Chapter 7: Glaciers, Deserts, and Wind
Diunggah oleh
Rishi KamalJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 7: Glaciers, Deserts, and Wind
Diunggah oleh
Rishi KamalHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
7/22/2016
Mr.Cox'sWebsite
Home|Biology|EarthScience|GradingPolicies&Expectations|BiologyLinks|EarthScienceLinks
Section1|Section2|Section3
Chapter7:Glaciers,Deserts,andWind
Ch.7.1Glaciers
TypesofGlaciers
15,000yearsago,30%ofEarthwascoveredbyglacialice
IceageaperiodoftimewhenmuchofEarth'slandiscoveredinglaciers
Glacierathickicemassthatmovesslowlyoverthelandsurface
Glaciersoccurinareaswheremoresnowfallsinthewinterthanmeltsinthesummer
Snowlinethelowestelevationinaparticularareathatremainscoveredinsnowallyear
Snowabovesnowlineaccumulatesandcompacts,causingrecrystalizationintocoursegrains,furtherpressure
changesittointerlockingcrystalsofglacierice
Gravitypullsglaciersdownhill:theyaccumulate,transport,anddepositsediment
ValleyGlaciersIcemassesthatslowlyadvancedownvalleysthatwereoriginallyoccupiedby
streams
*Avalleyglacierisastreamoficethatflowsbetweensteeprockwallsfromaplacenearthetopof
themountainvalley
IceSheetsEnormousicemassesthatflowinalldirectionsfromoneormorecentersandcover
everythingbutthehighestland
*Icesheetsaresometimescalledcontinentalicesheetsbecausetheycoverlargeregionswherethe
climateisextremelycold.Theyarehugecomparedtovalleyglaciers
Tworemainingicesheets:GreenlandandAntarctica
HowGlaciersMove
*Themovementofglaciersisreferredtoasflow.Glacialflowhappenstwoways:plasticflowandbasalslip
Plasticitythedistortionandchangingofshapeofbrittleiceunderhighpressure
Basalslipslippingoftheglacierdownhill,top50mnotunderpressuresodoesnothavebasalslip
RatesofGlacialMovement
Glacierstravelatdifferentspeeds,somealternatebetweenslowandfast
BudgetofaGlacier
Belowthesnowline,glacierslooseiceandnewsnowtomelting:calledthezoneofwastage
Iceisalsolostbycalving:largepiecesbreakingoff
Icebergs:10%ofmassisvisible
*Theglacialbudgetisthebalanceorlackofbalancebetweenaccumulationattheupperendofaa
glacierandloss,orwastage,atthelowerend
Glaciermayadvance,retreatortheterminus(front)mayremainthesame
GlacialErosion
Glaciersarenaturesbulldozersrockfragmentsthatareerodedbytheglacierdropattheglacier'sfootwherethe
icemelts
*Manylandscapeswerechangedbythewidespreadglaciersoftherecenticeage
HowGlaciersErode
Glaciersmainlyerodeintwoways:pluckingandabrasion
Plucking:watergetsintocracksbeneathice,freezingthenfracturestherocks,movingglacierthen
picksupthepiecesandincorporatesthem
Abrasion:iceandrockfragmentsscourbedrocktheycreaterockflour
Striationscanshowthedirectionofflow
Glacialerosiondependantonfourfactors:1)rateofmovement2)thicknessofice3)shape,
abundance,andhardnessoftherockfragmentsintheice4)typeofsurfacebelowglacier
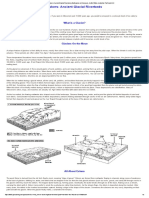
LandformsCreatedbyGlacialErosion
*Glaciersareresponsibleforavarietyoferosionallandscapefeatures,suchasglacialtroughs,hangingvalleys,
cirques,aretes,andhorns.
