Chemistry Notes
Diunggah oleh
Tanishq KapoorJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chemistry Notes
Diunggah oleh
Tanishq KapoorHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
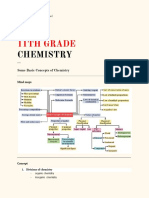
CHEMISTRY SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Chemistry is the branch of science that studies the composition, properties and interaction of matter.
Chemistry plays an important role in science and is often intertwined with other branches of science
such as physics, biology and geology.
Chemistry plays an important role in daily life such as weather patterns, functioning of brain, health
care products and other materials aimed at improving the quality of life.
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass.
Matter can exist in three physical states such as solid, liquid and gas.
Solids have definite volume and definite shape.
Liquids have definite volume but not definite shape.
Gases have neither definite volume nor definite shape.
These states of matter can be interconvertible by changing the conditions of temperature and
pressure.
At the macroscopic level, matter can be classified into mixtures or pure substances.
A mixture may be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Pure substances can be further classified into elements and compounds.
An element consists of only one type of particles.
Two or more atoms of different elements combine to form a molecule of a compound.
The constituents of a compound can be separated only by chemical methods.
A compound has properties different from its constituent elements.
Isotopes are elements with same atomic number but different mass number.
Every substance has unique properties that can be classified into two types: physical properties and
chemical properties.
The SI system (The International System of Units) has seven base units which pertain to the 7
fundamental scientific quantities:
www.topperlearning.com
CHEMISTRY SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
Base Physical Quantity
Symbol for quantity
Name of SI Unit
Symbol for SI Unit
Length
metre
Mass
Time
Electric current
M
T
I
kilogram
second
ampere
kg
s
A
Thermodynamic
temperature
Amount of substance
Luminous intensity
Kelvin
n
Iv
mole
candela
mol
cd
The unit is written on the right of the quantity with a space between them.
The SI system allows the use of prefixes to indicate the multiples or submultiples of a unit.
Multiple
10
10
Prefix
Symbol
Deci
Deca
Da
10
Hector
10
kilo
mega
106
There are three common scales to measure temperature: oC (degree Celsius), oF (degree Fahrenheit)
and K (Kelvin).
To indicate very small numbers, we use negative exponents.
To indicate large numbers, we use positive exponents.
Scientific notation is a proper representation of a number in exponential form N 10n, where n is an
exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary from 1 to 10.
Precision indicates how closely repeated measurements match each other.
Accuracy indicates how closely a measurement matches the correct or expected value.
A result is valid only if it is both accurate and precise.
Significant figures are meaningful digits which are known with certainty.
There are certain rules for determining the number of significant figures:
o All non-zero digits are significant.
o Zeros preceding the first non-zero digit are not significant.
o Zeros between two non-zero digits are significant.
www.topperlearning.com
CHEMISTRY SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
o Zeros at the end or right of the number are significant provided they are on the right side of the
decimal point, but otherwise the zeros are not significant.
During addition and subtraction, the result cannot have more digits to the right of the decimal point
than either of the original numbers.
In multiplication and division with significant figures, the answer cannot have more significant figures
than either of the original numbers.
There are 5 basic laws of chemical combinations that govern every reaction such as law of
conservation of mass, law of definite proportions, law of multiple proportions, Gay Lussacs law of
gaseous volumes and Avogadros law.
Law of conservation of mass: Antoine Lavoisier established the law of conservation of mass. It states
that matter can neither be created nor destroyed. In other words, we can say that during any physical
or chemical change, the total mass of reactants is equal to the total mass of products.
Law of definite proportions: Joseph Proust showed that a given compound always contains exactly the
same proportion of elements by weight.
Law of multiple proportions: Dalton proposed the law of multiple proportions. According to this law, if
two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the mass of one element that combines
with the fixed mass of the other element is in the ratio of small whole numbers.
Gay Lussacs law of gaseous volumes: When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reaction,
they do so in a simple ratio by volume, provided all the gases have the same temperature and
pressure.
Avogadro law: At the same temperature and pressure, equal volumes of gases contain equal number
of molecules.
Daltons atomic theory: In 1808, Dalton published A New System of Chemical Philosophy in which he
proposed the following:
o Matter consists of indivisible atoms.
o All the atoms of a given element have identical properties including identical mass. Atoms of
different elements differ in mass.
o Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in a fixed ratio.
o Chemical reactions involve reorganisation of atoms. These are neither created nor destroyed in a
chemical reaction.
