CHE 495 - Integrated Design Course (3-0-3) Course Credit 3-0-3 Course Description
Diunggah oleh
Waleed AhmedJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHE 495 - Integrated Design Course (3-0-3) Course Credit 3-0-3 Course Description
Diunggah oleh
Waleed AhmedHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHE 495 Integrated Design Course (3-0-3)
Course Credit 3-0-3
Course
Description:
Development of general engineering skills and judgment needed in the
solution of open-ended problems from a technical-economic viewpoint
are the major goals of this course. The design of a project from
conception to implementation including preliminary feasibility study,
preparation of process flow diagram, process design, preconstruction
cost estimate, equipment sizing (design), selection of materials of
construction and analysis of project. Applications will be in areas such
as petroleum, petrochemicals, emerging chemical industries and water
desalination. Design topics will be assigned to groups of students.
Textbook:
Handouts are distributed to students. These include
(a) A general statement of problem
(b) Tasks, dates, a program of progress and final reports and dates.
(c) List of relevant references
(d) Other materials as needed.
References:
Scientific Journals
1. Chemical Engineering Progress
2. Chemical Engineering
3. Hydrocarbon Processing
Encyclopedias:
1. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology (2004) This
has been acquired very recently by the Library
2. Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design (McKetta and
Cunningham, 1976).
3. Ullmans Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry
4. McGraw-Hill Encyclopedia of Science and Technology, 1987.
5. Van Nostrand Scientific Encyclopedia (Considine, 1988)
6. Encyclopedia of Fluid Mechanics (Cherminisoff, 1986).
7. Encyclopedia of Material Science and Engineering, (Bever, 1986).
Handbooks and Reference Books:
1. Perrys Chemical Engineers Handbook
2. Handbook of Physics and Chemistry, Pub. By CRC
3. JANAF Thermochemical Tables (Chase, 1985)
4. Unit Operations Handbook, Mcketta, 1993.
5. Hand book of Heat Exchangers Design, CRC Press (Spalding and
Taborek)
6. Plant Design and Economics for Chemical Engineers (4th edition)
by M. S .Peters and K. D. Timmerhaus, McGraw-Hill, 1991.
7. Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petroleum Plants (2nd
edition) by Ernest E. Ludwig, 1983, Gulf Publishing Company,
Book Div., vols1, 2 &3
8. Chemical Engineering by Coulson & Richardson, Pergamon Press,
1975, 2nd, edition.
9. Equilibrium Staged Separations by Philip C. Wankat, PrenticeHall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ 1988.
10. Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering by H. Scott Fogler,
2nd edition, Prentice-Hall International Inc., 1992.
11. Reaction Kinetics for Chemical Engineers by Stanley M. Walas,
McGraw-Hill, NY, 1959.
12. Preliminary Chemical Engineering Plant Design (2nd edition) by
William D. Bassel.
13. Equipment Design Handbook for Refineries and Chemical Plants
(2nd edition), Frank L. Evans, Jr., Vols. 1 & 2, Gulf Publishing
Company, Book Div., 1980.
14. Engineering Data Book, by the Gas Processors Suppliers
Association, Tulsa, Oklahoma, 9th Edition, 1977.
Objective:
The design of a project from conception to implementation including
preliminary feasibility study, preparation of process flow diagram,
process design, preconstruction cost estimate, equipment sizing
(design), selection of materials of construction and analysis of the
project.
Outcomes:
Upon successful completion of this course, the students will be able to:
1. Integrate the knowledge acquired in different chemical engineering
courses in the design of a chemical plant [1-3]*.
2. Conduct preliminary feasibility study of the plant design assigned
[3,4].
3. Function and work with others in teams [5].
4. Communicate effectively in English especially in presentations [6].
5. Apply modern process simulation software (such as HYSYS,
ASPEN) [7].
6. Function professionally and behave ethically [8].
7. Apply safety rules in the design of storage units or in the plant in
general [10].
8. Comply with environmental regulations in the design of the plant,
especially separation columns [9,11].
*
Pre-requisite:
The number in [ ] reference the corresponding chemical
engineering undergraduate program outcomes.
CHE 425
Pre-requisite by Topics:
Computer Usage:
Mass and Energy Balances
Thermodynamics.
Transport phenomena.
Kinetic and reactor design.
Separation processes.
Process dynamics and control.
Plant design and economics.
HYSYS or other process simulators software packages.
Process simulator software package + Computer aided report
writing and presentation.
Laboratory Projects:
Not applicable. Trips to similar plants are arranged depending
on the project.
Evaluation Methods:
1.
2.
3.
Topics:
Special equipment design Assignments.
Reports (progress reports and final report).
Oral Presentations.
