Motherboard Manaul Sata Sis 964
Diunggah oleh
Hercilio De Alcântara SilvaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Motherboard Manaul Sata Sis 964
Diunggah oleh
Hercilio De Alcântara SilvaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SiS 964 S-ATA Users Manual
Quick Users Guide
Version 0.1
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
CONTENTS
Introduction.............................................................................................1
Step 0. What is RAID..............................................................................3
KNOW HOW......................................................................................3
PERFORMANCE HINTS AND RECOMMEND SETTING ............3
Step 1. Hardware Setup ..........................................................................5
HARD DRIVES SETUP......................................................................5
Step 2. Installing Software Drivers.........................................................8
WINDOWS 2000/XP...........................................................................8
NEW WINDOWS 2000/XP INSTALLATION.............................................. 8
EXISTING WINDOWS 2000/XP INSTALLATION ..................................... 9
CONFIRMING WINDOWS 2000/XP DRIVER INSTALLATION................ 9
Step 3. BIOS Utility Operation (for RAID only)..................................10
CREATING AN ARRAY FOR PERFORMANCE..........................11
CREATING A MIRROR ARRAY ...................................................13
CREATING A JBOD ARRAY .........................................................16
CREATING A STRIPE-MIRROR ARRAY ....................................18
Step 4. SIS 964 RAID Utility Operation...............................................22
VIEWING THE CREATE RAID .................................................24
CREATE A RAID SET.....................................................................26
VIEWING THE RAIDTYPE MEANING........................................33
DELETE A RAID SET .....................................................................35
RAID RECOVERY OPERATION...................................................38
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
Introduction
The 964 S-ATA controller is a hybrid solution that combines two
independent SATA ports and one Ultra ATA port for support of up to two
Serial ATA (Serial ATA RAID) and two Ultra ATA (Ultra ATA RAID) drives.
Specifications are as follows:
Serial ATA Interface
Serial ATA (SATA) is the latest generation of the ATA interface. SATA hard
drives deliver blistering transfer speeds of up to 150MB/sec. Serial ATA
uses long, thin cables, making it easier to connect your drive and improving
the airflow inside your PC.
Supports 150 MB/s transfers with CRC error checking
Large LBA support for drives over 137 GB
Data handling optimizations including tagged command queuing, elevator seek
and packet chain command
Ultra ATA Interface
Standard ATA/IDE interface
Supports Ultra ATA/133, Ultra ATA/100, and Ultra ATA/66 drives
Supports CRC error checking for Ultra ATA drives
Separate timing control for two devices attached to one ATA channel
Serial/Ultra ATA RAID Interfaces
The Serial/Ultra ATA RAID is designed to provide a cost-effective, high
performance RAID solution that adds performance and/or reliability to PC
desktops and/or servers using Serial ATA/150, Ultra ATA/133, Ultra
ATA/100, Ultra ATA/66 hard disks.
Serial/Ultra ATA RAID function supports striping (RAID 0), mirroring (RAID
1), striping + mirroring (RAID 0+1) and span (JBOD). Please note that the
function supports hard disk drives only.
With striping, identical drives can read and write data in parallel to increase
performance. Mirroring increases read performance through load balancing
and elevator sorting while creating a complete backup of your files. Span
would increase the logic hard disk space.
Serial/Ultra ATA RAID striped arrays can double the sustained data transfer
rate of Serial ATA/150 and Ultra ATA/133 drives. Serial/Ultra ATA RAID
fully supports Serial ATA/150 and Ultra ATA/133 specification of up to
150MB/sec per drive, depending on individual drive specifications.
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
The technology also offers fault tolerant, data redundancy for entry-level
network file servers or simply for desktop PC users wanting to continually
protect valuable data on their PC. The Serial/Ultra ATA RAID offers RAID 1
mirroring (for two drives) to protect data. Should a drive that is part of a
mirrored array fail, Serial/Ultra ATA RAID technology uses the mirrored
drive (which contains identical data) to assume all data handling. When a
new replacement drive is later installed, Serial/Ultra ATA RAID rebuilds
data to the new drive from the mirrored drive to restore fault tolerance.
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
Step 0. What is RAID
Know How
This section will give you an overview about the RAID system and introduce
the basic background and glossary which you need to know before using
SiS 964 RAID Controller Application.
1. RAID: (Redundant Array of Independent Disk Drives) use jointly
several hard drives to increase data transfer rates and data security. It
depends on the number of drives present and RAID function you select
to fulfill the security or performance purposes or both.
2. RAID 0: Also known as Stripping. All of the data are distributed
evenly to all of the existing drives. You gain benefits on performance
because the data transfer rate is multiplied by the number of drives.
