2011 Physics 5058 O-Level Answers
Diunggah oleh
heyitsvanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2011 Physics 5058 O-Level Answers
Diunggah oleh
heyitsvanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
O-LEVEL 5058 PHYSICS NOVEMBER 2011
Internal circulation only
5058/1
MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS
5058/2
SECTION A
Please remember to quote the formula in all calculations.
1
(a)
Pressure is defined as the force acting per unit area.
[1]
(b)
Pressure of the gas = Patm + hg
= 1.0 x 105 + (0.60 x 1000 x 10)
= 1.1 x 105 Pa
[1]
[1]
(c)
When the temperature of the gas increases, the gas molecules gain kinetic
energy and move at a greater speed.
They will collide with the inner walls of the container with greater force at a
higher frequency.
Since pressure is defined as the force acting per unit area, the pressure of the
gas increases when the temperature increases.
[1]
[1]
[1]
O-LEVEL 5058 PHYSICS NOVEMBER 2011
Internal circulation only
(a)
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
It can be converted from one form to another, but the total energy remains
constant.
[1]
[1]
(b)
(i)
Loss in Ep = mgh
= 90 x 10 x 60
= 54 000 J
[1]
Gain in Ek = (1/2)mv2
= (1/2) x 90 x 122
= 6500 J
[1]
(ii)
(c)
(a)
(b)
The loss in gravitational potential energy (GPE) and the gain in kinetic energy
(KE) is different due to the presence of air resistance and frictional forces on
the hill.
By the law of conservation of energy, the loss in GPE is converted to a gain in
KE and other energy forms due to the resistive forces, such as thermal and
sound energy.
(a)
[1]
[1]
[1]
(i)
Thermocouple
[1]
(ii)
A thermocouple has a small junction and a low specific heat capacity,
hence only a small amount of thermal energy is required to produce a
change in temperature. This allows the thermocouple to respond quickly
to temperature changes.
[1]
Using Q = mc, 2500 x 1 = 75 x 1.1 x
= 30.3 C
[1]
Temperature of emergent air = 30.3 + 20
= 50 C (2 s.f.)
[1]
(i)
(ii)
[1]
Water boils at 100 C, which is higher than the temperature of the
emergent hot air. Since evaporation takes place at any temperature, the
water on the hands evaporates rather than boils.
The distance between adjacent particles alternates between increasing to a
maximum and decreasing to a minimum.
(b)
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
Accept any pair of Q1, Q2 or Q3.
(c)
(i)
Amplitude of the wave = (1/2) x 6.0 mm
= 3.0 mm
2
[1]
O-LEVEL 5058 PHYSICS NOVEMBER 2011
Internal circulation only
(ii)
Frequency of the wave = 1/T = 1/2.0 = 0.50 Hz
[1]
(iii)
Speed of the wave = f
= 0.5 x 40
= 20 cm/s
[1]
(iv)
[1]
[1]
t = 3.0 s is equal to 1.5 T i.e. the particles will undergo half an oscillation.
Hence, the centre of rarefaction (i.e. P) will become a centre of
compression.
5
(a)
Microwaves
[1]
(b)
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
[1]
[1]
[1]
(c)
All electromagnetic (EM) waves are transverse waves. However, ultrasound is
a longitudinal wave, hence it is not a component of the EM spectrum. OR
All electromagnetic (EM) waves can travel in vacuum. However, ultrasound
requires a medium to propagate, hence it does not belong to the EM spectrum.
Radio waves
Infra-red
Microwaves
(d)
(a)
[1]
[2]
Friction during the rubbing process causes negatively-charged electrons to be
transferred from the cloth to the plastic.
The plastic gains electrons and becomes negatively-charged. The cloth loses
electrons and becomes positively-charged.
[1]
(b)
A metal is a conductor, so when it is held in the hand, any excess charges will
be earthed through the hand, hence it remains uncharged.
