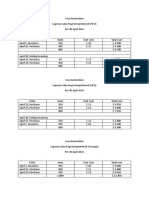
Warehose LSCM
Diunggah oleh
Rag LakJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Warehose LSCM
Diunggah oleh
Rag LakHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
41
I WAREHOUSING I
scientifically store, handle and retrieve business documents that business firms otherwise find difficult to
handle, as it is neither their core activity nor do they have any expertise in the preservation documents.
KarRox has a dedicated warehouse of 2 lakh sq ft and a fleet of specially designed vehicles to transport
documents from the clients' premises to their warehouse and vice versa. They ensure delivery of any
preserved document to the client within four hours, anywhere in Mumbai. Their customer base covers
leading banks, corporate business houses, and, insurance companies.
Source: Websites, Press Releases and Company Brochures
4.2 WAREHOUSING FUNCTIONS
The warehouse is the integral part of the logistical system and the effectiveness of customer
service, depends to a great extent, on the way warehouse operations are carried out. Broadly
speaking, the warehouse is a service function in the supply chain of the company and it performs
the following functions:
Material Storage Function
The primary task of a warehouse is to store material till it is delivered to the customer or end user. As
the manufacturing and consumption cycle never match, manufactured material has to be stored
somewhere till the demand for the same is generated and delivery is confirmed. In fact, storage is
designed to accomodate the following four functions:
Hold Holding is the most primary function of the warehouse for finished products ready for market
delivery. Depending on the demand or order booking pattern and the delivery schedule promised to
the customer by the marketing department, goods are despatched from the warehouse. At the
warehouse there is a continuous inflow and outflow of material. A proper record of the material,
which goes in and out, has to be maintained for information on inventory levels at any given point of
time. The area allocations for materials at different points of time is necessary to retrieve the material
as and when required for further delivery to a particular customer or markets. Hence, the material
holding function has to be carefully planned considering variables like product categories, product
mix, product charact teristics, shipment arrival time, expiry dates etc.
Manufacturing
Plant
Warehouse
(Finished Goods)
Customer
Figure 4.1 Finished goods warehouse
Consolidation If supplies are originating from various sources in small quantities, it may be
economical to collect these small shipments at one centre, to combine them, and make into a large
shipment to send it to the customer. Consolidation will ensure cost saving on freight.
For import or export of goods for large buyers, whose requirement does not warrant large
volumes for shipment from each source, consolidated shipments ensure potential cost savings. In
such cases planning a warehouse for shipment consolidation may be the ideal proposition. The
cost savings will offset the cost of setting up a place for consolidation.
42
I LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT
Source 1
C Source 2
Buyer 1
C minadacin _______
Warehouse
Source 3
C-Buyer 2
Buyer 3 Th
Figure 4.2 Consolidation warehouse
Break bulk The function of this facility is directly opposed to that of the consolidation warehouse.
Here, material that has arrived in bulk is divided into small shipments to deliver to the end customer.
Bulk cargo of fertilisers. oil, and chemicals coming from the manufacturer is broken into small consignments as per the requirements of buyers.
CustomerLD
eanufacturIng
Plant
13reekbullt
Wareho
Customer
Customer 3.)
Figure 4.3 Break-bulk warehouse
Distribution warehouses of manufacturing firms routinely break bulk. The firm saves substantially on
freight by despatching bulk shipments to its regional distribution centres, where they are divided into
small packets for further despatch to the end user, as per quantity requirements.
Cross docking This is similar to the break bulk activity, except that it involves multiple suppliers. The
usage of warehouse is for a short period of time. The material arriving in bulk or in fully loaded trucks is
broken into smaller consignments for further despatch to customers. The material stays in the
warehouse for a maximum of 48 hours. Cross docking is most commonly used in retail chains wherein
the mother warehouse receives different materials from multiple suppliers, which is divided into smaller
consignments or sorted (break bulk), and consolidated (repacked in small consignment) for despatch to
various retail stores, as per requirements.
Mixing A warehouse is sometimes used as a product mixing point in the case of companies having a
number of plants manufacturing different components, which are combined, at a convenient place, to
make the final product.