Daltons theory could explain the laws of chemical combination.
The number 6.022 1023 is called Avogadros constant or Avogadros number.
Atomic Mass: Average relative mass of an atom of an element as compared to the mass of a carbon
atom is taken as 12 amu. Atomic mass expressed in grams is called gram atomic mass.
www.topperlearning.com
CHEMISTRY SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
Atomic mass is donated by u, where u is the unified mass.
Molecular mass: It is the sum of atomic masses of elements present in a molecule. Molecular mass
expressed in grams is called gram molecular mass.
Formula mass: It is the sum of atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of the compound.
A mole is a collection of 6.022 1023 particles.
One mole is the amount of a substance that contains as many particles or entities as there are atoms
in exactly 12 g (or 0.012 kg) of 12C.
The mass of one mole of a substance in grams is called its molar mass.
The molar mass in grams is numerically equal to the atomic/molecular/formula mass in u..
Following relations given below can be summarized as
o One mole of atoms = 6.022 1023 atoms = Gram atomic mass of an element.
o One mole of molecules = 6.022 1023 molecules = Gram molecular mass of a substance.
Mass of that element in the compound
100
Molar mass of compound
Mass % of an element
The concentration of a solution can be expressed in any of the following ways: Mass per cent, mole
fraction, molarity and molality.
Mass per cent
Mole Fraction =
Molarity is the number of moles of solute in per liter of solution. Unit is moles per liter.
Molarity =
No. of mole of a particular component
Total No. of moles of solution
No. of moles of solute
Volume of solution in litres
Molality is the number of moles of solute present in 1 kg of solvent.
Molality
Mass of solute
100
Mass of solution
No. of moles of solute
Mass of solvent inkg
An empirical formula represents the simplest whole number ratio of various atoms present in a
compound.
www.topperlearning.com
CHEMISTRY SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
Molecular formula shows the exact number of different types of atoms present in a molecule of a
compound.
If the mass per cent of various elements present in a compound is known, then its empirical formula
can be determined.
Molecular formula = n (Empirical formula) , where n is a simple number and may have values 1, 2, 3.
Following steps should be followed to determine empirical formula of the compound:
o Step 1: Conversion of mass per cent of various elements into grams.
o Step 2: Convert mass obtained in step 1 into number of moles.
o Step 3: Divide the mole value obtained in step 2 by the smallest mole value (out of the mole value
of various elements calculated).
o Step 4: In case the ratios are not whole numbers, they may be converted into whole numbers by
multiplying by a suitable coefficient.
o Step 5: Write empirical formula by mentioning the numbers after writing the symbols of respective
elements.
Out of various reactants in a reaction, a reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction is
called limiting reagent.
Stoichiometry gives a quantitative relation between reactants and products in a reaction. It also helps
us in identifying limiting reagents.
www.topperlearning.com
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDari EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 6 - MolesDokumen16 halamanCsec Chemistry Chapter 6 - Moleschelsea AlexandriaBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Limit at InfinityDokumen11 halamanCalculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Limit at Infinityapi-1192241886% (7)
- Class 11 CH 1 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen6 halamanClass 11 CH 1 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistrySai Kotian50% (2)
- PUC Chemistry Question BankDokumen214 halamanPUC Chemistry Question BankSathish Kumar100% (1)
- 14 Programming MethodologyDokumen37 halaman14 Programming MethodologyTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of Chem Notes Class 11Dokumen8 halamanSome Basic Concepts of Chem Notes Class 11Jennika Jaison100% (1)
- Geometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDokumen29 halamanGeometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDinkar YeoleBelum ada peringkat
- Mole Concept Chapter1Dokumen30 halamanMole Concept Chapter1Kaluram Ninama100% (1)
- Revision Notes On Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen6 halamanRevision Notes On Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryGagan JainBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen13 halamanUnit 1: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistryjahir golandajBelum ada peringkat
- General ChemistryDokumen34 halamanGeneral ChemistryTrixie HicaldeBelum ada peringkat
- Complete Notes of Puc First YearDokumen182 halamanComplete Notes of Puc First YeardanielakhilkumarBelum ada peringkat