Literature review
Mass and Energy Balances
Process simulation using software packages
Detailed equipment design and sizing
Economics
Presentations
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Process Component Design PDFDokumen3 halamanProcess Component Design PDFWillian MazaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Engineering Equipment DesignDokumen55 halamanChemical Engineering Equipment Designabdo magdy100% (1)
- CHME 4703 SP2012 SyllabusDokumen9 halamanCHME 4703 SP2012 SyllabusFrank PiccirilloBelum ada peringkat
- New Concepts and Innovations: Students Inside An Industrial Chemistry Laboratory at MITDokumen4 halamanNew Concepts and Innovations: Students Inside An Industrial Chemistry Laboratory at MITAda AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Conceptual Desgn For Chemical Processes - pdf.2Dokumen3 halamanConceptual Desgn For Chemical Processes - pdf.2Audrey Patrick KallaBelum ada peringkat
- Master Chemical Engineering CoursesDokumen23 halamanMaster Chemical Engineering Courseskiranpatil1014532Belum ada peringkat
- Ch.E-403 Lecture 1 Chemical Engineering Plant DesignDokumen10 halamanCh.E-403 Lecture 1 Chemical Engineering Plant DesignAmna EhsanBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Engineering Plant DesignDokumen552 halamanChemical Engineering Plant DesignNajwa KusumaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Chemical Engineering?Dokumen4 halamanWhat Is Chemical Engineering?AdrianaBelum ada peringkat
- ChE 471 Equipment DesignDokumen2 halamanChE 471 Equipment DesignMera MohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion Engineering Course SyllabusDokumen2 halamanCorrosion Engineering Course SyllabusraghunaththakarBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Year Eng - Outline PDFDokumen7 halaman3rd Year Eng - Outline PDFkingBelum ada peringkat
- FYDP Part 2 Course InformationDokumen4 halamanFYDP Part 2 Course InformationWeimingTanBelum ada peringkat
- PED Lecture NoteDokumen196 halamanPED Lecture NoteSumit SwainBelum ada peringkat
- Velammal Institute of Technology Mechanical Engineering Course Outcomes Program OutcomesDokumen54 halamanVelammal Institute of Technology Mechanical Engineering Course Outcomes Program OutcomesshivakeesBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge ChemE SyllabusDokumen7 halamanCambridge ChemE SyllabusKeith SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Sneakers As A First Step in Chemical Engineering Author Margot Vigeant, Richard MooreDokumen12 halamanSneakers As A First Step in Chemical Engineering Author Margot Vigeant, Richard MooreTyler VintBelum ada peringkat
- Oilreservoirengineeringandexploration ARANDADokumen9 halamanOilreservoirengineeringandexploration ARANDAab cBelum ada peringkat
- Renewable Energy Systems DesignDokumen5 halamanRenewable Energy Systems DesignAdawiyah Az-zahraBelum ada peringkat
- Process Equipment Design Course HandoutDokumen4 halamanProcess Equipment Design Course HandoutAnonymous EBReO8vBelum ada peringkat
- MN217 Fluids Mechanics II 1 PDFDokumen3 halamanMN217 Fluids Mechanics II 1 PDFChak Arroyo SolanoBelum ada peringkat
- Ench4rt Outline 2012Dokumen5 halamanEnch4rt Outline 2012thirushkaBelum ada peringkat
- National University of Engineering College of Geological, Mining and Metallurgical Engineering Metallurgical Engineering ProgramDokumen3 halamanNational University of Engineering College of Geological, Mining and Metallurgical Engineering Metallurgical Engineering ProgramJhair JhamidhBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Outline and Introduction To Design: © HB Vuthaluru 2006Dokumen41 halamanUnit Outline and Introduction To Design: © HB Vuthaluru 2006Adrian John Soe MyintBelum ada peringkat
- History: History of Chemical EngineeringDokumen4 halamanHistory: History of Chemical EngineeringjahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Process Plant Design: Heinemann Chemical Engineering SeriesDari EverandProcess Plant Design: Heinemann Chemical Engineering SeriesPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (11)
- NIT DURGAPUR PROCESS CONTROL COURSEDokumen2 halamanNIT DURGAPUR PROCESS CONTROL COURSEpiyush dwivediBelum ada peringkat
- 1 ChemPlantDesign-Intro To Plant Design EconomicsDokumen33 halaman1 ChemPlantDesign-Intro To Plant Design Economicsfatiehah93Belum ada peringkat