WAREHOUSING I
43
PlantA
(Ingredient
1)
Plant A
<Customer 2")
(Ingredient
Plant A
C u s to m e r D
(Ingredient
Figure 4.4 Mixing warehouse
The process involved is simple mixing. Orders can be fulfilled without mixing, by sending the ingre'
ass in small uneconomical volumes from individual plants to the customer. However, transportation as
becomes prohibitive in the shipment of individual ingredients to customers. A common mixing peke
permits large volume shipments of ingredients to a single location where they are assembled and
iimpatched to the customer in sizable lots in order to economise on transportation cost.
raatponement With postponement, the anticipated risk of finished goods inventory maintenance is
minced considerably. Parts and components are warehoused at strategic locations and final assembly
*kept on hold till the customer places or modifies the order. Strategic suppliers in the supply chains are
seed to postpone the delivery of parts till other critical items required for assembly arrive at the
facturing plant. Thus, the postponement function of the warehouse reduces the risk of finished pods
inventory and space blockage.
Peddng This is the most important function carried out in the warehouse after break bulk operation.
Be repacking of material as per the ordered quantities of the individual customer, is done at the
warehouse. The packs are labelled and marked as per packaging regulations or as per requirements
of the customer.
Illetsrial Handling Function
function is divided into the following three activities:
Loading and unloading The unloading activity is performed when goods arrive at the warehouse.
I
a
U
The material is offloaded from the transportation vehicle. Loading is the last function performed in the
warehouse. The material packed in boxes is loaded on to the transportation vehicle at the loading area.
Lading includes additional efforts of bracing the load to prevent damages.
activities are carried out either
mantle or with the help of material handling equipment. The incoming material, which is unloaded, has
Material movement (to and from the storage area) These
to k moved to its assigned place in the warehouse for temporary storage, while during order pickup the
mistrial has to be moved from storage to the packing area and then to the loading area. For material
movement, the most common equipment in use are the trolley, crane, conveyor, and forklift.
Order filling The final material handling activity is order filling. This includes the selection of mate-ell
from various lots at various locations in the warehouse, as per the customer's order. This activity
44
LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT I
is done manually or with the help of robots. The order cycle time, which is the most critical parameter
in customer service, is very much dependent on the speed of material picking.
Information Handling Function
For effective and efficient customer service, it is essential for marketing personnel to know the availability of stocks and the likely despatch schedule. Also, at any point of time it is of crucial importance
to the top management, to know the inventory level and its impact on the cash flow of the firm. This is
possible with the help of a proper warehouse information system. Information regarding the following
is also required:
Goods inwards
Inspection and auditing
Goods outwards
Stock outs
Excess stocks
Invoicing
Warehouse expenses
Transit damage and breakage
Consignment tracking
Information is power and it helps in taking speedy decisions in today's highly competitive environment for building a competitive edge over the rivals. Hence, a proper warehouse information system
can considerably enhance the quality of customer service, to both internal and external customers of
the organisation leading to customer satisfaction.
4.3 WAREHOUSE OPTIONSA STRATEGIC DECISION
For acquiring warehouse space. the following three options are available:
Private warehouse
Public warehouse
Contract warehouse
Considerations for exercising these options depend on various factors such as product characteristics, demand fluctuations, investments, cost of operation, degree of control, scale economics etc.
Table 4.1 Warehouse Options
Private Public
Flexibility in
Contract
Investment
Material handling,
High
None
Location
Location
Very little
storage and throughput planning
Cost per unit stored
Inversely related to volumes
Low
Inversely related to volumes
Level of control
High
Low
Medium
Adequacy of goods stored High
Due to change in market
Risk
demand
centres
or
consumption
Low
Minimal
High
Minimal
I WAREHOUSING I
45
The warehouse option is a strategic decision having a long term effect on system efficiency and
effectiveness. The option may be exercised after a thorough evaluation of the logistics system design
mix. Firms invariably go in for a combination of the above three options at different locations.