- HSC Chemistry NotesDokumen5 halamanHSC Chemistry NotesananyahatesithereBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Units Chemistry Class XI.2022-23Dokumen73 halamanSummary of Units Chemistry Class XI.2022-23shilpa07.nairBelum ada peringkat
- JEE Main Short Notes Mole Concept and Stoichiometry - pdf-15Dokumen9 halamanJEE Main Short Notes Mole Concept and Stoichiometry - pdf-15PUSHKAR SAINIBelum ada peringkat
- Mole Concept: Mixture Pure SubstanceDokumen9 halamanMole Concept: Mixture Pure SubstancePRITAM KumarBelum ada peringkat
- 11chemistry OMEGA PDFDokumen96 halaman11chemistry OMEGA PDFChirAgBelum ada peringkat
- University of Northeastern Philippines (UNEP) Iriga CityDokumen9 halamanUniversity of Northeastern Philippines (UNEP) Iriga CityNica GumbaBelum ada peringkat
- Mole Concept & StoichiometryDokumen8 halamanMole Concept & StoichiometryNareshBelum ada peringkat
- Lessons 5 6Dokumen22 halamanLessons 5 6Datuesmail Ala AliBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen57 halamanSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryAshutosh KunduBelum ada peringkat
- Class 11th Chemistry Short Notes For NEETxfxuxtixuxzrizurxtjztizitzitxtiztixtjzDokumen136 halamanClass 11th Chemistry Short Notes For NEETxfxuxtixuxzrizurxtjztizitzitxtiztixtjzrockzergamerzBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen27 halamanSome Basic Concepts of ChemistrySARVESH VERMABelum ada peringkat
- Enjoy Chemistry: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen6 halamanEnjoy Chemistry: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryMaitri VyasBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement of Temperature: Precision: Accuracy: RulesDokumen3 halamanMeasurement of Temperature: Precision: Accuracy: RulesVinoth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen58 halamanSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryYOONMINBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Study Material-11Dokumen149 halamanChemistry Study Material-11Arun Sharma100% (1)
- Basic Terms of Chemical Engineering14Dokumen15 halamanBasic Terms of Chemical Engineering14Shrinil DesaiBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 1 Mark QuestionsDokumen14 halamanSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry 1 Mark QuestionsADITYANARAYAN SAMALBelum ada peringkat
- XI ChemistryDokumen86 halamanXI Chemistryadvietiya.fiverrBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen5 halamanChapter 1HARSHA VARDAN KARTHIK SELVAN 6466Belum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen5 halamanSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryDhana AryalBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry - Chapter SummaryDokumen4 halamanSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry - Chapter SummaryAnirudhBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry - WatermarkDokumen27 halamanSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry - WatermarkScienTechzBelum ada peringkat
- Revise Chemistry in 1day PDFDokumen196 halamanRevise Chemistry in 1day PDFAkshat PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter: Equations, Reactions and AmountDokumen21 halamanChapter: Equations, Reactions and AmountWorld EducationBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry NotesDokumen7 halamanSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry NotesEvelyn RiderBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 Quantitative ChemistryDokumen30 halamanTopic 1 Quantitative ChemistrybaterbeeBelum ada peringkat
- Lows of Chemical CombinationsDokumen5 halamanLows of Chemical CombinationsManoj BindalBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Standard Level Chapter 1Dokumen30 halamanChemistry Standard Level Chapter 1Güşta İrem SakızBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry SM XI 2021-22Dokumen154 halamanChemistry SM XI 2021-22SHRUTI AGARWALABelum ada peringkat
- Stoichiometry: Atomic Mass, Avogadro's Number, Mole ConceptDokumen30 halamanStoichiometry: Atomic Mass, Avogadro's Number, Mole Conceptstevenlloyd maybituin100% (1)
- Gen Chem q2 w1 To w3Dokumen12 halamanGen Chem q2 w1 To w3ARIEL ANGELIOBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Mole Concept - Chapter Notes - JEE - BASICS OF MOLE CONCEPT - NoteDokumen7 halamanBasics of Mole Concept - Chapter Notes - JEE - BASICS OF MOLE CONCEPT - NoteCaptain WininBelum ada peringkat
- Wa0028Dokumen107 halamanWa0028brian samBelum ada peringkat
- Atom 2Dokumen46 halamanAtom 2Beri NaysBelum ada peringkat
- Important Questions ChemistryDokumen6 halamanImportant Questions ChemistryNija GamingBelum ada peringkat
- General Guidelines For Balancing Simple Equations: StoichiometryDokumen6 halamanGeneral Guidelines For Balancing Simple Equations: StoichiometryJonel Mark CarandangBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch01 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen6 halaman11 Chemistry Notes Ch01 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistrypriya100% (1)
