Design and Modification of Bench Vice by Increasing The Degrees of Freedom
Diunggah oleh
GRD JournalsJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Design and Modification of Bench Vice by Increasing The Degrees of Freedom
Diunggah oleh
GRD JournalsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering | Volume 1 | Issue 11 | October 2016
ISSN: 2455-5703
Design and Modification of Bench Vice by
Increasing the Degrees of Freedom
Mr. A. S. Kadam
UG Student
Department of Mechanical Engineering
NBN Sinhgad School of Engg Pune
Mr. R. M. Rupanawar
UG Student
Department of Mechanical Engineering
NBN Sinhgad School of Engg Pune
Mr. T. V. Daundkar
UG Student
Department of Mechanical Engineering
NBN Sinhgad School of Engg Pune
Mr. S. R. Tanpure
UG Student
Department of Mechanical Engineering
NBN Sinhgad School of Engg Pune
Prof. V. V. Saidpatil
Assistant Professor
Department of Mechanical Engineering
NBN Sinhgad School of Engg Pune
Abstract
A Bench vice or fixture is a production tool. The main aim is to locate, support and hold the work securely so we can perform the
required machining operations. Feeler or thickness gauges and set blocks are also used to provide reference of the cutter with the
work piece. A bench vice must be easily fastened with the machine and the table. As a result, the work can be done. It can be used
for the other operations on most of the standard machining tools like drilling machine. Bench Vices are available in different size
and shapes ranging from cheap and simple devices to very expensive and complicated devices. Bench Vices can also help to
simplify the metalworking operations which are performed on the special equipment. Considering the advantages of fixture and
jigs, a fixture was designed to cater to our needs. We are going to design a work holding device which will be able to hold the
work piece in any direction. The one-part bottom assembly is free to rotate and other part of bottom assembly fixed to bench. This
type of assembly will assist to top assembly which consist jaws. These jaws are likewise pipe vice & conventional bench vice.
Lead screw is provided for engagement & disengagement of the jaws.
Keywords- Cutter, Gauges, Metal working operation, Jigs and fixture, Jaws, Lead screw, Industrial applications
I. INTRODUCTION
Increasing the accuracy and productivity are the two basic aims of mass production. As we know the solution to this is by reducing
the manual fatigue and also reducing the set up cost of the machine. In this case the device that fulfils our needs is the use of jigs.
Let us take one example. Let us consider that one gets an order of say 1000 products. There need to be drilled three holes on this
product. In such a case the designer tries to draw out every single hole with the help of square, straightners, scribers and center
hole. In order to align the axis of the drill with the axis of the hole we generally go for trial and error method. Accuracy is the main
problem in such cases. In doing so accuracy increases the work load on the operator. Hence using of jig to position and guide the
tool to its right path is preferred rather than using scribers, square, straightners or center punch etc. Thus, the productivity is
increased which is done by eliminating individual marking, positioning and frequent checking. Interchangeability is the chief
advantage here. All the parts fit in properly except only the similar components are interchangeable. One does not need to
repeatedly unclamp and clamp the object for various purposes like positioning as the locating, guiding and clamping of the tool is
done by the jig itself. Bushing is used which is a tool guiding tool. So, it reduces the presence of skilled laborer. Drill jig helps to
ream, drill and tap at a much faster speed and with great accuracy as compared to holes done conventionally by hand. The
responsibility to maintain the accuracy of the hole is now shifted from the operator and given to the jig. May it be a drill fixture or
a drill jig the necessity of a clamping device is inevitable. In case of a drill jig bushings are used. These drill bushings guide the
drill bit during the drilling operation. Generally, work piece is held by a fixture and the fixture is arranged in such a way that the
loading and unloading of the job is fast. As we all know a fixture is a production tool which is mainly used to hold, locate and
support the work piece firmly to the table. Feeler and Set blocks are sometimes used to provide reference of the cutter to the work
piece. The main concern is the fastening of the fixture. These fixtures also help in simplifying the network operations which are
performed on special equipment.
All rights reserved by www.grdjournals.com
21
Design and Modification of Bench Vice by Increasing the Degrees of Freedom
(GRDJE/ Volume 1 / Issue 11 / 004)
II. DESIGN
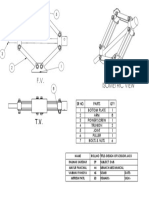
Fig. 1: Block Diagram of Bench Vice
A. Components Used
1) Jaws
Machine vises are mounted on grinding machines, drill presses and milling machines. Abrasive chop saws have a special type of
machine vise built in to the saw. Some people use a machine vise as a bench vise because of the low cost and small size.