[1]
(c)
(i)
[1]
Energy released = P x t
= 100 x 5.0 x 106
= 5.0 x 108 J
3
[1]
O-LEVEL 5058 PHYSICS NOVEMBER 2011
Internal circulation only
(ii)
Average power released = E / t
= (90 x 5.0 x 108) / 1
= 4.5 x 1010 W
[1]
(iii)
Average e.m.f. of a lightning strike = E / Q
= 5.0 x 108 / 4.0
= 1.3 x 108 V
[1]
(d)
Photocopier / Electrostatic spray painting / Laser printer (any one)
[1]
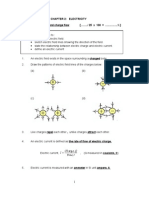
(a)
Since the two N-poles are closer to each other, the force of repulsion between
these like poles is greater than the force of attraction between the unlike poles.
Hence magnet B moves away from magnet A.
[1]
(b)
[3]
Note:
1. Field lines must not cross
each other, especially
near the poles.
2. Direction of field must be
correctly indicated.
(a)
When the coil rotates, it cuts the magnetic field between the poles of the
magnet, hence causing a change in the magnetic flux linking the coil. This
causes an e.m.f. to be induced in the coil.
(b)
The slip rings provide an electrical connection between the coil and the external
circuit. OR They prevent the coil from being entangled while rotating.
(c)
By Flemings left-hand rule, where the index finger represents the direction of
the magnetic field, the second finger represents the direction of the current and
the thumb represents the direction of the force produced, a downwards force
will be produced at X. Hence this opposes the rotation of the coil.
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
O-LEVEL 5058 PHYSICS NOVEMBER 2011
Internal circulation only
5058/2
SECTION B
9
(a)
(b)
The distance travelled between t = 0.40 s to 0.60 s is 0.82 m, while the distance
travelled between t = 0.20 s to 0.40 s is 0.55 m. Since a larger distance is
covered in the same time interval, its speed is increasing.
[1]
(i)
[2]
Note:
1. All points must be plotted.
2. Graph must start from the
origin and extend to the
last point.
(ii)
(c)
The gradient of the graph becomes constant after 0.80 s, which suggests
that the velocity of the shuttlecock reaches a constant value.
[1]
(iii)
Gradient of the graph = (9.81 - 3.68) / (2.00 - 1.00) = 6.13 m/s
Terminal velocity = 6.13 m/s
[1]
[1]
(iv)
As the speed of the shuttlecock increases when it falls, the air resistance
acting on it increases. When the air resistance acting upwards balances
the weight of the shuttlecock acting downwards, there will be no net force
acting on the shuttlecock and it will move with zero acceleration i.e.
terminal velocity.
(i)
(ii)
10
(a)
For the first 0.40 s, both shuttlecocks fall with the same initial
acceleration as the increase in speed is the same.
After 0.40 s, the heavy shuttlecock reaches terminal velocity at a later
time, around 1.40 s, while the light shuttlecock reaches terminal velocity
at an earlier timing of 1.00 s.
The heavier shuttlecock has a greater weight than the light shuttlecock,
hence a higher air resistance is required to balance its weight. Thus, the
heavy shuttlecock reaches terminal velocity at a later time.
Using P = IV,
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
IP = P/V = 100/240
= 0.42 A
IQ = 60/240 = 0.25 A
IR = 0.25 + 0.417 = 0.67 A
5
[2]
O-LEVEL 5058 PHYSICS NOVEMBER 2011
Internal circulation only
(b)
(c)
(i)
Using P = V2/R,
(ii)
Using 1/Reff = 1/RA + 1/RB,
[1]
Total resistance of A and B in parallel = (1/580 + 1/960)-1
= 360 (2 s.f.)
[1]
In the series circuit, the voltage across each lamp is lower than that of a
parallel circuit, hence a lower power is generated in each lamp.
This results in a lower temperature and hence a lower resistance in each
lamp, since the lamps are non-ohmic conductors.
[1]
Using VA = RA/(RA + RB) x V,
[1]
(i)
(ii)
R = 2402/60
= 960
[1]
VA = 95/(95 + 830) x 240 = 25 V (2 s.f.)
