Pythagorean Property Explained
Diunggah oleh
ventyemmachahyantiJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pythagorean Property Explained
Diunggah oleh
ventyemmachahyantiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Woorksheet English For Mathematics
Thursday, 13 Okt 2016
Name : Henie Destia Ningrum
NIM : RSA1C215030
THE PYTHAGOREAN PROPERTY
The ancient Egyptians discovered that in stretching ropes of lengths 3
units, 4 units and 5 units as shown below, the angles formed by the shorter
ropes is a right angle (Figure.1). The Greeks succeeded in finding other sets
of three numbers which gave right triangles and were able to tell without
drawing the triangles which ones should be right triangles, their method
being as follow. If you look at the illustration you will see a triangle with a
dashed interior (Figure.2).
5
3
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Each side of it is used as the side of a square. Count the number of
small triangular regions in the two smaller squares then compare with the
number of triangular regions in the largest square. The Greek philosopher
and mathematician, Pythagoras, noticed the relationship and was credited
with the proof of this property. Each side of right triangle was used as a side
of a square, the sum of the areas of the two smaller squares is the same as
the area of the largest square.
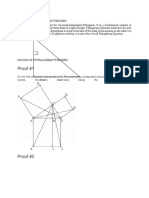
Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem
We would like to show that the Pythagorean Property is true for all right
angle triangles, there are several proofs of this property.
a
a
b
ab
a
c
ab
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Let us discuss one of them. Before giving the proof let us state the
Pythagorean Property in mathematical language. In the triangle (Figure.3), c
represents the measure of the hypotenuse, and a and b represent the
measures of the other two sides. If we construct squares on the three sides
2
2
2
of the triangle, the area measure will be a , b c . Then the Pythagorean
2
working with areas. To prove that
c =a + b
Property could be stated as follows:
2
c =a + b
. This proof will involve
for the triangle above, construct
two squares each side of which has a measure a + b as shown in figure 4 and
figure 5.
Separate the first of the two squares into two squares and two
rectangles as shown in figure 4. Its total area is the sum of the areas of the
two squares and two rectangles.
2
2
A=a +2 ab+b
In the second of two squares construct four right triangles as shown in
figure 5. Are they congruent? Each of the four triangles being congruent to
the original triangle, the hypotenuse has a measure c. It can be shown that
2
PQRS is a square, and its area is c . The total area of the second square is
the sum of the areas of the four triangles and the square PQRS.
1
A=c 2+ 4 ab
2
( )
The two squares being congruent to begin with, their area measures
are the same. Hence we may conclude the following:
a2 +2 ab+b 2=c 2 +4
( 12 ab)
( a2 +b 2 ) +2 ab=c2 +2 ab
By subtracting 2ab from both area measures we obtain
a2 +b 2=c 2
which proves the pythagorean Property for all right triangles.
1. Comprehension check
Which sentences in the text answer these questions.
A. Could the ancient Greeks tell the actual triangles without drawing?
Which ones would be right triangles?
Yes, they could. The actual triangles would be right
triangles by finding other sets of three numbers.
B. Who noticed the relationship between the number of small triangular
regions in the two smaller squares and in the largest square?
The Greek philosopher and mathematician Pythagoras
noticedthe relationship between the number of small
triangular regions in the two smaller squares and in the
largest square.
C. Is the Pythagorean Property true for all right triangles?
Yes, the Pythagorean Property is true for all right
triangles.
D. What must one do to prove that c = a + b for the triangle under
consideration?
To prove that c = a + b for the triangle under
consideration, we can let c represents the measure of the
hypotenuse, and a and b represent the measures of the
other two sides as Figure 3 shows in the passage. We
construct squares on the three sides of the triangle, the
2
2
2
area measure will be a , b c . Then the Pythagorean
2
Property could be stated as follows:
c =a + b
. For last,
we can construct two squares each side of which has a
measure a + b as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5 in the
passage.
E. What is the measure of the hypotenuse in which each of the four
triangles iscongruent to the original triangle?
The measure of the hypotenuse in which each of the four
triangles is congruent to the original triangle is a
measure c.