2) Lead Screw
The screw is the part that is in control of opening and closing the jaws of the vice. A lead screw, also known as a translation screw
or power screw, is a screw used as a linkage in a machine, to convert the turning motion into linear motion. Because of the large
area of sliding contact between their female and male members, frictional energy losses in the screw thread are more compared to
other linkages. They are not typically used to carry high power, but more for intermittent use in low power actuator and positioned
mechanisms. Common applications are linear actuators, machine slides (such as in machine tools), vises, presses, and jacks.
3) Handle
Machine vice commonly has a small crank handle which allows the user to get maximum clamping force when working without
turning the handle excessively. This is because the crank handle provides extra leverage when rotating, meaning the screw can
provide the greater pressure onto the jaws but without any extra effort from the user.
4) Base
Machine vices are mostly manufactured with a flat bottom base design which fits firmly against the machine's table. This allows
the vice to fit firmly on the table in horizontal alignment with the drill bit.
5) Swivel Arrangement
Spherical or Rolling pair is required to tilt both jaws in desired angle. Fixed jaw can be tilt without any extra effort because of the
swiveling attachment is provided.
6) Locking Pins
Once desired angle is achieved movable jaw is fixed with help of locking Pins.
1)
2)
3)
4)
7) Advantages
It can be used for diff angle
It provides better grip on work piece
It can be reducing manufacturing time
It also used for bending operation
8) Disadvantages
1) May be having less rigidity due to many moving parts.
III. MATHEMATICS
Selecting,
SAE 1020 as material of lead screw
Syt = 246 N/mm2, E= 250 103 N/mm2
All rights reserved by www.grdjournals.com
22
Design and Modification of Bench Vice by Increasing the Degrees of Freedom
(GRDJE/ Volume 1 / Issue 11 / 004)
Assume F.O.S = 2, W= 600N
Design of screw spindle
By Rankin formulae
Syt=
Fcr
A
[1+
( )2] = 246 N/ mm2
n k
Fcr = W F.O.S = 600 2= 600 2 = 1200N = 1.2 103 N
dc
k=
4
1.2103
246=
4
dc2
dc
[1+1 (300/ )2/ 10.03 103 0.25]
4
dc = 7.93mm
Nominal diameter of screw
dc = 0.84 do
7.93
do=
0.84
do = 9.44 = 10mm
Screw terms
P
Mean diameter,dm = do 2
dm = 24 - = 21.5mm
2
Lead = 2P = 10
lead
23
= tan-1[ ] = tan-1[
]
dm
21.5
= 5.070
0.12
-1
] = tan-1[
] = 6.840
= tan [
sin
sin 90
Load on screw thread
Torque,
W dm
T=[
] tan ( + )
2
W 21.5
=[
] tan (5.07+ 6.84)
T = 2.267 W, N-mm (1)
Torque due to applied force by lever
T = 600 200= 120000 N-mm
T= 120
103Nmm
(2)
Put the value of T in equation (1), we get,
120
103 = 2.267W
120103
W=
= 52933.39N
2.267
Power required
To engage the load
W dm
T1 = [
] tan ( + )
2
52.933103 21.5
=[
] tan (5.07+ 6.84)
2
T1 = 120017.1049N-mm
= 120.017N-m
Torque require to disengage
W dcc
52.933103 7.930.12
T2 =
=
= 25185.52N-mm
2
2
T2 = 25.18552N-m
Total Torque
T= T1+ T2
T= 120.017 + 25.18552
T= 145.2026N-m
Power Required
(N= 20 rpm) Assume for human being
2NT
P=
60
220145.2025
P=
60
P = 304.11KW
Stresses in lead screw
All rights reserved by www.grdjournals.com
23
Design and Modification of Bench Vice by Increasing the Degrees of Freedom
(GRDJE/ Volume 1 / Issue 11 / 004)
dc= 7.93mm
do= 10mm
W4dc2
comp=
=
16T
dc3
6004(7.93)2
161645
= 12.14N/mm2
(7.93)3
= 16.800N/mm2
Principal stresses
1
max= ( comp + comp + 4 2 )
2
= (12.14 + 12.14 + 4(16.800)2 )
2
max= 22.96N/mm2
1
max = (( comp)2 + 4 2 )= 16.89N/mm2
2
Number of thread in engagement
4W
Pb =
2
2
Pb=
(do dc )h
459.933103
(do2 dc2 )h
Take Pb= 15N/mm2
Safe bearing pressure
h= 121.05 = 1213 = 363 mm
SR. No
1
2
3
Table 1: Results
Quantity Name
Description or Conversion
Nominal diameter of screw
10 mm
Mean diameter
21.5 mm
Core diameter
7.93 mm
IV. CONCLUSIONS
For the project the required research work has been completed and the validation of project has been proved. Hence it can be said
that the aim of the project Design and modification of bench vice by increasing the degrees of freedom can be achieved
successfully.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
It is indeed a great pleasure and moment of immense satisfaction for we to present a project report on Development and
modification of bench vice by increasing the degree of freedom amongst a wide panorama that provided us inspiring guidance
and encouragement, we take the opportunity to thanks to thanks those who gave us their indebted assistance. We wish to extend
our cordial gratitude with profound thanks to our internal guide Prof. V.V. Saidpatil for his everlasting guidance. It was his
inspiration and encouragement which helped us in completing our project.