Private Warehouse
Private ownership of storage facility refers to having the entire facility under the financial and administrative control of the firm, ie, the firm owning the product operates the warehouses. The facilities may
either be owned by the firm or taken on lease, for a period of three to five years. These facilities may
include a production oriented captive warehouse or a distribution warehouse located in the field for
customer service. Private warehouses are an attractive proposition under certain circumstances, such
as:
Product specific material handling and storing facilities are required, which are not available
with other options
Volumes handled are high, ensuring full capacity utilisation and benefits of scale economics
A high degree of control over the operations is required
The benefits of private warehouses are flexibility, full management control, and lower operating
cost. Private warehouse operating cost is less, as they do not have a profit markup. Material handling
and storage facility can be changed as per product mix, which is not possible in the case of public or
contract facilities. Hence, there is complete flexibility. Private warehouse facilities can be planned
close to markets to service the customer efficiently and effectively. This enhances customer
confidence in the supplier.
Public Warehouse
Public warehouses are similar to private carriers in transportation service. Firms having warehousing
space. storage facility, and material handling equipment for their own use, provide these services to
others as well. These warehouses are extensively used in logistical systems. Public warehouses are
designed for handling the most general packaged products or commodities, which do not require
specialised storage or handling arrangement. The products normally stored are food grains, paper
rolls, bulk material (cement, fertilisers), furniture, chemicals etc.
Bonded warehouses under 'customs' control are mostly often public warehouses licensed to store
goods meant for exports or imports till the time they are cleared by the customs authority for further
movement.
The public warehouse provides financial flexibility. Newly formed firms, desirous of expanding
their distribution network need not invest in developing a private warehouses. They have the option of
hiring space in a public warehouse and channelling their funds into other productive activities. This
will substantially improve their performance and thereby increase return on investment. Public
warehouses allow locational flexibility. Due to geographical changes in consumption centres, firms
can close storage facilities in one market and open them at other places without any financial losses.
The greatest disadvantage of a public warehouse is the absence of control over operations. As
product specific facility is not available, product damages during storage and handling may be on the
higher side. The speed of order fulfillment is slow/resulting in a lower level of customer service.
Economies of scale can be achieved with public warehouses because of volumes generated through
a large number of facility users. Transportation charge can be considerably brought down,
leveraging large volume shipments of assorted products from various depositors.
46
I LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT
Contract Warehouse
These are the product specific warehouse facilities acquired for a specific period against fixed charges.
Contract warehouses can provide the benefits of both private and public warehouses. This facility
provides economies of scale, flexibility, and customised facilities. Resources like labour, material handling equipment, storage arrangement, and communication equipment can be shared with depositors
from the same industry to economise on operating costs. As the facilities are product specific, product
damages are few. The large volume will apportion fixed costs with co-users.
Obviously the choice between the above options will depend on the demand pattern of the product,
volumes handled, geographical location, seasonality of the product, standardisation of product packaging. financial strength of the firm. service level expectation\ of the customer. and competition.
4.4 WAREHOUSE SITE SELECTION
The consideration of warehouse site selection revolves around two major factors, ie, service and cost.
Product availability can be greatly enhanced by locating the warehouse near the market. Smaller and
frequent deliveries, which customers prefer nowadays, can be organised. This will enhance customer
confidence in the supplier. However, the transportation cost, which is the major element in logistical
cost, depends on the location of the warehouse. The other factors affecting site selection are:
Infrastructure The availability of proper infrastructure such as approach roads, utilities (water, electricity, communication), and labour has a great effect on the efficiency and effectiveness of warehouse
operations. For cold storage warehouses, the availability of electricity is a major factor influencing site
selection. The non-availability of proper road or rail siding facility will have an adverse effect on the
operations of the warehouse and result in transportation costs going up considerably. The lack of
infrastructure, such as wagon platform and material handling equipment, may pose problems in the
loading and unloading of materials and special provisions may escalate cost.
Market Distribution warehouses arc located in proximity to markets or consumption centres for
offering better service to customers. Frequent deliveries in small quantities, as required by the custom ers, can be easily organised within limited geographical area coverage.