GlaciatedValleys
Asaglaciermovesdownavalleyonceoccupiedbyastream,theglacierwidens,deepens,and
straightensthevalley
GlacialtroughUshapedvalleyformedfromglacialerosion
Mainglacierscutdeeperthansideglaciers,whenrecedingoccurs,itleaveshangingvalleysthatoften
formwaterfalls
Cirques
Abowlshapeddepressionattheheadofaglacialvalleythatissurroundedonthreesidesbysteep
rockwalls
Beginasirregularitiesinthemountainside,pluckingbyglaciercarvesthecirque,movementofglacier
carriesawayrock
AretesandHorns
http://coxclasses.com/earthscience/ch7/esch7.html
1/4
7/22/2016
Mr.Cox'sWebsite
Aretesformwhencirquesonoppositesidesofaridgegrow,thedivideseparatingthemisreducedtoa
narrow,sharpridge
Hornsformwhereseveralcirquessurroundasinglehighmountainleavingasharppyramidlikepeak
GlacialDeposits
Glacierstransporthugeloadsofdebris,whentheglaciermeltsitdepositsitssediment
TypesofGlacialDrift
*Glacialdriftappliestoallsedimentsofglacialorigin,nomatterhow,where,orinwhatformthey
weredeposited.Therearetwotypesofglacialdrift:tillandstratifieddrift
Tillmaterialdepositeddirectlybytheglacier
Tillisusuallyunsortedmixturesmadeupofmanyparticlesizes
Stratifieddriftsedimentlaiddownbyglacialmeltwater
Stratifieddriftissortedbysizeandweight,oftenconsistsofsandandgravel
Glacialerratics:bouldersfoundintillorlyingfreeontheground,differinmineralcontentthan
surroundingunderlyingbedrock
Moraines,OutwashPlains,andKettles
*Glaciersareresponsibleforavarietyofdepositionalfeatures,includingmoraines,outwashplains,kettles,
drumlins,andeskers
Moraineslayersorridgesoftillleftbyglacierswhentheymelt
LateralMoraines
Lateralmorainesareridgesthatformalongthesidesofglacialvalleysfromdebrisofthevalleywalls
Medialmorainesareformedwhentwovalleyglaciersjointoformasingleicestream
EndMorainesandGroundMoraines
EndMoraineisformedwhenaglacierisstationarytheicecontinuestoflowandcarriesdebristothe
endoftheglacier
GroundMorainesareformedwhenglacierrecedesatasteadyrateleavingarockstrewn,gently
rollingplain
Groundmorainesfillinlowspotsandblockoldstreamchannels,possiblyresultinginpoorlydrained
swamplands
TerminalandRecessionalMoraines
Asaglaciermeltsithasperiodsofrecessionandequilibrium,formingendmorainesandground
moraines
Terminalmoraineisthefarthestendmoraine,othersarerecessionalendmoraines
OutwashPlains
Abroad,ramplikeaccumulationofsedimentdownstreamfromanendmoraineformedwhenglacier
isstationary
Kettles
Kettlesformwhenblocksofstagnanticebecomeburiedindriftandeventuallymelt,leavingbehind
smalllakesordepressions
DrumlinsandEskers
Drumlinsarestreamlinedhillscomposedoftill,occurinclusterscalleddrumlinfields
Drumlinsaresteeperononeendthesteepsidefacesthedirectiontheicecamefrom,andthegentler
slopepointsinthedirectionthemoved
Eskersaresnakelikeridgescomposedofsandandgravelthatweredepositedbystreamsonceflowing
intunnelsbeneathglaciers
GlacialLandforms
GlaciersoftheIceAge
Duringrecenticeage,glacierscoveredalmost30%ofEarth'sland,theNorthernHemispherehadtwicetheiceof
theSouthernHemisphere
IceAgeEffectsonDrainage
Duringtherecenticeage,glacialerosiontransformedlowlandsintowide,deepbasinsthatfilledwithwaterand
eventuallybecametheGreatLakes
Formationandgrowthoficesheetstriggeredchangesinclimatearidregionsbecamecoolerandwetterresultingin
theformationoflakes
ReturntoTop
Ch.7.2Deserts
Desertlandscapesshowtheeffectsofbothrunningwaterandwind
GeologicProcessesinAridClimates
Desertshaveangularrocks,sheercanyonwalls,andsurfacescoveredinpebblesorsand
Weathering
http://coxclasses.com/earthscience/ch7/esch7.html
2/4
7/22/2016
Mr.Cox'sWebsite
Humidregionsreflectthestronginfluenceofchemicalweathering
*Muchoftheweathereddebrisindesertshasresultedfrommechanicalweathering
Rockweatheringisgreatlyreducedbecauseofthelackofmoistureandscarcityoforganicacidsfrom
decayingplants,asaresultdebrisconsistsofrockwhosemineralsremainunchanged
*Chemicalweathering,however,isnotcompletelyabsentindeserts.Overlongtimespans,claysand
thinsoilsdoform.
