HNBB
Diunggah oleh
Sheen Ivashkov-BelikovHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
HNBB
Diunggah oleh
Sheen Ivashkov-BelikovHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
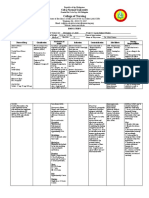
Name
Diagnosis
Physician
DRUG DATA
Generic Name:
Hyoscine-Nbutylbromide
Trade Name:
Buscopan
Patients Dose:
10mg ivtt q8hrs
Minimum Dose: 1
tab bid
Maximum Dose:
100mg ivtt daily
Available Forms:
ampule, tablet
Route of
Administration:
P.O., I.V.
Age:
Sex:
Date of Admission:
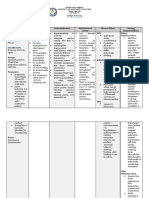
CLASSIFICATION
Therapeutic:
Anticholinergic
Pregnancy risk
category: Category C
Pharmacologic:
antispasmodic, belladona
alkaloid
MECHANISM OF
ACTION
Pharmacokinetics:
Onset: immediate
Peak:unknown
Duration:
unknown
Half-life: 5 hrs
Chemical: acts by
interfering with the
transmission of nerve
impulses by
acetylcholine in the
parasympathetic
nervous system;
exerts a spasmolytic
action on the smooth
muscle of the
gastrointestinal,
biliary and urinary
tracts
Ht:
Wt:
Body Type:
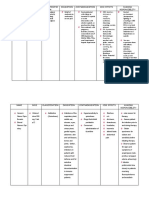
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
NURSING
RESPONSIBILITIES
General:
Acute GI, biliary &
genitourinary spasm
including biliary &
renal colic.
Parenterally also as
an aid in diagnostic &
therapeutic
procedures (e.g.,
gastroduodenal
endoscopy, radiology)
Contraindicated in
patients:
-hypersensitive to the
drug
-with myasthenia
gravis, megacolon
and narrow angle
glaucoma
*use cautiously in
patients with hepatic
dysfunction
Patients:
Preoperative
medication
Interactions:
Drug-to-drug:
Intensifies
anticholinergic
effects of TCAs,
antihistamines,
quinidine,
amantadine,
disopyramide & other
anticholinergics (eg
tiotropium,
ipratropium).
Enhanced
tachycardiac effects
of -adrenergic
agents. Dopamine
antagonists reduce
effects of both drugs
on GIT.
CCNS: dizziness,
anaphylactic reactions,
anaphylactic shock,
increased ICP,
disorientation,
restlessness,
irritability, dizziness,
drowsiness, headache,
confusion,
hallucination, delirium,
impaired memory
CV: hypotension,
tachycardia,
palpitations, flushing
GI: Dry mouth,
constipation, nausea,
epigastric distress
DERM: flushing,
dyshidrosis
GU: Urinary
retention, urinary
hesitancy
Resp: dyspnea,
bronchial plugging,
depressed respiration
EENT: mydriasis,
dilated pupils, blurred
vision, photopobia,
increased intraocular
pressure, difficulty of
swallowing.
Before:
1.Check doctors
order
2.Assess whether
patient is
contraindicated to
the drug
3.Prepare
medication ahead
of time
4.Dilute with 20cc
compatible
intravenous fluid
5.Verify drug, dose,
route, timing and
pt.s identity
6.Explain procedure
to pt.
During:
1.Administer on
right route
2.Observe aseptic
techniques
3.Ensure patency
4.Introduce
medication slowly
After:
1.Educate pt. about
possible adverse
reactions
2.Instruct patient to
report any
unusual reaction
3.Chart accordingly
4.Institute safety
precautions
5.Ensure adequate
ventilation
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cefoxitin and Ketorolac Edited!!Dokumen3 halamanCefoxitin and Ketorolac Edited!!Bryan Cruz VisarraBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study (CELECOXIB)Dokumen1 halamanDrug Study (CELECOXIB)Angela Mae Cabajar100% (3)
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanDokumen5 halamanCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanBelum ada peringkat
- Arixtra & Plavix Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanArixtra & Plavix Drug StudyShayneAngelMarieMatubangBelum ada peringkat
- CephalexinDokumen1 halamanCephalexinJehadadBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen13 halamanDrug StudyRamon Carlo Almiranez100% (2)
- Drug Study - HNBBDokumen4 halamanDrug Study - HNBBCamilogs100% (3)
- OB Drug StudyDokumen5 halamanOB Drug Studyvanni213Belum ada peringkat
- CefoxitinDokumen3 halamanCefoxitinAngelica Cassandra VillenaBelum ada peringkat
- Final Drug StudyDokumen9 halamanFinal Drug StudyCherry Lou Correos Tejada100% (2)
- Drug Study CefuroximeDokumen2 halamanDrug Study CefuroximeTipey Segismundo100% (1)
- OxacillinDokumen1 halamanOxacillinSergi Lee OrateBelum ada peringkat
- DRUG RovuvastatinDokumen2 halamanDRUG RovuvastatinDharyl JoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- DRUG STUDY - AmoxicillinDokumen7 halamanDRUG STUDY - AmoxicillinFaye Gatchalian100% (1)
- Ciprofloxacin and Paracetamol Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanCiprofloxacin and Paracetamol Drug StudyRichard MendejaBelum ada peringkat