Access The location of the warehouse has the greatest effect on primary transportation costs. Diffi culty in access will have influence on transportation cost.
Primary transportation cost Transportation cost is the largest component in product cost, particularly
for low unit price products. The location of the warehouse will have the greatest influence on primary
transportation cost. The product demand pattern will influence transportation cost in two ways
on the frequency of truck trips and on the loading pattern (full or partial) of transportation
vehicles.
Availability The availability of warehousing space in urban areas, particularly in metros, at cheap
rates is a remote possibility. In such cases storage has to be shifted beyond municipal limits, where
space is available at a considerably cheaper rate. However, this arrangement may add to the
transportation cost.
Product The type of product will have a profound effect on the number of warehouses required and
their location. For example, perishable products need to be delivered to the cutomer within their expiry
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Accounting and Purchase SystemDokumen2 halamanAccounting and Purchase SystemRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- 1st ReviewDokumen8 halaman1st ReviewRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Designation Location Country Job Family Job Description (Posting)Dokumen2 halamanDesignation Location Country Job Family Job Description (Posting)Rag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting Fundamentals ExplainedDokumen4 halamanAccounting Fundamentals ExplainedRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Mech Grace MarksDokumen1 halamanMech Grace MarksRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Benefits OF ERP: Reduction of Lead-TimeDokumen4 halamanBenefits OF ERP: Reduction of Lead-TimeRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Hydro ElectricityDokumen7 halamanHydro ElectricityRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus StatisticsDokumen1 halamanSyllabus StatisticsSivakumar NatarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Why Plants Are ImportantDokumen2 halamanWhy Plants Are ImportantRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Foreign CurrenciesDokumen15 halamanForeign CurrenciesRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Manual PDFDokumen33 halamanManual PDFRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Mini ProjectDokumen14 halamanMini ProjectRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Types of LoansDokumen15 halamanTypes of LoansRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Merchant Banking April May 2015 Important QuesionDokumen2 halamanMerchant Banking April May 2015 Important QuesionRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Venture CapitalDokumen7 halamanVenture CapitalRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Work Breakdown StructureDokumen3 halamanWork Breakdown Structuredonraghu07Belum ada peringkat
- Monitoring and Controlling Project PerformanceDokumen30 halamanMonitoring and Controlling Project PerformanceRag Lak100% (1)
- Research Reports: Issue M Anagement: Activities/ProcecluresDokumen1 halamanResearch Reports: Issue M Anagement: Activities/ProcecluresRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- PackagingDokumen9 halamanPackagingRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Service ManagementDokumen20 halamanService Managementjoga_13Belum ada peringkat
- Unit-52 MbaDokumen5 halamanUnit-52 MbaRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- English Grammar SecretsDokumen66 halamanEnglish Grammar SecretsMbatutes94% (33)
- Adb CommandsDokumen1 halamanAdb CommandsRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- NewsDokumen1 halamanNewsRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Concept of StrategyDokumen2 halamanConcept of StrategyRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Legal Aspects of Business UT IIDokumen1 halamanLegal Aspects of Business UT IIRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- WorksheetWorks Cursive Handwriting Practice 1Dokumen1 halamanWorksheetWorks Cursive Handwriting Practice 1Rag Lak100% (1)
