C Ste Ftrs
Diunggah oleh
suraj dhulannavarJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
C Ste Ftrs
Diunggah oleh
suraj dhulannavarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
P01-03 06.11.
1 09:49 AM 1
CONTENTS
2-Phase Hybrid Stepping Motor
Selection Guide
KH39EM2
KH39FM2
KH39GM2
KH42HM2
KH42JM2
KH42KM2
KH56JM2
KH56KM2
KH56QM2
3-Phase Hybrid Stepping Motor
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
Selection Guide
KT35FM1
KT42M06
KT42M1
KT42M4
KT50KM1
KT50LM1
KT56KM1
KT56QM1
KT60KM06
KT60LM06
KT60KM1
KT60LM1
KT60RM1
KT86M1
KR42HM4
KR42JM4
KR42KM4
2-Phase Stepping Motor Driver
SERVEX FSD 22
28
30
32
34
36
38
38
40
40
42
44
46
48
50
52
54
56
58
3-Phase Stepping Motor Driver
SERVEX FTD 60
Max. Allowable Load / Runout for motor shaft
Load for motor shaft
L
Radial load
Type
Thrust load
Load
KH39
Mounting flange
Radial load
Thrust load
Motor
KH42
KT35
14.7N1.5kgf
19.6N2.0kgf
Motor shaft
10mm
KT42
KR42
KH56
KT60
40N4.1kgf
70N7.1kgf
Shaft run out
0.075A
0.05T.I.R.mm
0.05
A
Shaft run out
Concentricity between shaft
and mounting circle
0.075T.I.R.mm
Perpendicularity between shaft
and mounting face
0.075T.I.R.mm
0.075A
T.I.R.Total Indicator Reading
P01-03 06.11.1 09:49 AM 2
2-Phase Hybrid Stepping Motors
& Drivers
Product Number Code
Stepping motors
KH 42 H M 2 - 901
Drivers
FSD 2 U 2 P 14 - 01
Accessories
(Connector of lead wires)
with 01: with cable
without 01: without cable
Winding specifications
Step angle(degree)
060.6
11.2
21.8
43.75
Motor Type
M : HB Type
Serial number
Supply voltage
P : DC
Output current
2 : 2A
3 : 3A
Drive systems
2U : 2Ph Unipolor
2B : 2Ph Bipolor
Series name
FSD Series
2Ph Type(KH Series model)
Motor length(mm)
E : 20.8
: 4042
F : 27
K : 5054
G : 31
Q : 76
H : 34
Mounting size(mm)
Series name
KH Series : 2Ph Stepping motors
System Configuration
UNI-POLAR
BI-POLAR
Driver for UNI-POLAR
KH39M2-801
KH39M2-851
FSD2U2P14-01
Pulse
signal
Power supply
12V30VDC
Driver for UNI-POLAR
KH42M2-901, 911
KH42M2-951, 961
FSD2U3P13-01
Pulse
signal
Power supply
24VDC
Driver for BI-POLAR
nt
me
p
lo
ve
De
r
de
Un FSD2B2P13-01
KH56M2-902, 912
KH56M2-951, 961
KH56M2-901, 911
P01-03 06.11.1 09:49 AM 3
- PHASE STEPPING MOTORS
.Unipolar type
Stepping angle = 1.8 deg./step
Standard size
mm
inch
20.8
1.54
27
39 sq.x
sq.x
31
34
Holding Torque
Winding
Current Voltage Inductance
Resistance
mNm
/phase A/phase
ozin
56 sq.x
54
76
Page
8.3
14
0.4
5.6
6.4
KH39EM2-801
13.0
15
0.42
6.3
8.5
KH39FM2-801
1.22
127
18.0
13.6
0.47
6.4
9.8
KH39GM2-801
3.4
0.9
3.06
2.4
KH42HM2-901, 911
1.34
140
20
9.6
0.58
5.57
