Clinical Enquiry Comment/Case Management
Diunggah oleh
Mian EhsanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Clinical Enquiry Comment/Case Management
Diunggah oleh
Mian EhsanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1
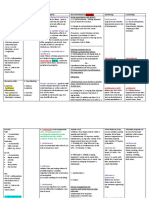
Clinical Enquiry
Simvastatin +
Amiodarone/
Amlodipine/Verapa
mil/ Diltiazem
(simvastatin
should be max
20mg)
Told that
hypercholesterola
emia has been
stabilised for past
3 months. (not
relevant?)
Comment/Case
-patient has been just diagnosed with
rhabdomyolysis due to enhanced effect
of simvastatin. CK levels raised. Urine is
darkly coloured.
Management
Withdraw Simvastatin and reintroduce at capped dose of max
20mg, once myopathy subsides.
OR
Q. Reason for dark urine?
Dark urine and muscle weakness and
muscle pain are symptoms of
rhabdomyolysis. When muscle is
damaged, a protein called myoglobin is
released into the
bloodstream. Myoglobin effects kidney.
You can suggest changing
simvastatin to pravastatin
because its not significantly
metabolised by CYP 450 so it will
not be affected by the diltiazem
and hence reduce the risk of
myopathy. (lectures: Where there is a
potential for drug interactions, pravastatin can be
recommended over simvastatin, as it is not significantly
metabolised by the CYP450 enzymes in the liver).
Verapamil and diltizem act as enzyme
inhibitor!
Simvastatin +
fibrate = max
simvastatin 10mg
Pravastatin and fluvastatin have
lower number of reported cases
of myopathy and
rhabdomyolysis.
OR
change simvastatin to
atorvastatin
also
If transaminases (ALT, AST) are
raised to three times the upper
limit of normal consider
stopping statin.
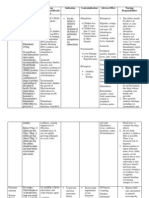
2
Lithium and
NSAIDs =
TOXICITY
Patient is on regular Lithium tablets he
started suffering nervousness, tremor,
vomiting.
He also says he was prescribed two
antibiotics (Penicillin, Flucloxacillin) and
Ibuprofen 400mg TDS two days ago in
walk in clinic.
NSAIDs can deteriorate renal function;
and lithium is renally excreted so less is
eliminated from body therefore toxicity
occurs as its a narrow therapeutic drug.
Lithium levels should be 0.4-1mmol/L.
Early signs of toxicity (Li+ ~
1.5mmol/L): tremor, agitation, twitching
Intermediate: lethagy
Late (Li+ ~ >2mmol/L) spasms, coma,
fits, renal failure
Stop ibuprofen and monitor
lithium.
Lithium levels should be taken
12 hours after the last dose and
if the level is toxic then
management is essentially to try
and increase urine flow (without
diuretics as they can also affect
renal function).
Li+ above 1.5mmol/l can be
fatal and toxic-this patient is
exhibiting signs of Li+ toxicity!
ACEI + NSAIDs =
both cause renal
deterioration
Paracetamol, Diclofenac, Aspirin,
Simvastatin, Ramipril and Atenolol.
Change NSAID to weak opioid
e.g. codeine.
Patient has had previous cardiovascular
event and osteoarthritis. Renal function
is dropping. What should you do?
Withhold ACEI until renal
function improves.
-Interaction between diclofenac and
ramipril = increased risk of renal
impairment
Recheck U&Es and reintroduce
at lower dose perhaps and retitrate up or if renal function
adequate can reintroduce same
dose!
-Diclofenac reduces blood flow to
kidneys so replace to weak opioid.
4
Iron-deficiency
anaemia
Low MCV, Low haematocrit, low Hb, Low
RBC.
Must mention
Microcytic
Anaemia
What are the signs and symptoms, how
would you treat it? Signs = pallor
symptoms=fatigue, dyspnoea (SOB),
palpitations, headaches
Causes of the iron-deficiency anaemia
are blood loss, particularly menorrhagia
or GI bleeding e.g. from oesophagitis,
peptic ulcer, carcinoma, colitis,
diverticulitis or haemorrhoids.