11
[1]
[1]
EITHER
(a)
(i)
[1]
Note:
Construction lines (i.e. dotted lines)
should be drawn.
(b)
(ii)
Angle correctly labeled in the diagram as i.
[1]
(iii)
The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the
normal at the point of incidence.
[1]
(i)
Angle of incidence = 40
[1]
Using n = sin i / sin r,
sin r = sin 40/1.5
r = 25 (2 s.f.)
[1]
[1]
(ii)
Note:
Emergent ray must be drawn parallel
to incident ray.
[1]
O-LEVEL 5058 PHYSICS NOVEMBER 2011
Internal circulation only
(c)
11
(i)
Total internal reflection is a phenomenon in which all the light is reflected
back into the optically denser medium when it travels from an optically
denser medium to an optically less dense medium at an incident angle
greater than the critical angle.
[1]
(ii)
The light is travelling from an optically less dense medium to an optically
denser medium, hence total internal reflection cannot occur since the
condition for it to occur is otherwise.
[1]
(iii)
A ray of light that enters the glass through surface A will have an incident
angle less than the critical angle at surface B, hence total internal
reflection cannot occur.
[1]
OR
(a)
(i)
Note:
1. W should be drawn vertically
with a ruler passing through
the CG.
2. F should be drawn vertically
from the point of contact
between the wheel and the
ground.
3. E should be drawn such that
it leads to a clockwise
moment.
(b)
(c)
[1]
[1]
[1]
(ii)
When an object is in equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments about
any pivot is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments about the same
pivot.
[1]
(iii)
The truck is designed such a way that the perpendicular distance
between the pivot and the line of action of the effort is larger than that of
the weight of the load.
Since moment produced = force x perpendicular distance, the effort
required to lift the load will be less than its weight due to the larger
perpendicular distance, hence it is easier to lift the load.
[1]
Total moment = F x d
= 2 x (140 x 0.8)
= 220 Nm (2 s.f.)
[1]
[1]
Taking moments about S,
Sum of clockwise moments = Sum of anticlockwise moments
FR x 1.2 = 180 x 0.8
FR = 120 N
[1]
[1]
[1]
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 2012 Physics 5058 O-Level AnswersDokumen7 halaman2012 Physics 5058 O-Level AnswersheyitsvanBelum ada peringkat
- 2015 OLevel Pure Chemistry Paper 2 5073/02 AnswersDokumen14 halaman2015 OLevel Pure Chemistry Paper 2 5073/02 AnswersMethodology OfStudiesBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 OLevel Pure Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and AnswersDokumen13 halaman2012 OLevel Pure Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and AnswersMethodology OfStudies100% (6)
- GCE O Level Pure Chemistry 507302 Suggested Answers 2016Dokumen5 halamanGCE O Level Pure Chemistry 507302 Suggested Answers 2016DjBelum ada peringkat
- Sec 3 Chemistry Practice QuestionsDokumen4 halamanSec 3 Chemistry Practice Questionschong56100% (1)
- 2010 H2 Physics Paper 9646/03 suggested solutionsDokumen8 halaman2010 H2 Physics Paper 9646/03 suggested solutionslaslover100% (1)
- June 1999 Paper 1Dokumen16 halamanJune 1999 Paper 1YasirBelum ada peringkat
- Gce o Level Physics Questions Faq 2013Dokumen12 halamanGce o Level Physics Questions Faq 2013api-235555080Belum ada peringkat
- O-LEVEL PHYSICS Light WORKDokumen41 halamanO-LEVEL PHYSICS Light WORKojilong100% (1)
- Physics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8Dokumen9 halamanPhysics-Worksheet 1-Thermal Physics-Grade 8dhureyaaBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Past Paper - P4 - 2013-20 PDFDokumen308 halamanPhysics Past Paper - P4 - 2013-20 PDF123 456Belum ada peringkat
- Igcse 61 Magnetism&ElectromagnetismDokumen32 halamanIgcse 61 Magnetism&ElectromagnetismHany ElGezawy100% (4)
- 2012 OLevel Science Physics Paper 2 Questions and AnswersDokumen10 halaman2012 OLevel Science Physics Paper 2 Questions and AnswersMethodology OfStudiesBelum ada peringkat