6.0
-902, 912
14.7
0.46
6.76
9.3
-903, 913
2.85
1.2
3.42
2.5
KH42JM2-901, 911
5.5
0.88
4.4
5.1
-902, 912
0.5
9.25
16.3
-903, 913
12
18.5
14
236
340
1.65
2.2 sq.x
Driver
88
1.97
42
Model
59
1.58
50
mH/phase
1.06
sq.x
40
0.82
1.65
42 sq.x
Vcc = 24 V
422
2.13
2.99
834
1324
33
48
60
118
187
3.1
1.2
3.72
3.1
KH42KM2-901, 911
0.58
3.0
1.74
0.61
KH56JM2-901, 911
1.39
2.0
2.78
1.8
-902, 912
4.9
1.0
4.9
6.68
-903, 913
0.77
3.0
2.3
1.04
KH56KM2-901, 911
1.79
2.0
3.6
3.0
-902, 912
6.71
1.0
6.71
9.36
-903, 913
1.18
3.0
3.54
2.4
KH56QM2-901, 911
2.73
2.0
5.46
5.4
-902, 912
9.9
1.0
9.9
21.6
-903, 913
10
16
18
20
Note; Driver model FSD2U2P14-01 is applicable to the motors with
Note; Driver model FSD2U3P13-01 is applicable to the motors with
.Bipolar type
Stepping angle = 1.8 deg./step
Standard size
mm
inch
20.8
39 sq.x
Winding
Current Voltage Inductance
Resistance
mNm
/phase A/phase
ozin
mH/phase
Model
Driver
Page
KH39EM2-851
78
11
6.0
0.6
3.6
5.5
1.06
118
17
6.0
0.67
4.0
6.8
KH39FM2-851
1.22
157
22
7.0
0.65
4.6
9.8
KH39GM2-851
1.34
197
28
3.1
1.0
3.1
4.3
KH42HM2-951, 961
10
1.58
314
44
5.4
0.85
4.59
9.3
KH42JM2-951, 961
12
50
1.97
403
57
2.3
1.2
2.76
4.0
KH42KM2-951, 961
14
42
1.65
490
69
0.98
2.0
1.96
2.27
KH56JM2-951, 961
16
2.13
932
132
1.32
2.0
2.4
3.19
KH56KM2-951, 961
18
2.99
1373
194
2.0
2.0
4.0
7.35
KH56QM2-951, 961
20
27
34
56 sq.x
Holding Torque
0.82
1.54 sq.x
31
42 sq.x
Vcc = 24 V
40
54
1.65 sq.x
2.2 sq.x
76
Note; Driver model FSD2B2P13-01 is applicable to the motors with
- Phase Drivers
Applicable
motors type
Standard size
mm
inch
Power supply
Uni-poler
577342 2.252.881.65 12-30V DC
Uni-poler
577356 2.252.882.21
OUTPUT current
A
24V DC
Bi-poler
Step angle
Model
Page
0.33-2.0
11, 12, 14 FSD2U2P14-01
22
0.5-3.0
11, 12, 14 FSD2U3P13-01
24
11, 12, 14 FSD2B2P13-01
26
P28-31 06.11.1 09:53 AM 28
3-Phase Hybrid Stepping Motors
& Drivers
HIGH TORQUE, SILENT ROTATION
Product Number Code
Stepping Motors
KT 42 H M 06 - 551
Drivers
FTD 3 S 2 P 22 - 01
Winding specifications
Accessories
(Connector of lead wires)
with 01: with cable
without 01: without cable
Serial number
Step angle(degree)
060.6
11.2
21.8
43.75
Motor type
M : HB Type
Supply voltage
P : DC
Output current
2 : 2A
3 : 3A
Drive systems
3S : 3Ph Bipolor
Series name
FTD Series
Motor length(mm)
E : 20.8
K : 4754
F : 28
L : 5865
H : 34
Q : 76
: 4042
Mounting size(mm)
Series Name
KT Series : 3Ph Stepping motors
KR Series : 3Ph Ring Rotor Type Stepping motors
28
P28-31 06.11.1 09:53 AM 29
- PHASE STEPPING MOTORS
.Low speed high torque type
Step
Standard size
angle
deg./step