The cause will need to be
investigated and treated = STOP
NSAID change painkiller to weak
opioid, or stronger as this
patient is already getting a weak
opioid.
PPI for treatment and prevention
for NSAID associated GI
bleed/ulceration.
If Hb<8g/dl patient should be
considered for blood transfusion.
Patient on diclofenac, paracetamol and
codeine for pain relief = potentially
NSAID-induced GI bleed so remove
Diclofenac.
She would be offered oral iron
eg ferrous sulphate 200mg TDS
(side effects include constipation
and black stools) Hb should
rise 1g/dL/week continue until
Hb is normal and for atleast 3
months to replenish stores
Iron-deficiency
anaemia
Pt on Codeine, warfarin, digoxin,
paracetamol.
Withhold warfarin, as patient
may be suffering from
haemorrhage. (Check INR) If
bleed confirmed and Vit K for
reversal! (BNF)
Treatment of anaemia ferrous
sulphate 200mg TDS and 3
months after!
Vit b12 deficiency
(macrocytic
anaemia)
High MCV, but Low Hb/Hct/RBCs
Further tests = low B12
Treated by replenishing stores
with hydroxocobalamin (B12)
1mg IM alternate days for 2
weeks. Maintenance 1mg IM
A raised MCV indicates vitamin B12 or
folate deficiency, these should therefore
be tested.
Low B12 then further Schillings test to
determine whether there is
malabsorption or whether there is a lack
of intrinsic factor.
A reduced vitamin B12 and Hb and
raised MCV suggests pernicious
anaemia. This disease affects all the
cells of the body and is due to
malabsorption of B12 resulting from
atrophic gastritis and lack of intrinsic
factor secretion.
every 2 months FOR LIFE
-any counselling related to
condition and treatment?
(oxford handbook)
Symptoms - tiredness and weakness,
dyspnoea, sore red tongue, diarrhoea
and mild jaundice
7
Morphine to
fentanyl patch
Currently = MST 30mg BD and Oramorph
10mg/5mL, 15mL daily. So currently
taking 30mg for breakthrough pain.
What would she take and how much for
breakthrough pain?
Total daily dose of morphine = 90mg
So fentanyl 25 patch (25mcg/hour for
72 hours) can be given.
New dose for breakthrough pain = 90/6
= 15mg (so 7.5mL of Oramorph
10mg/5mL)
1/6 total daily dose every four hours
when required
What should be done when switching
patient from oral morphine to fentanyl
patches?
Make sure patients chronic pain is
generally controlled. Patch is not suitable
for acute pain.
Should we gradually reduce
morphine? No.
Counselling on patient: How the
fentanyl patch can be
administered?
Apply the patch to dry, nonirritated, non-irradiated, and
non-hairy skin on upper arm or
torso. Remover after 72 hours
and apply a new patch to a
different area. (BNF under
Fentanyl, p.272)
How to initiate fentanyl?
Fentanyl patch should be
applied at the same time as last
m/r morphine tablet so allow
time for fentanyl to reach steady
state.
Patch will take 12-24hrs to reach
steady state can advise to
apply first patch at the same
time as taking their last
morphine tablet this gives 12
hrs pain relieve while plasma
levels of fentanyl rise
Switch MAOI to
SSRI
Phenelzine to
fluoxetine
A patient was on MAOI (Phenelzine). He
asks his GP to switch him to Fluoxetine
because he heard theres more evidence
for it.
Phenelzine is an MAOI, fluoxetine
is an SSRI
If an antidepressant is taken for
longer than 8 weeks must
gradually decrease over a period
of 4 weeks.
So gradual withdrawal of MAOI
(slowly reduce the dose) due to
risk of withdrawal syndrome.
Symptoms on withdrawal can be
agitation, irritability, movement
disorders, insomnia, etc.
Then allow a 2 week washout
period (MAOI stopped
completely) before starting SSRI,
to prevent risk of serotonin
syndrome.