- BuscopanDokumen3 halamanBuscopanJulie May100% (1)
- Acetylcysteine Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanAcetylcysteine Drug StudyArabelle GOBelum ada peringkat
- OfloxacinDokumen2 halamanOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Generic NameDokumen2 halamanGeneric NameMichael PalmaBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationDokumen2 halamanGeneric Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationRadicalRayBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study 1 Ferrous SulfateDokumen2 halamanDrug Study 1 Ferrous SulfateKrizzia Mae ColladoBelum ada peringkat
- CEFOXITINDokumen30 halamanCEFOXITINJaessa FelicianoBelum ada peringkat
- Carboprost Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanCarboprost Drug StudyAjay SupanBelum ada peringkat
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDokumen3 halamanClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - DelanDokumen3 halamanDrug Study - DelanJuliana Sophia DelanBelum ada peringkat
- Ceftazidime (Zeptrigen)Dokumen4 halamanCeftazidime (Zeptrigen)105990Belum ada peringkat
- Felodipine CefuroximeDokumen3 halamanFelodipine CefuroximecotyboyBelum ada peringkat
- Cebu Normal University: Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanCebu Normal University: Drug StudyGwen Marie Taboada100% (1)
- Drug Study LosartanDokumen3 halamanDrug Study LosartanLouie Danielle SegarraBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexDokumen3 halamanDrug Study For Paracetamol, Omeprazole and Vitamin B ComplexMichelle Manibale R.N100% (4)
- Drug Study - Tramadol, Hyoscine-N-Butylbromide, Co-Trimoxazole, Potassium CitrateDokumen4 halamanDrug Study - Tramadol, Hyoscine-N-Butylbromide, Co-Trimoxazole, Potassium CitratemissmakaiBelum ada peringkat
- Tramadol UltramDokumen2 halamanTramadol UltramatchiekBelum ada peringkat
- Losartan Potassium Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanLosartan Potassium Drug StudyJonieP84100% (4)
- Drug-Study CefepimeDokumen2 halamanDrug-Study Cefepimeprince gonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Dokumen2 halamanNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Pre Gabal in Drug StudyDokumen1 halamanPre Gabal in Drug StudyHailMarieSBarcenasBelum ada peringkat
- AtorvastatinDokumen2 halamanAtorvastatinJasmin T LarizaBelum ada peringkat
- CefoxitinDokumen1 halamanCefoxitinDaryl PaglinawanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen13 halamanDrug StudyAbdullah Mascardo BarabagBelum ada peringkat
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDokumen12 halamanDelivery Room Drug StudyJoe Anne Maniulit, MSN, RN100% (6)
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug Studymike_steven12Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)Dokumen6 halamanDrug Study (Oxytocin & HNBB)NE TdrBelum ada peringkat
- OxytocinDokumen1 halamanOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisBelum ada peringkat
- DRUG STUDY OXYTOCIN, METHERGINE EtcDokumen9 halamanDRUG STUDY OXYTOCIN, METHERGINE EtcPatricia Reese YutiamcoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanDrug Studyarianne javierBelum ada peringkat
- IrbesartanDokumen3 halamanIrbesartanapi-3797941Belum ada peringkat
- KETOROLAC Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanKETOROLAC Drug StudyChoox PriiBelum ada peringkat
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDokumen2 halamanDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen15 halamanDrug StudyCheyee MaeBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen17 halamanDrug StudyKrishelle Kate PannigBelum ada peringkat
- DS Ibuprofen Osteo ARLEDDokumen11 halamanDS Ibuprofen Osteo ARLEDvivi's eyebrowsBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanDrug StudyDONITA DALUMPINESBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Log - Fracture of ClavicleDokumen10 halamanLearning Log - Fracture of Claviclestd.salrajkumarsinghBelum ada peringkat
- Drug TylenolDokumen1 halamanDrug TylenolSrkocherBelum ada peringkat
- For Drug Recitation 1Dokumen33 halamanFor Drug Recitation 1Abigail LonoganBelum ada peringkat
- MetoclopramideDokumen3 halamanMetoclopramideKrizzia CarlosBelum ada peringkat
- DS Fenofibrate Osteo ARLEDDokumen9 halamanDS Fenofibrate Osteo ARLEDvivi's eyebrowsBelum ada peringkat
- All Kinds of DrugsDokumen11 halamanAll Kinds of DrugsRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Complete Drugs StudyDokumen13 halamanComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: Atropine: RecommendedDokumen6 halamanDrug Study: Atropine: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisBelum ada peringkat