mm
21
34
42 sq.x
40
48
60 sq.x
inch
0.8
1.34
1.65 sq.x
1.58
1.89
42 sq.x
50 sq.x
56 sq.x
60sq.x
86 dia.x
3.75
42 sq.x
6.4
12.7
25.5
28.3
42
500
69
600
83
900
125
1.10
0.8
1.34
1.58
1.89
2.02
2.56
2.04
2.98
1.85
1.85
2.29
2.29
3.37
2.40
3.74
0.79
1.34
59
70
140
210
280
440
580
690
1100
320
320
600
600
1680
2000
4000
70
130
8.3
9.9
19.8
29.7
39.6
62.3
82.1
97.4
156
45.3
45.3
85
85
238
278
556
9.7
18
1.58
180
25
2.36 sq.x
28
21
34
40
48
51
65
52
76
47
47
58
58
86
61
95
20
34
mNm
45
90
180
200
300
1.85
58
35 sq.x
Winding
Current Voltage Inductance
Resistance
ozin /2phase A/2phase
V
mH/2phase
Holding Torque
47
0.6
1.2
Vcc = 24 V
2.29
1.38 sq.x
1.65 sq.x
1.97 sq.x
2.21 sq.x
2.36 sq.x
3.38dia.x
1.65 sq.x
40
5.9
1.2
1.3
2.0
0.55
1.6
0.55
1.6
0.73
2.2
0.73
2.2
39.0
5.9
1.1
1.2
1.5
1.3
1.6
1.4
1.7
0.55
1.6
0.73
2.2
2.0
1.8
2.8
6.6
3.4
8.8
4.3
11.0
0.9
2.4
2.4
2.3
3.8
2.2
3.8
2.2
3.8
2.2
3.8
2.2
0.3
0.9
2.4
2.4
2.4
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.8
2.2
3.8
2.2
3.0
3.0
2.5
0.8
1.3
0.8
1.2
0.8
5.3
2.88
3.12
4.6
2.09
3.52
2.09
3.52
2.77
4.84
2.77
4.84
11.7
5.3
2.6
2.88
3.6
3.9
4.8
4.2
5.1
2.09
3.52
2.77
4.84
6.0
5.4
7.0
5.28
4.42
7.04
5.16
8.8
Model
Driver
3.1
0.8
1.3
1.4
1.0
KT60KM06-751
3.1
1.0
KT60KM06-551
3.0
1.8
KT60LM06-751
5.7
1.7
5.6
26.0
2.6
0.5
0.8
1.0
1.6
1.6
1.4
1.7
0.8
2.5
1.0
3.3
3.2
18.0
36.6
5.7
4.7
12.3
8.7
22.0
KT42EM06-551
KT42HM06-551
KT42JM06-551
KT42KM06-551
-752
-552
-752
KT60LM06-551
-552
KT 3 5 F M 1 - 552
KT 4 2 E M 1 - 551
KT 4 2 H M 1 - 551
KT 4 2 J M 1 - 551
KT 4 2 K M 1 - 551
KT 5 0 K M 1 - 551
KT 5 0 L M 1 - 551
KT 5 6 K M 1 - 551
KT 5 6 QM 1 - 551
KT 6 0 K M 1 - 551
-552
KT 6 0 L M 1 - 551
-552
KT 6 0 RM1- 551
KT 8 6 L M 1 - 551
KT 8 6 S M 1 - 551
KT 4 2 E M 4 - 551
KT42HM4-551
-552
KT 4 2 J M 4 -551
-552
Page
34
44
46
32
36
40
42
48
50
52
54
38
Note-1; Driver model FTD3S2P22-01 is applicable to the motors with The MAX output current is 2 A/phase.
Note-2; Driver model FTD3S3P17-01 is applicable to the motors with
.High speed steady torque type
Step
Standard size
angle
mm
deg./step
Holding Torque
inch
34
3.75
42 sq.x
40
Vcc = 24 V
1.65 sq.x
48
mNm
ozin
1.34
49
6.9
1.58
88
12.5
1.89
118
16.7
Winding
Current Voltage Inductance
Resistance
mH/2phase
V
/2phase A/2phase
1.4
3.4
1.75
4.3
1.4
5.0
2.0
1.3
2.0
1.2
2.5
1.3
2.8
4.42
3.5
5.16
3.5
6.5
1.7
4.0
2.1
8.7
1.7
7.7
Model
Driver
KR42HM4-551
-552
KR42JM4-551
-552
KR42KM4-551
-552
Page
56
58
60
Note-1; Driver model FTD3S2P22-01 is applicable to the motors with
Note-2; Driver model FTD3S3P17-01 is applicable to the motors with .
