Urinary Tract Infections in Children
Diunggah oleh
GerardLum0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
267 tayangan1 halamanUrinary Tract Infections in Children
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniUrinary Tract Infections in Children
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
267 tayangan1 halamanUrinary Tract Infections in Children
Diunggah oleh
GerardLumUrinary Tract Infections in Children
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
jslum.
com | Medicine
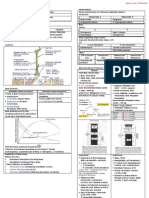
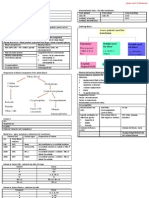
Urinary Tract Infections in Children
Epidemiology Urine samping
Female predominance Midstream
Clean catch
Complications Catheterisation
Permanent scarring of kidney Bag samples (contamination rate ↑ with longer application)
Sepsis
Hypertension Investigations
Renal failure Urine microscopy (gram stain)
Pyuria No Pyuria
Bacteriology Phimosis wash out Still can be UTI
Enterobacteriaceae Vaginal wash out Leukopaenia
E coli Glomerulonephritis
Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Proteus, Providencia, Morgenella, Febrile illnesses
Serratia, Salmonella Dip sticks
Pseudomona s species Leukocyte esterase – 88-95% sensitivity pyuria
Pseudomonas Nitrites – less sensitive, less specific
Gram +ve species Cultures
Staphylococcus Positive (> CFU/mL) Positive (< CFU/mL)
Enterococcus UTI/ (contamination) Contamination
UTI
Virulence Factors Frequent voiding
Enhance colonisation ↓ Urinary pH
Aid in persistence in urinary tract ↑ Fluid intake
Capacity for inflammation Mixed Growth No Growth
Adherence (Hydrophobic, Electrostatic, Receptors ) Contamination No infection
Motility (Flagellae) UTI may present/ not present Infection but organism has not
Bacterial survival enhanced UTI with > 1 organism (rare) grown
(K-antigen, Proteins enhancing Fe uptake, Complement resistance)
Damage to tissues (Haemolysins, Colicine) Therapy Antibiotic Therapy
Normal Hygiene IV or Oral
Host Defence Factors Normal Voiding Habits Duration
Mechanical Treat Constipation 1 dose for Cystitis
Hydrodynamic Treat Worm Infestation Longer for PN, Infants, Pregnant
Anti-adherent Drinking Habits Antibiotic of Choice
Receptor dependant Trimetoprim
Immunologic Cotrimoxazole
Nitrofurantoin (Nalidixic acid)
Pathogenesis 2nd or 3rd generation Cephalosporins
Ascending Descending (Not ampi- or amoxicillin)
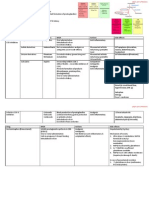
Infants
Perinephric abscess Investigations
Ultrasound
Perineal/ Urethral Factors VUR (Not most reliable method)
Phimosis/ non -circu mcision Presence of 2 kidneys
Short urethra (Female) Exclude obstruction
Bubble bath, Wiping techniques Measure kidneys
Hygiene Bladder residual volume post micturation
1st UTI at 0-2 y/o
Pinworms
Prophylaxis antibiotics Ultrasound
+/- 6 weeks after infection MCU (Boys)
Bladder Factors
Isotope Cystography (Girls)
Infrequent voiding
DMSA
Incomplete voiding
1st UTI at 2-7 y/o
Neurogenic bladder VUR a bit ↓ common Ultrasound
Constipation, Encopresis MCU might be traumatic DMSA
If 1st UTI no scar, unlikely for next UTI If abnormal, MCU/ Isotope
Upper Urinary Tract to scar cystography
Vesico-ureteral Reflux Obstruction 1st UTI > 7 y/o
50% of children with UTI Pelvi-Ureteric Junction Ultrasound
Residual urine post micturition Vesico-Ureteric Junction (Urodynamics on indi cation)
Posterior Urethral Valves If all Investigations –ve
Ectopic ureters +/- Ureterocoeles Stop antibiotic prophylaxis
Examine urine (at every febrile episode, whenever child unwell)
Clinical Presentation Quick response to eventual new UTI
Infants Lower tract symptoms If VUR present
Irritability Urgency Depend on
Poor feeding Frequency • Degree of reflux
Failure to gain weight Enuresis • Presence & extend of renal scarring
Vomiting, Diarrhoea Dysuria • Discuss with surgeon
Jaundice (late onset) Vulvitis • Expected compliance
Fever Bubble bath irritation Conservative treatment
Urethritis Surgery
Voiding dysfunction
Asymptomatic Cystitis Pyelonephritis
↑ grade Fever
Flank pain/ tenderness
↑ WBC, ESR, CRP
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Ford Taurus Service Manual - Disassembly and Assembly - Automatic Transaxle-Transmission - 6F35 - Automatic Transmission - PowertrainDokumen62 halamanFord Taurus Service Manual - Disassembly and Assembly - Automatic Transaxle-Transmission - 6F35 - Automatic Transmission - Powertraininfocarsservice.deBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDokumen4 halamanPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen4 halamanUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDokumen5 halamanPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDokumen5 halamanPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Prostate GlandsDokumen3 halamanProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicBelum ada peringkat
- Pituitary DysfunctionDokumen2 halamanPituitary DysfunctionGerardLum0% (1)
- Pituitary Gland PathologyDokumen4 halamanPituitary Gland PathologyGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology of DiabetesDokumen4 halamanPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Pathology of TestesDokumen4 halamanPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- Soft Tissue TumoursDokumen8 halamanSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Shorthand TheoryDokumen75 halamanShorthand Theorysubhashcb100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Pathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesDokumen5 halamanPathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesGerardLum100% (1)
