ZN 2
Diunggah oleh
Joseph Neos Cruz0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
78 tayangan3 halamanJudul Asli
Zn2+.docx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
78 tayangan3 halamanZN 2
Diunggah oleh
Joseph Neos CruzHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
Joseph Neos C.
Cruz
Renz Carlo G. Evangelista
IV-Tau
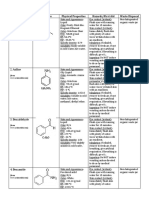
1. Name and Symbol
Zinc; Zn2+
2. State how it is detected with corresponding reactions involved.
The confirmatory test of Zn2+:
If a yellow precipitate is formed when
two drops of 0.1 M K3Fe(CN)6 are added
to about five drops of the unknown
solution, then the presence of Zn 2+ is
confirmed.
Zn2+ (aq) + Fe(CN)63- (aq)
Zn3[Fe(CN)6]
(s) (yellow ppt)
However, Zn2+ can also react to various compounds that can produce
noticable products confirming the presence of Zn2+:
A white gelatinous precipitate of zinc hydroxide is formed when sodium
hydroxide solution if added in a solution with zinc ions.
Zn2+ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) Zn(OH)2 (s)
The precipitate is soluble in dilute acids and in excess sodium
hydroxide with the
formation of zincate [ZnO22- or Zn(OH)42-] which
makes it amphoteric.
Zn(OH)2
Zn(OH)2
(s)
(s)
+ 2H+
+ 2OH-
(aq)
(aq)
Zn2+
ZnO22-
(aq)
+ 2H2O
(aq)
(l)
+ 2H2O
(l)
When a solution with zinc ions is reacted with ammonia, a white
precipitate will form. However, this white precipitate is soluble in
excess aqueous ammonia to form a colorless solution.
Zn2+ (aq) + 2OH-(aq) Zn(OH)2 (aq) (white ppt)
Zn(OH)2 (aq) + 4NH3(aq) [Zn(NH3)4]2+ (aq)
2. Common sources of nature of the ion
Zinc is prevalently found in foods
especially in oysters that are rich in zinc. A
typical oyster weighing approximately one
ounce will contain about 8-9 milligrams of zinc;
thus, the consumption of two oysters would put
a person over the WHFoods (World's Healthiest
Foods) recommended daily amount of 11
milligrams. In addition to oysters, other shellfish
tend to be rich in this mineral, as are many
other animal foods.
It is also true that many nuts and seeds are rich in zinc. Sesame
seeds and pumpkin seeds are included in the Top 10 WHFoods sources for
this mineral. Elemental zinc makes up about 75 ppm of Earth's crust, making
it the 24th most abundant element. The element is normally found in
association with other base metals such as copper and lead in ores.
Moreover, zinc is a chalcophile or it has a low affinity for oxides and prefers
to bond with sulfides.
4. Applications of the ion
Metallic zinc is used in the production of alloys and in galvanizing to
protect steel structures. Other zinc compounds include the oxides (ZnO)
which are used in ceramics, rubber industries, and in ink production. Zinc
sulfates (ZnSO4) are used in textile industry and the treatment of zinc
deficiency in soils. Moreover, zinc chloride is used to preserve wood and as
deodorant in several fluids. This compound is also used in dry cells, and in
paint production.
5. Risks and Hazards connected to the ion
Zinc is a metal. It is called an essential trace element because very
small amounts of zinc are necessary for human health. However, excessive
intake of zinc an be harmful for the body. Zinc metal is a human skin irritant
and is a severe fire hazard, but it is considered as non-toxic. Many zinc
compounds are not very toxic but a few zinc salts may be carcinogenic, yet
the use of some zinc compounds is permitted around food. Moreover,
pollution from industrial smoke containing zin
may cause lung disease.
References:
Zinc. Whfoods.org. Retrieved March 15, 2015 from http://www.whfoods.com/genp age.php?
tname=nutrient&dbid=115
Group IIIB: (Zinc group) nickel, manganese, cobalt and zinc. Hishamezzat.