- Phase Drivers
Standard size
Power supply
mm
inch
577342 2.252.881.65 12-24V DC
7013435 2.765.281.38
24V DC
V DC
OUTPUT current
A
1.0-2.0
Step angle
Model
Page
1/1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8
FTD3S2P22-01
62
1.5-3.0
1/1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8
FTD3S3P17-01
64
29
P28-31 06.11.1 09:53 AM 30
3-Phase Hybrid Stepping Motor Driver
HIGH TORQUE, SILENT ROTATION
Features
Features
Applications
1. Drive circuit is simplified because the motor is
driven with star wiring connection.
2. High torque is obtained at low speed with the microstep driver.
3. Ultra-low vibration and low noise achieved with our
micro-step driver.
4. The step angle of 1/1, 1/2, 1/4, and 1/8 may be
chosen using our micro-step driver.
Suitable as controlled driving
source in scientific or high precision
industrial equipment such as OA
equipment, measuring equipment,
medical treatment equipment,
physics and chemistry equipment,
optical equipment, semiconductor
processing equipment, and other
precision machinery.
System Configuration
Drivers for 3-phase stepping motor
KT42 Series
KT60 Series
FTD3S3P17-01
KT50 Series
KT86 Series
FTD3S2P22-01
KR42 Series
KT56 Series
Pulse
signal
30
Power
supply:
5VDC
Power
supply:
24VDC
P28-31 06.11.1 09:53 AM 31
Vibration Comparison
Micro-Step drive 1/8
Full-Step drive
G10
G10
200.0PPS/ div
100.0PPS/ div
Advantage
divided by an electronic circuit and
sliced in the switching circuit
than applied to the motor coil.
The current is maintained at a
constant level whether the motor
angle.
The
rotates by a fixed angle by turning
the magnetizing phase on and off
through an input pulse. On the other
With this method the output
hand, with the micro-step driving
torque
speed
method, the current of one phase of
rotation is greatly improved with
the magnetizing phase can be
power consumption minimized.
gradually increased while the current
high
conventional
excitation method makes a rotor
is rotating at low or high speed.
during
the motor is gradually rotated by a
fine
High speed
capability
angle (3.75
, 1.2or 0.60) is
voltage, of the motor, is finely
the
High speed
specified
than
Low speed
the mechanically determined step
higher
Vibration
With the micro-step drive method,
method, a voltage sufficiently
Noise level
With the fixed current drive
Torque
Micro-step drive
Micro-step driver
Rectangular wave drive
Constant current driver
of other phase is decreased thereby
further dividing the step angle of the
motor and making rotation even
smoother.
THE
FTD3S3P17
driver,
the
FTD3S2P22 enable to set to step
divisions of 1/4 and 1/8. Micro
stepping drive is effective to reduce
mechanical driving noise particularly
when divisions not exceeding 1/8.
Rectangular wave drive
2-phase excitation (full-step)
This is then or mal 2-phase
excitation method. Torque is large
and damping characteristics are
excellent.
31
P62-68 06.11.1 09:56 AM 66
Explanation of the Dynamic Torque Curve
Slow acceleration/slow deceleration
This is a kind of control to raise or lower the pulse rate to
drive stepping motors in the slew region so they exhibit their
full capability. There are various methods but one example,
called trapezoidal driving, is shown in Fig. 2.
Torque
oz-in
Pull-out
torque
Pull-in
torque
f
Driving
frequency
Slew region
Self-starting
region
Rise-up
frequency
Pulse rate
pps
Driving
pulse rate
t
Maxiumum Maximum response
self-starting frequency
frequency
Regular
speed
Acceleration
Deceleration
Fig1 Torque/speed characteristics curve
Self-starting region
This is the region in which motors can be started and stopped
instantaneously.
Pulse rate
The number of pulses in a unit of time, and is shown in the
unitppswhich meanspulses per second. The relation
between pulse rate, speed (rpm) and angular velocity (rad/s)
is given below.
End of
slow-up
180
sP P
180
Start of
slow up
1
6N
N sP
P
6
s
Stop
where Angular velocityrad/s
sStep angledeg.
NSpeedrpm
PDriving pulse ratepps
Slow up
42ms
Regular
speed
Fig Trapezoidal drive of slow-up/slow down
control
Maximum self-starting frequency (pps)
This is the maximum pulse rate in the self-starting region. Care
must be taken, because it varies depending on the load
inertia.