REFERENCES
Website References
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
http://explore.ijert.org/
http://www.ijetcse.com/
http://industrialscience.org/
[5]
[6]
Hazra Choudhary,Workshop Technology.
Dr.Chapmans. 5th ed.Workshop Technology.
http://www.ijist.net/
Basic Format for Handbooks
Basic Format for Journals (When Available Online)
Mr. Shrikant M. Chougule (2015, July). Design & Manufacturing of Components of Modified Bench Vise on Rapid Prototype Machine. volume4
(7). Available:www.ijaiem.org
[8] Y. Ras mathew (Design and Fabrication of Work Holding Device for Drilling and Spot Facing of Bucket Wheel Excavator Teeth Y. Ras Mathew and J.
Gowtham
[9] Design and fabrication of work holding device for a drilling machine Pritam Kumar Kundu
[10] Pivoted yoke pipe vise Patent No. US 2616320A Inventor Richard W. Vosper
[11] PNEUMATIC VICE Amit G. Korat, Harshil R. Thakkar, Tahir J. Saiyad, Satish A. Miyani and Vishal M. Purohit
[7]
All rights reserved by www.grdjournals.com
24
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Angle and Tilting Vice - SynopsisDokumen6 halamanAngle and Tilting Vice - SynopsisTanvi Khurana100% (3)
- Cam Vice ReportDokumen52 halamanCam Vice ReportAnonymous rvhOrVmmbBelum ada peringkat
- Knuckle Joints DesignDokumen10 halamanKnuckle Joints DesignKvrd Prasad100% (1)
- Capstone and Turret LatheDokumen1 halamanCapstone and Turret Lathesanjeevbijarnia01Belum ada peringkat
- 02 Knuckle JointDokumen24 halaman02 Knuckle JointTeaching ClubBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Keys and CouplingsDokumen37 halamanDesign of Keys and Couplingskeval patelBelum ada peringkat
- Static and Dynamic BalancingDokumen4 halamanStatic and Dynamic BalancingRAKESH SINGHBelum ada peringkat
- Tilting and Angle ViceDokumen36 halamanTilting and Angle ViceBoopathi KalaiBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Chapter 3 Design of ClampDokumen54 halaman3 Chapter 3 Design of ClampKhaled HamdyBelum ada peringkat
- Ansys Report of Knuckle JointDokumen27 halamanAnsys Report of Knuckle JointNíthìsh GøwdåBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Fabrication of Toggle JackDokumen30 halamanDesign and Fabrication of Toggle JackJitendra Rout0% (1)
- Report Screw Jack (1) TDokumen47 halamanReport Screw Jack (1) TAshish Sharma80% (5)
- JJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 5Dokumen21 halamanJJ309 Fluid Mechanics Unit 5Adib AzharBelum ada peringkat
- ME8651qb Design of Transmission SystemsDokumen18 halamanME8651qb Design of Transmission SystemsMURALI KRISHNAN RBelum ada peringkat
- Sagar Institute of Research & Technalogy-Excellence, BhopalDokumen14 halamanSagar Institute of Research & Technalogy-Excellence, BhopalfadyaBelum ada peringkat
- Design II MDE 221 Mott CH 8 and CH 9 Spur GearsDokumen42 halamanDesign II MDE 221 Mott CH 8 and CH 9 Spur GearsThieroy PelendaBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Fabrication of Can CrusherDokumen5 halamanDesign and Fabrication of Can CrusherBrightchip TechnologiesBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Puller PDFDokumen8 halamanDesign of Puller PDFSadakat Mahaldar100% (1)
- Isometric View F.V.: SR No. SR NoDokumen1 halamanIsometric View F.V.: SR No. SR NoMayur Panchal100% (1)
- 15ME3112 Design of Machine ElementsDokumen29 halaman15ME3112 Design of Machine Elementslikhith saiBelum ada peringkat
- Adaptive Design of Machine Tool GearboxesDokumen9 halamanAdaptive Design of Machine Tool Gearboxesأحمد دعبسBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Angles in Drill BitsDokumen2 halamanTypes of Angles in Drill BitsAbdul AhadBelum ada peringkat
- LAB REPORT of Gear Hobbing MachineDokumen6 halamanLAB REPORT of Gear Hobbing MachineAhtisham AmjadBelum ada peringkat