However, RAID 0 has high risks of data security. All of the stored data
will be lost if even any one drive in the RAID set crashes.
3. RAID 1: Also known as Mirroring. Two hard drives are required. The
goal of RAID 0 is to ensure data security. Data is written to two or
more drives synchronously. That is, 100% duplication of data from one
drive to another.
4. RAID 0+1: Also known as StripeMirror. At least four hard drivers are
required. RAID 0+1 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. Data is
striped into two drives then mirrored. It provides high performance and
high data protection. This is a costly solution as RAID 1 because the
two mirrored drives represent an expensive insurance
5. JBOD: (Just a Bunch of Drives). Also known as Spanning. Two or
more hard drives are required. Several hard disk types configured as a
single hard disk. The hard drives are simply hooked up in series. This
expands the capacity of your drive and results in a useable total
capacity. However, JBOD will not increase any performance or data
security.
Performance hints and recommend setting
For the best performance and reliability, please read the following
suggestions.
1. In serial ATA port, use Native serial ATA drives. Parallel ATA to Serial
ATA converter board is NOT suggested.
2. In parallel ATA port, use ATA 66/100/133 hard drives
3. Use the same model hard drives.
4. If you have only two serial ATA drives, the auto-configure function will
assign each on a different channel as a master drive. Using only two
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
parallel ATA drives to create a RAID array is NOT suggested. It might
decrease performance.
5. Always use 80-conductor cables.
6. We strongly recommend you should use DMA transfer mode.
7. The recommended block size is 64K when creating RAID 0 and
RAID 0+1.
8. The best selecting sequence of creating RAID 0+1 is Primary
Master(1) -> Secondary Master(3) -> Primary Slave(2) ->
Secondary Slave(4).
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
Step 1. Hardware Setup
Hard Drives setup
The 964 controller supports up to two Serial ATA hard drives and two
Parallel ATA hard drives.
Any combination to 2, 3 or 4 Hard disk would combine to a strip
system.
HDD Population Rules for RAID 0 (Striping)
Ultra ATA (Master)
Ultra ATA (Slave)
Serial ATA (Master 1)
Serial ATA (Master 2)
10
11
V = Install; X = Uninstall
NOTE: Storage Capacity: the number of hard drives times the capacity of
the smallest drive in the disk array
Working Speed: the speed of the lowest drive in the disk array
Any of 2 Hard Disk would make a mirror system.
HDD Population Rules for RAID 1 (Mirroring)
Ultra ATA (Master)
Ultra ATA (Slave)
Serial ATA (Master 1)
Serial ATA (Master 2)
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
2
V = Install; X = Uninstall
NOTE: Storage Capacity: the capacity of the smallest drive in the disk array
Working Speed: the speed of the lowest drive in the disk array
4 Hard disk would set up a RAID 0 + 1
HDD Population Rules for RAID 0+1 (Striping + Mirroring)
Ultra ATA (Master)
Ultra ATA (Slave)
Serial ATA (Master 1)
Serial ATA (Master 2)
V = Install; X = Uninstall
NOTE: Storage Capacity: the capacity of the smallest drive in the disk array
Working Speed: the speed of the lowest drive in the disk array
Any combination to 2, 3 or 4 Hard disk would combine to a JBOD system.
HDD Population Rules for JBOD (Spanning)
Ultra ATA (Master)
Ultra ATA (Slave)
Serial ATA (Master 1)
Serial ATA (Master 2)
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
10
11
V = Install; X = Uninstall
NOTE: Storage Capacity: the number of hard drives times the capacity of
the smallest drive in the disk array
Working Speed: the speed of the lowest drive in the disk array
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
Step 2. Installing Software Drivers
SiS provides Mini IDE driver for SiS964 SATA function and RAID driver for
SiS964 SATA with RAID function.
SiS Mini IDE driver for Windows 2000/XP
SiS RAID driver for Windows 2000/XP
1.
2.
For SATA function, both of Mini IDE driver and RAID driver support
SATA.
For RAID function, SiS964 support RAID0, RAID, RAID0+1 and JBOD
by software RAID driver only.
For special occasions, users can refer to the following section with
details on the SiS964 driver installation when used with various
operating systems.
Windows 2000/XP
New Windows 2000/XP Installation
The following details the installation of the drivers while installing
Windows 2000/XP.
1. Start the installation:
Boot from the CD-ROM. Press F6 when the message Press F6
key if you need to install third party SCSI or RAID driver appears.
2. When the Windows 2000/XP Setup window is generated, press S
key to specify an Additional Device(s).