TheRoleofWater
*Inthedesert,moststreamsareephemeraltheyonlycarrywaterafteritrains
Westernstatescallthesestreamswashesorarroyos
Flashfloodsarecommon,lackofvegetationallowswatertoquicklyrunoffthelanderosioncanbe
extreme
BasinandRange:ADesertLandscape
Aridregionshaveinternaldrainage,nottooceans
Waterrunningoutofcanyonsareheavilyloadedwithsediment,emergingfromtheconfinesofthecanyonsthe
runoffspreadsandlosesvelocity,dumpingitsload
Alluvialfanconeofdebrisatthemouthofacanyon
Onrareoccasion,streamsmayflowacrossthealluvialfanstothecenterofthebasinconvertingittoalakecalled
Playalakes
*Mostdesertstreamsdryuplongbeforetheyeverreachtheocean.Thestreamsarequicklydepletedby
evaporationandsoilinfiltration
Ifwatersourceislargeenough,astreamcancontinuethroughadesert
*Mostdeserterosionresultsfromrunningwater.Althoughwinderosionismoresignificantindesertsthan
elsewhere,waterdoesmostoftheerosionalworkindeserts
ReturntoTop
Ch.7.3LandscapesShapedbyWind
WindErosion
Strongdesertwindspickup,transport,anddepositgreatquantitiesoffinesediment
*Winderodesinthedesertintwoways:deflationandabrasion
Deflationtheliftingandremovaloflooseparticlessuchasclayandsilt,canleadtoblowouts
Saltationlargerparticlesrollorskipalongthesurface
Desertpavementstonysurfacelayercomposedofcoarserparticles
Abrasionwindblownsandcutsandpolishesexposedrocksurfaces
Sandrarelytravelsmorethanameterabovethesurfacesoeffectislimitedinaverticalextent
WindDeposits
*Windcancreatelandformswhenitdepositsitssediments,especiallyindesertsandalongcoasts.Bothlayersof
loessandsanddunesarelandscapefeaturesdepositedbywind
Loesswindblownsiltthatblanketsthelandscape
SandDunes
Windreleasessedimentwhenitsvelocityfalls,sandaccumulateswhereveranobstructioncrossesits
pathandslowsitsmovement
*Unlikedepositsofloess,whichformblanketlikelayersoverbroadareas,windscommonlydeposit
sandinmoundsorridgescalleddunes
Dunescanoccuratanobstruction,oncethesandmoundsupitservesasitsownobstruction
Dunesoftenhavegentleslopefacingthewindandasteeperslopeontheshelteredside
Dunestendtomigrateinthedirectionofthewind
Crossbeds:layersofsedimentdepositedformlayersinclinedinthedirectionthewindisblowing
TypesofSandDunes
*Whatformsanddunesassumedependsonthewinddirectionandspeed,howmuchsandisavailable,andthe
amountofvegetation.
BarchanDunessolitarydunesshapedlikecrescentsformedonhard,flatgroundwithlimitedsand
andvegetation
TransverseDunesdunesinaseriesoflongridgesformedwhenwindissteady,sandisplentiful,
vegetationislimitedareperpendiculartowind
BarchanoidDunesintermediatebetweenabarchanandtransverseduneformatrightanglestowind
LongitudinalDuneslongridgesthatformparalleltotheprevailingwindformwhensandis
moderateandwinddirectionvariesslightly
ParabolicDunesbackwardbarchandunestipspointintowindformwheresomevegetationcovers
thesand
StarDunesisolatedhillsofsandusuallyhave3or4sharpridgesthatmeetinthemiddleformin
areasofvariablewinddirection
ReturntoTop
2012byDaveCoxWebmaster.Anypartofthisdocumentmaybereproducedorutilizedinany
formorbyanymeansprovidedpropercitationandcreditaregivenfortheworkandnocostdisseminationisintended.
