Thyroid Physiology and Development: - The Major Fraction of Circulating T
Diunggah oleh
Ayu InsafiDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Thyroid Physiology and Development: - The Major Fraction of Circulating T
Diunggah oleh
Ayu InsafiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
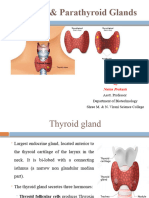
THYROID PHYSIOLOGY
AND DEVELOPMENT
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), a tripeptide synthesized
in the hypothalamus, stimulates the release of pituitary
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Pituitary TSH is a glycoprotein
that stimulates the synthesis and release of thyroid
hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyroid function develops
in three stages. At the end of the first trimester, the gland
descends from the floor of the primitive oral cavity to its
definitive position in the anterior lower neck. The hypothalamicpituitary-thyroid axis becomes functional in the second
trimester. Peripheral metabolism of thyroid hormones matures
in the third trimester.
Thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and TSH do not
cross the placenta in significant amounts. Concentrations in
fetal serum reflect primarily fetal secretion and metabolism.
Maternal thyroid antibodies, iodides (including radioactive
iodides), and medications given to mothers to treat hyperthyroidism
(methimazole and propylthiouracil) cross the
placenta and affect fetal thyroid function. An infant born prematurely
or with intrauterine growth restriction may have an
interruption of the normal maturational process and appear to
have hypothyroidism by standard tests.
The thyroid gland concentrates iodine and binds it to
tyrosine molecules to produce either monoiodotyrosine or
diiodotyrosine, with subsequent coupling of two tyrosines, T4
or T3. The major fraction of circulating T3 (approximately two
thirds) is derived from peripheral deiodination of T4 to T3, but
some is produced by the thyroid gland itself. The conversion of
T4 to T3 requires the removal of one iodine from the outer ring
Newborn screening is crucial to make an early
diagnosis and initiate thyroid replacement therapy by younger
than 1 month of age. Findings at various stages after birth
include hypothermia, acrocyanosis, respiratory distress, large
fontanels, abdominal distention, lethargy and poor feeding,
prolonged jaundice, edema, umbilical hernia, mottled skin,
constipation, large tongue, dry skin, and hoarse cry. Thyroid
hormones are crucial for maturation and differentiation of tissues,
such as bone and brain (most thyroid-dependent brain
maturation occurs 2 to 3 years after birth)
When treatment (with levothyroxine) is initiated within 1
month or less after birth, the prognosis for normal intellectual
development is excellent; screening programs usually
offer therapy within 1 to 2 weeks of birth.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Pathophysiology of Nontoxic Nodular GoiterDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Nontoxic Nodular GoiterJan Jewey80% (10)
- Case Study About HyperthyroidismDokumen11 halamanCase Study About HyperthyroidismRheciel Abarquez Briones RN100% (4)
- The Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Dokumen12 halamanThe Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Leslie PaguioBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid HormonesDokumen6 halamanThyroid Hormonesحوراء عارف الموسويBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital HipotiDokumen18 halamanCongenital HipotiAlly DomenicBelum ada peringkat
- 9 HipertiroidDokumen13 halaman9 HipertiroidBembie Purwono100% (1)
- 1 ADokumen15 halaman1 AzuliaahmadBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid HormonesDokumen7 halamanThyroid HormonesAbdullah EssaBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid HormonDokumen13 halamanThyroid HormonWira SentanuBelum ada peringkat
- ThyroidDokumen84 halamanThyroidMeLissa Pearl GuillermoBelum ada peringkat
- CR-6 Chapter 47 PDFDokumen58 halamanCR-6 Chapter 47 PDFbinbinadiBelum ada peringkat