Resonance phenomenon
When stepping motors are driven, torque decrease, misssteps, vibration and other unfavorable phenomena may occur
at some specific frequencies. This is called a Resonance
phenomenon, and is caused by the coincidence of intrinsic
vibration frequency and input pulse frequency of the motor. It
is experienced generally in the range of 100 to 200 pps. It is
impossible to eliminate this resonance fully, but the defect can
be reduced by changing the excitation mode or providing
damper.
Slew region
In this region, driving is possible only by slow acceleration/slow
deceleration control.
Maximum response frequency (pps)
This is the maximum pulse rate in the slew region.
Pull-in torque
This is the torque generated when started in the self-starting
region. It is also called the synchronization torque.
Pull-out torque
This is the torque generated when driven in the slew region.
Pull-out
This means the motor is coming out of synchronized operation
by being not able to follow the pulse signal from the pulse
generator.
Over-loading is the general cause, but noise (Electric/
Electro-magnetic) is also a cause in some cases.
66
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Caracteristicas Motores PDFDokumen60 halamanCaracteristicas Motores PDF0ZKRCITHOBelum ada peringkat
- CSK2Dokumen20 halamanCSK2呂宗原Belum ada peringkat
- Ax MS PDFDokumen2 halamanAx MS PDFClaudiuMaxmiucBelum ada peringkat
- 30Dokumen18 halaman30richard anishBelum ada peringkat
- MDX A and Compact To MDXB (En)Dokumen21 halamanMDX A and Compact To MDXB (En)Josmar GuidinoBelum ada peringkat
- Yaskawa Manuals 212Dokumen31 halamanYaskawa Manuals 212Pham LongBelum ada peringkat
- Drum Motor 80SDokumen5 halamanDrum Motor 80SManekGorisBelum ada peringkat
- SIM Holland Onan Cummins Onan Marine Pocket GuideDokumen32 halamanSIM Holland Onan Cummins Onan Marine Pocket GuideMarine CoreBelum ada peringkat
- Uci224d PDFDokumen8 halamanUci224d PDFRanu JanuarBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical One Line DiagDokumen5 halamanElectrical One Line DiagdownloadizBelum ada peringkat
- Ac Crane ControlDokumen28 halamanAc Crane ControlErc Nunez VBelum ada peringkat
- DC Motor DriveDokumen1 halamanDC Motor DrivealaxyadBelum ada peringkat
- Control Boxes Cat PagesDokumen8 halamanControl Boxes Cat PagesLuis Elí Silva ValdiviaBelum ada peringkat
- Price ListDokumen30 halamanPrice ListJagadeesh PalavalasaBelum ada peringkat
- 6121 Catalog DC Crane ControlDokumen30 halaman6121 Catalog DC Crane ControlcenicercBelum ada peringkat
- 04 LG7 StarteriDokumen108 halaman04 LG7 StarteriAbhijeet DurgeBelum ada peringkat
- GE Power Management: Modular Voltage RelaysDokumen27 halamanGE Power Management: Modular Voltage Relaysnabil160874Belum ada peringkat
- Driver DFC MotorDokumen24 halamanDriver DFC Motorda.dientuhnBelum ada peringkat
- LCD Display VID29 - Manual - EN-080606Dokumen10 halamanLCD Display VID29 - Manual - EN-080606RacielMCBelum ada peringkat
- Hagglunds Viking MK 64 163000 Bo LN 0100 PDFDokumen26 halamanHagglunds Viking MK 64 163000 Bo LN 0100 PDFKOSTAS100% (1)
- NPM ptm24h SpecsheetDokumen1 halamanNPM ptm24h SpecsheetElectromateBelum ada peringkat
- O5bt25 (1) SY-5BTDokumen2 halamanO5bt25 (1) SY-5BTtermoplaneBelum ada peringkat
- Lo-Cog DC Servo Motors: Series 8000Dokumen20 halamanLo-Cog DC Servo Motors: Series 8000papaandiBelum ada peringkat
- MotorDokumen48 halamanMotorHernan CuevasBelum ada peringkat
- HanbellRC2 TM ManualDokumen109 halamanHanbellRC2 TM Manualdcallahanmasonbarry100% (3)
- Stamford PM734F-Wdg 28 4 Pole 6 Wire Technical Data SheetDokumen6 halamanStamford PM734F-Wdg 28 4 Pole 6 Wire Technical Data SheetKVRamananBelum ada peringkat