PagelastupdatedJuly24,2012.
http://coxclasses.com/earthscience/ch7/esch7.html
3/4
7/22/2016
Mr.Cox'sWebsite
http://coxclasses.com/earthscience/ch7/esch7.html
4/4
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- GlacierDokumen12 halamanGlacierAl Sakib RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- 07.glaciers Deserts and WindDokumen33 halaman07.glaciers Deserts and WindChristine ValerioBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers and GlaciationDokumen2 halamanGlaciers and GlaciationVera BalmesBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers Notes Part 1Dokumen6 halamanGlaciers Notes Part 1David ZhaoBelum ada peringkat
- Earth Science Chapter on Glaciers, Deserts, and Wind ErosionDokumen33 halamanEarth Science Chapter on Glaciers, Deserts, and Wind ErosionpaulaOrialBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers and Glaciation: Definition of A GlacierDokumen9 halamanGlaciers and Glaciation: Definition of A GlacierS Hashim RizviBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers and Glaciation: Definition of A GlacierDokumen9 halamanGlaciers and Glaciation: Definition of A GlacierHarsh DevBelum ada peringkat
- Glacier and Periglacial LandformsDokumen4 halamanGlacier and Periglacial LandformsPeter PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquakes: Seismic Waves and OriginsDokumen5 halamanEarthquakes: Seismic Waves and OriginsSathya RauBelum ada peringkat
- Glacier Course MIT Earthsurface 7Dokumen81 halamanGlacier Course MIT Earthsurface 7Iván Cáceres AnguloBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers: How They Form and Their ImportanceDokumen4 halamanGlaciers: How They Form and Their ImportanceFlorence FlorahBelum ada peringkat
- Presented By: Moises Malone R. MontealegreDokumen47 halamanPresented By: Moises Malone R. MontealegreClifford Cobsilen Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Science Ch. 6 SummaryDokumen15 halamanScience Ch. 6 SummaryYuan MadriagaBelum ada peringkat
- geo notes for finalDokumen20 halamangeo notes for finalzane yapBelum ada peringkat
- Earth's Spheres: An Overview of the Geosphere, Biosphere, Hydrosphere and AtmosphereDokumen4 halamanEarth's Spheres: An Overview of the Geosphere, Biosphere, Hydrosphere and AtmosphereHarris AbdulganiBelum ada peringkat
- GlacierDokumen2 halamanGlacierPhuong NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers 101: Understanding Glacier Formation and DynamicsDokumen6 halamanGlaciers 101: Understanding Glacier Formation and DynamicsZadem PintoBelum ada peringkat
- Geo-Chapter 12-FinalDokumen32 halamanGeo-Chapter 12-FinalPaul Mangoma100% (1)
- Geo Final Study GuideDokumen3 halamanGeo Final Study GuideBrianna Lynn BauchBelum ada peringkat
- CryosphereDokumen20 halamanCryosphereJG MercadoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture The CryosphereDokumen22 halamanLecture The CryosphereKiara TongBelum ada peringkat
- Glacial Cirque PaperDokumen5 halamanGlacial Cirque PaperDylan BrazierBelum ada peringkat
- Insights into Glacial Geology and MorphologyDokumen12 halamanInsights into Glacial Geology and MorphologyGeo CUKBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Glaciers and GlaciationsDokumen4 halaman11 Glaciers and GlaciationsMUHAMMAD NUMANBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers and Ice: Physical Properties and LandformsDokumen31 halamanGlaciers and Ice: Physical Properties and LandformsIvanne BrionesBelum ada peringkat
- Continental (Aeolian Desert Glacial Systems)Dokumen76 halamanContinental (Aeolian Desert Glacial Systems)Siyad AbdulrahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciation: A Cool Look at Dynamic Planet ProcessesDokumen4 halamanGlaciation: A Cool Look at Dynamic Planet Processesbohongnih0% (1)
- GlaciersDokumen19 halamanGlaciersMurtaza MazharBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 7 - Glaciers, Deserts, WindDokumen32 halamanChapter - 7 - Glaciers, Deserts, WindRinen ParacadBelum ada peringkat