- Examiner Tips For O Level Physics 5054Dokumen10 halamanExaminer Tips For O Level Physics 5054muzaahBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Checklist For O Level Physics 5054 FINALDokumen24 halamanRevision Checklist For O Level Physics 5054 FINALYenny Tiga100% (3)
- Level Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-11 Waves PAPER-1 Multiple ChoiceDokumen12 halamanLevel Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-11 Waves PAPER-1 Multiple Choiceelty Tan0% (1)
- Concise SEO-Optimized Title for Organic Chemistry DocumentDokumen14 halamanConcise SEO-Optimized Title for Organic Chemistry DocumentGertrude Ramsbottom50% (2)
- 2012 OLevel Science Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and AnswersDokumen10 halaman2012 OLevel Science Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and AnswersMethodology OfStudies100% (1)
- The Particulate Nature of Matter 1 MSDokumen7 halamanThe Particulate Nature of Matter 1 MSKHANBelum ada peringkat
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: Chapter 9 Industrial Inorganic ChemistryDokumen2 halamanAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: Chapter 9 Industrial Inorganic ChemistryMP3 MusicBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolysis Mechanisms and ApplicationsDokumen17 halamanElectrolysis Mechanisms and ApplicationsInnocent EbilBelum ada peringkat
- Notes 5.turning Effects of ForcesDokumen10 halamanNotes 5.turning Effects of ForcesNg Yong Hui Melvin69% (13)
- Worksheet 11 PDFDokumen4 halamanWorksheet 11 PDFVijay Bhaskar50% (2)
- Magnetism - Science Year 8Dokumen15 halamanMagnetism - Science Year 8b_syiera100% (7)
- Pressure MCQ Physics TopicDokumen3 halamanPressure MCQ Physics TopicFahimDayhan67% (3)
- Notes - Topic 5 Forces, Density and Pressure - CAIE Physics A-LevelDokumen5 halamanNotes - Topic 5 Forces, Density and Pressure - CAIE Physics A-LevelMahamIsmailBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry O Level Notes 1Dokumen12 halamanChemistry O Level Notes 1lubna naz100% (1)
- Sec 3e Chem My 09 p2 (Ans)Dokumen14 halamanSec 3e Chem My 09 p2 (Ans)martynchekycBelum ada peringkat
- 1.4 BondingDokumen29 halaman1.4 BondingIlincaVasilescuBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 13 PDFDokumen4 halamanWorksheet 13 PDFVijay Bhaskar50% (2)
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Organic Compounds and Carbon TerminologyDokumen16 halamanSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Organic Compounds and Carbon Terminologyakusabrina2012Belum ada peringkat
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 2 - Teacher'sDokumen15 halamanForm 5 Physics Chapter 2 - Teacher'sPavithiran100% (4)
- O Level Chemistry Organic Practice QuestionDokumen2 halamanO Level Chemistry Organic Practice QuestionMINGHUI86Belum ada peringkat
- 6 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Dokumen3 halaman6 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Ruby Chong67% (3)
- IGCSE Chemistry - Types of Chemical BondsDokumen7 halamanIGCSE Chemistry - Types of Chemical BondsdanielmahsaBelum ada peringkat
- 1123 w10 Ms 22Dokumen12 halaman1123 w10 Ms 22Fatima HashmiBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 June 1999Dokumen4 halamanPaper 2 June 1999MSHBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundDokumen23 halamanChemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundMudzaffar Shah100% (3)
- Electrolysis Questions PDFDokumen14 halamanElectrolysis Questions PDFNeen Naaz50% (2)
- St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesDokumen6 halamanSt. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesMsLiewBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry - Textbook Answers Chapter 5Dokumen20 halamanChemistry - Textbook Answers Chapter 5angelina_boseBelum ada peringkat
- Stoichiometry Review 1Dokumen27 halamanStoichiometry Review 1mostafa barakat100% (1)
- Chem Insights Chapter 7 WSDokumen3 halamanChem Insights Chapter 7 WSwakakkaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Deformation of SolidsDokumen31 halamanUnderstanding Deformation of SolidsWadood Ahmed100% (4)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 16.1Dokumen1 halamanIGCSE Physics Worksheet 16.1Alex DatsyukBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Form 3 NotesDokumen52 halamanPhysics Form 3 NotesDISHON100% (5)