- LG L1511S Chassis CL32Dokumen28 halamanLG L1511S Chassis CL32Jose AlbertoBelum ada peringkat
- Camco Na B RDM 082009Dokumen14 halamanCamco Na B RDM 082009Lucas RolanBelum ada peringkat
- Sevcon SC2000 Manual - With Calibrator Section PDFDokumen58 halamanSevcon SC2000 Manual - With Calibrator Section PDFRicardo Marquez ValenciaBelum ada peringkat
- ST7565PDokumen71 halamanST7565PsureshotstudioBelum ada peringkat
- Motor Catalog EN20190620 A6LDokumen69 halamanMotor Catalog EN20190620 A6LThai SalemBelum ada peringkat
- 3-Phase Stepping Motor VRDM 39x: Document: 100000116 Edition: d013, 2005.02Dokumen15 halaman3-Phase Stepping Motor VRDM 39x: Document: 100000116 Edition: d013, 2005.02TRAN TANBelum ada peringkat
- Section 8 (Recovery & Sorting) : Screens S8-S12Dokumen26 halamanSection 8 (Recovery & Sorting) : Screens S8-S12obedBelum ada peringkat
- Vexta Motor BrochureDokumen56 halamanVexta Motor BrochureSandy KohlndorferBelum ada peringkat
- Texas Instruments TSB83AA22AZAJ1418Dokumen25 halamanTexas Instruments TSB83AA22AZAJ1418pepegotera454Belum ada peringkat
- Otis Mcs 220c Gen2Dokumen96 halamanOtis Mcs 220c Gen2krp85734982% (49)
- Catalogue Card: Piston Type Steering GearsDokumen10 halamanCatalogue Card: Piston Type Steering GearsSenol SeidaliBelum ada peringkat
- ST7565R DatasheetDokumen72 halamanST7565R DatasheetRaissan ChedidBelum ada peringkat
- Low Voltage Final Distribution Products: Price ListDokumen30 halamanLow Voltage Final Distribution Products: Price ListAnonymous ufMAGXcskMBelum ada peringkat
- UCM224D - Technical Data SheetDokumen8 halamanUCM224D - Technical Data Sheet3efooBelum ada peringkat
- MAX1858 Evaluation Kit: General Description FeaturesDokumen7 halamanMAX1858 Evaluation Kit: General Description Features9183290782Belum ada peringkat
- 04 AirCircuitBreakerACBDokumen20 halaman04 AirCircuitBreakerACBtomi tintiaBelum ada peringkat
- YEG2 SDokumen2 halamanYEG2 Swpt_meBelum ada peringkat
- Villiers Engine Type DataDokumen4 halamanVilliers Engine Type DataPacoBelum ada peringkat
- UCM224CDokumen8 halamanUCM224C3efooBelum ada peringkat
- GEK-105281B (Guia de Seleccion de Motores)Dokumen4 halamanGEK-105281B (Guia de Seleccion de Motores)Erick Daniel Toyo MarinBelum ada peringkat
- LG Cl-18 Lb563t 563le Lb563t-Gr-gt TFT LCD Full 730Dokumen26 halamanLG Cl-18 Lb563t 563le Lb563t-Gr-gt TFT LCD Full 730Fidel ArroyoBelum ada peringkat
- Atv312 Quick Start en S1a10942 01Dokumen4 halamanAtv312 Quick Start en S1a10942 01Auliya UrrochmanBelum ada peringkat
- FuelPurifier WestfaliaDokumen193 halamanFuelPurifier WestfaliaHorst100% (2)
- UDN6118ADokumen8 halamanUDN6118AkizonzBelum ada peringkat
- SEW MOVITRAC 31C Crane Control ManualDokumen25 halamanSEW MOVITRAC 31C Crane Control ManualRoman JambrekBelum ada peringkat
- DELTA - IA-MDS - VFD-EL - C - EN - 20210420 MICRO DriveDokumen12 halamanDELTA - IA-MDS - VFD-EL - C - EN - 20210420 MICRO DriveJulian Ruiz SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- User Manual: HGM6310D/6320D Auto Start ModuleDokumen35 halamanUser Manual: HGM6310D/6320D Auto Start ModuleVaam Group sasBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkDari EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkBelum ada peringkat
- Variable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersDari EverandVariable Speed AC Drives with Inverter Output FiltersBelum ada peringkat