- Partido State University: Module 14: Formation of World GlaciersDokumen6 halamanPartido State University: Module 14: Formation of World GlaciersRalph NavelinoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture9 - Glaciers and LandformsDokumen86 halamanLecture9 - Glaciers and LandformsAniket KannoujiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers and GlaciationDokumen45 halamanGlaciers and Glaciationmanica.arevaloBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel Geography A-level Glaciated Landscapes & Change GlossaryDokumen4 halamanEdexcel Geography A-level Glaciated Landscapes & Change GlossarySashiBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers Reaction PaperDokumen1 halamanGlaciers Reaction PaperJay AnnBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Notes - Glaciated Landscapes and Change - Edexcel Geography A-LevelDokumen28 halamanDetailed Notes - Glaciated Landscapes and Change - Edexcel Geography A-LevelHelp GloPosNetBelum ada peringkat
- Geology 101 - Introduction to Physical Geology Basics - Glaciers and Ice AgesDokumen1 halamanGeology 101 - Introduction to Physical Geology Basics - Glaciers and Ice AgesJazmine VegaBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Notes - Glaciated Landscapes and Change - Edexcel Geography A-LevelDokumen8 halamanEssential Notes - Glaciated Landscapes and Change - Edexcel Geography A-LevelSashiBelum ada peringkat
- GEO 110 NotesDokumen9 halamanGEO 110 NotesaliBelum ada peringkat
- Earth Science: Weathering and Erosion AgentsDokumen85 halamanEarth Science: Weathering and Erosion AgentsElijah Raphael YasaBelum ada peringkat
- Avalanche ProjectDokumen13 halamanAvalanche ProjectSauri ChaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- What Are GlaciersDokumen14 halamanWhat Are GlaciersDanielaRRBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers: Types and LandformsDokumen7 halamanGlaciers: Types and LandformsTEAM ROGUE PAKISTANBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Strategies and Glacier FormationDokumen7 halamanReading Strategies and Glacier FormationNoor AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- GlaciersDokumen33 halamanGlaciersArtav SaurabhBelum ada peringkat
- Glacial Processes and LandformsDokumen33 halamanGlacial Processes and LandformsSimona Andreea BurlacuBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers Deserts Wind LandscapesDokumen6 halamanGlaciers Deserts Wind LandscapesJulius BorrisBelum ada peringkat
- SelectionDokumen12 halamanSelectionMuhammad SarifBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3 - Glaciers & Ice CapsDokumen15 halamanTopic 3 - Glaciers & Ice CapsLove Grace DavinBelum ada peringkat
- Glacial Landforms and Depositional ProcessesDokumen7 halamanGlacial Landforms and Depositional ProcessesSahibzada AizazBelum ada peringkat
- Yr 8 Ice On The Land KODokumen5 halamanYr 8 Ice On The Land KOHadad LwazeBelum ada peringkat
- Ice Age Facts and Information - Environment Books | Children's Environment BooksDari EverandIce Age Facts and Information - Environment Books | Children's Environment BooksPenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- Glaciers & Glaciation: - A Glacier: Is A Thick Ice Mass That Forms OverDokumen48 halamanGlaciers & Glaciation: - A Glacier: Is A Thick Ice Mass That Forms OverTamer AbuaitaBelum ada peringkat
- Ses 2103 Lectures - Unit Three-1Dokumen8 halamanSes 2103 Lectures - Unit Three-1TREVOR MAVUNGABelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers: II. Subdivided Into 3 Major CategoriesDokumen4 halamanGlaciers: II. Subdivided Into 3 Major CategoriesNayoon KimBelum ada peringkat
- Short Paper GlacierDokumen4 halamanShort Paper GlacierBrittany DelaCruzBelum ada peringkat
- GCSE GEOGRAPHY The Glacial System RevisionDokumen2 halamanGCSE GEOGRAPHY The Glacial System RevisionlottiewrightBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciers, Desert, and WindDokumen45 halamanGlaciers, Desert, and WindDURANO, ROSELLE Z.SCIBelum ada peringkat
- Petros Mjali Student Number: 207111588 Assignment 3: Question 1 CoastsDokumen11 halamanPetros Mjali Student Number: 207111588 Assignment 3: Question 1 CoastsOluseyi AbegundeBelum ada peringkat
- Interesting Facts About Glaciers - Geology for Beginners | Children's Geology BooksDari EverandInteresting Facts About Glaciers - Geology for Beginners | Children's Geology BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Els Week 6Dokumen3 halamanEls Week 6Jessica BorromeoBelum ada peringkat