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDokumen6 halamanSexually Transmitted DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- Theorizing Eco-Dystopia: Science Fiction, The Anthropocene, and The Limits of Catastrophic ImageryDokumen15 halamanTheorizing Eco-Dystopia: Science Fiction, The Anthropocene, and The Limits of Catastrophic ImageryLaura QuintanaBelum ada peringkat
- ThalassaemiaDokumen4 halamanThalassaemiaGerardLum100% (4)
- SAM Project 1bDokumen13 halamanSAM Project 1bNolan Blair0% (2)
- Posterior Pituitary SyndromeDokumen1 halamanPosterior Pituitary SyndromeGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Nerve InjuryDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Nerve InjuryGerardLum100% (1)
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDokumen5 halamanPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Iso 27001 Auditor TrainingDokumen19 halamanIso 27001 Auditor TrainingITOPS TeamBelum ada peringkat
- Obstructive UropathyDokumen3 halamanObstructive UropathyGerardLum100% (1)
- Komatsu HD785-7 Shop Manual PDFDokumen1.491 halamanKomatsu HD785-7 Shop Manual PDFIB EldinBelum ada peringkat
- Ledger - Problems and SolutionsDokumen1 halamanLedger - Problems and SolutionsDjamal SalimBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDokumen3 halamanRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDokumen3 halamanSoft Tissue InfectionsGerardLum100% (1)
- ThrombophiliaDokumen3 halamanThrombophiliaGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathogenesis Bleeding DisordersDokumen4 halamanPathogenesis Bleeding DisordersGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Training (Tarun Kumar) - Final ReprtDokumen46 halamanIndustrial Training (Tarun Kumar) - Final ReprtSaumya GargBelum ada peringkat
- Vesico Ureteral RefluxDokumen1 halamanVesico Ureteral RefluxGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid PhysiologyDokumen2 halamanThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDokumen1 halamanSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsGerardLum100% (2)
- Renal Function in Disease StateDokumen2 halamanRenal Function in Disease Statedamai140390Belum ada peringkat
- Principles of Blood TransfusionDokumen2 halamanPrinciples of Blood TransfusionGerardLum100% (3)
- Overview of AnaemiaDokumen2 halamanOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Nsaids DrugsDokumen2 halamanNsaids DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoBelum ada peringkat
- Nocturnal EnuresisDokumen1 halamanNocturnal EnuresisGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Material For Werable AntennaDokumen4 halamanMaterial For Werable AntennaMujeeb AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- KoL Mekflu - 9Dokumen104 halamanKoL Mekflu - 9Maha D NugrohoBelum ada peringkat
- Parameter Pengelasan SMAW: No Bahan Diameter Ampere Polaritas Penetrasi Rekomendasi Posisi PengguanaanDokumen2 halamanParameter Pengelasan SMAW: No Bahan Diameter Ampere Polaritas Penetrasi Rekomendasi Posisi PengguanaanKhamdi AfandiBelum ada peringkat
- Justification: Justification: Doctrine of Council of TrentDokumen4 halamanJustification: Justification: Doctrine of Council of TrentMihai SarbuBelum ada peringkat
- Key-Words: - Techniques, Reflection, Corporal Punishment, EffectiveDokumen7 halamanKey-Words: - Techniques, Reflection, Corporal Punishment, EffectiveManawBelum ada peringkat
- The Photoconductive CellDokumen4 halamanThe Photoconductive Cellfasdasd123Belum ada peringkat
- Circle, Cube, and CuboidsDokumen27 halamanCircle, Cube, and CuboidsYohanes DhikaBelum ada peringkat
- English NotesDokumen39 halamanEnglish NotesNorAini MohamadBelum ada peringkat
- PHY3 BJune 2004Dokumen1 halamanPHY3 BJune 2004api-3726022Belum ada peringkat
- Tie Technology DK SKDokumen32 halamanTie Technology DK SKVladimir PleșcaBelum ada peringkat
- SYKES Home Equipment Agreement UpdatedDokumen3 halamanSYKES Home Equipment Agreement UpdatedFritz PrejeanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter #11: Volume #1Dokumen35 halamanChapter #11: Volume #1Mohamed MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Sexual ExtacyDokumen18 halamanSexual ExtacyChal JhonnyBelum ada peringkat
- Lab No.7: Measurement of Coupling Coefficient, Directivity and Insertion Loss of A Directional CouplerDokumen3 halamanLab No.7: Measurement of Coupling Coefficient, Directivity and Insertion Loss of A Directional CouplerM. Ahmad RazaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7Dokumen22 halamanChapter 7one loveBelum ada peringkat
- Holiday Tradition Lesson PlanDokumen2 halamanHoliday Tradition Lesson Planapi-458585393Belum ada peringkat
- Embodied experience at the core of Performance StudiesDokumen10 halamanEmbodied experience at the core of Performance StudiesVictor Bobadilla ParraBelum ada peringkat
- AI vs ML: A Brief ExplanationDokumen3 halamanAI vs ML: A Brief Explanationkhaoula BelghitiBelum ada peringkat
- The Remains of The Day-Excerpts-1Dokumen2 halamanThe Remains of The Day-Excerpts-1DajanaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance of Filler Material in GabionsDokumen4 halamanPerformance of Filler Material in GabionsPreetham N KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Bill Porter Updated PDFDokumen3 halamanBill Porter Updated PDFapi-362500677Belum ada peringkat
- BV14 Butterfly ValveDokumen6 halamanBV14 Butterfly ValveFAIYAZ AHMEDBelum ada peringkat