Assignment 1 & 2
Diunggah oleh
Ravindra KumarDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Assignment 1 & 2
Diunggah oleh
Ravindra KumarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
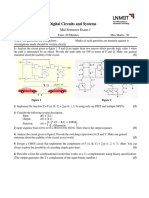
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION
SUBJECT- MICROWAVE ENGINEERING(EEC-601)
ASSIGNMENT-I
1) What are the high frequency limitations of conventional tubes? Explain clearly.
2) Explain with suitable sketch the operation of two-cavity Klystron amplifier. explain the concept of velocity
and current modulations. Explain how velocity modulation creates density modulation in a Klystron amplifier.
How does the reflex Klystron differ from amplifier Klystron?
3) Explain with schematic diagram the operation of Reflex Klystron Oscillator. Draw Applegate diagram for the
Reflex Klystron Oscillator.
4) Obtain relation between repeller voltage and frequency of operation of Reflex Klystron Oscillator..
5) What are modes in Reflex Klystron oscillator? Sketch output power and frequency of Klystron versus repeller
voltage for Reflex Klystron.
6) Derive an expression for the efficiency of the Klystron amplifier.
7) A two-cavity Klystron amplifier has the following parameters: Vo = 1000V, Ro = 40 K ohms, Io = 25 mA, f =
3 GHz. Gap spacing in either cavity (d) = 1 mm. Spacing between the two cavities (L) = 4 cms. Effective
shunt impedance, excluding beam loading (Rsh) = 3 p K ohms. Find (i) The input gap voltage to give
maximum voltage (V2) (ii) The voltage gain, neglecting the beam loading in the output cavity, (iii) The
efficiency of the amplifier, neglecting beam loading. (Ans: 96.5V, 8.595, 46.2%)
8) A two-cavity Klystron operates at 4.5GHz. The dc beam voltage is 10KV. Cavity gap spacing is 2mm. For a
given input, the magnitude of the gap voltage is 100V. Calculate the time the electrons are in the gap, the
transit angle, and the range of velocities of electrons as they leave the gap region. (Ans. 33.7 psec, 0.95 rad,
0.598x108m/s and 0.588x108 m/s).
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION
SUBJECT- MICROWAVE ENGINEERING(EEC-601)
ASSIGNMENT-II
1) Describe with suitable diagram the following Microwave (i) Travelling wave tube (TWT) (ii) Magnetron.
2) A Reflex Klystron is operating at 9GHz and the mode number n is 2. Calculate the transit time in secs.
3) What is a re-entrant cavity? Explain it. In Reflex Klystron, the re-entrant cavity is resonant at 9 GHz. The
half power frequencies are separated? 15 MHz from the centre frequency. Calculate the loaded Q for the
cavity.
4) Describe qualitatively the mechanism of operation of a travelling wave tube amplifier. How the
oscillations are prevented in practice.
5) What is a slow wave structure? Give some typical structures, which support slow waves.
6) Explain the working of a magnetron oscillator. With the help of the Rieke diagram, discuss its
performance under varying load conditions. What is the typical range of efficiencies obtainable in a
magnetron?
7) What is strapping of Magnetrons? Describe the techniques used in magnetrons for mode separation and
for tuning its output frequency.
8) What is meant by -mode operation in a magnetron? Describe how strapping separates the ?mode from
other possible modes.
9) With the aid of a sketch, explain the operation of a backward-wave oscillator (BWO).