- 5.2 Flanged Bolt CouplingDokumen11 halaman5.2 Flanged Bolt CouplingShayneBumatay0% (1)
- ACD Lab Manual Spur Gear DesignDokumen4 halamanACD Lab Manual Spur Gear Designbalaguru780% (1)
- Bench ViceDokumen10 halamanBench ViceAthul John100% (3)
- Description of A Standard Bumper JackDokumen2 halamanDescription of A Standard Bumper JackDouglas EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Gears: Looking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!Dokumen8 halamanGears: Looking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!Akash SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Alignment Test DrillingDokumen4 halamanAlignment Test DrillingVivek Fegade33% (3)
- Module 5-Shaper (Handouts)Dokumen9 halamanModule 5-Shaper (Handouts)Fayyaz NadeemBelum ada peringkat
- ME308 Second Project PDFDokumen13 halamanME308 Second Project PDFOzan OzgenBelum ada peringkat
- Auto CadDokumen21 halamanAuto CadMohammed AminBelum ada peringkat
- Haacon 4202+4585 Gebruiksaanwijzing enDokumen6 halamanHaacon 4202+4585 Gebruiksaanwijzing enBasvanLeeuwen100% (2)
- Evolution of Radial Drilling MachineDokumen52 halamanEvolution of Radial Drilling MachineHari Krishna75% (4)
- Planer Quick Return MechanismDokumen21 halamanPlaner Quick Return MechanismchristadcrBelum ada peringkat
- Screw JackDokumen10 halamanScrew JackNarasimhaPrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Experment On Watt and Porter GovernorDokumen7 halamanExperment On Watt and Porter GovernorAgare TubeBelum ada peringkat
- Power ScrewsDokumen53 halamanPower ScrewsEko bellick0% (1)
- Catalog: Servo TechnologyDokumen180 halamanCatalog: Servo Technologyhagh_mostafa2787Belum ada peringkat
- Closed Coiled Helical Springs Subjected To Axial LoadsDokumen6 halamanClosed Coiled Helical Springs Subjected To Axial LoadsSnehasish Ishar100% (1)
- Experiment No: 04 Experiment Name: Study and Observation of Compression Test of A HelicalDokumen5 halamanExperiment No: 04 Experiment Name: Study and Observation of Compression Test of A Helicalmd.Aktaruzzaman aktarBelum ada peringkat
- Design of RivetsDokumen20 halamanDesign of RivetsRavishanker BaligaBelum ada peringkat
- Cam and Follower: Omar Ahmad Ali Ayman Mohammad Alkhwiter Eid Sunhat AlharbiDokumen17 halamanCam and Follower: Omar Ahmad Ali Ayman Mohammad Alkhwiter Eid Sunhat AlharbiOmar AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDokumen6 halaman4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- Design of Machine Members II R5320305 Set 3Dokumen2 halamanDesign of Machine Members II R5320305 Set 3Ravi Kumar KamarthiBelum ada peringkat
- Automats and Tool LayoutsDokumen20 halamanAutomats and Tool LayoutsAyesha IshuBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Analysis of PROTECTED FLANGE COUPLING Solidworks 2016 and ANSYS WorkbenchDokumen27 halamanDesign and Analysis of PROTECTED FLANGE COUPLING Solidworks 2016 and ANSYS Workbenchamu100% (1)
- Experiment No - 1: AIM: Study of Various Types of Gear Boxes Such As Industrial Gear Box, SynchromeshDokumen3 halamanExperiment No - 1: AIM: Study of Various Types of Gear Boxes Such As Industrial Gear Box, SynchromeshParas KumbalwarBelum ada peringkat
- Lab ManualDokumen34 halamanLab ManualSamuelPannierselvamShirleyBelum ada peringkat
- Stress Analysis of Tractor Trolley Chassis With Effect of Various Thickness and Design Optimization For Weight Reduction Ijariie1894Dokumen7 halamanStress Analysis of Tractor Trolley Chassis With Effect of Various Thickness and Design Optimization For Weight Reduction Ijariie1894anil sajjanarBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 - Mechanical Advantage, Transmission AngleDokumen3 halamanLecture 4 - Mechanical Advantage, Transmission AngleMohankumarBelum ada peringkat