- HypothyroidismDokumen7 halamanHypothyroidismGkdhdhdgdgidBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDokumen3 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDuchess Ciedelle Abano ManatadBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study Congenital HyperthyroidismDokumen10 halamanCase Study Congenital HyperthyroidismCamille CaraanBelum ada peringkat
- 3.thyroid Hormones and DisordersDokumen46 halaman3.thyroid Hormones and DisorderssinayupeBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Disease: Pathophysiology and Diagnosis: Laurence M. Demers, PHD, Dabcc, FacbDokumen10 halamanThyroid Disease: Pathophysiology and Diagnosis: Laurence M. Demers, PHD, Dabcc, FacbDewi PrasetiaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of The Endocrine SystemDokumen74 halamanPharmacology of The Endocrine SystemarpanabiswassshetyeBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of The Endocrine System PDFDokumen74 halamanPharmacology of The Endocrine System PDFGlenn Perez71% (7)
- Pathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic DysfunctionsDokumen12 halamanPathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic Dysfunctionskate_borovicBelum ada peringkat
- Wa0000.Dokumen10 halamanWa0000.parabharshita2709Belum ada peringkat
- HyperthyroidismDokumen24 halamanHyperthyroidismelaine grace arataBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Vitamin C NewDokumen59 halamanAnalysis of Vitamin C Newrose mariaBelum ada peringkat
- Session-9 Thyroid-2024Dokumen29 halamanSession-9 Thyroid-2024LT DRAGONXBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid DiseasesDokumen47 halamanThyroid Diseasesbiniam MesfinBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)Dokumen96 halaman1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)hamidBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology: Pharmacology of Endocrine System: Thyroid Hormone& Anti-Thyroid DrugsDokumen8 halamanPharmacology: Pharmacology of Endocrine System: Thyroid Hormone& Anti-Thyroid DrugsRaj Nemala Raj NemalaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen4 halamanAnatomy and PhysiologyCL100% (3)
- Antithyroid Drugs by Sejal Khuman Advanced phARMACOLGY 2Dokumen29 halamanAntithyroid Drugs by Sejal Khuman Advanced phARMACOLGY 2Sejal khumanBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology of ThyroidDokumen9 halamanPhysiology of ThyroidAbby EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Tyroid (PA)Dokumen75 halamanBahan Tyroid (PA)Raja FadhilBelum ada peringkat
- Dawood ThesisDokumen50 halamanDawood ThesisDawood khanBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid and ParathyroidDokumen29 halamanThyroid and Parathyroidpranutan739Belum ada peringkat
- Week 3 Pharmaco Part 2Dokumen34 halamanWeek 3 Pharmaco Part 2Tiko JomidavaBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders of The Thyroid GandDokumen167 halamanDisorders of The Thyroid GandWendy Figueroa MijaresBelum ada peringkat
- Name# Khursheed Ali Reg No# 17-ARID-6126Dokumen15 halamanName# Khursheed Ali Reg No# 17-ARID-6126shahzeb bilalBelum ada peringkat
- Persu Project FinalDokumen15 halamanPersu Project FinalAshwinBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid and Thyroid DiseasesDokumen22 halamanThyroid and Thyroid DiseasesAnushka Sharma82% (17)
- Thyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono DjuwantonoDokumen49 halamanThyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono Djuwantonoyuyu tuptupBelum ada peringkat
- Metabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)Dokumen8 halamanMetabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)wasimsafdarBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportDokumen5 halamanThyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportAnonymous UTUWFODCEYBelum ada peringkat
- 6e - Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy A Literature Review (Perbaiki Dafpus)Dokumen5 halaman6e - Thyroid Dysfunction in Pregnancy A Literature Review (Perbaiki Dafpus)KESEBELASAN RESOG 2023Belum ada peringkat