Choose the main idea of the text.
a. The Pythagorean theorem is true for all right triangles and it
could be stated as follows: c = a + b
2
2.
b. The text shows that the Pythagorean Property is true for all right
triangles.
c. The Greek mathematician, Pythagoras, contributed to maths history his
famoustheorem which was proved to be true for all right triangles.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 1Dokumen19 halaman1darshanBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagoras Theorem Verification Using SquaresDokumen6 halamanPythagoras Theorem Verification Using SquaresSanifer PlayzBelum ada peringkat
- The Pythagorean Theorem ProofsDokumen11 halamanThe Pythagorean Theorem ProofsfireblastbeamBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorass Theorem SADokumen12 halamanPythagorass Theorem SAsiddhi thakkar100% (1)
- MATHS PROJECT Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1 Chakeri Kanpur, InDIADokumen57 halamanMATHS PROJECT Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1 Chakeri Kanpur, InDIASAURABH VERMA83% (6)
- Pythagoras Theorem Project by Group 5Dokumen23 halamanPythagoras Theorem Project by Group 5sakti_badalaBelum ada peringkat
- Phi in The Great PyramidDokumen9 halamanPhi in The Great Pyramidsraghunathan42Belum ada peringkat
- GR09 Q3W08D00 H Mat 00 SLM GRDokumen10 halamanGR09 Q3W08D00 H Mat 00 SLM GRAddy LoveBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometry and Analytical Geometry EssentialsDokumen88 halamanTrigonometry and Analytical Geometry EssentialsSakote Tobiloba IsaacBelum ada peringkat
- MATH'S Project Report On Pythagoras Theorem Submitted To Mr. Munish Sharma Submitted by Class - X-B ROLL. NO.13 Uspc Jain Public SchoolDokumen5 halamanMATH'S Project Report On Pythagoras Theorem Submitted To Mr. Munish Sharma Submitted by Class - X-B ROLL. NO.13 Uspc Jain Public Schoolashutosh singhBelum ada peringkat
- Synergetics in The PlaneDokumen27 halamanSynergetics in The PlaneIan BeardsleyBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagoras TheoremDokumen7 halamanPythagoras Theoremananya9119afmcBelum ada peringkat
- Math Pro Pythagorean TheoremDokumen21 halamanMath Pro Pythagorean TheoremYeshey LhendupBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorean theorem proofsDokumen5 halamanPythagorean theorem proofsFinley alexander FurucBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Pythagorean TheoremDokumen4 halamanWhat Is Pythagorean Theoremapi-140032165Belum ada peringkat
- Pythagoras Theorem Pythagoras Theorem: Mathematics Project Mathematics ProjectDokumen15 halamanPythagoras Theorem Pythagoras Theorem: Mathematics Project Mathematics ProjectJunaid AkhterBelum ada peringkat
- James Garfield's Proof of The Pythagorean TheoremDokumen4 halamanJames Garfield's Proof of The Pythagorean TheoremBlaise09Belum ada peringkat
- TRIGONOMETRYDokumen61 halamanTRIGONOMETRYMapurisa TriciahBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Pythagorean TheoremDokumen4 halamanWhat Is The Pythagorean Theoremapi-150547803Belum ada peringkat
- International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Dokumen6 halamanInternational Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDBelum ada peringkat
- Applications of The Pythagorean TheoremDokumen7 halamanApplications of The Pythagorean Theoremapi-290938633Belum ada peringkat
- PythagorasDokumen16 halamanPythagorasGiridharanBelum ada peringkat
- PYTHAGORAS THEOREM Project (Simple Holiday Package)Dokumen8 halamanPYTHAGORAS THEOREM Project (Simple Holiday Package)helloandhaiBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorean TheoremDokumen1 halamanPythagorean TheoremMehdi KhyriBelum ada peringkat
- The Pythagorean Theorem: A Wonder For All AgesDokumen44 halamanThe Pythagorean Theorem: A Wonder For All Agesمكي مسرحي100% (19)
- Pythagorean Theorem PDFDokumen136 halamanPythagorean Theorem PDFDianaMae23100% (1)
- Spec Maths Foliowrite-Up How Big Is The EarthDokumen9 halamanSpec Maths Foliowrite-Up How Big Is The Earthapi-318983448Belum ada peringkat