- Lathe MachineDokumen22 halamanLathe MachineRaghavMaheshwariBelum ada peringkat
- GRDJEV01I110053Dokumen4 halamanGRDJEV01I110053ajiejohn56Belum ada peringkat
- Motorized Benchh ViseDokumen46 halamanMotorized Benchh ViseAlmubeen83% (18)
- 360 Degree Flexible Drilling Machine ReportDokumen26 halaman360 Degree Flexible Drilling Machine ReportSapna KumariBelum ada peringkat
- 3455 PDF PDFDokumen6 halaman3455 PDF PDFrezBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Fabrication of Work Holding Device For A Drilling MachineDokumen62 halamanDesign and Fabrication of Work Holding Device For A Drilling MachineSreejith S NairBelum ada peringkat
- Downloads Papers N58db490466ce0Dokumen7 halamanDownloads Papers N58db490466ce0Sharad FugatBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Manufacturing of Lathe Tool Post Grinding AttachmentDokumen3 halamanDesign and Manufacturing of Lathe Tool Post Grinding AttachmentAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rBelum ada peringkat
- Samuthra Projects PDFDokumen9 halamanSamuthra Projects PDFsageetha756Belum ada peringkat
- Design and Analysis of Underground Circular & Rectangular Water Tank and Intze Water TankDokumen5 halamanDesign and Analysis of Underground Circular & Rectangular Water Tank and Intze Water TankGRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Image Based Virtual Try On NetworkDokumen4 halamanImage Based Virtual Try On NetworkGRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- GRDJEV06I060005Dokumen7 halamanGRDJEV06I060005GRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney Disease Stage Prediction in HIV Infected Patient Using Deep LearningDokumen8 halamanChronic Kidney Disease Stage Prediction in HIV Infected Patient Using Deep LearningGRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Optimization of Xanthan Gum Fermentation Utilizing Food WasteDokumen11 halamanOptimization of Xanthan Gum Fermentation Utilizing Food WasteGRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluate The Performance of MongoDB NoSQL Database Using PythonDokumen5 halamanEvaluate The Performance of MongoDB NoSQL Database Using PythonGRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Automatic Face Recognition Attendance System Using Python and OpenCvDokumen7 halamanAutomatic Face Recognition Attendance System Using Python and OpenCvGRD Journals100% (1)
- Simulation and Prediction of LULC Change Detection Using Markov Chain and Geo-Spatial Analysis, A Case Study in Ningxia North ChinaDokumen13 halamanSimulation and Prediction of LULC Change Detection Using Markov Chain and Geo-Spatial Analysis, A Case Study in Ningxia North ChinaGRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Grdjev06i010003 PDFDokumen4 halamanGrdjev06i010003 PDFGRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Simulation of LNA Using Advanced Design Systems (ADS)Dokumen6 halamanDesign and Simulation of LNA Using Advanced Design Systems (ADS)GRD JournalsBelum ada peringkat
- CV Michael Naughton 2019Dokumen2 halamanCV Michael Naughton 2019api-380850234Belum ada peringkat
- Sucesos de Las Islas Filipinas PPT Content - Carlos 1Dokumen2 halamanSucesos de Las Islas Filipinas PPT Content - Carlos 1A Mi YaBelum ada peringkat
- Sumit Kataruka Class: Bcom 3 Yr Room No. 24 Roll No. 611 Guide: Prof. Vijay Anand SahDokumen20 halamanSumit Kataruka Class: Bcom 3 Yr Room No. 24 Roll No. 611 Guide: Prof. Vijay Anand SahCricket KheloBelum ada peringkat