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorDari Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- DC Motors, Speed Controls, Servo Systems: An Engineering HandbookDari EverandDC Motors, Speed Controls, Servo Systems: An Engineering HandbookPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- (IJCST-V4I4P3) :reema Patel, A.N.Shewale, C.S.PatilDokumen3 halaman(IJCST-V4I4P3) :reema Patel, A.N.Shewale, C.S.PatilEighthSenseGroupBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Suku - Mar o Automatic PDFDokumen4 halaman2 Suku - Mar o Automatic PDFsuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- E RationingDokumen3 halamanE Rationingsuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Vibration Damping in Machine ToolsDokumen6 halamanAnalysis of Vibration Damping in Machine Toolssuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 199 Iphv7i3008xDokumen7 halaman199 Iphv7i3008xsuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 03 e Pipetube en WebDokumen18 halaman03 e Pipetube en Websuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- Wind Driven Mobile Charging of Automobile BatteryDokumen7 halamanWind Driven Mobile Charging of Automobile Batterysuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- FrameDokumen1 halamanFramesuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
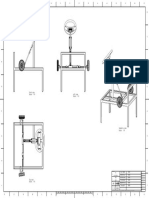
- D e S I G N o F A N A U T o M A T e D S o R T I N G o F o B J e C T R e J e C T I o N A N D C o U N T I N G M A C H I N eDokumen13 halamanD e S I G N o F A N A U T o M A T e D S o R T I N G o F o B J e C T R e J e C T I o N A N D C o U N T I N G M A C H I N esuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 1:1 XXX A1: Toshavi PCDokumen1 halaman1:1 XXX A1: Toshavi PCsuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 1:1 XXX A1: Designed By: DateDokumen1 halaman1:1 XXX A1: Designed By: Datesuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- Visvesvaraya Technological University BelgaumDokumen2 halamanVisvesvaraya Technological University Belgaumsuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 44 Tapsa Mech 006Dokumen9 halaman44 Tapsa Mech 006suraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 1:1 XXX A4: Designed By: DateDokumen1 halaman1:1 XXX A4: Designed By: Datesuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 55Dokumen3 halaman55md junuBelum ada peringkat
- FrameDokumen1 halamanFramesuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
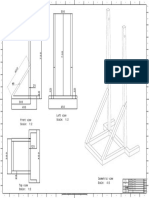
- Left View Scale: 1:2: 1:1 XXX A0Dokumen1 halamanLeft View Scale: 1:2: 1:1 XXX A0suraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 1:1 XXX A1: Toshavi 5/3/2016Dokumen1 halaman1:1 XXX A1: Toshavi 5/3/2016suraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 5Dokumen4 halaman5suraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- Dam Shutter Control Using Servo MotorDokumen3 halamanDam Shutter Control Using Servo MotorkarthikBelum ada peringkat
- M.H.Saboo Siddik PolytechnicDokumen5 halamanM.H.Saboo Siddik Polytechnicsuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 437NDokumen8 halaman437Nsuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- FrameDokumen1 halamanFramesuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- WWW Mechengg Net 2015 09 Design and Fabrication of InjectionDokumen17 halamanWWW Mechengg Net 2015 09 Design and Fabrication of Injectionsuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- MSHDokumen20 halamanMSHsuraj dhulannavar100% (1)
- 1:1 XXX A1: Toshavi 5/3/2016Dokumen1 halaman1:1 XXX A1: Toshavi 5/3/2016suraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 1:1 XXX A4: Designed By: DateDokumen1 halaman1:1 XXX A4: Designed By: Datesuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- 1:1 XXX A1: Designed By: DateDokumen1 halaman1:1 XXX A1: Designed By: Datesuraj dhulannavarBelum ada peringkat
- Dam Shutter Control Using Servo MotorDokumen3 halamanDam Shutter Control Using Servo MotorkarthikBelum ada peringkat