- Geometry ProblemsDokumen10 halamanGeometry ProblemsAphrocamsieBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometry in Real LifeDokumen6 halamanTrigonometry in Real LifeJea TaladroBelum ada peringkat
- 02 GeometryDokumen5 halaman02 GeometryhongnhBelum ada peringkat
- 15 Spherical TrigonometryDokumen9 halaman15 Spherical TrigonometrySadiq SarfarazBelum ada peringkat
- Area of The TriangleDokumen6 halamanArea of The Triangleapi-126876773Belum ada peringkat
- Formal Proofs of The Pythagorean TheoremDokumen2 halamanFormal Proofs of The Pythagorean TheoremLauren EricksonBelum ada peringkat
- Similarity and Trigonometry - DocDokumen19 halamanSimilarity and Trigonometry - DocJuan Moya Moreno100% (1)
- Exploration Pythagorean Theorem: Sam Otten MTH 210A W04Dokumen9 halamanExploration Pythagorean Theorem: Sam Otten MTH 210A W04Nikki AmuraoBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorean Theorem PDFDokumen24 halamanPythagorean Theorem PDFC Subrahmanya KarthikBelum ada peringkat
- Portfolio 5Dokumen2 halamanPortfolio 5api-282464166Belum ada peringkat
- Hyperbolic TrianglesDokumen5 halamanHyperbolic Trianglesdewamanchunian_54565Belum ada peringkat
- Trigonometry Project Explains Its History, Functions and ApplicationsDokumen13 halamanTrigonometry Project Explains Its History, Functions and ApplicationsA for Arunabha33% (3)
- NSM 8 CB Ch03Dokumen22 halamanNSM 8 CB Ch03DanBelum ada peringkat
- KV Sangathan Maths HOTS Questions Chapter 1Dokumen20 halamanKV Sangathan Maths HOTS Questions Chapter 1microdotcdmBelum ada peringkat
- Math 103 Lecture Notes: Leah Keshet January 9, 2005Dokumen28 halamanMath 103 Lecture Notes: Leah Keshet January 9, 2005nagaraj108Belum ada peringkat
- S4 Amath 1Dokumen6 halamanS4 Amath 1Teo Liang WeiBelum ada peringkat
- Volumes, Surface Areas and Radian Measure: Review of Areas and Perimeters of Planar FiguresDokumen15 halamanVolumes, Surface Areas and Radian Measure: Review of Areas and Perimeters of Planar Figuresmasyuki1979Belum ada peringkat
- Pythagoras Theorem ProofDokumen5 halamanPythagoras Theorem Proofburgesss87Belum ada peringkat
- Foundations of TrigonometryDokumen8 halamanFoundations of TrigonometryGenevieve MerroBelum ada peringkat
- DGLP 1Dokumen13 halamanDGLP 1Vaishika GopiBelum ada peringkat
- Project 1Dokumen2 halamanProject 1Samir KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Jan Roze B. Pythagorean TheoremDokumen4 halamanJan Roze B. Pythagorean TheoremFinley alexander FurucBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagoras' Theorem GuideDokumen6 halamanPythagoras' Theorem GuideHamza KahemelaBelum ada peringkat
- Math 108Dokumen22 halamanMath 108ShailendraPatelBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter08 - Trigonometry Ratio SOH CAH TOADokumen37 halamanChapter08 - Trigonometry Ratio SOH CAH TOALy ShanBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorean Theorem: Proof and Applications: Kamel Al-Khaled & Ameen AlawnehDokumen8 halamanPythagorean Theorem: Proof and Applications: Kamel Al-Khaled & Ameen Alawnehtsilimides1Belum ada peringkat
- Additional Mathematics Project WorkDokumen35 halamanAdditional Mathematics Project WorkRaakeshTharmanathanBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorean Theorem SolverDokumen6 halamanPythagorean Theorem SolverTunay Na Karl OlimpoBelum ada peringkat
- Pythagorean Theorem ExplainedDokumen8 halamanPythagorean Theorem ExplainedFinley alexander FurucBelum ada peringkat
- Circle’s True Pi Value Equals the Square Root of TenDari EverandCircle’s True Pi Value Equals the Square Root of TenBelum ada peringkat
- The Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsDari EverandThe Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Quantitative Techniques for Management DecisionsDokumen4 halamanQuantitative Techniques for Management DecisionsFiraa'ool Yusuf100% (1)
- Powershape: Training CourseDokumen18 halamanPowershape: Training CourseZulhendriBelum ada peringkat