- Evidentiary Value of NarcoDokumen2 halamanEvidentiary Value of NarcoAdv. Govind S. TehareBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection in Children: CC MagbanuaDokumen52 halamanUrinary Tract Infection in Children: CC MagbanuaVanessa YunqueBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDokumen2 halamanDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesShailac RodelasBelum ada peringkat
- Erika Nuti Chrzsoloras Pewri Tou Basileos LogouDokumen31 halamanErika Nuti Chrzsoloras Pewri Tou Basileos Logouvizavi21Belum ada peringkat
- Ma HakalaDokumen3 halamanMa HakalaDiana Marcela López CubillosBelum ada peringkat
- 67-Article Text-118-1-10-20181206Dokumen12 halaman67-Article Text-118-1-10-20181206MadelBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Thesis Plural FormDokumen8 halamanWhat Is Thesis Plural Formtracyjimenezstamford100% (2)
- Administrative LawDokumen7 halamanAdministrative LawNyameka PekoBelum ada peringkat
- Designing A Peace Building InfrastructureDokumen253 halamanDesigning A Peace Building InfrastructureAditya SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Cognitive ApprenticeshipDokumen5 halamanCognitive ApprenticeshipRandall RobertsBelum ada peringkat
- (U) Daily Activity Report: Marshall DistrictDokumen6 halaman(U) Daily Activity Report: Marshall DistrictFauquier NowBelum ada peringkat
- Sop 2Dokumen43 halamanSop 2naveengargnsBelum ada peringkat
- The Personal Law of The Mahommedans, According To All The Schools (1880) Ali, Syed Ameer, 1849-1928Dokumen454 halamanThe Personal Law of The Mahommedans, According To All The Schools (1880) Ali, Syed Ameer, 1849-1928David BaileyBelum ada peringkat
- Oda A La InmortalidadDokumen7 halamanOda A La InmortalidadEmy OoTeam ClésBelum ada peringkat
- HIS Unit COMBINES Two Birthdays:: George Washington's BirthdayDokumen9 halamanHIS Unit COMBINES Two Birthdays:: George Washington's BirthdayOscar Panez LizargaBelum ada peringkat
- Sysmex HemostasisDokumen11 halamanSysmex HemostasisElyza L. de GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- The Cognitive Enterprise For HCM in Retail Powered by Ibm and Oracle - 46027146USENDokumen29 halamanThe Cognitive Enterprise For HCM in Retail Powered by Ibm and Oracle - 46027146USENByte MeBelum ada peringkat
- Survey Results Central Zone First LinkDokumen807 halamanSurvey Results Central Zone First LinkCrystal Nicca ArellanoBelum ada peringkat
- Rubrics For Field Trip 1 Reflective DiaryDokumen2 halamanRubrics For Field Trip 1 Reflective DiarycrystalBelum ada peringkat
- Risteski Space and Boundaries Between The WorldsDokumen9 halamanRisteski Space and Boundaries Between The WorldsakunjinBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Mark QuestionsDokumen8 halaman1 Mark QuestionsPhani Chintu100% (2)
- Roofing Shingles in KeralaDokumen13 halamanRoofing Shingles in KeralaCertainteed Roofing tilesBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 - FluidDokumen26 halamanChapter 8 - FluidMuhammad Aminnur Hasmin B. HasminBelum ada peringkat
- Birds (Aves) Are A Group Of: WingsDokumen1 halamanBirds (Aves) Are A Group Of: WingsGabriel Angelo AbrauBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Response of Elevated Liquid Storage Steel Tanks Isolated by VCFPS at Top of Tower Under Near-Fault Ground MotionsDokumen6 halamanSeismic Response of Elevated Liquid Storage Steel Tanks Isolated by VCFPS at Top of Tower Under Near-Fault Ground MotionsciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Rosenberg Et Al - Through Interpreters' Eyes, Comparing Roles of Professional and Family InterpretersDokumen7 halamanRosenberg Et Al - Through Interpreters' Eyes, Comparing Roles of Professional and Family InterpretersMaria AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Indus Valley Sites in IndiaDokumen52 halamanIndus Valley Sites in IndiaDurai IlasunBelum ada peringkat