3. Insert the driver diskette into drive A: and press Enter.
4. Choose one of the following items:
WinXP SiS Raid/IDE Controller (for RAID),
WinXP SiS Mini IDE Controller (for SATA),
Win2000 SiS Raid/IDE Controller (for RAID),
Win2000 SiS Mini IDE Controller (for SATA) that appears on
screen, and then press the Enter key.
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
5. Press Enter to continue with installation or if you need to specify
any additional devices to be installed, do so at this time. Once all
devices are specified, Press Enter to continue with installation.
6. From the Windows 2000/XP Setup screen, press the Enter key.
Setup will now load all device files and then continue the Windows
2000/XP installation.
7. Please install the driver package again (ex. SiS RAID driver v1.00)
while the operation system has been setup.
Remark:
If you would like to install windows to any RAID set, you should
create RAID from BIOS utility first and then follow the steps above.
Existing Windows 2000/XP Installation
1.
Install the driver by execute SiS driver setup utility.
2.
The drivers and WinXP RAID utility will be automatically installed.
Confirming Windows 2000/XP Driver Installation
1.
From Windows 2000/XP, open the Control Panel from My
Computer followed by the System icon.
2.
Choose the Hardware tab, then click the Device Manager tab.
3.
Click the + in front of SCSI and RAID Controllers hardware type.
The driver WinXP SiS964 Raid Controller (for RAID) or
Win2000/XP SiS964 IDE Controller (for SATA) should appear.
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
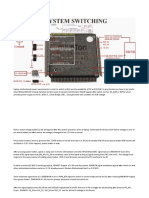
Step 3. BIOS Utility Operation (for RAID
only)
Note: For the best performance and reliability, please read Performance
Hints and Recommend Setting section in Step 0
1.
Boot your system. If this is the first time you have booted with the SIS
964 and the drives installed, the onboard BIOS will display the
following screen.
Silicon Integrated Systems Corp. RAID Card BIOS Setting Utility
1.00.0.XX
(c) 2003-2006 Silicon Integrated Systems Corp. All Rights
Reserved.
Press <Ctrl><S> to run BIOS Setting Utility
2.
Press <Ctrl-S> keys to display the SIS964 Utility Main Menu.
3.
Press R to display the RAID setup menu below. This is the fastest
and easiest method to creating your first array.
10
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
Creating an Array for Performance
NOTE: SIS 964 enables users to create striped arrays with 1, 2, 3, or 4
drives.
To create an array for best performance, follow these steps:
1.
Press A to create array .
2.
Press <2> and <Enter> to select Stripe .
3.
Press <1><7> keys and <Enter> to select Block Size. ( Default : 32K )
4.
Press <1><2> keys and <Enter> to select Transfer Mode. ( Default :
DMA )
5.
Use<> <> to select disk , and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q> to
exit.
11
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
6.
Press <N> and <Enter> to Create Stripe only. (If Press <Y> and
<Enter>, it will split the data on source disk to other disks)
7.
Press <Q> until escape the setup menu
12
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
8.
Press <Y> and <Enter> to save changes.
9.
Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format
the array as if it were a new single hard drive.
Creating a Mirror Array
To create an Mirror array , follow these steps:
1.
Press A to create array .
13
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
2.
Press <3> and <Enter> to select Mirror.
3.
Press <1><2> keys and <Enter> to select Transfer Mode. ( Default :
DMA )
4.
Use<> <> to select disk , and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q> to
exit.
14
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
5.
Press <N> and <Enter> to Create Mirror only. (If Press <Y> and
<Enter>, it will Duplicate the data on source disk to mirror disk)
6.
Press <Q> until escape the setup menu
15
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
7.
Press <Y> and <Enter> to save changes.
8.
Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format
the array as if it were a new single hard drive.
Creating a JBOD Array
To create an JBOD array , follow these steps:
1.
Press A to create array .
16
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
2.
Press <1> and <Enter> to select JBOD.
3.
Press <1><2> keys and <Enter> to select Transfer Mode. ( Default :
DMA )
4.
Use<> <> to select disk , and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q> to
exit.
17
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
5.
Press <Q> until escape the setup menu
6.
Press <Y> and <Enter> to save changes.
7.
Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format
the array as if it were a new single hard drive.
Creating a Stripe-Mirror Array
To create an Stripe-Mirror array, follow these steps:
1.
Press A to create array.
18
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
2.
Press <4> and <Enter> to select Strpie-Mirror.
3.
Press <1><7> keys and <Enter> to select Block Size. ( Default : 32K )
4.
Press <1><2> keys and <Enter> to select Transfer Mode. ( Default :
DMA )
5.
Use<> <> to select disk , and press <Enter> to select disk, <Q> to
exit.
19
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
6.
Press <Q> until escape the setup menu
7.
Press <Y> and <Enter> to save changes.
20
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
8.
Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and
format the array as if it were a new single hard drive.
21
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
Step 4. SIS 964 RAID Utility Operation
Note: For the best performance and reliability, please read Performance
Hints and Recommend Setting section in Step 0.
1) After installing the SiS RAID utility, go to Start menu and choose
Programs. From the Programs menu, choose SiS RAID Utility and
click on SiSRaid
2) The SiS RAID Utility window opens as below. The main interface has
two tabs: View and Configuration. You can switch to different tabs by
clicking on it. On View tab, we can see some device information. The
default value is the information of the first device.
22
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
3) Click the tab configuration, you can find three tabs: Create Raid,
Delete Raid and Raid Recovery. In the same way, you can switch to
different tabs by clicking on it.
23
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
4) Click the tab Create Raid, you can find three drop-down box and three
panes. Those meaning will be showing below.
Viewing the Create Raid
a)
Raid Type: Click the drop-down box Raid Type. This box enables the
user to select array type. There are four array types that the user can
select: JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1 and RAID 0+1. User can select any
one array type to create a RAID set.
b)
Block Size: If user selected RAID 0 and RAID 0+1 array types in the
Array Type box, the Block Size drop-down box will be enabled and
user must select a block size. Clicking the drop-down box Block Size,
there are seven block size that the user can select: 8k, 16k, 32k, 64k,
128k, 256k and 512k. User can select any one block size to create a
RAID 0 or RAID 0+1 set. The default selection is 64k.
24
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
c)
Mode Type: Click the drop-down box Mode Type. This box enables
the user to select mode type. There are two mode types that the user
can select: PIO and DMA. User can select any one mode type to
create a RAID set. The default selection is DMA.
d)
Available Disks: This pane will list out all the disks that can be used to
create a RAID set currently. It will show some disk information (ex.
Location, serial numbers, the ability of boot and the status of
recovering).
25
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
e)
Selected Disks: This pane will list out all the disks that have been
selected to create a RAID set. User can highlight the specific disk that
we wants in the Available Disks pane and click the downward arrow
icon or double click the marked disk to select that disk into the
Selected Disks pane. In the same way, user can click the upward
arrow icon or double click the marked disk in the Selected Disks to
get back the disk that we might select wrong to the Available Disks
pane.
f)
Information: This pane will show the information about creating a
RAID set after clicking the button Create. The information may be
Please select the <Raid Type> first!, "Please select the <Mode
Type> first!", "Please select the <Block Size> first!", "Please select the
disk you want first!", "Mirror supports TWO DISKS only.",
"StripeMirror needs least FOUR DISKS.", "Raid Created successful!
Reboot please!!" or "Raid Creation failed!".
Create a RAID set
a) To create a JBOD array, follow these steps:
1. Configuration Create Raid Raid Type JBOD.
2. From the drop-down box Mode Type, select the mode type you
want.
3. From the Available Disks pane, select the disk and click downward
arrow icon or double click it to add the disk on the Selected Disks
pane.
26
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
NOTE: You must have at least two hard disks to create a JBOD array.
4. When the JBOD arrays configuration is finished, click the button
Create. Then a warning message will be popup. Pay attention to the
warning message, and then click Yes button to finish the creation of
JBOD array, or click No button to cancel.
NOTE: If the disk you selected has the ability of booting, another
warning message will be popup before SiS Software RAID
message. You can click Yes button to continue or click No
button to cancel.
27
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
5. Next, another message box will be popup to tell user that disk setting
has been changed and ask whether to restart the computer or not.
Click Yes button to restart the computer or click Cancel button to
skip restarting.
NOTE: New Setting will take effect after restarting only.
b) To create a RAID 0 (Stripe) array, follow these steps:
1. Configuration Create Raid Raid Type RAID 0.
2. From the drop-down box Block Size, select the block size you want.
3. From the drop-down box Mode Type, select the mode type you
want.
4. From the Available Disks pane, select the disk and click downward
arrow icon or double click it to add the disk on the Selected Disks
pane.
28
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
NOTE: You must have at least two hard disks to create a RAID0 array.
5. When the RAID0 arrays configuration is finished, click the button
Create. Then a Create Stripe RaidSet dialog will be popup.
<Note>
Source: The first selected disk.
Target: All other disks but first one.
Create Only: This operation will destroy all data on all the selected
disks and create a clean stripe array without any data
on it.
Split data (Boot from IDE): Split operation will split data from source
disk into all the selected disks. In this
29
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
operation, the boot disk cant be placed
on 964.
Split data (Boot from 964): This operation is similar to Split data
into Raid0 operation, but system boots
from 964.
Ok: Start the operation.
Cancel: Cancel the operation.
<Disk Copy Remaining Sector>: Show the remaining splitting data.