Continue to avoid tyramine rich
foods (e.g mature cheese) for 2
weeks after stopping MAOI.
Switch SSRI to
MAOI
Fluoxetine to MAOI
SSRI withdrawal symptoms = GI
disturbances, headaches,
anxiety sweating. Tapper the
dose off over a few weeks;
gradual withdrawal.
Then stop SSRI. Washout period
is generally 1 week before
starting MAOI (or RIMA). BUT
wait 2 weeks after stopping
sertraline.
Fluoxetine have longer half-life
so washout period is 5 weeks.
10
Reduced renal
function and
Metformin
eGFR = 30ml/min. Patient on
simvastatin, aspirin, metformin high
doses for all -- patient had declined renal
function. A list of blood results and had a
high creatinine level and patient on
metformin and the red flag was to
mention lactic acidosis.
blood lactate >5mmol/L
Signs of Lactic Acidosis = N+V,
hyperventilation. Specialist referral
Withhold metformin until renal
function improves. (eGFR must
be above 45ml/min)
Simvastatin max dose =10mg
when eGFR is <30ml/min
If patient is also on ACEI =
carefully
monitored to ensure its ongoing
suitability
11
Choosing
antibiotic for UTI
Pregnant lady with UTI, the infection was
sensitive to trimethoprim or
nitrofurantoin.
eGFR low
Reduced Renal function means
nitrofurantoin is not very
effective therefore trimethoprim
should be selected. BUT
trimethoprim is teratogenic and
should be avoided in pregnancy.
Can suggest trimethoprim if
patient isnt in 1st trimester of
pregnant = 7 days supply
200mg bd (3days may enough
for women!)
In pregnancy. Can choose
amoxicillin or Cefalexin= not
known to be harmful however
broad spectrum so can have a
higher chance of resistance
concerns!
e.g Cefalexin (2 tablets a day for
3 days but can give upto 7 days
tx)
12
NSAID associated
renal impairment
A 50 yr old man with osteoarthritis
suddenly experienced renal failure.
There was a list of drugs. He was
prescribed Diclofenac two weeks ago
and he had been taking the other drugs
for at least 2 months.
Most likely cause would be the NSAID.
-The mechanism of action of NSAIDS and
how they affected renal function?
NSAIDs M/A = inhibit COX-1 and COX-2
which inhibit inflammatory PGs.
stop NSAID immediately and
manage his pain using
alternatives weak opioid such as
codeine, continue Paracetamol.
Monitor renal function closely.
Renal perfusion is reduced by NSAIDs
and can cause renal function to
deteriorate as they are vasoconstrictors
of the afferent artertioles
13
Cholestatic
jaundice caused
by co-amoxiclav
Raised ALP and total bilirubin. Also
has nausea and abdominal discomfort.
Started taking co-amoxiclav 10 days.
Cholestatic jaundice is a complication of
drugs including co-amoxiclav,
Flucloxacillin, erythromycin and
chlorpromazine.
Stop co-amoxiclav and monitor
hepatic function!
It is self-limiting once the drug is
stopped it will correct itself so
yes with drugs that cause a chile
static reaction
Jaundice and it said it is self-limiting
(BNF) provided that co-amoxiclav isnt
taken for more than 14 days. It is very
rarely fatal.
The CSM has advised that cholestatic
jaundice can occur either during or
shortly after the use of co-amoxiclav. An
epidemiological study has shown that
the risk of acute liver toxicity was about
6 times greater than with amoxicillin.
Cholestatic jaundice is more common in
patients above the age of 65 years and
in men.
14
Hyperkalaemia (A
CEI +
Spironolactone)
Hyperkalaemia with mild renal
impairment.
Taking Digoxin, Furosemide, Lisinopril
and Spironolactone and a few more.
Digoxin excreted through kidneys, risk of
toxicity.
15
Hyperglycaemia
related to Steroid
and acute
infection
Patient on COPD and diabetes (humulin,
metformin) meds. Given amoxicillin and
prednisolone short-term [for
exacerbation of COPD].
Hyperglycaemia, confusion experienced.