- ChE 108B Syllabus PDFDokumen4 halamanChE 108B Syllabus PDFnadimBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter1 What ChemEng - FinalDokumen10 halamanChapter1 What ChemEng - FinalAgin AdwisanBelum ada peringkat
- CHE 414 Part 1Dokumen87 halamanCHE 414 Part 1ifiokBelum ada peringkat
- Intro to Environmental Materials EngineeringDokumen2 halamanIntro to Environmental Materials EngineeringFarazBelum ada peringkat
- Course Syllabus (Mechanical Engineering Program) : T.D. Eastop& A. McconkeyDokumen6 halamanCourse Syllabus (Mechanical Engineering Program) : T.D. Eastop& A. McconkeyGordon ChaiBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Syllabus FinalDokumen4 halamanThermodynamics Syllabus FinalVpr NaturalsBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of The ModuleDokumen11 halamanOverview of The ModuleyoyogiftuBelum ada peringkat
- Model Petroleum Engineering CurriculumDokumen13 halamanModel Petroleum Engineering CurriculumVinod KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chhattisgarh Technical University Semester VI Chemical Engineering Subject SchemeDokumen15 halamanChhattisgarh Technical University Semester VI Chemical Engineering Subject SchemeFarwa MalikBelum ada peringkat
- EGM 311 - Solving Mechanical ProblemsDokumen38 halamanEGM 311 - Solving Mechanical ProblemsAnthony MulengaBelum ada peringkat
- QB Final YearDokumen201 halamanQB Final YearmaniBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Handling of SolidsDokumen10 halaman1-Handling of SolidsAgus Wahyudhi100% (1)
- OBE Syllabus in Thermo2Dokumen6 halamanOBE Syllabus in Thermo2charmaine fosBelum ada peringkat
- Download ebook Simultaneous Mass Transfer And Chemical Reactions In Engineering Science Pdf full chapter pdfDokumen67 halamanDownload ebook Simultaneous Mass Transfer And Chemical Reactions In Engineering Science Pdf full chapter pdfprincess.royce571100% (23)
- Course Title Credits Th. Pr. Tr. Tu. Total Pre-Requisites: Course Role in Curriculum Catalogue DescriptionDokumen2 halamanCourse Title Credits Th. Pr. Tr. Tu. Total Pre-Requisites: Course Role in Curriculum Catalogue Descriptionkumar_chemicalBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Thermodynamics COs, POs and OBE PlanDokumen22 halamanEngineering Thermodynamics COs, POs and OBE Plansharon marishka wilfredBelum ada peringkat
- Untitled PresentationDokumen12 halamanUntitled PresentationimmortaloorchimaruBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Project List For StudentDokumen26 halamanMechanical Project List For StudentKhusi1Belum ada peringkat
- Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer (SHMT) : 7th Semester, B.Sc. Chemical Engineering Session 2014 Delivered byDokumen11 halamanSimultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer (SHMT) : 7th Semester, B.Sc. Chemical Engineering Session 2014 Delivered byAzeemBelum ada peringkat
- Process Equipment Design and EconomicsDokumen2 halamanProcess Equipment Design and EconomicsAmol RastogiBelum ada peringkat
- BMM 4623 Mechanical System Design - Rev01 July 31, 2013Dokumen6 halamanBMM 4623 Mechanical System Design - Rev01 July 31, 2013huszsBelum ada peringkat
- Download Simultaneous Mass Transfer And Chemical Reactions In Engineering Science 1St Edition Bertram Chan all chapterDokumen67 halamanDownload Simultaneous Mass Transfer And Chemical Reactions In Engineering Science 1St Edition Bertram Chan all chaptersara.coon444Belum ada peringkat
- BEng ME Module SynopsisDokumen4 halamanBEng ME Module SynopsisjeffreymacaseroBelum ada peringkat
- Process Design Decisions and Project EconomicsDokumen3 halamanProcess Design Decisions and Project EconomicsSrikanthBelum ada peringkat
- CAPS - 3170507 - Coomon Assignment With AcknowDokumen12 halamanCAPS - 3170507 - Coomon Assignment With AcknowVarun pandeyBelum ada peringkat
- 1 CHEN401 - First Day Package - Prof. N.S. MainaDokumen5 halaman1 CHEN401 - First Day Package - Prof. N.S. Mainasaminumusa217Belum ada peringkat
- History: History of Chemical EngineeringDokumen4 halamanHistory: History of Chemical EngineeringjahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Engineering Is The Branch Of: o o o o o o oDokumen7 halamanChemical Engineering Is The Branch Of: o o o o o o oriz2010Belum ada peringkat
- Bioen 492 - Surface Analysis Techniques and ApplicationsDokumen4 halamanBioen 492 - Surface Analysis Techniques and ApplicationsMahir MahmoodBelum ada peringkat
- Modeling Processes for Optimal DesignDokumen10 halamanModeling Processes for Optimal DesignDivyanshuBelum ada peringkat