- Dr. Nesrine Salah El Dine: Thyroid Gland From Pharmacology To Clinical PracticeDokumen24 halamanDr. Nesrine Salah El Dine: Thyroid Gland From Pharmacology To Clinical Practiceamaal ramadanBelum ada peringkat
- Hypothyroid PIR 2009Dokumen10 halamanHypothyroid PIR 2009Imanuel Far-FarBelum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine System - Thyroid Gland: Department of Physiology Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineDokumen51 halamanThe Endocrine System - Thyroid Gland: Department of Physiology Diponegoro University Faculty of MedicineYustina Wahyu NBelum ada peringkat
- HypothyroidismDokumen146 halamanHypothyroidismAisha Wadiwala100% (1)
- Jurnal 2 (2019)Dokumen11 halamanJurnal 2 (2019)Inryuu ZenBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Thyroid MedicationsDokumen3 halamanTypes of Thyroid MedicationsfennarioBelum ada peringkat
- Review Article: Thyroid Disorders and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen6 halamanReview Article: Thyroid Disorders and Chronic Kidney DiseaseMariano CadeBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Disorders: Dr. Lubna DwerijDokumen52 halamanThyroid Disorders: Dr. Lubna DwerijNoor MajaliBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid DisordersNewDokumen47 halamanThyroid DisordersNewTri Octavia SitorusBelum ada peringkat
- Fuction Hormons ThyrodsDokumen26 halamanFuction Hormons Thyrodsgiselle155204Belum ada peringkat
- Thyroid & Parathyroid HormonesDokumen53 halamanThyroid & Parathyroid Hormonesrehmanmughal87654Belum ada peringkat
- Congenital HypothyroidismDokumen37 halamanCongenital HypothyroidismAwaluddin SalamBelum ada peringkat
- BB Module IV Thyroid and Anti-Thyroid Drugs 26.08.2021Dokumen17 halamanBB Module IV Thyroid and Anti-Thyroid Drugs 26.08.2021Gunjan KalyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Seminars in Cell and Developmental BiologyDokumen10 halamanSeminars in Cell and Developmental BiologyKarina PalaciosBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Gland and Disordwr KuliahDokumen67 halamanThyroid Gland and Disordwr KuliahRoby KieranBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Gland: Hayder Hussien AlawiDokumen17 halamanThyroid Gland: Hayder Hussien AlawiHayder HussienBelum ada peringkat
- Pregnancy and The ThyroidDokumen16 halamanPregnancy and The ThyroidDwinta AnggrainiBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric in ReviewDokumen10 halamanPediatric in ReviewkafosidBelum ada peringkat
- 2 TSHDokumen7 halaman2 TSHNashat SaadiBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedDari EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- Cerebral Palsy: Ayu Insafi Mulyantari 12100118016 Novi Fauziah 12100118052 Preseptor: H. Satryo Waspodo, DR., SP - KFRDokumen12 halamanCerebral Palsy: Ayu Insafi Mulyantari 12100118016 Novi Fauziah 12100118052 Preseptor: H. Satryo Waspodo, DR., SP - KFRAyu InsafiBelum ada peringkat
- Blepharitis: Ayu InsafiDokumen17 halamanBlepharitis: Ayu InsafiAyu InsafiBelum ada peringkat
- Abstract Mental Health Status Among Preschooler Children With Gadget Use HabitualDokumen1 halamanAbstract Mental Health Status Among Preschooler Children With Gadget Use HabitualAyu InsafiBelum ada peringkat
- LI Case 3 DMS AngiogenesisDokumen2 halamanLI Case 3 DMS AngiogenesisAyu InsafiBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics of Human Neural Tube DefectsDokumen7 halamanGenetics of Human Neural Tube DefectsAyu InsafiBelum ada peringkat
- Ten Step To Successful Breeastfeeding Is An Goverment Attempt To Increase The ExclusiveDokumen1 halamanTen Step To Successful Breeastfeeding Is An Goverment Attempt To Increase The ExclusiveAyu InsafiBelum ada peringkat
- How To Wash Your HandsDokumen13 halamanHow To Wash Your HandsAyu InsafiBelum ada peringkat
- COBAS 6000: E601 Reagent Inventory MONTH/YEAR: - AUGUST 2020Dokumen3 halamanCOBAS 6000: E601 Reagent Inventory MONTH/YEAR: - AUGUST 2020Charmaine CorpuzBelum ada peringkat