Infection (most likely upper respiratory
tract) and the steroids (prednisolone)
contribute to hyperglycaemia.
stop treatment and give an
alternative antibiotic if
necessary.
Other drugs can cause
hepatitis characterised by
prominent elevation of
ALT (which is not elevated in this
case) for example isoniazid,
hydralazine,
rifampicin and paracetamol (in
overdose).
Stop spironolactone and also
withhold ACEI. Recheck K+
levels and can reintroduce while
monitoring U&Es and renal
function.
Patient is only given
prednisolone for 5 to 7 days so
theres no need to stop it.
Continue course or infection
might not be fully cleared and
could reoccur and cause another
exacerbation of asthma/ COPD.
Monitor more closely blood
glucose levels and amend
diabetic meds according to
response (i.e. increase dose to
improve glycaemic control)
Also hyperglycaemia in short
term is not usually a problem.
Chronic hyperglycaemia is
associated with complications.
Why is the patient confused?
Excessively high blood glucose. Need to
increase diabetic control. Insulin should
help but keep monitoring blood glucose.
Hyperglycaemia in type
1 DM
Need insulin
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) may be cause due to
excessively high glucose levels. Symptom of DKA
includes confusion.
DKA occurs because the body has insufficient
insulin to process glucose into fuel, so the body
breaks down fats to use for energy. When the body
breaks down fat, ketones are produced as byproducts. It this occurs, its a medical emergency.
16
17
Angioedema
induced by ACEI
Compliance issues
with alendronic
acid
65 years old afro carribean male on
Bendoflumethiazide, Lisinopril
Simvastatin. He had angioedema. The
causative drug is Lisinopril.
Heartburn and mouth ulcers caused by
alendronic acid of daily supply and
patient chew tablets because couldn't
swallow.
Incorrect usage of the drug. Alendronic
acid should not be chewed as it can
cause mouth ulcers. And the patient may
not have been taking it correctly hence
the oesophageal irritation (heartburn).
Swallowing difficulty oesophageal
irritation
Also not sutiable to give oral
bisphosphonates in bed ridden patients
who cant sit/stand upright.
So stop ACEI monitor renal
function, add amplodipine (CCB
first line anyways) for
hypertension control and reduce
the dose of simvastatin to max
20mg (because of the addition
of amlodipine).
Investigate further to ensure
patient is not suffering from
oesophageal ulceration. Refer to
specialist? STOP alendronic acid!
Mouth ulcers management?
Options
Oral solution: Patient cant
swallow tablets so should be
offered oral solution instead
(which is available as
70mg/100mL). Still counsel that
the oral solution should be taken
with plenty of water on an
empty stomach at least
30minutes before food, and the
patient should sit or stand to
remain upright for 30 minutes
post dose.
IV infusion annually given as day
patient
IV Ibandronic acid for tx of postmenopausal women give iv inj
over 15 to 30 seconds 3mg
every 3 months (BNF)
Denosumab inj every 6 months
Also can suggest
for the alternative
for alendronic is strontium ranelate (but
cant find why)
18
Long term risks of
prednisolone
Long term risks of prednisolone for a
COPD patient
-Bisphosphonates for
prophylaxis of osteoporosis.
-Advice on balanced diet as it
can increase appetite and it also
increases risk of induce diabetes
in long-term use. (monitoring of
blood glucose may be needed)
-Avoid abrupt withdrawal.
-Avoid infectious people!
(increased risk of susceptibility
to infections)
-Carry your steroid card with
you.
GI protection..
Take prednisolone
tablets with food. The
enteric-coated tablets may
be taken before or after
food. But there is still GI
risk!
If you have been given
enteric-coated
prednisolone, swallow
these tablets whole. Do
not chew or crush them.
You should avoid taking
indigestion remedies at the
same time as entericcoated prednisolone as
these can interfere with the
special coating on your
tablets.
19
Amiodarone skin
reaction
Amiodarone was stopped a month ago
but patients been in sun and
experienced very red skin.
Photosensitivity known ADR of
amiodarone.