NOTE: miniCapacity x N > SourceCapacity
miniCapacity: The minimum size of all selected disks.
SourceCapacity: The size of source disk.
N: Total disk numbers.
6. Next, you can click Cancel button to leave or click Ok button to
continue after the operation being selected. The differential warning
messages will be popup following the differential operations. The
warning messages are similar to JBOD array creation but the
operation is Split data into Raid0.
7. If the operation is Split data into Raid0, a warning message will be
popup, seeing below:
Next, you can click Yes button to start the operation or click No
button to cancel.
8. When the operation is finished, the restart warning message will be
popup as well as JBOD array creation except for the operation Split
boot OS into Raid0.
30
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
Next, you can click Ok button to restart the windows and start the
operation Split boot OS into Raid0. Or click Cancel button to
suspend this operation. But, this operation is still done after
restarting the windows next time.
c) To create a RAID 1 (Mirror) array, follow these steps:
1. Configuration Create Raid Raid Type RAID 1.
2. From the drop-down box Mode Type, select the mode type you
want.
3. From the Available Disks pane, select the disk and click downward
arrow icon or double click it to add the disk on the Selected Disks
pane.
NOTE: The RAID1 array supports two hard disks only.
4. When the RAID1 arrays configuration is finished, click the button
Create. Then a Create Mirror RaidSet dialog will be popup.
31
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
<Note>
Source: The first selected disk.
Target: The second selected disk.
Create Only: This operation will destroy all data on all the selected
disks and create a clean mirror array without any data
on it.
Create and Duplicate: Duplicate operation will reserve data on the
source disk and copy them onto the target
disk.
Ok: Start the operation.
Cancel: Cancel the operation.
<Disk Copy Remaining Sector>: Show the remaining copying data.
5. Next, you can click Cancel button to leave or click Ok button to
continue after the operation being selected. The warning messages
will be popup following the differential operations and the message
is similar to JBOD array creation.
6. When the operation is finished, the restart warning message will be
popup as well as JBOD array creation.
d) To create a RAID 0+1 (StripeMirror) array, follow these steps:
1. Configuration Create Raid Raid Type RAID 0+1.
2. From the drop-down box Block Size, select the block size you want.
3. From the drop-down box Mode Type, select the mode type you
want.
4. From the Available Disks pane, select the disk and click downward
arrow icon or double click it to add the disk on the Selected Disks
pane. Please see the Performance hints and recommend setting
section for best settings.
5. When the RAID0+1 arrays configuration is finished, click the button
32
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
Create. Then a warning message will be popup. The message is
similar to JBOD array creation.
6. Next, the restart message will be popup.
NOTE: The RAID0+1 array support at least four hard disks.
5) Click the tab Delete Raid, you can find some panes and two
buttons. The RaidType meaning will show below.
Viewing the RaidType meaning
General case: RAID0 (A = B C | D E)
<Meaning>
RAID0: Raid Type
A: total number of disks in this Raid
B,C: the serial number of each disk in this Raid
D,E: a) Raid is correct, B=D C=E
b) Raid is error, D or E will show ? or !.
In which, the meaning of ? and ! will show below.
33
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
<Example>
<Showing its information>
34
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
Delete a Raid set
a) To delete a JBOD, RAID0 or RAID1 array, follow these steps:
1. Configuration Delete Raid, the following windows will appear:
2. Highlight the disk array in the Current RaidType pane, and then click
the Information button or double click the array. You can get some
information about the disk array.
35
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
3. If you want to delete a disk array you selected, you can highlight the
disk array and then click the button Delete. Then a warning message
will be popup, and pay attention to the warning message. You can click
Yes to delete the selected disk array or click No to cancel.
4. Next, another message will be popup to tell user the setting of these
disks have been changed and ask whether to restart the computer.
b) To delete a RAID0+1 array, , follow these steps:
1. Configuration Delete Raid, highlight the disk array in the Current
RaidType pane, and then click the Information button or double click
the array. You can get some information about the disk array. The
following windows will appear:
36
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
2. If you want to delete a disk array you selected, you can highlight the
disk array and then click the button Delete. Then a warning message
will be popup, and pay attention to the warning message.
3. Next, you can click the button Delete to delete this RAID0+1 array
and all disk will become single disk. Then some warning messages
which are the same with previous those will be popup.
4. Or, you can click the button Degrade to degrade RAID0+1 set to
become a completed RAID0 set. See below:
NOTE: The degrading operation is workable only when the RAID 0+1
set has any one completed RAID 0 set existed.
37
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
6) Click the tab Raid Recovery, you can find two panes and some
buttons. Those meaning will be showing below.