- IB Chemistry SL and HLDokumen108 halamanIB Chemistry SL and HLVed JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 121 - NotesDokumen2 halamanChem 121 - NotesIqra DadaBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concept of ChemistryDokumen61 halamanSome Basic Concept of ChemistrychinnuexampointBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Reporte QuimicaDokumen9 halamanPre Reporte QuimicaIsabel Sofia Corredor MendezBelum ada peringkat
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDokumen6 halamanSome Basic Concepts of ChemistrySatyam MittalBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Chapter 1 ReviewDokumen10 halamanChem Chapter 1 ReviewAnonymous TGVQ4jF42Belum ada peringkat
- SelfStudys DocumentDokumen3 halamanSelfStudys DocumentManjot SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Ib Screwed Chapter 1Dokumen16 halamanIb Screwed Chapter 1Adnan YousafBelum ada peringkat
- ChemistryDokumen21 halamanChemistryAruba DhadukBelum ada peringkat
- Rates and Equilibria of Organic Reactions: As Treated by Statistical, Thermodynamic and Extrathermodynamic MethodsDari EverandRates and Equilibria of Organic Reactions: As Treated by Statistical, Thermodynamic and Extrathermodynamic MethodsBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry for Students: The Only Chemistry Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseDari EverandChemistry for Students: The Only Chemistry Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseBelum ada peringkat
- New Doc 2017-12-19 - 1-1Dokumen1 halamanNew Doc 2017-12-19 - 1-1Tanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- t1 Sem 2 2016 SDFDokumen1 halamant1 Sem 2 2016 SDFTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Printer TestDokumen2 halamanPrinter TestTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Vector 3DDokumen15 halamanWorksheet Vector 3DTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 1Dokumen5 halamanExercise 1Tanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Rhel Advanced Linux Cheat Sheet r3v1Dokumen5 halamanRhel Advanced Linux Cheat Sheet r3v1testdottest9251Belum ada peringkat
- NHDokumen2 halamanNHRamesh Babu PindigantiBelum ada peringkat
- IIO Syllabus Class 12Dokumen1 halamanIIO Syllabus Class 12Tanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Motion Tion Tion Tion TionDokumen1 halamanSimple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Motion Tion Tion Tion Tionrohan.riteshBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Motion Tion Tion Tion TionDokumen1 halamanSimple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Mo Simple Harmonic Motion Tion Tion Tion Tionrohan.riteshBelum ada peringkat
- Projects Icbse ComDokumen4 halamanProjects Icbse ComTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Comp. SC Class XII: Classes and ObjectsDokumen3 halamanAssignment Comp. SC Class XII: Classes and ObjectsTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- PMSS English Ad (2016 17)Dokumen1 halamanPMSS English Ad (2016 17)iit JeeBelum ada peringkat
- Planet Rigo No Met 00 Cole GoogDokumen147 halamanPlanet Rigo No Met 00 Cole GoogTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Day 34 - Probability 2Dokumen4 halamanWorksheet Day 34 - Probability 2Tanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Day 37 - MatricesDokumen10 halamanWorksheet Day 37 - MatricesTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Projects Icbse ComDokumen4 halamanProjects Icbse ComTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Important TopicDokumen2 halamanImportant TopicTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Day 29 - Definite 2Dokumen8 halamanWorksheet Day 29 - Definite 2Tanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Viteee - 2017 - Sample Questions PhysicsDokumen1 halamanViteee - 2017 - Sample Questions PhysicsRaghuvendra SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines JMIDokumen17 halamanGuidelines JMImunibfazalBelum ada peringkat
- Apple Cups Printer Test PageDokumen1 halamanApple Cups Printer Test PageprinttesterBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Day 10Dokumen3 halamanWorksheet Day 10Tanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- 03 ExerciseDokumen42 halaman03 ExerciseTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- ComputerScience MSDokumen35 halamanComputerScience MSNirvana Adithya Visiobibliophobiatic GuyBelum ada peringkat
- Projects Icbse ComDokumen4 halamanProjects Icbse ComTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Cheat Sheet Calculus PDFDokumen6 halamanCheat Sheet Calculus PDFmichael17ph2003Belum ada peringkat
- M.MARKS: 30 Duration: 3 Hrs Split Up of Marks During Practical Exam According To CbseDokumen2 halamanM.MARKS: 30 Duration: 3 Hrs Split Up of Marks During Practical Exam According To CbseTanishq KapoorBelum ada peringkat