSQL LessonMusammat Samina100% (1)
- Linked ListsDokumen29 halamanLinked ListsgdskumarBelum ada peringkat
- Perl in Design Flow Automation AnDokumen37 halamanPerl in Design Flow Automation Anvpsampath100% (1)
- O? O? O? O? O? O? O? O? O? O?Dokumen18 halamanO? O? O? O? O? O? O? O? O? O?jaa_neeBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment3Init V2 RevisionLogDokumen2 halamanAssignment3Init V2 RevisionLogVinh Phuoc100% (2)
- A Very Short Intro To Linux: Laura Alisic October 8, 2008Dokumen4 halamanA Very Short Intro To Linux: Laura Alisic October 8, 2008biltu100% (1)
- Database Lab: NAME:-Ashish Jain ROLL NUMBER: - 19/548 University Roll Number: - 19eucit005 Batch: - 5it1 Branch: - ItDokumen7 halamanDatabase Lab: NAME:-Ashish Jain ROLL NUMBER: - 19/548 University Roll Number: - 19eucit005 Batch: - 5it1 Branch: - ItSubhash ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Background: Alter TableDokumen6 halamanBackground: Alter TableWong Chee InnBelum ada peringkat
- List of SQL Commands - CodecademyDokumen9 halamanList of SQL Commands - Codecademyaqua2376Belum ada peringkat
- List of SQL Commands - CodecademyDokumen9 halamanList of SQL Commands - CodecademySchool OthersBelum ada peringkat
- List of SQL CommandsDokumen5 halamanList of SQL CommandsNeleRS100% (1)
- List of SQL Commands: BackgroundDokumen6 halamanList of SQL Commands: BackgroundOana AchiteiBelum ada peringkat
- SQL Integrity Constraints 1Dokumen64 halamanSQL Integrity Constraints 1Nilay GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- GraftingDokumen10 halamanGraftingtxungoBelum ada peringkat
- College Algebra Quick ReferDokumen2 halamanCollege Algebra Quick Refertxungo100% (1)
- Chain RuleDokumen8 halamanChain RuletxungoBelum ada peringkat
- Week 3 01 - Fresh ForageDokumen9 halamanWeek 3 01 - Fresh ForagetxungoBelum ada peringkat
- Recruitment and SelectionDokumen50 halamanRecruitment and SelectionAmrita BhatBelum ada peringkat
- Dynamic Analysis of Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drives Based On Simulink and Finite Element ModelDokumen5 halamanDynamic Analysis of Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drives Based On Simulink and Finite Element ModelenmnabilBelum ada peringkat
- Catholic Social TeachingsDokumen21 halamanCatholic Social TeachingsMark de GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- 12V140 Seris Engine Shop ManualDokumen471 halaman12V140 Seris Engine Shop ManualRaed Mahyoub100% (4)
- Straightforward Pre-Intermediate Progress Test 4: Language Section VocabularyDokumen8 halamanStraightforward Pre-Intermediate Progress Test 4: Language Section VocabularyStrange BrawlerBelum ada peringkat
- Vishay Load Cell Calibration System - ENDokumen3 halamanVishay Load Cell Calibration System - ENSarhan NazarovBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Assessment, Solution Manual, Electrons in Atoms, Glencoe, ChemistryDokumen9 halamanChapter 5 Assessment, Solution Manual, Electrons in Atoms, Glencoe, Chemistrypumeananda100% (3)
- Definition, Scope and Nature of EconomicsDokumen29 halamanDefinition, Scope and Nature of EconomicsShyam Sunder BudhwarBelum ada peringkat
- DOPE Personality TestDokumen8 halamanDOPE Personality TestMohammed Hisham100% (1)
- Bachelors - Project Report 1Dokumen43 halamanBachelors - Project Report 1divyaBelum ada peringkat
- Aljotronic Control 2Dokumen30 halamanAljotronic Control 2Fuzzbuddy100% (1)
- DP 900T00A ENU TrainerHandbookDokumen288 halamanDP 900T00A ENU TrainerHandbookAndré baungatnerBelum ada peringkat
- Inspection List For Electrical PortableDokumen25 halamanInspection List For Electrical PortableArif FuadiantoBelum ada peringkat
- Example of Presentation Planning Document 1uf6cq0Dokumen2 halamanExample of Presentation Planning Document 1uf6cq0Wilson MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- A.O: Against Order: Desktop Hard Disk Laptop Hard Disk Scsi Hard Disk Adaptec Cards External Hard DiskDokumen28 halamanA.O: Against Order: Desktop Hard Disk Laptop Hard Disk Scsi Hard Disk Adaptec Cards External Hard DiskArul brittoBelum ada peringkat
- Command Center Processing and Display System ReplacementDokumen2 halamanCommand Center Processing and Display System ReplacementImranBelum ada peringkat
- Lifestyle Mentor. Sally & SusieDokumen2 halamanLifestyle Mentor. Sally & SusieLIYAN SHENBelum ada peringkat
- TrapsDokumen11 halamanTrapsAmandeep AroraBelum ada peringkat
- Piramal Revanta - Tower 3Dokumen13 halamanPiramal Revanta - Tower 3bennymahaloBelum ada peringkat
- Comsigua HBIDokumen0 halamanComsigua HBIproxywarBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Curriculum For Secondary Schools: Mathematics Form 2Dokumen139 halamanIntegrated Curriculum For Secondary Schools: Mathematics Form 2Izawaty IsmailBelum ada peringkat
- ACFrOgDVly789-6Z8jIbi7pBoLupubEgMyOp7PczEvUguHoW3uj oR2PKzDvuhRzzkIhacYjxXRrU6iA7sHt t6MhtpZFq0t uZL2pF5Ra NNZ kmcl5w7BCQeUegKhjRhNuou88XxLodzWwbsrDokumen14 halamanACFrOgDVly789-6Z8jIbi7pBoLupubEgMyOp7PczEvUguHoW3uj oR2PKzDvuhRzzkIhacYjxXRrU6iA7sHt t6MhtpZFq0t uZL2pF5Ra NNZ kmcl5w7BCQeUegKhjRhNuou88XxLodzWwbsrJohn Steven LlorcaBelum ada peringkat
- Strain GaugeDokumen7 halamanStrain GaugefahadarizkiBelum ada peringkat
- Project TitleDokumen2 halamanProject TitleVISHAL S. VBelum ada peringkat
- Mechatronics Course PlanDokumen3 halamanMechatronics Course PlanMohammad Faraz AkhterBelum ada peringkat
- KaranDokumen4 halamanKarancristioronaldo90Belum ada peringkat
- How To Get Jobs in Neom Saudi Arabia 1703510678Dokumen6 halamanHow To Get Jobs in Neom Saudi Arabia 1703510678Ajith PayyanurBelum ada peringkat
- PVTP Complete PDF FreeDokumen680 halamanPVTP Complete PDF FreemaxliraBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of Plate Count Agar and R2A Medium For Enumeration of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Natural Mineral WaterDokumen4 halamanComparison of Plate Count Agar and R2A Medium For Enumeration of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Natural Mineral WaterSurendar KesavanBelum ada peringkat
- The Roosh ProgramDokumen2 halamanThe Roosh ProgramVal KerryBelum ada peringkat