Raid Recovery Operation
NOTE: The recovering operation is workable only when error RAID1
set or error RAID0+1 set (must at least an error RAID0 set)
exist.
a) First, you can click the button Available Raid to find whether any error
Raid set existing. See below:
Next, highlight the error Raid set you want to recovery. And you can click
the button Ok to continue or click Cancel to cancel this operation.
38
Serial ATA RAID Quick Users Guide
b) After Available RAID selected, click the button Available Disk to find
whether any empty hard disk existing. See below:
Next, highlight the empty hard disk you want to select. And you can click
the button Ok to continue or click Cancel to give up this selection.
c) When the Available Raid and Available Disk is finished, you can click
the button Start to start this operation. And the button Start will
become Pause. Then you can click the button Pause to pause the
thread operation. And the button Pause will become Start. Or you
can click the button Stop to cancel this operation.
39
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Adobe Crack MethodDokumen4 halamanAdobe Crack MethodJason Roberts20% (5)
- LCD Common Bad Phenomenon and Repair Methods (Figure)Dokumen14 halamanLCD Common Bad Phenomenon and Repair Methods (Figure)Minh NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges of SSD Forensic Analysis (37p)Dokumen37 halamanChallenges of SSD Forensic Analysis (37p)Akis KaragiannisBelum ada peringkat
- Lenovo IdeaPad 310-15ISK 510-15ISK LCFC DIS CG411 CG511 NM-A751 Discrite r1.0Dokumen60 halamanLenovo IdeaPad 310-15ISK 510-15ISK LCFC DIS CG411 CG511 NM-A751 Discrite r1.0dinnhow100% (1)
- Windows 10 Enterprise N KeyDokumen10 halamanWindows 10 Enterprise N KeyGSSS SOGPURABelum ada peringkat
- Laptop Motherboard Repair Parts DocumentsDokumen2 halamanLaptop Motherboard Repair Parts Documentslucky_4u15Belum ada peringkat
- Gambit MLK MT - A00 - 20180202 - 01Dokumen107 halamanGambit MLK MT - A00 - 20180202 - 01Tin Học Chí CôngBelum ada peringkat
- Sony PDP-01 Plasma TrainingDokumen91 halamanSony PDP-01 Plasma Trainingdann222Belum ada peringkat
- Hasee HP500 Laptop SchematicsDokumen41 halamanHasee HP500 Laptop SchematicsbrunnofranklinBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Personal Computers and Hardware ComponentsDokumen70 halamanIntroduction to Personal Computers and Hardware ComponentsBiha RoseliBelum ada peringkat
- Fixing A Seagate 7200.11 Hard DriveDokumen22 halamanFixing A Seagate 7200.11 Hard Driveajlapria100% (1)
- Compal La-8951p r0.1 SchematicsDokumen55 halamanCompal La-8951p r0.1 SchematicsPaulo AmaralBelum ada peringkat
- Module Photo PDFDokumen21 halamanModule Photo PDFINTERSOFT khansirBelum ada peringkat
- Ic ListDokumen8 halamanIc ListAvik Ghara100% (1)
- Beginning STM32: Developing with FreeRTOS, libopencm3 and GCCDari EverandBeginning STM32: Developing with FreeRTOS, libopencm3 and GCCBelum ada peringkat
- MB Level 2 - 1 Training MaterialsDokumen24 halamanMB Level 2 - 1 Training MaterialsFernando Amaro HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Home About Contact: How To Fix Bricked Seagate Hard Disk (With Illustrations)Dokumen12 halamanHome About Contact: How To Fix Bricked Seagate Hard Disk (With Illustrations)ClaudioBelum ada peringkat
- Asus Notebook Training Actre l2-1 PDFDokumen27 halamanAsus Notebook Training Actre l2-1 PDFJúnior CremonezBelum ada peringkat
- 8c347 Compal LA-9901P r1.0 2013 PDFDokumen64 halaman8c347 Compal LA-9901P r1.0 2013 PDFBruno CoutoBelum ada peringkat
- Ssc5x86h ManDokumen29 halamanSsc5x86h ManValdenir DuarteBelum ada peringkat
- Quanta Et2t r3c SchematicsDokumen27 halamanQuanta Et2t r3c Schematicsrmartins_239474Belum ada peringkat