- Final Advertisement of 551 NON Gazetted Posts of PBS - 220220 - 182252Dokumen6 halamanFinal Advertisement of 551 NON Gazetted Posts of PBS - 220220 - 182252Ghulam HadiBelum ada peringkat
- 1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetDokumen8 halaman1-15-15 Kinematics AP1 - Review SetLudwig Van Beethoven100% (1)
- HIMA - WhitePaper - Hybrid Systems For Smart Pipeline Management - finalEUDokumen6 halamanHIMA - WhitePaper - Hybrid Systems For Smart Pipeline Management - finalEUAndrew XuguomingBelum ada peringkat
- Head Nurses Leadership Skills Mentoring and Motivating Staff Nurses On Rendering High-Quality Nursing CareDokumen23 halamanHead Nurses Leadership Skills Mentoring and Motivating Staff Nurses On Rendering High-Quality Nursing CareDaniel RyanBelum ada peringkat
- Etabs NotesDokumen11 halamanEtabs Noteskarimunnisa sheikBelum ada peringkat
- Optimizing Planetary Gear Design for Load DistributionDokumen17 halamanOptimizing Planetary Gear Design for Load DistributionANURAAG AAYUSHBelum ada peringkat
- A Tutorial On Cross-Layer Optimization in Wireless NetworksDokumen12 halamanA Tutorial On Cross-Layer Optimization in Wireless Networkshendra lamBelum ada peringkat
- Lightning Performance of 500-kV Double-Circuit Line Schemes For The Three-Gorge ProjectDokumen8 halamanLightning Performance of 500-kV Double-Circuit Line Schemes For The Three-Gorge ProjectAlcides NetoBelum ada peringkat
- Divya MishraDokumen1 halamanDivya MishraKashish AwasthiBelum ada peringkat
- Predicting Star Ratings Based On Annotated Reviews of Mobile AppsDokumen8 halamanPredicting Star Ratings Based On Annotated Reviews of Mobile AppsAbdul KhaliqBelum ada peringkat
- Noorul Islam Centre For Higher Education Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil M.E. Biomedical Instrumentation Curriculum & Syllabus Semester IDokumen26 halamanNoorul Islam Centre For Higher Education Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil M.E. Biomedical Instrumentation Curriculum & Syllabus Semester Iisaac RBelum ada peringkat
- MSC Mathematics 2014Dokumen21 halamanMSC Mathematics 2014Muralikrishna SingamaneniBelum ada peringkat
- Java Object-Oriented Programming ExercisesDokumen116 halamanJava Object-Oriented Programming ExercisesMuhammad Al-RasyidBelum ada peringkat
- Urriculum Itae Et TudiorumDokumen21 halamanUrriculum Itae Et TudiorumEnricoBelum ada peringkat
- World-GAN - A Generative Model For MinecraftDokumen8 halamanWorld-GAN - A Generative Model For MinecraftGordonBelum ada peringkat
- 29a ΙΡΙΔΟΛΟΓΙΑ EGDokumen28 halaman29a ΙΡΙΔΟΛΟΓΙΑ EGO TΣΑΡΟΣ ΤΗΣ ΑΝΤΙΒΑΡΥΤΗΤΑΣ ΛΙΑΠΗΣ ΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣBelum ada peringkat
- Decision Modeling Using SpreadsheetDokumen36 halamanDecision Modeling Using SpreadsheetamritaBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan on Subtracting 2-3 Digit NumbersDokumen7 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan on Subtracting 2-3 Digit NumbersNhor Jehan SaydinBelum ada peringkat
- Sachin S. Pawar: Career ObjectivesDokumen3 halamanSachin S. Pawar: Career ObjectivesSachin PawarBelum ada peringkat
- Irace Comex TutorialDokumen5 halamanIrace Comex TutorialOmarSerranoBelum ada peringkat
- EGA Revisited: Key Concepts in Grothendieck's Foundational WorkDokumen50 halamanEGA Revisited: Key Concepts in Grothendieck's Foundational WorkTomás CampoBelum ada peringkat
- Earthworks Computations and MethodsDokumen24 halamanEarthworks Computations and MethodsBryan ResullarBelum ada peringkat
- Docs Slides Lecture1Dokumen31 halamanDocs Slides Lecture1PravinkumarGhodakeBelum ada peringkat
- G (X) F (X, Y) : Marginal Distributions Definition 5Dokumen13 halamanG (X) F (X, Y) : Marginal Distributions Definition 5Kimondo KingBelum ada peringkat
- Uranian PlanetsDokumen12 halamanUranian PlanetsPongwuthBelum ada peringkat
- ME 354A Vibration Problems and SolutionsDokumen4 halamanME 354A Vibration Problems and SolutionsAkhilBelum ada peringkat
- Public Relations Review: Juan Meng, Bruce K. BergerDokumen12 halamanPublic Relations Review: Juan Meng, Bruce K. BergerChera HoratiuBelum ada peringkat