10) A cylindrical magnetron has the following parameters. Inner radius = 0.15m Outer radius = 0.45m
Magnetic flux density = 1.2 milliwebers/m2 (a) Calculate the Hull cut off voltage (b) Determine the cut
off magnetic flux density of the beam voltage is 6KV.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- TUTORIAL of Microwave NGGDokumen6 halamanTUTORIAL of Microwave NGGArunima Banerjee0% (1)
- Ec7105-Microwave EngineeringDokumen9 halamanEc7105-Microwave EngineeringKushal GellaBelum ada peringkat
- Mwe Mid 2Dokumen2 halamanMwe Mid 2Veerayya JavvajiBelum ada peringkat
- Mw&oc Unit 1 Important QuestionsDokumen2 halamanMw&oc Unit 1 Important QuestionsVikas CollegeBelum ada peringkat
- ECT 401 MICROWAVE AND ANTENNAS - Assignment - 2Dokumen2 halamanECT 401 MICROWAVE AND ANTENNAS - Assignment - 2Anwarshahin NKBelum ada peringkat
- B G1025 Pages: 2: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksDokumen2 halamanB G1025 Pages: 2: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksBinesh KannothBelum ada peringkat
- Satyam College of Engineering and Technology, Aralvoimozhi Ece Iv-Semester Revision Questions Electronic Circuits Ii 2 Mark Questions Revision IDokumen4 halamanSatyam College of Engineering and Technology, Aralvoimozhi Ece Iv-Semester Revision Questions Electronic Circuits Ii 2 Mark Questions Revision ISaranya MohanBelum ada peringkat
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Dokumen3 halamanQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)GOJAN ECEBelum ada peringkat
- Microwave Engineering QuestionsDokumen5 halamanMicrowave Engineering Questionsgkhanna_3Belum ada peringkat
- Microwave Engineering University Questions-Moduleii 2 MarkDokumen1 halamanMicrowave Engineering University Questions-Moduleii 2 MarkSherin JominBelum ada peringkat
- Mwe Questions1Dokumen3 halamanMwe Questions1satyaBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Instrument atDokumen8 halamanElectronic Instrument atkushalchandel0% (1)
- EC403 Microwave & Radar Engineering, May 2019Dokumen2 halamanEC403 Microwave & Radar Engineering, May 2019Vishnu prasad SBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank-Converted 1Dokumen3 halamanQuestion Bank-Converted 1Vaibhavraje GaikwadBelum ada peringkat
- MWE Imp QsDokumen2 halamanMWE Imp QsCHINNA VENKATA VARMABelum ada peringkat
- Microwave EngineeringDokumen4 halamanMicrowave EngineeringVenkat SwamiBelum ada peringkat
- Important Questions From Microwave Engineering (REC-601) : o SH 11 R RDokumen3 halamanImportant Questions From Microwave Engineering (REC-601) : o SH 11 R RAkanksha BhadauriaBelum ada peringkat
- Ec IiDokumen1 halamanEc IisramkmBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank With Sol (BEFORE MID-SEM)Dokumen81 halamanQuestion Bank With Sol (BEFORE MID-SEM)Atul SahBelum ada peringkat
- PDC 1Dokumen4 halamanPDC 1Lavanya_123Belum ada peringkat
- Uwavenov 2012Dokumen2 halamanUwavenov 2012anandvj10387Belum ada peringkat
- Descriptive Questions Class: III/IV B.TECH SUB: Microwave EngineeringDokumen3 halamanDescriptive Questions Class: III/IV B.TECH SUB: Microwave EngineeringsatyaBelum ada peringkat
- Btech 2nd Year Question PaperDokumen32 halamanBtech 2nd Year Question PaperPolireddi Gopala KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank Microwave 2013Dokumen6 halamanQuestion Bank Microwave 2013LakshmanaKumarBelum ada peringkat
- Code - No: 25042: Freespace Guide CutoffDokumen8 halamanCode - No: 25042: Freespace Guide CutoffSRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- Mwe - QPDokumen4 halamanMwe - QPashokvaasanBelum ada peringkat
- Q Bank MLL Cbse 2022-23Dokumen5 halamanQ Bank MLL Cbse 2022-23Deepesh kumarBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Ece - 15.4.13 (Mod)Dokumen2 halaman4 Ece - 15.4.13 (Mod)BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANBelum ada peringkat
- Microwave Engineering November Am Rr311701Dokumen8 halamanMicrowave Engineering November Am Rr311701Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryBelum ada peringkat
- 12 2005 Physics 2Dokumen5 halaman12 2005 Physics 2Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Fed Question BankDokumen5 halamanFed Question BankAnonymous eWMnRr70qBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation of A 700-Mhz, 1-Mw CW Klystron For The Komac by Using Magic2DDokumen6 halamanSimulation of A 700-Mhz, 1-Mw CW Klystron For The Komac by Using Magic2DMohammad MousavikBelum ada peringkat
- EC Question PaperDokumen3 halamanEC Question PaperGna Senthil KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 1348 PhysicsDokumen5 halaman1348 PhysicsSubhadip DasBelum ada peringkat
- Analog Circuits IIDokumen2 halamanAnalog Circuits IIVictor SealBelum ada peringkat
- Viswas VVM Ec2 Rno 36Dokumen2 halamanViswas VVM Ec2 Rno 36Jeeshma Krishnan KBelum ada peringkat