- Ms Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Dokumen5 halamanMs Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Aries SungaBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid ProblemDokumen2 halamanThyroid ProblemHebara AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Control of Hormone SecretionDokumen77 halamanControl of Hormone Secretionjohanna deguzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Nejmoa 2111953Dokumen10 halamanNejmoa 2111953Andreea VlădanBelum ada peringkat
- Yo2pesbjsuqblw4hme2y5jvhDokumen2 halamanYo2pesbjsuqblw4hme2y5jvhArghya Roy ChaudhuriBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Seven: The Endocrine SystemDokumen8 halamanUnit Seven: The Endocrine SystemTofik MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System QuizDokumen4 halamanEndocrine System QuizIrams KitchenBelum ada peringkat
- Elecsys FT4 II: 06437281 190 Cobas e 411 Cobas e 601 Cobas e 602 English System InformationDokumen4 halamanElecsys FT4 II: 06437281 190 Cobas e 411 Cobas e 601 Cobas e 602 English System InformationAli KING FREDDYBelum ada peringkat
- Reference Brochure Thyroid 2011Dokumen27 halamanReference Brochure Thyroid 2011ViktarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Co-Ordination and Integration: Diagram Based QuestionsDokumen5 halamanChemical Co-Ordination and Integration: Diagram Based QuestionsJai Mata DiBelum ada peringkat
- Hypothalamus and Its Hormones, Hormones of The Pituitary GlandDokumen28 halamanHypothalamus and Its Hormones, Hormones of The Pituitary GlandAnirudh AcharyaBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Biochemistry Units Result Test Description: Biological Reference RangesDokumen1 halamanClinical Biochemistry Units Result Test Description: Biological Reference RangesVenkat Reddy AvulaBelum ada peringkat
- Review - Animal Endocrine SystemDokumen3 halamanReview - Animal Endocrine SystemkjhBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System - QuizizzDokumen8 halamanEndocrine System - QuizizzushduBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid GlandDokumen28 halamanThyroid Glandahmed alkramyBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Endocrine SystemDokumen4 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan in Endocrine Systemjonelllantero032Belum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine System - Integral PartsDokumen3 halamanThe Endocrine System - Integral PartsDavid TanBelum ada peringkat
- 05 Chapter Endrocrine SystemDokumen40 halaman05 Chapter Endrocrine SystemMSKCBelum ada peringkat
- 26 PDFDokumen13 halaman26 PDFMonica TrifitrianaBelum ada peringkat
- ID Hubungan Jenis Alat Kontrasepsi Hormonal Dengan Tingkat Kelainan Tiroid Pada PasDokumen9 halamanID Hubungan Jenis Alat Kontrasepsi Hormonal Dengan Tingkat Kelainan Tiroid Pada PasDilla FebriyantiBelum ada peringkat
- The Prevalence of Anti-Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Children and Adolescents in An Iodine Replete AreaDokumen7 halamanThe Prevalence of Anti-Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Children and Adolescents in An Iodine Replete AreaAkshay BankayBelum ada peringkat
- Maternal Physiology 25th OB WilliamsDokumen62 halamanMaternal Physiology 25th OB WilliamsDee SarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Malignant Struma OvariiDokumen4 halamanMalignant Struma Ovariixwahyu 108Belum ada peringkat
- Feline Occult Hyperthyroidism: Consultant On CallDokumen3 halamanFeline Occult Hyperthyroidism: Consultant On CallNguyễn Tấn TàiBelum ada peringkat
- 9400215141: Patient ID 94009314 Sid No Tirur Branch Ms. THASNIYA 273864Dokumen1 halaman9400215141: Patient ID 94009314 Sid No Tirur Branch Ms. THASNIYA 273864Abdul LatheefBelum ada peringkat
- Cushing - AddisonDokumen27 halamanCushing - AddisonMelissa-Andreea Ardeleanu Carvajal OsorioBelum ada peringkat
- Phlebo India 659Dokumen2 halamanPhlebo India 659Dharma GagganapallyBelum ada peringkat
- flgx213 (2) Pkjun2015Dokumen6 halamanflgx213 (2) Pkjun2015Jason Van Den HeeverBelum ada peringkat