- PCH TemplateDokumen2 halamanPCH TemplateWaleed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDokumen2 halamanNew Microsoft Word DocumentWaleed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- PCH TemplateDokumen2 halamanPCH TemplateWaleed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- PCH TemplateDokumen2 halamanPCH TemplateWaleed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Behavioral Situational Based Interview QuestionsDokumen26 halamanBehavioral Situational Based Interview QuestionsWaleed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Formaldehyde, Oligomeric Reaction Products With Aniline and PhosgeneDokumen7 halamanFormaldehyde, Oligomeric Reaction Products With Aniline and PhosgeneWaleed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 - Stress-Life ApproachDokumen97 halamanLecture 4 - Stress-Life Approache pBelum ada peringkat
- MCS & MPS Exam SyllabusDokumen165 halamanMCS & MPS Exam SyllabusMangeshBelum ada peringkat
- Osmosis Diffusion AP Biology Lab ReportDokumen11 halamanOsmosis Diffusion AP Biology Lab ReportJameson SchultsBelum ada peringkat
- EST QB - StudentsDokumen8 halamanEST QB - Students114-Lobhan PatilBelum ada peringkat
- SumiSmall 2015-16 CATALOG LR PDFDokumen249 halamanSumiSmall 2015-16 CATALOG LR PDFAlbertBelum ada peringkat
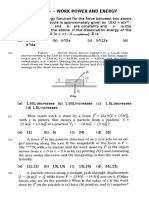
- PHYSICS - WORK, POWER AND ENERGY FORMULASDokumen3 halamanPHYSICS - WORK, POWER AND ENERGY FORMULASSandeepKumarBelum ada peringkat
- NaOH Lİme SodaDokumen6 halamanNaOH Lİme SodaallatcoolBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Chapter 1 ReviewDokumen20 halamanThermodynamics Chapter 1 ReviewReinzo GallegoBelum ada peringkat
- USP Monographs: PamabromDokumen3 halamanUSP Monographs: PamabromMayur JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- x2.6. - Strouhal Instability - Von Karman Vortex StreetDokumen4 halamanx2.6. - Strouhal Instability - Von Karman Vortex StreetcteranscribdBelum ada peringkat
- GP208 HW3 SolutionsDokumen4 halamanGP208 HW3 SolutionsSofiaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Culture TroubleShootingDokumen2 halamanCell Culture TroubleShootingCynthia Adeline SBelum ada peringkat
- Filtration Competency Exam 20132 For Students No AnswerDokumen2 halamanFiltration Competency Exam 20132 For Students No AnswerMad MaxBelum ada peringkat
- Standard Proctor Compaction Test ResultsDokumen12 halamanStandard Proctor Compaction Test Resultsaidil adhaBelum ada peringkat
- Retrowrap Materials Performance FactsDokumen2 halamanRetrowrap Materials Performance FactsMBelum ada peringkat
- Litron Bernoulli B PIV 145 15Dokumen4 halamanLitron Bernoulli B PIV 145 15RaviVelugulaBelum ada peringkat
- A New Sol-Gel Route Using Inorganic Salt For Synthesizing Ai, O, NanopowdersDokumen8 halamanA New Sol-Gel Route Using Inorganic Salt For Synthesizing Ai, O, NanopowderstaheralnajjarBelum ada peringkat
- References and AbstractDokumen11 halamanReferences and AbstractZaid AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 21 Cutting Tools: MET 33800 Manufacturing ProcessesDokumen25 halamanChapter 21 Cutting Tools: MET 33800 Manufacturing ProcessesAlissa Saphira PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Energy: SciencedirectDokumen18 halamanSolar Energy: SciencedirectMohamed AliBelum ada peringkat
- Differential Equations Mass PDFDokumen27 halamanDifferential Equations Mass PDFDiana Marcela Sierra Varela100% (1)
- Physics Investogatory Project 2023Dokumen17 halamanPhysics Investogatory Project 2023revBelum ada peringkat
- Keller Stone Column Method Statement - SCDokumen7 halamanKeller Stone Column Method Statement - SCHema plays0% (1)
- Calculate Flow Rate of Air Through A Pressurized HoleDokumen2 halamanCalculate Flow Rate of Air Through A Pressurized Holeleonard1971Belum ada peringkat
- RSC Li/chemical-ScienceDokumen24 halamanRSC Li/chemical-SciencePunita BathlaBelum ada peringkat
- Tribolube 64Dokumen2 halamanTribolube 64JasonBelum ada peringkat
- Aventura Corporate BrochureDokumen52 halamanAventura Corporate Brochurejugal ranaBelum ada peringkat
- Science Involved in Floating Paper Clip Science Experiment GuidelinesDokumen4 halamanScience Involved in Floating Paper Clip Science Experiment GuidelinesSHIELA RUBIOBelum ada peringkat
- Thermochemistry: Practice Questions For H2 Chemistry Remedial ClassesDokumen7 halamanThermochemistry: Practice Questions For H2 Chemistry Remedial ClassesTimBelum ada peringkat