Retrieved
March
15,
2015
from
http://hishamezzat.weebly.com/uploads/9/0/6/0/9060375/chapter_5cation.pdf
Teoh, A. (2004). Confirmatory tests for cations and anions. Retrieved March 15, 2015 from
http:// alexteoh.com/2008qaions.pdf
Zinc:
biological information. Webelements. Retrieved
http://www.webelements.com/zinc/biology.html
March
15,
2015
from
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Solved Topical and Yearly (READANDWRITE PDFDokumen275 halamanSolved Topical and Yearly (READANDWRITE PDFabdul majeed100% (1)
- Learning Activity No. 3 Reactions of The Hydrogen Sulfide Group (Ions Are Separated As Sulfides in Their Acid Solutions)Dokumen23 halamanLearning Activity No. 3 Reactions of The Hydrogen Sulfide Group (Ions Are Separated As Sulfides in Their Acid Solutions)sampong mga dalere100% (1)
- A Closer Look at Silicon - Chemistry Book for Elementary | Children's Chemistry BooksDari EverandA Closer Look at Silicon - Chemistry Book for Elementary | Children's Chemistry BooksBelum ada peringkat
- ZincDokumen29 halamanZinczidaaanBelum ada peringkat
- Zinc Chloride Determination ProcedureDokumen13 halamanZinc Chloride Determination ProcedureSreedhar Patnaik.MBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Science 2nd Term Jss2Dokumen15 halamanBasic Science 2nd Term Jss2Adio Babatunde Abiodun Cabax100% (1)
- Anodes and Cathodes in Corrosion ReactionsDokumen10 halamanAnodes and Cathodes in Corrosion ReactionsSyed50% (4)
- Zinc, Is A Metallic Chemical Element It Has The Symbol ZN and Atomic Number 30. It Is The FirstDokumen6 halamanZinc, Is A Metallic Chemical Element It Has The Symbol ZN and Atomic Number 30. It Is The FirstVaishali SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Zinc (Pronounced: o o o o o o o oDokumen21 halamanZinc (Pronounced: o o o o o o o oDinar Adi CahyaBelum ada peringkat
- 4 CyanidationDokumen50 halaman4 CyanidationJose Carlos YvBelum ada peringkat
- Construction Materials Assignment No.3Dokumen10 halamanConstruction Materials Assignment No.3Pranay NagpureBelum ada peringkat
- 13.2 Predicting Redox ReactionsDokumen14 halaman13.2 Predicting Redox ReactionsCarmen PurewalBelum ada peringkat
- Exer 12Dokumen8 halamanExer 12MarinellaQuitainEscanoBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Properties: Zinc Is ADokumen2 halamanPhysical Properties: Zinc Is AVinod NairBelum ada peringkat
- Vodni RezmvdvdvDokumen6 halamanVodni RezmvdvdvArben Abela LjajicBelum ada peringkat
- Occurrence: Zinc MineralsDokumen5 halamanOccurrence: Zinc MineralsRonaldBelum ada peringkat
- Sulphur SS2 2024 - 092511Dokumen12 halamanSulphur SS2 2024 - 092511lindaoeghagharaBelum ada peringkat
- Zinc 123Dokumen20 halamanZinc 123Sujan ThapaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Ques Ans Chem X Apr 28, 2021Dokumen5 halamanQues Ans Chem X Apr 28, 2021Atif AnsariBelum ada peringkat
- Valdeviezo Micah Exp9Dokumen8 halamanValdeviezo Micah Exp9BelenBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory 1: Detection of AgDokumen9 halamanLaboratory 1: Detection of AgactriciaBelum ada peringkat
- Sulphur and Its CompoundsDokumen20 halamanSulphur and Its CompoundsBilingwe YohmehBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 01 Chemical Reactions and Equations Test Paper 01Dokumen7 halamanChapter 01 Chemical Reactions and Equations Test Paper 01laurelmatthewlBelum ada peringkat
- Cbse Test Paper-01 01 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDokumen7 halamanCbse Test Paper-01 01 Chemical Reactions and Equationsashish.raj242008Belum ada peringkat
- Inorganic Chemistry/Qualitative Analysis/Tests For AnionsDokumen11 halamanInorganic Chemistry/Qualitative Analysis/Tests For AnionsakileshBelum ada peringkat
- Freelancers - G10 - Chem - Metals and Non-Metals PDFDokumen13 halamanFreelancers - G10 - Chem - Metals and Non-Metals PDFKodati Durga Prasad KodatiBelum ada peringkat
- Identifyingions Final 671585Dokumen9 halamanIdentifyingions Final 671585Rahaf AljboriBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry Part II 5 6Dokumen109 halamanGeneral Chemistry Part II 5 6LUH EKA YANTHIBelum ada peringkat
