Geriatric OSCE Stroke Exam
Diunggah oleh
Ami FebrizaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Geriatric OSCE Stroke Exam
Diunggah oleh
Ami FebrizaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Geriatric OSCE: Stroke Assessment
General assessment:
-
Assess the patient, their state, any aids / equipment etc.
Motor function, standing / sitting / lying
Facial appearance, speech
Examination:
-
Facial movements:
o Raise eyebrows
o Scrunch eyes
o Puff out cheeks and hold them out
o Open mouth, and against resistance
o Tongue in / out / left / right
Facial sensation:
o Ocular / maxillary / mandibular branches
o Tongue
Ocular:
o PLRs
o Movements: Double-H
o Visual fields: seeing, and when movement stops
Upper limbs:
o Tone
o Gross motor
o Sensation
o Reflexes: including grasping
Lower limbs:
o Tone
o Gross motor
o Sensation
o Reflexes: including Babinski
Speech:
o Orientation in time / place / person
o General use of words:
o Stating names and purposes of finger / pen / watch, name things starting with F
Nominal aphasia if cant name it
Agnosia if cant identify purpose
o Identify their ownership of left / right hands
Hemi-neglect
Actions:
o Act as if youre brushing your teeth
Dyspraxia if cant carry out actions
o Draw a clock
May detect hemi-neglect, impaired executive function,
o Simple maths: 2+6 = 8
May detect acalculia
o Write their name
May detect agraphia or dyspraxia
Interpretation:
-
Dominant (Left) MCA lesion:
o Right weakness / impaired sensation
o Aphasia Wernickes or Brocas
o Dysarthria distinguish from cerebellar speech
o Right visual field deficit
o Impaired reading / writing / calculating (acalculia, agraphia)
Non-dominant (Right) MCA lesion:
o Left weakness / impaired sensation
o Spatial disorientation
o Left visual field deficit
o Dysarthria (distinguish from cerebellar speech)
Brainstem lesion:
o 4-limb weakness and sensory impairment
o Ataxia
o Nystagmus
o Bilateral visual field deficits
Anterior Cerebral Artery lesion
o Slowed mentation, decreased executive function
o Incontinence
o Frontal release of primitive reflexes
Lateral Medullary Syndrome:
o Ipsilateral numbness, limb ataxia, Horners Syndrome, pain over eye
o Contralateral loss of sensation (pin prick and hot-cold)
o Vertigo, nausea, hoarseness, hiccups, dysphagia
Questions:
-
Treatment for acute stroke:
o Rule out intracranial haemorrhage first
o Thrombolysis if less than 4hrs (exact timeframe of who benefits at what time is
still unclear)
o Rehabilitation: rehabilitation physician, physiotherapy, speech and occupational
therapy
Outcomes of stroke:
o Majority of recovery occurs within first 3 months, minimal neuro improvement
past 6 months
o At 1 yr: 1/3 die, 1/3 permanently impaired, 1/3 minimally or no residual
impairment
o High rate of post-stroke depression
Secondary prevention:
o Anticoagulation (aspirin / clopidogrel / other antiplatelets, NOACs, warfarin)
o Lipid, diabetes, HTN control
o Carotid endarterectomy
CT findings:
o Haemorrhagic stroke:
Hyperdense diffuse region of haemorrhage
Mass effect, increased intracranial pressure, herniation / displacement
o Ischaemic stroke:
Loss of grey-white distinction
Loss of clarity of basal ganglia
MRI findings:
o Haemorrhagic stroke:
Poor for detection of subarachnoid haemorrhage
o Ischaemic stroke:
Loss of grey-white distinction
Loss of clarity of basal ganglia
Differentials:
o Thromboembolic stroke
o Haemorrhagic stroke
o Mass lesion (+/- acute necrosis / haemorrhage within mass)
o Hypoglycaemia
o Electrolyte abnormalities, esp hyponatraemia +/- overly rapid correction
o Delirium
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Brew Your Own Big Book of Clone Recipe - Brew Your OwnDokumen716 halamanThe Brew Your Own Big Book of Clone Recipe - Brew Your OwnFrederico Ribeiro67% (3)