- Construction and Operation of Megger ExplainedDokumen11 halamanConstruction and Operation of Megger ExplainedRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Phase Wiring Installation in Multi Story BuildingDokumen5 halaman3 Phase Wiring Installation in Multi Story BuildingRishi Kamal100% (1)
- MarketingDokumen6 halamanMarketingRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Geoid - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen3 halamanGeoid - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- List of Useful Websites For IAS Preparation - ClearIAS 2Dokumen17 halamanList of Useful Websites For IAS Preparation - ClearIAS 2Rishi Kamal100% (1)
- Comparison Between IES 2016 and 2017 Syllabus For Electrical EngineeringEEDokumen5 halamanComparison Between IES 2016 and 2017 Syllabus For Electrical EngineeringEERishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- R 126 J 99 ApplicationformDokumen1 halamanR 126 J 99 ApplicationformRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Latitude - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen8 halamanLatitude - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Print FriendlyDokumen3 halamanPrint FriendlyRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- ESE Reforms PublicityDokumen11 halamanESE Reforms PublicityChirag PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Glaciation's Environmental ImpactsDokumen1 halamanGlaciation's Environmental ImpactsRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- GC1X75Z Eskers - Ancient Glacial Riverbeds (Earthcache) in Wisconsin, United States Created by ThePharmGirlDokumen2 halamanGC1X75Z Eskers - Ancient Glacial Riverbeds (Earthcache) in Wisconsin, United States Created by ThePharmGirlRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Barrier Island - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen3 halamanBarrier Island - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Glacial Landforms and Features - The Shape of The Land, Forces and Changes, Spotlight On Famous Forms, For More InformationDokumen7 halamanGlacial Landforms and Features - The Shape of The Land, Forces and Changes, Spotlight On Famous Forms, For More InformationRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Geography 101 OnlineDokumen2 halamanGeography 101 OnlineRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Practice QuestionsDokumen6 halamanChapter 3 Practice QuestionsRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Continental Ice Sheets and Polar RegionsDokumen1 halamanContinental Ice Sheets and Polar RegionsRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Erosion and Deposition - Action of Wind and Waves - Clear IASDokumen4 halamanErosion and Deposition - Action of Wind and Waves - Clear IASRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Download Voot VideosDokumen3 halamanDownload Voot VideosRishi Kamal100% (1)
- Bay - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen1 halamanBay - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Tech Hacks Learned in 10 MinutesDokumen9 halaman10 Tech Hacks Learned in 10 MinutesRishi Kamal100% (1)
- List of Useful Websites For IAS Preparation - ClearIASDokumen2 halamanList of Useful Websites For IAS Preparation - ClearIASRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Moraine SDokumen4 halamanMoraine SRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Accounting DefinitionsDokumen4 halamanFinancial Accounting DefinitionsRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Learn About Ground Moraines And Their Importance For AgricultureDokumen1 halamanLearn About Ground Moraines And Their Importance For AgricultureRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Mahendra Singh Dhoni - A Timeline - The HinduDokumen2 halamanMahendra Singh Dhoni - A Timeline - The HinduRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Rishi Kamal FT174070 MRP ScheduleDokumen5 halamanRishi Kamal FT174070 MRP ScheduleRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Zhou Enlai - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen25 halamanZhou Enlai - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Patent Act - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen2 halamanPatent Act - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRishi KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual For Mathematics For EconomicsDokumen42 halamanSolution Manual For Mathematics For EconomicsMarcia Smith0% (1)