- NickelDokumen7 halamanNickelkadegemunratBelum ada peringkat
- Sifat Dan Reaksi ZincDokumen3 halamanSifat Dan Reaksi ZincDefi ElfridaBelum ada peringkat
- For Water and Wastewater Zincon Method: ZN ZN (CN) (2) 4 4 4OH 4H O C OH NDokumen1 halamanFor Water and Wastewater Zincon Method: ZN ZN (CN) (2) 4 4 4OH 4H O C OH NNoel LamBelum ada peringkat
- P Block Elements 3Dokumen28 halamanP Block Elements 3Shruti GaurBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Corrected Material Unit 12-17Dokumen55 halamanChemistry Corrected Material Unit 12-17Pandu RockingBelum ada peringkat
- Nitric AcidDokumen9 halamanNitric Acidaditya varteBelum ada peringkat
- 856 - Sulphur and Its Compound1Dokumen9 halaman856 - Sulphur and Its Compound1KevinBelum ada peringkat
- ZN ExtractionDokumen5 halamanZN ExtractionNdumiBelum ada peringkat
- ChemicalreportDokumen2 halamanChemicalreportapi-276156926Belum ada peringkat
- OxygenDokumen10 halamanOxygenFaheem HaiderBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 9 - Properties of MetalDokumen30 halamanActivity 9 - Properties of MetalAbbey Frosty'Knight Dawn MortaleBelum ada peringkat
- Nitric Acid Semester 2Dokumen11 halamanNitric Acid Semester 2Aditya M GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Sources of SulphurDokumen3 halamanSources of SulphurMadonnaAdanna UdokaluBelum ada peringkat
- TH Hemical Reaction and Equation Questions With Solution: Document Downloaded From: 2018Dokumen4 halamanTH Hemical Reaction and Equation Questions With Solution: Document Downloaded From: 2018Lavanya Priya SathyanBelum ada peringkat
- Sodium HistoryDokumen2 halamanSodium HistorySherman OngBelum ada peringkat
- MetalsDokumen7 halamanMetalsritesh kavuruBelum ada peringkat
- Q1. Write A Brief Note On OxygenDokumen3 halamanQ1. Write A Brief Note On OxygenRonnith NandyBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry 12 CH05SQsDokumen4 halamanChemistry 12 CH05SQsFurqan ZahidBelum ada peringkat
- Compounds ZincDokumen2 halamanCompounds ZincmeimeiliuBelum ada peringkat
- A Report On Metallurgy of LeadDokumen5 halamanA Report On Metallurgy of LeadJohnson AanuoluwapoBelum ada peringkat
- Group 15 Elements: - D (Pi) BondDokumen7 halamanGroup 15 Elements: - D (Pi) BondSanju PatelBelum ada peringkat
- SulphurDokumen21 halamanSulphurKevinBelum ada peringkat
- 100L Lecture 4 SaltsDokumen6 halaman100L Lecture 4 SaltsMichael EhondorBelum ada peringkat
- 856 - Sulphur and Its Compound1Dokumen9 halaman856 - Sulphur and Its Compound1KevinBelum ada peringkat
- Some Investigations On The Corrosion of IronDokumen6 halamanSome Investigations On The Corrosion of IronHannah MercadoBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation1 ChemistryDokumen52 halamanPresentation1 ChemistryKrishna KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Chemical Equation and ReactionDokumen7 halamanChemistry Chemical Equation and Reactionsmriti khannaBelum ada peringkat
- Additional 2M Chemistry 1st Year PDFDokumen20 halamanAdditional 2M Chemistry 1st Year PDFShaik irfan basha Shaik irfan bashaBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsDokumen10 halamanNCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsHari PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Cbse Sample Paper-05: 2ki + CL 2Kcl + IDokumen9 halamanCbse Sample Paper-05: 2ki + CL 2Kcl + ISudeep GoelBelum ada peringkat
- Sulphur and Its CompoundsDokumen19 halamanSulphur and Its Compoundspaqurette3Belum ada peringkat
- Laboratory ManualDokumen17 halamanLaboratory ManualSithara JayarathnaBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Materials Metals and Non MetalsDokumen6 halamanNotes On Materials Metals and Non Metalsmatho logyBelum ada peringkat
- Notes For DoxorubicinDokumen6 halamanNotes For DoxorubicinJoseph Neos CruzBelum ada peringkat
- White & Wu, 2001Dokumen2 halamanWhite & Wu, 2001Joseph Neos CruzBelum ada peringkat
- White & Wu, 2001Dokumen2 halamanWhite & Wu, 2001Joseph Neos CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Chromosome 4Dokumen2 halamanChromosome 4Joseph Neos CruzBelum ada peringkat