Despite having discontinued, likely to be
causing the ADR as it has a long half-life
(extending to several weeks)
Stay out of the sun
Use high factor sunscreen
Has a long half life so cause for
weeks after discontinuation
20
SSRI+ tramadol
Increased risk of serotonin syndromeIncreased risk of seizures.
Other signs mental status, autonomic
hyperactivity (tachycardia, diarrhoea)
and neuromuscular abnormalities
(hyperreflexia)
Avoid both together, change
tramadol to different analgesic
see if patient has tried codeine
first
21
SSRI + NSAIDS
Increased risk of GI bleeds
Change NSAID
22
Paracetamol
overdose but
hypersensitive to
acetylcysteine
Patient also on enzyme inducing
carbamazepine so high risk
Use methionine if within 10-12
hours of overdose and make
sure patient isnt vomiting!
23
Epileptic patient
needing
ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin = quinolone = lower the
threshold of seizures
Change antibiotic
24
NSTEMI
Also avoid NSAIDs with
quinolones = can also cause
convulsions
2 antiplatelet for 1 year
(clopidogrel + aspirin)
Also beta-blocker/ statin/ ACEI
GTN spray 999
-spray under tongue wait 5 mins
- can do that up to 3 times and if
pain doesnt go away = call 999
= suggests further MI
Good luck in sha Allah it will be cool Hira
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Coaching: Confidential Page 1 of 52 5/1/2009Dokumen52 halamanChapter 1: Introduction To Coaching: Confidential Page 1 of 52 5/1/2009James ZacharyBelum ada peringkat
- IV Push MedicationsDokumen67 halamanIV Push Medicationsbtalera100% (1)
- Poison and Antidote ChartDokumen5 halamanPoison and Antidote ChartSusanne Mae Gonzales50% (2)
- 1st Line Medication of An e CartDokumen5 halaman1st Line Medication of An e CartColette Marie PerezBelum ada peringkat
- AntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFDokumen28 halamanAntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFSunilBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Drug CardsDokumen32 halamanNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Dari EverandBasic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Regulatory Compliance Planning GuideDokumen70 halamanRegulatory Compliance Planning GuideriestgBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen12 halamanDrug StudyQueenie Gail Duarte RodrigoBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Used in Pregnancy, Labour and Puerperium: Presented By:-Ms Lisa Chadha F.Y. MSC Nursing Bvcon, PuneDokumen87 halamanDrugs Used in Pregnancy, Labour and Puerperium: Presented By:-Ms Lisa Chadha F.Y. MSC Nursing Bvcon, PuneSanjay Kumar SanjuBelum ada peringkat
- Hypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandHypercalcemia, (High Blood Calcium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs and Renal DiseasesDokumen31 halamanDrugs and Renal DiseasesStanley Tatenda MukonoBelum ada peringkat
- Dear Reader, These Papers Were Meant To Be As An Extremely Quick Review and Ultra-Short Summary ofDokumen9 halamanDear Reader, These Papers Were Meant To Be As An Extremely Quick Review and Ultra-Short Summary ofHazel D. Venus100% (2)
- Health and Safety at Work SlidesDokumen195 halamanHealth and Safety at Work SlidesZulfiqar Hyder100% (2)
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Architecture For AutismDokumen16 halamanArchitecture For AutismSivaRamanBelum ada peringkat
- CFPC SampsDokumen39 halamanCFPC SampsSumer Chauhan100% (9)
- Antiepileptic Drugs-Good LectureDokumen55 halamanAntiepileptic Drugs-Good LecturealijanmarwatBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen5 halamanDrug StudyVic MagtotoBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetic Nephropathy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandDiabetic Nephropathy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Ultrasound ReportDokumen3 halamanSample Ultrasound ReportPapadoveBelum ada peringkat
- ImipramineDokumen6 halamanImipramineMuhammed Faruk JambazBelum ada peringkat