- Laptop SchematicDokumen111 halamanLaptop SchematicnegrusrlBelum ada peringkat
- Seagate 7200.11 Terminal Commands - Hard Disk Drive TechnoDokumen9 halamanSeagate 7200.11 Terminal Commands - Hard Disk Drive TechnoOlga BurlakovaBelum ada peringkat
- Chip SetsDokumen29 halamanChip SetsDrift Gee100% (1)
- Wiistron Raichu WL Pikachu WL 18730 R-1mDokumen106 halamanWiistron Raichu WL Pikachu WL 18730 R-1mPhan ThanhBelum ada peringkat
- Ecs V10il1 - 37GV10000-C0 - Rev CDokumen32 halamanEcs V10il1 - 37GV10000-C0 - Rev CHendra R. Rattu75% (4)
- Intersoft Basic Notes For Pci Pinout DetailDokumen63 halamanIntersoft Basic Notes For Pci Pinout DetailZulfiqar AliBelum ada peringkat
- MS Office 2007 - NotesDokumen89 halamanMS Office 2007 - NotesmanuBelum ada peringkat
- Dell Beep CodeDokumen1 halamanDell Beep CodeBivek BasnetBelum ada peringkat
- Power Sequence TrainingDokumen15 halamanPower Sequence TrainingRaju KhajjidoniBelum ada peringkat
- AMD Power Sequence - Foxconn Safina 5 - Rev - MV For HP LaptopDokumen2 halamanAMD Power Sequence - Foxconn Safina 5 - Rev - MV For HP LaptopEduinMaracuchoFernandezChaparroBelum ada peringkat
- E2900 - Status Chs ComponentDokumen5 halamanE2900 - Status Chs ComponentKang AmengBelum ada peringkat
- Ryans Product Book - April 2015 - Issue 75Dokumen44 halamanRyans Product Book - April 2015 - Issue 75Ryans Computers Ltd.Belum ada peringkat
- Adiedkhaz Book of Laptop IndexDokumen5 halamanAdiedkhaz Book of Laptop Indexavancealdemar56Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Laptop Fix and DiagnosesDokumen51 halamanIntroduction To Laptop Fix and Diagnosesablacon64Belum ada peringkat
- Laptop DIS Block Diagram BreakdownDokumen52 halamanLaptop DIS Block Diagram BreakdownLeoned Cova Orozco100% (2)
- 66 EasyDokumen10 halaman66 EasyDarius WhiteBelum ada peringkat
- Chiplevel RepairingDokumen3 halamanChiplevel Repairingshriram1082883Belum ada peringkat
- Sony Vaio VGN-AW Series MBX-194 M780 SD FOXCONN M780 CantigaP WPCE775LDokumen77 halamanSony Vaio VGN-AW Series MBX-194 M780 SD FOXCONN M780 CantigaP WPCE775LChetin TekinBelum ada peringkat
- Intel chipset specs with code names, part numbers and release datesDokumen4 halamanIntel chipset specs with code names, part numbers and release datesEletrônica Goiano100% (1)
- Computer - Hardware - Diagnosing & Fixing Motherboard FaultsDokumen4 halamanComputer - Hardware - Diagnosing & Fixing Motherboard Faultsscribdraza786Belum ada peringkat
- Seagate Command ReferenceDokumen17 halamanSeagate Command ReferenceTrevor HallBelum ada peringkat
- Determine If Your Motherboard Is DeadDokumen8 halamanDetermine If Your Motherboard Is DeadSasi DharanBelum ada peringkat
- Samsung UN46C7000WF Chassis N80A PDFDokumen129 halamanSamsung UN46C7000WF Chassis N80A PDFJoseGyEjBelum ada peringkat
- Sony Vaio Vgn-Ns Series Foxconn m790!1!01 Rev 1.0 SCHDokumen54 halamanSony Vaio Vgn-Ns Series Foxconn m790!1!01 Rev 1.0 SCHCarlos Henrique RibasBelum ada peringkat
- Msi b85m Pro-Vd (Ms-7a01) Rev 1.1Dokumen34 halamanMsi b85m Pro-Vd (Ms-7a01) Rev 1.1Angel RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Lenovo DMI DecodeDokumen14 halamanLenovo DMI DecodeMarcelloBelum ada peringkat
- Laptop Imp1 PDFDokumen2 halamanLaptop Imp1 PDFMagarishi TechBelum ada peringkat
- Ducati2 Trouble Shooting Guide20140611 PDFDokumen12 halamanDucati2 Trouble Shooting Guide20140611 PDFRiza VirsadaBelum ada peringkat
- BQ 25601Dokumen60 halamanBQ 25601Epran SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- Gigabyte - Mobo TrainningDokumen17 halamanGigabyte - Mobo TrainningEverton DoradoBelum ada peringkat
- Desktop Power Seq.Dokumen1 halamanDesktop Power Seq.vinu100% (1)
- Laptop SIO Power-UpDokumen2 halamanLaptop SIO Power-Upbong bernalbongBelum ada peringkat