- How To Draw A PoliticianDokumen2 halamanHow To Draw A PoliticianJoseph Neos CruzBelum ada peringkat
- THOUGHT QUESTIONS (Second Exam)Dokumen5 halamanTHOUGHT QUESTIONS (Second Exam)Lara Sabrina LumangBelum ada peringkat
- MSDS Exprt 1Dokumen6 halamanMSDS Exprt 1Joseph Neos CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Eq For Different TestsDokumen2 halamanSummary of Eq For Different TestsJoseph Neos CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Le ChateliersDokumen10 halamanLe ChateliersOrekaj DattebayoBelum ada peringkat
- TRANSISIDokumen61 halamanTRANSISIAlanBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry SummaryDokumen132 halamanChemistry SummarySebuta HuzaimaBelum ada peringkat
- Acids Bases and Salts.Dokumen50 halamanAcids Bases and Salts.DavyieBelum ada peringkat
- SDS 23 Pages - 156Dokumen29 halamanSDS 23 Pages - 156Pranay PatnaikBelum ada peringkat
- 78 128Dokumen51 halaman78 128Anonymous qKeDFDBelum ada peringkat
- D BlockDokumen20 halamanD BlockRaju SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis: CRCL Blue SolutionDokumen8 halamanAnalysis: CRCL Blue Solutionayu irsalinaBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM 4 NotesDokumen334 halamanCHEM 4 NotesMokayaBelum ada peringkat
- Cation Lab ReportDokumen5 halamanCation Lab Report2020-1-77-042Belum ada peringkat
- Determination of Copper and Zinc in Brass - Two Basic MethodsDokumen2 halamanDetermination of Copper and Zinc in Brass - Two Basic MethodsAngeloBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of PH On ZnO Nanoparticle Properties Synthesized by Sol-Gel CentrifugationDokumen8 halamanEffect of PH On ZnO Nanoparticle Properties Synthesized by Sol-Gel CentrifugationEduardoValdesBelum ada peringkat
- ZN 2Dokumen3 halamanZN 2Joseph Neos CruzBelum ada peringkat
- CH2 Transition Metals Unit V A2 LevelDokumen9 halamanCH2 Transition Metals Unit V A2 LevelbillaljavedBelum ada peringkat
- QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS TESTS For Metal Cations Identifying Positive Ions, Carbonates, Ammonium Ion, Hydrogen Ions, Acids IdentificationDokumen6 halamanQUALITATIVE ANALYSIS TESTS For Metal Cations Identifying Positive Ions, Carbonates, Ammonium Ion, Hydrogen Ions, Acids IdentificationShubham ChapterBelum ada peringkat
- SBA # 9 - Identification of CationsDokumen5 halamanSBA # 9 - Identification of CationsFina ShoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Three Major Classes of Chemical Reactions: Follow-Up ProblemsDokumen72 halamanChapter 4 Three Major Classes of Chemical Reactions: Follow-Up Problems원철이Belum ada peringkat
- 9.2 Solubility Equilibria TeacherDokumen4 halaman9.2 Solubility Equilibria TeacherMichelle NgBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory Ion TestDokumen50 halamanInorganic Chemistry Laboratory Ion TestTrescia Mae EstilloreBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Chapter 8 SaltsDokumen32 halamanChemistry Chapter 8 SaltsnorlieyBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Lab Manual - Grade 10 - 2022-23 (Finalized)Dokumen26 halamanChemistry Lab Manual - Grade 10 - 2022-23 (Finalized)Hanish Chowdary .NBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Ch. 17 Test BankDokumen36 halamanChemistry Ch. 17 Test BankZara V. Feldman67% (6)
- Unit 5 Exam Questions MSDokumen201 halamanUnit 5 Exam Questions MSTahirBelum ada peringkat
- CL CL: Handout Webinar Skor A+ Chemistry SPM '21Dokumen40 halamanCL CL: Handout Webinar Skor A+ Chemistry SPM '21MUHAMMAD HAZRIQ BIN ARIS JABATAN SAINSBelum ada peringkat
- 10th ICSE Chemistry Answers (Chapter 3B)Dokumen19 halaman10th ICSE Chemistry Answers (Chapter 3B)Archit ShetyeBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Chemistry MCQs - FinalDokumen15 halamanAnalytical Chemistry MCQs - FinalMd AtifBelum ada peringkat
- SCES3023 Practical 3Dokumen5 halamanSCES3023 Practical 3Moo Moo ThongBelum ada peringkat
- Act9 1Dokumen12 halamanAct9 1GenSan PnpBelum ada peringkat