- Ultimate Pre-Reg BNF NotesDokumen29 halamanUltimate Pre-Reg BNF NotesBob100% (7)
- Boracay Rehabilitation: A Case StudyDokumen9 halamanBoracay Rehabilitation: A Case StudyHib Atty TalaBelum ada peringkat
- الشرنوبي اطفالDokumen160 halamanالشرنوبي اطفالMahmoud HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile Health Clinic InitiativeDokumen47 halamanMobile Health Clinic InitiativededdyBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanDrug StudyLea FestejoBelum ada peringkat
- SBMWSM2016Dokumen491 halamanSBMWSM2016maimaiyeuem123100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateDokumen4 halamanDRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateTempoBelum ada peringkat
- Human Factors and Safety Culture in Maritime Safety (Revised)Dokumen10 halamanHuman Factors and Safety Culture in Maritime Safety (Revised)Al-aayan D. IsmaelBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Enquiry Comment/Case ManagementDokumen7 halamanClinical Enquiry Comment/Case ManagementIzzah AhsanBelum ada peringkat
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Dokumen4 halamanHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoBelum ada peringkat
- Preeclampsia and Severe Preeclampsia GuidelineDokumen10 halamanPreeclampsia and Severe Preeclampsia GuidelineAcitta Raras WimalaBelum ada peringkat
- IV Hydrocortisone/oral Prednisone Corticosteroids CorticosteroidsDokumen4 halamanIV Hydrocortisone/oral Prednisone Corticosteroids CorticosteroidsShira LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Magnesium SulfateDokumen2 halamanMagnesium SulfateKarla Karina Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- SPC Pramipexole 0.7 MGDokumen14 halamanSPC Pramipexole 0.7 MGJehan SarahdiniBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study Case PresentationDokumen5 halamanDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- FDCDokumen10 halamanFDCAnkit PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Acting On Gastrointestinal SystemDokumen41 halamanDrugs Acting On Gastrointestinal SystemDivya JoyBelum ada peringkat
- Magnesium Sulfa-WPS OfficeDokumen21 halamanMagnesium Sulfa-WPS OfficeNeha SinghBelum ada peringkat
- RX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelDokumen6 halamanRX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelntootBelum ada peringkat
- Mefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysiaDokumen1 halamanMefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysianuruladyanisaifuzzamanBelum ada peringkat
- Cloxacillin, Sodium: How Should I Take Cloxacillin?Dokumen7 halamanCloxacillin, Sodium: How Should I Take Cloxacillin?Stacy MC PelitoBelum ada peringkat
- Po512 Mid Fall 19 ModelDokumen3 halamanPo512 Mid Fall 19 ModelDr.PharmacistBelum ada peringkat
- PharmacologyDokumen116 halamanPharmacologyvargheseBelum ada peringkat
- Epilepsy Questions 2021Dokumen5 halamanEpilepsy Questions 2021z_sadiqBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokumen4 halamanNursing ResponsibilitiesMaureen Joy Cascayan EspirituBelum ada peringkat
- Medications Sheet AaaDokumen3 halamanMedications Sheet AaaLori Aucoin OlsenBelum ada peringkat
- Lupus: Therapy T.Dokumen10 halamanLupus: Therapy T.Sharifah ManuelBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Tuberculosis AgentsDokumen15 halamanAnti-Tuberculosis AgentsNick van ExelBelum ada peringkat
- OxcarbazepineDokumen4 halamanOxcarbazepineahmad_makhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanDrug Studymaryhiromi10Belum ada peringkat
- Lisinopril PDFDokumen3 halamanLisinopril PDFHannaBelum ada peringkat
- Summaries July 2022Dokumen14 halamanSummaries July 2022ibunaraBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Poisoning of Therapeutic Agents: by Alemayehu TomaDokumen42 halamanAcute Poisoning of Therapeutic Agents: by Alemayehu TomaYohannis AsefaBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs and Kidney DiseasesDokumen46 halamanDrugs and Kidney Diseasesمرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكBelum ada peringkat