- Blank Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanBlank Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovBelum ada peringkat
- Tobramycin + Dexamethasone Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanTobramycin + Dexamethasone Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovBelum ada peringkat
- Clomid Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanClomid Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovBelum ada peringkat
- Why Are Clouds WHITEDokumen5 halamanWhy Are Clouds WHITESheen Ivashkov-Belikov100% (1)
- Anticholinergic Drugs: ClassificationDokumen13 halamanAnticholinergic Drugs: ClassificationVishnu TharakanBelum ada peringkat
- MPR Potentially Inappropriate Drugs For The Elderly (Beers List)Dokumen3 halamanMPR Potentially Inappropriate Drugs For The Elderly (Beers List)Brian Harris100% (1)
- Cooper 2020Dokumen18 halamanCooper 2020Lohann MedeirosBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of CYP450Dokumen2 halamanEffects of CYP450CherylBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study Ready TEMPLATEDokumen1 halamanDrug Study Ready TEMPLATECezanne CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Nalbuphine HCLDokumen1 halamanNalbuphine HCLShereen Al-ObinayBelum ada peringkat
- Advantage and Risk of Psychiatric PolypharmacyDokumen14 halamanAdvantage and Risk of Psychiatric PolypharmacyFiarry FikarisBelum ada peringkat
- Mouse Dosage CalculatorDokumen5 halamanMouse Dosage CalculatorOlayide Israel RobinsonBelum ada peringkat
- Stopping The Harm Report by Dr. Bonnie HenryDokumen49 halamanStopping The Harm Report by Dr. Bonnie HenryAshley WadhwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Tallman LettersDokumen5 halamanTallman LettersJames Lindon0% (1)
- Experiment 8 Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory WorksheetDokumen17 halamanExperiment 8 Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory WorksheetJANNIE BELLE RODRIGUEZBelum ada peringkat
- General ToxicilogyDokumen19 halamanGeneral ToxicilogyShailesh ParateBelum ada peringkat
- ةلجسملا تارضحتسملا Tablets: ليجستلا خيرات مقر ليجستلا Trade Name Trade Name NoDokumen2 halamanةلجسملا تارضحتسملا Tablets: ليجستلا خيرات مقر ليجستلا Trade Name Trade Name Noahmed kindiBelum ada peringkat
- Accord Product ListDokumen14 halamanAccord Product ListANIRUDDHA KAPADNISBelum ada peringkat
- Cluster SPKDokumen2 halamanCluster SPKHeru Khairul UmamBelum ada peringkat
- Handy Chart DepressionDokumen2 halamanHandy Chart DepressionsteadiBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry IV Sem 8 CBGS 1Dokumen12 halamanPharmaceutical Chemistry IV Sem 8 CBGS 1Sara NurhussienBelum ada peringkat
- Eli Lilly PresentationDokumen30 halamanEli Lilly PresentationvarundurejaBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Daftar Produk Terjual: (Dalam RUPIAH)Dokumen3 halamanLaporan Daftar Produk Terjual: (Dalam RUPIAH)JufriBelum ada peringkat
- A Guide To Psychotropic DrugsDokumen16 halamanA Guide To Psychotropic DrugsNokz M. Raki-inBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Obat KomposisiDokumen3 halamanDaftar Obat KomposisiAnggun Ajjen Hartiningsiih IIBelum ada peringkat
- RKO 2019 Dan SO 31 Nov 2018.fixDokumen14 halamanRKO 2019 Dan SO 31 Nov 2018.fixjihanBelum ada peringkat
- Opiates TipsDokumen39 halamanOpiates TipsroooBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Individu - Nur Indah Sari (PO713251201030) - 1Dokumen6 halamanTugas Individu - Nur Indah Sari (PO713251201030) - 1Nur indah sariBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: Risperidone RisperdalDokumen2 halamanDrug Study: Risperidone RisperdalSophia Kaye AguinaldoBelum ada peringkat
- GHB PowerpointDokumen14 halamanGHB Powerpointapi-273992327Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Facts For Your Personal Formulary - I Xmlns - Xlink - Http...Dokumen4 halamanDrug Facts For Your Personal Formulary - I Xmlns - Xlink - Http...Dragutin PetrićBelum ada peringkat
- Whitesboro Isd - 1995 TEXAS SCHOOL SURVEY OF DRUG AND ALCOHOL USEDokumen6 halamanWhitesboro Isd - 1995 TEXAS SCHOOL SURVEY OF DRUG AND ALCOHOL USETexas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar Obat-Obatan Rumah Sakit AzzahraDokumen12 halamanDaftar Obat-Obatan Rumah Sakit Azzahraelimawati elimawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Alcoholism Case StudyDokumen5 halamanAlcoholism Case StudySharmaigne Rose100% (1)