- Dell Inspiron 5150 Motherboard Schematics Document Compal LA-1682Dokumen44 halamanDell Inspiron 5150 Motherboard Schematics Document Compal LA-1682Claudiu Petrache100% (1)
- LGA1150 Cpu: System Chipset: Lynxpoint-H81 Main Memory:: IH81S-MHS IH81S-MHS IH81S-MHSDokumen39 halamanLGA1150 Cpu: System Chipset: Lynxpoint-H81 Main Memory:: IH81S-MHS IH81S-MHS IH81S-MHSdương hoàngBelum ada peringkat
- Multifunction Peripherals for PCs: Technology, Troubleshooting and RepairDari EverandMultifunction Peripherals for PCs: Technology, Troubleshooting and RepairBelum ada peringkat
- The Special Keys PDFDokumen10 halamanThe Special Keys PDFjhon martinezBelum ada peringkat
- BIMx LogDokumen5 halamanBIMx LogVeliDaBelum ada peringkat
- Debug 1214Dokumen19 halamanDebug 1214Beverly MarshallBelum ada peringkat
- (HOW-To) How To Update BIOS and EC For U2442 - v1Dokumen20 halaman(HOW-To) How To Update BIOS and EC For U2442 - v1anon_664289275Belum ada peringkat
- How Do I Manually Boot HP-UX On Integrity (Itanium) Based SystemsDokumen6 halamanHow Do I Manually Boot HP-UX On Integrity (Itanium) Based Systemsnilu772008Belum ada peringkat
- Delete Temp WindowsDokumen29 halamanDelete Temp WindowsDiego Fernando TrujilloBelum ada peringkat
- How To Fully Remove Lexmark Drivers From WindowsDokumen4 halamanHow To Fully Remove Lexmark Drivers From WindowsMikael JonesBelum ada peringkat
- Functions of Every KeyDokumen9 halamanFunctions of Every KeyThomas JillBelum ada peringkat
- CajaterrazaDokumen8 halamanCajaterrazaFelix Malo ABelum ada peringkat
- Windows 10: Course OutlineDokumen5 halamanWindows 10: Course OutlineMuhsen KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Connecting To WMI On A Remote ComputerDokumen4 halamanConnecting To WMI On A Remote Computerleon_galBelum ada peringkat
- DX DiagDokumen36 halamanDX Diagreibeiro velasquez florezBelum ada peringkat
- Caracteristicas de La Placa BaseDokumen6 halamanCaracteristicas de La Placa BaseingridBelum ada peringkat
- Windows 7 Ultimate SP1 32 Bit LITEDokumen7 halamanWindows 7 Ultimate SP1 32 Bit LITEAbu Salma WisnuBelum ada peringkat
- Hardening Windows XPDokumen20 halamanHardening Windows XPsmartyamit86100% (6)
- RMExtractionDokumen21 halamanRMExtractionRam RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- SP 56122Dokumen1 halamanSP 56122Dallas OaBelum ada peringkat
- 430HX PDFDokumen25 halaman430HX PDFchaitany nagpureBelum ada peringkat
- Software Installation Notes B7586 Rev ADokumen1 halamanSoftware Installation Notes B7586 Rev ARafael CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Transferring FSMO Roles in Windows Server 2008Dokumen11 halamanTransferring FSMO Roles in Windows Server 2008Quang TranBelum ada peringkat
- Manual GT9600Dokumen28 halamanManual GT9600Viorel Daniel NegrutBelum ada peringkat
- ReadmeDokumen3 halamanReadmeAndrew BaghdasaryanBelum ada peringkat
- Dragon Nest Crash ReportDokumen1 halamanDragon Nest Crash Reportyuda44Belum ada peringkat
- Windows 10 Pro Redstone 5 X64 OEM ESD It-IT MAR 2019 (Gen2)Dokumen2 halamanWindows 10 Pro Redstone 5 X64 OEM ESD It-IT MAR 2019 (Gen2)Sheetal BhaisareBelum ada peringkat
- KB00194 - DCOM Settings For The OPC Interface That Cause The Following Errors - Advise Returns Error 8004020 - or PIPCDokumen1 halamanKB00194 - DCOM Settings For The OPC Interface That Cause The Following Errors - Advise Returns Error 8004020 - or PIPCJunior PassosBelum ada peringkat
- TEMS UDP Server User's Manual PDFDokumen12 halamanTEMS UDP Server User's Manual PDFConstantin GîlcaBelum ada peringkat
- Duplicate (Sorry Guys)Dokumen7 halamanDuplicate (Sorry Guys)jtobias_26Belum ada peringkat
- Geforce RTX 4060 Ti Ventus 2x Black 8g OcDokumen1 halamanGeforce RTX 4060 Ti Ventus 2x Black 8g OcDavid BrudinBelum ada peringkat