- Bartos P. J., Glassfibre Reinforced Concrete - Principles, Production, Properties and Applications, 2017Dokumen209 halamanBartos P. J., Glassfibre Reinforced Concrete - Principles, Production, Properties and Applications, 2017Esmerald100% (3)
- PathophysiologyDokumen3 halamanPathophysiologyKristel Jane LasacaBelum ada peringkat
- Expanded 3P Study Guide YasminaIrinaDokumen79 halamanExpanded 3P Study Guide YasminaIrinaikBelum ada peringkat
- PE Cases Part 1Dokumen15 halamanPE Cases Part 1Kylie YuBelum ada peringkat
- Gemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsDokumen13 halamanGemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsAnna-Tammy HumanBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Complete History and PhysicalDokumen2 halamanSample Complete History and PhysicalhugosaysBelum ada peringkat
- MedCAS Cardiology Clinical Notes by DR Navneeth & DR SanketDokumen61 halamanMedCAS Cardiology Clinical Notes by DR Navneeth & DR SanketBhageerath AttheBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatrics OSCE, 6th Year, 2008, by Ghanem Al-BashaDokumen2 halamanPediatrics OSCE, 6th Year, 2008, by Ghanem Al-BashaMobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (1)
- H&P and Daily Progress NotesDokumen1 halamanH&P and Daily Progress NotesМилица СвиларBelum ada peringkat
- (APJ) Common ENT CasesDokumen31 halaman(APJ) Common ENT CasesApryl Phyllis JimenezBelum ada peringkat
- Paeds Complete PDFDokumen176 halamanPaeds Complete PDFjljoioiuBelum ada peringkat
- OSCE DermaDokumen8 halamanOSCE DermaameerabestBelum ada peringkat
- OSPE AnswersDokumen4 halamanOSPE AnswersLiyana SulaimanBelum ada peringkat
- Cme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Dokumen36 halamanCme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Hakimah K. SuhaimiBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Session 2003-2004Dokumen246 halamanReview of Session 2003-2004The Royal Society of Edinburgh0% (1)
- Examination of The Central Nervous SystemDokumen3 halamanExamination of The Central Nervous Systemkenners100% (13)
- A Seminar About History TakingDokumen13 halamanA Seminar About History Takingdr_jamal1983Belum ada peringkat
- Assessment 1. The Patient'S Identity: Name: Rosmayani Nim: 14235101101 Class: IibDokumen3 halamanAssessment 1. The Patient'S Identity: Name: Rosmayani Nim: 14235101101 Class: IibBrother Vs CanonBelum ada peringkat
- HB PT Osce SPDokumen10 halamanHB PT Osce SPAli NofalBelum ada peringkat
- August - September - 2002 Osce Stations MelbourneDokumen12 halamanAugust - September - 2002 Osce Stations Melbournemnigam64Belum ada peringkat
- Main Clinical Syndromes in Respiratory SystemDokumen111 halamanMain Clinical Syndromes in Respiratory Systemnewtype0% (1)
- Step-Wise Approaches in Clinical Examination - SampleDokumen8 halamanStep-Wise Approaches in Clinical Examination - Samplecsbully913Belum ada peringkat
- Clinical ExDokumen123 halamanClinical ExDeepti ChaharBelum ada peringkat
- Paediatrics:: Case 1nsionDokumen16 halamanPaediatrics:: Case 1nsionYwagar YwagarBelum ada peringkat
- Management of HypertensionDokumen93 halamanManagement of Hypertensionhasibsb28Belum ada peringkat
- WK 6 Study QsDokumen7 halamanWK 6 Study Qsapi-479720222Belum ada peringkat
- 24 HR History 2Dokumen2 halaman24 HR History 2Arjun KatariaBelum ada peringkat
- Foundations of Patient Care: University of California, San Francisco School of MedicineDokumen41 halamanFoundations of Patient Care: University of California, San Francisco School of MedicinePaul Carty SorianoBelum ada peringkat
- Medicine I OSCE Grand HistoryDokumen4 halamanMedicine I OSCE Grand HistoryAndréAmistosoBelum ada peringkat
- Surgery OSCE SpotsDokumen1 halamanSurgery OSCE SpotsAbdulBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular BigDokumen37 halamanCardiovascular Bigfaiz nasirBelum ada peringkat