- MBA ScheduleDokumen2 halamanMBA ScheduleRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- Eva Stalin Business School MBA Program DetailsDokumen6 halamanEva Stalin Business School MBA Program DetailsRag LakBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- 7057 English IranArze PDFDokumen12 halaman7057 English IranArze PDFTanish PatelBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 BL HandbookDokumen262 halaman2012 BL HandbookAzeem DilawarBelum ada peringkat
- Ilovepdf MergedDokumen318 halamanIlovepdf MergedCricket HiLitesBelum ada peringkat
- Managing ERP Systems and Enterprise Strategy: A Dynamic Enterprise Reference GridDokumen23 halamanManaging ERP Systems and Enterprise Strategy: A Dynamic Enterprise Reference GridShah Maqsumul Masrur TanviBelum ada peringkat
- Ecommerce Fulfillment Strategies Drive Revenue and Customer SatisfactionDokumen14 halamanEcommerce Fulfillment Strategies Drive Revenue and Customer SatisfactionMohammed KhurramBelum ada peringkat
- UNCTAD DTL KDB 2016 1 Port Management Series Volume 4 - E - Web PDFDokumen53 halamanUNCTAD DTL KDB 2016 1 Port Management Series Volume 4 - E - Web PDFHeb RuBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 9Dokumen41 halamanPertemuan 9Melly HaileyBelum ada peringkat
- POM II Final Report On SCM of Flipkart PDFDokumen18 halamanPOM II Final Report On SCM of Flipkart PDFraazBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine National Railways Caloocan Depot Ramp Connection To NLEX SLEX Connector ProjectDokumen6 halamanPhilippine National Railways Caloocan Depot Ramp Connection To NLEX SLEX Connector ProjectMario FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- IncotermsDokumen12 halamanIncotermschandra sekhar reddyBelum ada peringkat
- Flipkart Supply Chain ManagementDokumen22 halamanFlipkart Supply Chain Managementaparnaiyer88100% (15)
- Namibia - The New Port of Walvis Bay Container Terminal Project - Appraisal ReportDokumen38 halamanNamibia - The New Port of Walvis Bay Container Terminal Project - Appraisal ReportMohamed ElfawalBelum ada peringkat
- Warehouse Management Systems: Industrial Engineering Department University of SurabayaDokumen45 halamanWarehouse Management Systems: Industrial Engineering Department University of SurabayaRIZKY FIQRIBelum ada peringkat
- RESEARCH REPORT Jyoti SinghDokumen110 halamanRESEARCH REPORT Jyoti SinghJyoti SinghBelum ada peringkat
- NotesDokumen2 halamanNotesjaya lakshmiBelum ada peringkat
- SCP Analysis of Indian Online Retail IndustryDokumen18 halamanSCP Analysis of Indian Online Retail IndustryPiyush JainBelum ada peringkat
- PPI Technical Guide 01 Five LeversDokumen21 halamanPPI Technical Guide 01 Five LeversMilagros PortugalBelum ada peringkat
- What Is CabotageDokumen6 halamanWhat Is CabotageAzmi Majid100% (5)
- FedEx - Drivers of ChangeDokumen10 halamanFedEx - Drivers of ChangeMjCBelum ada peringkat
- DGDDokumen2 halamanDGDmarksahaBelum ada peringkat
- What Are IncotermsDokumen19 halamanWhat Are IncotermsAlvaro BabiloniaBelum ada peringkat
- Modes of TransportationDokumen17 halamanModes of TransportationChaitu Un PrediCtbleBelum ada peringkat
- Forum S11 Thread Soal Valuation of Inventories 1-FIFO, LIFO, and AVERAGE - Diaz Hesron Deo Simorangkir - 2602202526Dokumen2 halamanForum S11 Thread Soal Valuation of Inventories 1-FIFO, LIFO, and AVERAGE - Diaz Hesron Deo Simorangkir - 2602202526Diaz Hesron Deo SimorangkirBelum ada peringkat
- CV Dewald Wahlstrand 2018Dokumen10 halamanCV Dewald Wahlstrand 2018Dewald WahlstrandBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Supply Chian Strategies - CompressDokumen24 halaman10 Supply Chian Strategies - CompresslimaayltonBelum ada peringkat
- 01 - Introduction To Information SystemsDokumen45 halaman01 - Introduction To Information SystemsRudy AriyantoBelum ada peringkat
- Project Proposal Preparation GuideDokumen16 halamanProject Proposal Preparation Guideronnel mauzarBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Service AssignmentDokumen23 halamanCustomer Service AssignmentLucas SalamBelum ada peringkat
- Green Logistics StrategiesDokumen60 halamanGreen Logistics StrategiesdaadiBelum ada peringkat
- TT Warehouse Cost Index 2020Dokumen10 halamanTT Warehouse Cost Index 2020Arci metriBelum ada peringkat