- Form 3 Science Chapter 7 WorksheetDokumen1 halamanForm 3 Science Chapter 7 WorksheetAaliyah Wendy ChongBelum ada peringkat
- Force and Motion EquationsDokumen13 halamanForce and Motion EquationsniknadhiraBelum ada peringkat
- 2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Zhonghua Secondary AnswerDokumen10 halaman2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Zhonghua Secondary AnswerUZAIR MAHBUB BHUYAINBelum ada peringkat
- Refraction and Total Internal Reflection ProblemsDokumen2 halamanRefraction and Total Internal Reflection Problemsmydadawalfn50% (2)
- TWSS 2018 5076 SciPhy 4E5N Prelims MS v2 (Edited)Dokumen5 halamanTWSS 2018 5076 SciPhy 4E5N Prelims MS v2 (Edited)leetaishenBelum ada peringkat
- MGS 2008Dokumen4 halamanMGS 2008Andy YanBelum ada peringkat
- 5054 MJ 2023 P22Dokumen16 halaman5054 MJ 2023 P22Raahin RahimBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 4EXP Physics MYE marking schemeDokumen6 halaman2017 4EXP Physics MYE marking schemeKs WangBelum ada peringkat
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Skema Modul 2Dokumen5 halamanTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Skema Modul 2Cikgu FaizalBelum ada peringkat
- 2015 JC2 MYA H2 SectionBC SolutionsDokumen14 halaman2015 JC2 MYA H2 SectionBC SolutionszhangBelum ada peringkat
- 5054 On 2021 P21Dokumen14 halaman5054 On 2021 P21Raahin RahimBelum ada peringkat
- 2010 H2 Physics Ans - HCIDokumen14 halaman2010 H2 Physics Ans - HCIKhim YangBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Paper 1 Quarter Year Examination 2013 Marking SchemeDokumen23 halamanPhysics Paper 1 Quarter Year Examination 2013 Marking SchemeAnonymous IyNfIgG4ZBelum ada peringkat
- EdUnit 5 Answers (1995-2006) Excel PhysicsDokumen141 halamanEdUnit 5 Answers (1995-2006) Excel PhysicsAravinth Pushparaj100% (2)
- Design Standard For Street LightingDokumen41 halamanDesign Standard For Street LightingKhaldoon Alnashi100% (2)
- Wireless World 1990 12 PDFDokumen92 halamanWireless World 1990 12 PDFMilton NastBelum ada peringkat
- Forces, Motion, and Energy: ScienceDokumen39 halamanForces, Motion, and Energy: ScienceElizabeth Inocencio Facundo - SagotBelum ada peringkat
- Size, Location, Type of Entrance of A Darkroom: Processing Room DesignDokumen3 halamanSize, Location, Type of Entrance of A Darkroom: Processing Room DesignMaemae Mon0% (1)
- Science ReviewerDokumen39 halamanScience ReviewerAngeline Flare MarantalBelum ada peringkat
- LNX 6514DS VTMDokumen2 halamanLNX 6514DS VTMLucas GonçalvesBelum ada peringkat
- Module 12 Behavior of Light in Optical DevicesDokumen21 halamanModule 12 Behavior of Light in Optical DevicesEUNICE EL DACUMOSBelum ada peringkat
- OPT261 Spr19 Homework3Dokumen2 halamanOPT261 Spr19 Homework3KIKIBelum ada peringkat
- 0.6m (2ft) Low Profile Antennas Microwave Antenna SpecificationsDokumen15 halaman0.6m (2ft) Low Profile Antennas Microwave Antenna SpecificationsDarwin Lopez AcevedoBelum ada peringkat
- Dual-Sensor Cameras Deliver Full-Colour Night VisionDokumen8 halamanDual-Sensor Cameras Deliver Full-Colour Night Visionkunene07Belum ada peringkat
- Atomstack M100 Laser Module Installation Manual PDFDokumen48 halamanAtomstack M100 Laser Module Installation Manual PDFDirce NunesBelum ada peringkat
- Ghost Events in Optical Time - NewDokumen3 halamanGhost Events in Optical Time - NewsekutunetBelum ada peringkat
- Tut3 OLET1640 Student NotesDokumen4 halamanTut3 OLET1640 Student Notesdesheng wangBelum ada peringkat
- YX-552FS3: Ultra WDR Waterproof IR Dome Camera User ManualDokumen2 halamanYX-552FS3: Ultra WDR Waterproof IR Dome Camera User ManualaseguradoBelum ada peringkat
- The Physics of Neutron StarDokumen28 halamanThe Physics of Neutron StarAlberto SernaBelum ada peringkat
- Sigma BetaDokumen5 halamanSigma BetaMuhammad Budie DharmaBelum ada peringkat
- KCNDokumen2 halamanKCNMAI NGUYỄN PHƯƠNGBelum ada peringkat
- BiPAP AVAPS and BiPAP ST Service ManualDokumen126 halamanBiPAP AVAPS and BiPAP ST Service ManualIBRAHIMBelum ada peringkat