- F8 Chapter 01Dokumen3 halamanF8 Chapter 01Tay Joo FangBelum ada peringkat
- The Reception Office: Monday September 28, 2020Dokumen2 halamanThe Reception Office: Monday September 28, 2020Chikanma OkoisorBelum ada peringkat
- Richard Swinburne - MiraclesDokumen10 halamanRichard Swinburne - Miraclesrosskirk24Belum ada peringkat
- Dubai Workshop RegistrationDokumen2 halamanDubai Workshop RegistrationmfkmughalBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment I Topics: LevellingDokumen2 halamanAssignment I Topics: LevellingsagarBelum ada peringkat
- Environtment Factor - Light Rev Asr 130918Dokumen60 halamanEnvirontment Factor - Light Rev Asr 130918Irvan MahmudiBelum ada peringkat
- Heritage Theme Resort: Thesis ReportDokumen8 halamanHeritage Theme Resort: Thesis ReportNipun ShahiBelum ada peringkat
- ABAP - Dynamic Variant Processing With STVARVDokumen12 halamanABAP - Dynamic Variant Processing With STVARVrjcamorim100% (1)
- Summarizing and ParaphrasingDokumen2 halamanSummarizing and ParaphrasingKylle VillafloresBelum ada peringkat
- Purcell 10.2: Solutions To Problem Set 12Dokumen5 halamanPurcell 10.2: Solutions To Problem Set 12Eugene YiBelum ada peringkat
- CGC Construction Handbook Ch9 Acoustical Ceiling Design and Application Can en PDFDokumen26 halamanCGC Construction Handbook Ch9 Acoustical Ceiling Design and Application Can en PDFKeri Gobin SamarooBelum ada peringkat
- Nikola Tesla: Mysterious Facts (Essay)Dokumen2 halamanNikola Tesla: Mysterious Facts (Essay)DenisKisurkinBelum ada peringkat
- Database AdministrationDokumen12 halamanDatabase AdministrationjayBelum ada peringkat
- Open Area Test SitesDokumen15 halamanOpen Area Test SitesSravani KorapakaBelum ada peringkat
- Geometric and Algebraic Foundations of Computational OrigamiDokumen25 halamanGeometric and Algebraic Foundations of Computational Origamisqrt_2_Complex100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Design For TheatreDokumen15 halamanChapter 2 - Design For TheatreShannaiah Jade BoracBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Inventory Module ProcessDokumen37 halamanSAP Inventory Module ProcessRajesh ChalkeBelum ada peringkat
- Manuel V. Gallego Foundation Colleges, Inc. Cabanatuan City, PhilippinesDokumen12 halamanManuel V. Gallego Foundation Colleges, Inc. Cabanatuan City, PhilippinesEdelmar BenosaBelum ada peringkat
- Journal Final For WEBDokumen84 halamanJournal Final For WEBnormanwillowBelum ada peringkat
- Microsoft Excel - Application Note - Crunching FFTsDokumen5 halamanMicrosoft Excel - Application Note - Crunching FFTsvoltus88Belum ada peringkat
- E Role of Natural Resources in Economic Development PDFDokumen31 halamanE Role of Natural Resources in Economic Development PDFLisaMarieGaranBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Terapi Marital IndonesiaDokumen10 halamanJurnal Terapi Marital IndonesiaErickson Arthur SiahaanBelum ada peringkat
- EN 388 StandardDokumen11 halamanEN 388 StandardEngr Saeed Anwar100% (1)
- Divemaster Repasos ManualDokumen9 halamanDivemaster Repasos ManualIsrael Mauricio Olivares Millán100% (1)
- Rekha RaniDokumen2 halamanRekha RaniSANDEEP SinghBelum ada peringkat
- An Integrative Approach To Enhancing Small-Scale Poultry Slaughterhouses by Addressing Regulations and Food Safety in Northern - ThailandDokumen9 halamanAn Integrative Approach To Enhancing Small-Scale Poultry Slaughterhouses by Addressing Regulations and Food Safety in Northern - ThailandgustiBelum ada peringkat
- Process States and Memory Management LabDokumen8 halamanProcess States and Memory Management LabJámesBelum ada peringkat
- Body Language and AttractionDokumen21 halamanBody Language and Attractionpoiqwe1Belum ada peringkat
- Fisher Faculty Letter Re Giuliani 04.17.15Dokumen2 halamanFisher Faculty Letter Re Giuliani 04.17.15Rochester Democrat and ChronicleBelum ada peringkat