- 1614978209sampleDokumen9 halaman1614978209sampleReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Antihypertensive AgentsDokumen33 halamanAntihypertensive AgentsJuwairia tariqBelum ada peringkat
- Metoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDokumen9 halamanMetoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDominique RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Metoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDokumen9 halamanMetoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDominique RamosBelum ada peringkat
- DiazepamDokumen11 halamanDiazepamDina HaryantiBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology CaptoprilDokumen14 halamanPharmacology Captoprildalilaarshad31Belum ada peringkat
- Gout and HyperuricemiaDokumen7 halamanGout and HyperuricemiaTaj lamajedBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Tuberculosis AgentsDokumen15 halamanAnti Tuberculosis Agentsejg26100% (1)
- Case Presentation On Ischemic Cardiomyopathy & Ccf-1-1Dokumen18 halamanCase Presentation On Ischemic Cardiomyopathy & Ccf-1-1Maliha aliBelum ada peringkat
- Labs Drug Study 1Dokumen17 halamanLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoBelum ada peringkat
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteDari EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteBelum ada peringkat
- Fast Facts: Ottimizzazione del trattamento delle fluttuazioni motorie nella malattia di ParkinsonDari EverandFast Facts: Ottimizzazione del trattamento delle fluttuazioni motorie nella malattia di ParkinsonBelum ada peringkat
- Format OpnameDokumen21 halamanFormat OpnamerestutiyanaBelum ada peringkat
- Abg PalicDokumen82 halamanAbg PalicHarry James PotterBelum ada peringkat
- MDSAP QMS ManualDokumen43 halamanMDSAP QMS ManualmamjaguarBelum ada peringkat
- ANGIOSARCOMA pdf3 PDFDokumen9 halamanANGIOSARCOMA pdf3 PDFعبدالعزيز عماد محمودBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Year Medical BooksDokumen3 halaman2nd Year Medical Bookskent_mazawBelum ada peringkat
- School Form 2 (SF2) Daily Attendance Report of LearnersDokumen4 halamanSchool Form 2 (SF2) Daily Attendance Report of LearnersRyan A. CabalidaBelum ada peringkat
- Citations Issued Due To COVID-19Dokumen726 halamanCitations Issued Due To COVID-19Maritza NunezBelum ada peringkat
- SUMMATIVE English8Dokumen4 halamanSUMMATIVE English8Therese LlobreraBelum ada peringkat
- MHFA For SchoolsDokumen45 halamanMHFA For SchoolsLING KUOK LIMBelum ada peringkat
- 978 3 642 25446 8Dokumen166 halaman978 3 642 25446 8Gv IIITBelum ada peringkat
- Insomnia: Management of Underlying ProblemsDokumen6 halamanInsomnia: Management of Underlying Problems7OrangesBelum ada peringkat
- Case Write Up 3Dokumen4 halamanCase Write Up 3E learningBelum ada peringkat
- REFERENCES in APA Style 7th EditionDokumen2 halamanREFERENCES in APA Style 7th EditionReabels FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Annual Investment Plan: Municipality of JAGNADokumen17 halamanAnnual Investment Plan: Municipality of JAGNA39mtn7Belum ada peringkat
- Qand ADokumen5 halamanQand AJoshua PascasioBelum ada peringkat
- Aferisis Transfuncional Teromuco BCTDokumen310 halamanAferisis Transfuncional Teromuco BCTNorma RamosBelum ada peringkat
- 3.21.17 When Human Life Begins PDFDokumen5 halaman3.21.17 When Human Life Begins PDFJosue Gallegos SalasBelum ada peringkat
- RP 11 - Measuring Concentration of Glucose Using A Calibration CurveDokumen4 halamanRP 11 - Measuring Concentration of Glucose Using A Calibration CurveAlfred SangBelum ada peringkat
- Neonatal Thrush of Newborns Oral CandidiasisDokumen3 halamanNeonatal Thrush of Newborns Oral CandidiasisYeni PuspitasariBelum ada peringkat
- MSDS Baybl T65 901510Dokumen8 halamanMSDS Baybl T65 901510gnavarroBelum ada peringkat
- PrelimDokumen10 halamanPrelimHeide Basing-aBelum ada peringkat






![Basic Pharmacology And Drug Calculations [Practice Questions And Answers]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/475660044/149x198/2c7fc45015/1691161640?v=1)