- Dwnload Full Accounting For Decision Making and Control 9th Edition Zimmerman Solutions Manual PDFDokumen36 halamanDwnload Full Accounting For Decision Making and Control 9th Edition Zimmerman Solutions Manual PDFdietzbysshevip813100% (14)
- LightDokumen47 halamanLightHomemade BarquillosBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring Planck'c Constant Using LEDDokumen4 halamanMeasuring Planck'c Constant Using LEDmarkmejia_025Belum ada peringkat
- Ex2wmp 2021Dokumen5 halamanEx2wmp 2021Yaroslav DavletshinBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To NIght Photography EPDokumen27 halamanAn Introduction To NIght Photography EPCsilla PintérBelum ada peringkat
- The Microscope PowerpointDokumen26 halamanThe Microscope Powerpointapi-250530867Belum ada peringkat
- NEET TEST Series QN PaperDokumen2 halamanNEET TEST Series QN PaperLeap Up JEE NEETBelum ada peringkat
- AWP Lecture Notes-MIMPDokumen110 halamanAWP Lecture Notes-MIMPdesai vijayendra100% (1)
- Microscope Usage and Handling ProceduresDokumen5 halamanMicroscope Usage and Handling Proceduresgrafei pennaBelum ada peringkat
- Submarine Optical Communication Research ReviewDokumen5 halamanSubmarine Optical Communication Research ReviewBinoy VargheseBelum ada peringkat
- Mumbai University Electronics Exam QuestionsDokumen10 halamanMumbai University Electronics Exam QuestionsHammad MominBelum ada peringkat
- Fiber Optic BlakeDokumen4 halamanFiber Optic BlakenicklingatongBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDari EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDari EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniversePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (69)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceDari EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain SciencePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDari EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1395)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDari EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishDari EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (18)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDari EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (500)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDari EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2193)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDari EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (125)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDari EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (409)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsDari EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (94)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDari EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (48)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsDari EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (57)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDari EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in SciencePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDari EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (8)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Dari EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (155)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDari EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (76)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDari EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeBelum ada peringkat
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityDari EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (380)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseDari EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniversePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (13)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationDari EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (158)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsDari EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)