- DocumentDokumen3 halamanDocumentJeeshma Krishnan KBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Ke 3 Elka TelkomDokumen5 halamanTugas Ke 3 Elka TelkomAzHar HrBelum ada peringkat
- Microwave Engineering Assignment 1 To 5Dokumen6 halamanMicrowave Engineering Assignment 1 To 5Anonymous 4bUl7jzGqBelum ada peringkat
- Microwave CommunicationsDokumen6 halamanMicrowave CommunicationsAkhil AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Important Questions in RF and Microwave Engineering EC2403 EC 2403 Subject For NOVDokumen2 halamanImportant Questions in RF and Microwave Engineering EC2403 EC 2403 Subject For NOVeldhosejmBelum ada peringkat
- Question Paper Code: (10×2 20 Marks)Dokumen3 halamanQuestion Paper Code: (10×2 20 Marks)Gokul NathBelum ada peringkat
- EDC UNIT - VIII Previous QuestionsDokumen2 halamanEDC UNIT - VIII Previous QuestionssandeepecetBelum ada peringkat
- Answer All QuestionsDokumen1 halamanAnswer All QuestionsBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANBelum ada peringkat
- NR 311701 Microwave EngineeringDokumen7 halamanNR 311701 Microwave EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GBelum ada peringkat
- EC403: Microwave & Radar EngineeringDokumen70 halamanEC403: Microwave & Radar EngineeringBindu Narayanan NampoothiriBelum ada peringkat
- Conf Rahma SmacdDokumen4 halamanConf Rahma SmacdRahma AloulouBelum ada peringkat
- 171001Dokumen2 halaman171001vishalsanziraBelum ada peringkat
- Physice 2011 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFDokumen5 halamanPhysice 2011 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFSunita AnandBelum ada peringkat
- MW QuestionsDokumen6 halamanMW Questionsalkesh.engBelum ada peringkat
- N Revision Test Set II 2007Dokumen7 halamanN Revision Test Set II 2007VgokulGokulBelum ada peringkat
- Ec1403 Microwave EngineeringDokumen3 halamanEc1403 Microwave EngineeringsubhazBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Papers Class 12 PhysicsDokumen53 halamanSample Papers Class 12 Physics0910ashuBelum ada peringkat
- MW & DC Lab Manual 2018Dokumen66 halamanMW & DC Lab Manual 2018NanduBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Model Paper XIIDokumen4 halamanPhysics Model Paper XIIKamal KishoreBelum ada peringkat
- Ec432 Microwave EngineeringDokumen3 halamanEc432 Microwave EngineeringGanapathi100% (1)
- Without This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFDokumen4 halamanWithout This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFAmit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyDari EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis and Optimal Design of Microstrip Sensors: P.W. WebbDokumen9 halamanAnalysis and Optimal Design of Microstrip Sensors: P.W. WebbRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chp4 Microwave FiltersDokumen77 halamanChp4 Microwave FiltersRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Radiation Damage Studies of Silicon Microstrip Sensors: B. Stugu4, R. Takashima', K. Tanizaki', S - Terada2, Y. Unno2Dokumen7 halamanRadiation Damage Studies of Silicon Microstrip Sensors: B. Stugu4, R. Takashima', K. Tanizaki', S - Terada2, Y. Unno2Ravindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- These Are The Opening Words of The Preamble To The Indian ConstitutionDokumen32 halamanThese Are The Opening Words of The Preamble To The Indian ConstitutionRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- RFID Coverage Extension Using Microstrip-Patch Antenna ArrayDokumen7 halamanRFID Coverage Extension Using Microstrip-Patch Antenna ArrayRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- DIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM 1st TermDokumen1 halamanDIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM 1st TermRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- DIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM Mid Term-IIDokumen1 halamanDIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM Mid Term-IIRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Solved ProblemsDokumen10 halamanSolved ProblemsRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- DIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM End TermDokumen2 halamanDIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM End TermRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- DIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM Mid Term-IDokumen1 halamanDIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM Mid Term-IRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- B. Tech.: Hours (Total Marks: 100Dokumen3 halamanB. Tech.: Hours (Total Marks: 100Ravindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Notes of Unit 5 (EMW)Dokumen5 halamanNotes of Unit 5 (EMW)Ravindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- DIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM Mid TermDokumen1 halamanDIGITAL CIRCUIT AND SYSTEM Mid TermRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics and Communication Department The Lnmiit, Jaipur Digital Circuits and Systems (Code: DCS)Dokumen4 halamanElectronics and Communication Department The Lnmiit, Jaipur Digital Circuits and Systems (Code: DCS)Ravindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Classes 6 To 8 Half Yearly Examination (2018-19) DatesheetDokumen1 halamanClasses 6 To 8 Half Yearly Examination (2018-19) DatesheetRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Frequency BandsDokumen4 halamanFrequency BandsRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Firing Scheme For Ultrasonic Sensors Used in Mobile RobotsDokumen10 halamanRapid Firing Scheme For Ultrasonic Sensors Used in Mobile RobotsRavindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Writing Capstone Research Project For Senior High School A Modified Guide ManualDokumen9 halamanWriting Capstone Research Project For Senior High School A Modified Guide ManualIOER International Multidisciplinary Research Journal ( IIMRJ)Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 - Practical ResearchDokumen17 halamanLesson 3 - Practical ResearchBenBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Spoken English in Half The TimeDokumen86 halamanLearning Spoken English in Half The TimeΔέσποινα ΤζουτBelum ada peringkat
- R820T Datasheet-Non R-20111130 UnlockedDokumen26 halamanR820T Datasheet-Non R-20111130 UnlockedKonstantinos GoniadisBelum ada peringkat
- Calling An Oracle Stored Proc in JasperDokumen10 halamanCalling An Oracle Stored Proc in Jasperlorenzofranchi6371Belum ada peringkat
- Activities For Learner-Centered TeachingDokumen56 halamanActivities For Learner-Centered TeachingAmiga Mi100% (1)
- Form ConstructionDokumen36 halamanForm ConstructionYhoga DheviantBelum ada peringkat
- The Design and Development of Organic Chemistry Module For College StudentsDokumen6 halamanThe Design and Development of Organic Chemistry Module For College StudentsEight AlykBelum ada peringkat
- Webinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018Dokumen62 halamanWebinar WinCC SCADA NL 29052018AlexBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Teaching PracticeDokumen14 halamanThe Impact of Teaching PracticemubarakBelum ada peringkat
- ToobaKhawar 6733 VPL Lab Sat 12 3 All TasksDokumen38 halamanToobaKhawar 6733 VPL Lab Sat 12 3 All TasksTooba KhawarBelum ada peringkat
- Wincam TornoDokumen3 halamanWincam Tornocaballerillo100% (1)
- 7TH Maths F.a-1Dokumen1 halaman7TH Maths F.a-1Marrivada SuryanarayanaBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 ESIA Guideline Edited AaDokumen102 halaman2020 ESIA Guideline Edited AaAbeje Zewdie100% (1)
- Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDokumen14 halamanDownloaded From Manuals Search EngineAl AlBelum ada peringkat
- LIT Era - Module 1Dokumen24 halamanLIT Era - Module 1Kemuel Tabamo100% (1)
- Semi Formal Asking To Borrow BooksDokumen75 halamanSemi Formal Asking To Borrow BooksPei Cheng WuBelum ada peringkat
- Zielinski AnArcheology For AnArchivesDokumen10 halamanZielinski AnArcheology For AnArchivesPEDRO JOSEBelum ada peringkat
- Essentials of Repertorization Tiwari Link PageDokumen11 halamanEssentials of Repertorization Tiwari Link PageBibin TSBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - RA-Erecting and Dismantling of Scaffolds (WAH) (Recovered)Dokumen6 halaman3 - RA-Erecting and Dismantling of Scaffolds (WAH) (Recovered)hsem Al EimaraBelum ada peringkat
- Usp3 ComDokumen5 halamanUsp3 ComMike MelgaBelum ada peringkat
- LGDokumen36 halamanLGNanchavisBelum ada peringkat
- Subject-Verb AgreementDokumen10 halamanSubject-Verb AgreementLouie Jay Cañada AbarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Chen Probable Cause Affidavit 050714Dokumen7 halamanChen Probable Cause Affidavit 050714USA TODAYBelum ada peringkat
- The Secret of Forgiveness of Sin and Being Born Again by Pastor Ock Soo Park 8985422367Dokumen5 halamanThe Secret of Forgiveness of Sin and Being Born Again by Pastor Ock Soo Park 8985422367Justinn AbrahamBelum ada peringkat
- CH 6 - Performance AppraisalDokumen50 halamanCH 6 - Performance AppraisalMark SullivanBelum ada peringkat
- GE2410 Student Booklet (UpdatedDec27)Dokumen88 halamanGE2410 Student Booklet (UpdatedDec27)markhoBelum ada peringkat
- Caribbean Examination Council: School Based AssessmentDokumen17 halamanCaribbean Examination Council: School Based AssessmentDiana FrillsBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Public ExpenditureDokumen1 halamanPrinciples of Public ExpenditureNikhil Shenai100% (1)
- Lesson PlansDokumen12 halamanLesson Plansapi-282722668Belum ada peringkat