- Med OSCEDokumen82 halamanMed OSCECarly BladesBelum ada peringkat
- Nephrotic Syndrome: BackgroundDokumen25 halamanNephrotic Syndrome: BackgroundsDamnBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Year OSCE StationsDokumen6 halaman3rd Year OSCE StationsrutendonormamapurisaBelum ada peringkat
- Mental State Exam OSCE Mark SchemeDokumen2 halamanMental State Exam OSCE Mark SchemeoluseyeBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Diagnosis Information OverviewDokumen119 halamanPhysical Diagnosis Information OverviewNarcis PopaBelum ada peringkat
- CVS Examination 3rd MBDokumen30 halamanCVS Examination 3rd MBsnowlover boyBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Observed HX - Ms J - AsthmaDokumen5 halamanSample Observed HX - Ms J - AsthmaZi SongBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory System - History & Physical Examination: Mohan KumarDokumen35 halamanRespiratory System - History & Physical Examination: Mohan KumaraagarwalmdBelum ada peringkat
- YEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas PayneDokumen30 halamanYEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas Payneminayoki100% (1)
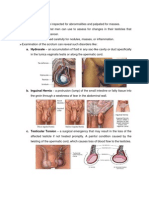
- Testicular ExamDokumen3 halamanTesticular ExamminikatitingBelum ada peringkat
- ScenarioDokumen23 halamanScenarioAakashBelum ada peringkat
- Internal MedicineDokumen83 halamanInternal MedicineSumbul PBelum ada peringkat
- Ed Adult and PaedsDokumen2 halamanEd Adult and PaedsPrashin RocharamBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Examination - Eric Sarpong-NtiamoahDokumen52 halamanClinical Examination - Eric Sarpong-NtiamoahFathimathBelum ada peringkat
- CKD History TakingDokumen2 halamanCKD History TakingNadia Salwani80% (5)
- pGALS Examination OSCE GuideDokumen18 halamanpGALS Examination OSCE GuideFanny PritaningrumBelum ada peringkat
- 03 PAEDS NeurologyDokumen13 halaman03 PAEDS Neurologyfire_n_iceBelum ada peringkat
- PRO 2012 Short Case (Surgical) CompilationDokumen24 halamanPRO 2012 Short Case (Surgical) CompilationvijayaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction History and ExaminationDokumen43 halamanIntroduction History and ExaminationDanyal Hassan100% (1)
- DR Ashiq Tutorials Pre-Krok 1222Dokumen66 halamanDR Ashiq Tutorials Pre-Krok 1222Praveen KpBelum ada peringkat
- Electrocardiogram12 LeadsDokumen28 halamanElectrocardiogram12 LeadsshyluckmayddpBelum ada peringkat
- MUSCULOSKELETAL Assessment ScripyDokumen2 halamanMUSCULOSKELETAL Assessment ScripyKristinelou Marie N. ReynaBelum ada peringkat
- Mohammed Gogandy - Puerperium History Sheet & - 40 2007-2008& - 41 PDFDokumen2 halamanMohammed Gogandy - Puerperium History Sheet & - 40 2007-2008& - 41 PDFJennifer Ross-ComptisBelum ada peringkat
- Etiology and Clinical Profile of Pericardial Effusion PatientsDokumen4 halamanEtiology and Clinical Profile of Pericardial Effusion PatientsIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- GIT Examination - Clinical Skills With DRDokumen8 halamanGIT Examination - Clinical Skills With DRNaveen KovalBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular Shoutouts: When She Says You SayDokumen7 halamanCardiovascular Shoutouts: When She Says You SayGbotemi AlaladeBelum ada peringkat
- Amazing Esqs With Answers Pediatrics-ShelfDokumen31 halamanAmazing Esqs With Answers Pediatrics-ShelfDrSajid BuzdarBelum ada peringkat
- Shoulder ExamDokumen24 halamanShoulder ExamMuhammad FahmyBelum ada peringkat
- MG Case StudyDokumen12 halamanMG Case StudyPiyali SahaBelum ada peringkat
- Neurological ExaminationDokumen86 halamanNeurological Examinationtips and HAcKSBelum ada peringkat
- Salmonella Infected Model On MiceDokumen14 halamanSalmonella Infected Model On MiceAmi FebrizaBelum ada peringkat