- Square Hole Drilling MachineDokumen4 halamanSquare Hole Drilling Machineedisonmech_erfBelum ada peringkat
- A Field Method For Measurement of Infiltration PDFDokumen31 halamanA Field Method For Measurement of Infiltration PDFHamza MamiBelum ada peringkat
- Filmgate Technical Screen Print InformationDokumen34 halamanFilmgate Technical Screen Print InformationramakrishnafacebookBelum ada peringkat
- Ficha Tecnica 750 GPMDokumen156 halamanFicha Tecnica 750 GPMByron Chele0% (2)
- F80 Press ReleaseDokumen2 halamanF80 Press Releasespscribd1Belum ada peringkat
- C617Dokumen5 halamanC617Rajesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ch4 Fluid KinematicsDokumen30 halamanCh4 Fluid Kinematicsa u khan100% (1)
- National Institute of Technology Durgapur: Department of Chemical EngineeringDokumen2 halamanNational Institute of Technology Durgapur: Department of Chemical Engineeringpiyush dwivediBelum ada peringkat
- R.pearson - Key To Consciousness. Quantum GravitationDokumen16 halamanR.pearson - Key To Consciousness. Quantum GravitationJorgee_Porgee_8203Belum ada peringkat
- Sade-5tnqzd r12 enDokumen9 halamanSade-5tnqzd r12 enPop-Coman SimionBelum ada peringkat
- Astronomy - November 2013 (Gnv64)Dokumen80 halamanAstronomy - November 2013 (Gnv64)edies50% (2)
- HGV Gas Fuel Throttle ValveDokumen41 halamanHGV Gas Fuel Throttle ValveSayayinBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report On AdsorptionDokumen12 halamanLab Report On AdsorptionElizabeth Polancos BruaBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Servo RobotDokumen40 halamanMicro Servo Robotlokesh mahor0% (1)
- ASh SeriesDokumen48 halamanASh SeriesAyman Saber100% (2)
- The Definite Integral and Its ApplicationsDokumen13 halamanThe Definite Integral and Its Applicationsapi-312673653100% (1)
- Neuro ThermodynamicsDokumen32 halamanNeuro ThermodynamicsNanjit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ahmed BodyDokumen15 halamanAhmed Bodyk sai krishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Frac To GraphyDokumen639 halamanFrac To GraphyBHARANIBelum ada peringkat
- Lift Stability AnalysisDokumen23 halamanLift Stability Analysisaiyubi2Belum ada peringkat
- Valve and Pipeline Design Notes - Part 1Dokumen29 halamanValve and Pipeline Design Notes - Part 1Anilduth Baldan100% (2)
- Long-Life Asphalt Pavements - Technical2007Dokumen24 halamanLong-Life Asphalt Pavements - Technical2007Sen HuBelum ada peringkat
- ACA 2010 Abstracts Manish Chandra PathakDokumen602 halamanACA 2010 Abstracts Manish Chandra Pathakpmcy2Belum ada peringkat
- A. Kitaigorodsky - I Am A Physicist (1971, Mir Publishers)Dokumen221 halamanA. Kitaigorodsky - I Am A Physicist (1971, Mir Publishers)dal pesBelum ada peringkat
- BSC Combined SO (8 Banks & FIs) - 2018 (Written Math Solution) by Ajgar Ali - PDF Version 1Dokumen10 halamanBSC Combined SO (8 Banks & FIs) - 2018 (Written Math Solution) by Ajgar Ali - PDF Version 1Zia UddinBelum ada peringkat
- Applied SciencesDokumen25 halamanApplied SciencesMario BarbarossaBelum ada peringkat
- Filetype PDF Photoconduction SemiconductorDokumen2 halamanFiletype PDF Photoconduction SemiconductorGregBelum ada peringkat
- Part 5 MT Drives and Mechanisms 1Dokumen11 halamanPart 5 MT Drives and Mechanisms 1Anonymous YaJlLHYBelum ada peringkat
- Physics - Thermal Physics - Lab ReportDokumen6 halamanPhysics - Thermal Physics - Lab ReportKali stringsBelum ada peringkat
- Bass Instruments: Installation and Instruction ManualDokumen34 halamanBass Instruments: Installation and Instruction ManualYul GoncalvesBelum ada peringkat
- Permutations and CombinationsDokumen69 halamanPermutations and CombinationsNikhil0% (2)