- Utsi Brochures Apply PG 1Dokumen4 halamanUtsi Brochures Apply PG 1Ami FebrizaBelum ada peringkat
- Jadwal Fisiologi Biomedik 3Dokumen9 halamanJadwal Fisiologi Biomedik 3Ami FebrizaBelum ada peringkat
- Bebas Remed Anatomi 3Dokumen1 halamanBebas Remed Anatomi 3Ami FebrizaBelum ada peringkat
- The Use of The Body Mass Index in Under 18 Year OldsDokumen0 halamanThe Use of The Body Mass Index in Under 18 Year OldsAmi FebrizaBelum ada peringkat
- MSDS of Poly Aluminum ChlorideDokumen5 halamanMSDS of Poly Aluminum ChlorideGautamBelum ada peringkat
- Carbo Hi DratDokumen11 halamanCarbo Hi DratILHAM BAGUS DARMA .NBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Features, Evaluation, and Diagnosis of Sepsis in Term and Late Preterm Infants - UpToDateDokumen42 halamanClinical Features, Evaluation, and Diagnosis of Sepsis in Term and Late Preterm Infants - UpToDatedocjime9004Belum ada peringkat
- Medical Nutrition Therapy For DiabetesDokumen27 halamanMedical Nutrition Therapy For Diabetesdr.Uci BaharBelum ada peringkat
- Ethics, Privacy, and Security: Lesson 14Dokumen16 halamanEthics, Privacy, and Security: Lesson 14Jennifer Ledesma-Pido100% (1)
- 2016 Uptown Parksuites D3 PDFDokumen54 halaman2016 Uptown Parksuites D3 PDFArafat Domado100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q4 - Lessons 7 and 8) Electrochemical ReactionsDokumen11 halamanLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q4 - Lessons 7 and 8) Electrochemical Reactionsprincess3canlasBelum ada peringkat
- Chef Basics Favorite RecipesDokumen58 halamanChef Basics Favorite Recipesbillymac303a100% (2)
- Dual Laminate Piping HandbookDokumen46 halamanDual Laminate Piping HandbookA.Subin DasBelum ada peringkat
- Product Term and ConditionsDokumen50 halamanProduct Term and Conditionsain2Belum ada peringkat
- Sampoong Department Store - A Literary Critique (Mimetic Theory)Dokumen2 halamanSampoong Department Store - A Literary Critique (Mimetic Theory)Ron Marc CaneteBelum ada peringkat
- B737-800 Air ConditioningDokumen7 halamanB737-800 Air ConditioningReynaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Om Deutz 1013 PDFDokumen104 halamanOm Deutz 1013 PDFEbrahim Sabouri100% (1)
- Bi RadsDokumen10 halamanBi RadsFeiky Herfandi100% (1)
- Krispy Kreme Doughnut Recipe - Immaculate BitesDokumen2 halamanKrispy Kreme Doughnut Recipe - Immaculate Bitesdaisydrops6Belum ada peringkat
- Practice Test For Exam 3 Name: Miguel Vivas Score: - /10Dokumen2 halamanPractice Test For Exam 3 Name: Miguel Vivas Score: - /10MIGUEL ANGELBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Visit ReportDokumen8 halamanIndustrial Visit ReportAnuragBoraBelum ada peringkat
- Evidence-Based Strength & HypertrophyDokumen6 halamanEvidence-Based Strength & HypertrophyAnže BenkoBelum ada peringkat
- 7 LevelDokumen5 halaman7 LevelACHREF RIHANIBelum ada peringkat
- Proposal Semister ProjectDokumen7 halamanProposal Semister ProjectMuket AgmasBelum ada peringkat
- Sikadur 42 HSDokumen2 halamanSikadur 42 HSthe pilotBelum ada peringkat
- Starters Flash CardsDokumen28 halamanStarters Flash CardsNara GarridoBelum ada peringkat
- Intraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor DynamicsDokumen36 halamanIntraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor DynamicsIntan EkarulitaBelum ada peringkat
- Essence Veda Vyasa Smriti PDFDokumen51 halamanEssence Veda Vyasa Smriti PDFmadhav kiranBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Stra Bill FinalDokumen41 halaman1 Stra Bill FinalRajesh JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Natu Es Dsmepa 1ST - 2ND QuarterDokumen38 halamanNatu Es Dsmepa 1ST - 2ND QuarterSenen AtienzaBelum ada peringkat
- Sterillium Gel-MsdsDokumen9 halamanSterillium Gel-MsdsVasanthakumar VenkatesanBelum ada peringkat