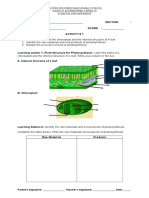
Grade 9 Syllabus Revised
Diunggah oleh
api-340406981Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Grade 9 Syllabus Revised
Diunggah oleh
api-340406981Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
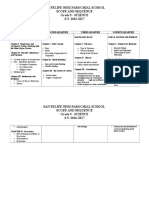
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED
LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
SUBJECT SYLLABUS IN SCIENCE 9
TOPICS
SKILLS
A/M/
T
Classifications of Skills
LOT
HOT
R
21st
Century
Literacies
FIRST QUARTER
1. explain how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together
to transport nutrients, gases, and other molecules to and from the
different parts of the body;
Eco-Literacy
2. infer how ones lifestyle can affect the functioning of respiratory and
circulatory systems;
Global/
Multicultural
Literacy
2. Heredity: Inheritance and
Variation
2.1 Location of genes on
chromosomes
2.2 Non-Mendelian inheritance
2.2.1 Incomplete dominance
2.2.2 Sex-linked traits
2.2.3 Multiple alleles
2.3 Multiple genes
3. describe the location of genes in chromosomes;
ICT Literacy
4. explain the different patterns of non-Mendelian inheritance;
3. Biodiversity and Evolution
3.1 Causes of Species Extinction
3.1.1 natural
3.1.2 anthropogenic
4. Ecosystems
4.1 Flow of Energy and Matter in
Ecosystems
4.1.1 Photosynthesis
4.1.2 Respiration
5. relate species extinction to the failure of populations of organisms to adapt to
abrupt changes in the environment; and
6. differentiate basic features and importance of photosynthesis and respiration.
1. Respiratory and Circulatory
Systems Working with the other
Organ Systems
SECOND QUARTER
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED
LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
SUBJECT SYLLABUS IN SCIENCE 9
1. Mole Concept
1.1 Mass
1.2 Moles
1.3 Percentage Composition of a
Compound
1. use the mole concept to express mass of substances; and
2. determine the percentage composition of a compound given its chemical
formula and vice versa.
1. Chemical Bonding
1.1 Ionic and Covalent Bonding
3. explain the formation of ionic and covalent bonds;
4. recognize different types of compounds (ionic or covalent) based on their
properties such as melting point, hardness, polarity, and electrical and thermal
conductivity;
5. explain properties of metals in terms of their structure;
6. explain how ions are formed;
2. The Variety of Carbon
Compounds
2.1 Carbon Atoms
2.2 Organic Compounds
7. explain how the structure of the carbon atom affects the type of bonds it
forms;
8. recognize the general classes and uses of organic compounds;
1.Volcanoes
1.1 Type of volcanoes
1.2 Volcanic Eruption
1.3 Energy from volcanoes
1. describe the different types of volcanoes;
Eco-Literacy
2. differentiate between active and inactive volcanoes;
3. explain what happens when volcanoes erupt ;
Global/
Multicultural
Literacy
4. illustrate how energy from volcanoes may be tapped for human use;
5. explain how different factors affect the climate of an area;
1.2 Metallic Bonding
Physical
Fitness and
Health Literacy
Eco-Literacy
ICT literacy
THIRD QUARTER
2.Climate
2.1 Factors that affect climate
SocioEmotional
Literacy
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED
LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
SUBJECT SYLLABUS IN SCIENCE 9
2.2 Global climate phenomenon
6. describe certain climatic phenomena that occur on a global level;
3. Constellations
3.1 Characteristics of stars
3.2 Arrangement of stars in a group
3.3 Changing position of constellations
during the night and at different times
of the year
3.4 Beliefs and practices about
constellations and astrology
7. infer the characteristics of stars based on the characteristics of the Sun;
8. infer that the arrangement of stars in a group (constellation) does not change;
9. observe that the position of a constellation changes in the course of a night;
and
10. show which constellations may be observed at different times of the year
using models.
1. Motion in Two Dimensions
1. Projectile Motion
1.2.Impulse, Momentum and Impulse
1.3.Conservation of Linear Momentum
1. describe the horizontal and vertical motions of a projectile;
2. investigate the relationship between the angle of release and the height and
range of the projectile;
3. relate impulse and momentum to collision of objects (e.g., vehicular
collision);
4. infer that the total momentum before and after collision is equal;
5. examine effects and predict causes of collision-related damages/injuries;
6. explain energy transformation in various activities/events (e.g., waterfalls,
archery, amusement rides);
7. perform activities to demonstrate conservation of mechanical energy;
8. infer that the total mechanical energy remains the same during any process;
FOURTH QUARTER
2. Work Power and Energy
2.1 Changes in form of mechanical
energy
2.2 Conservation of energy
Physical
Fitness and
Health Literacy
Eco-Literacy
ICT literacy
SAN FELIPE NERI PAROCHIAL SCHOOL
PAASCU ACCREDITED
LEVEL II
SCIENCE DEPARTMENT
SUBJECT SYLLABUS IN SCIENCE 9
3. Heat, Work, and Efficiency
4. Electricity and magnetism
4.1 Power generation and energy
losses
4.2 Transmission and distribution of
electrical energy from power plants to
homes
9. make a model to demonstrate that heat can do work;
10. infer that heat transfer can be used to do work, and that work involves the
release of heat;
11. explain why machines are never 100-percent efficient;
12. explain how heat transfer and energy transformation make heat engines like
geothermal plants work; and
13. explain how electrical energy is generated, transmitted, and distributed.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Modern Biology. Chapter Tests With Answer Key General and AdvancedDokumen250 halamanModern Biology. Chapter Tests With Answer Key General and AdvancedWllatakam100% (8)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Student's Book AnswersDokumen51 halamanEdexcel IGCSE Chemistry Student's Book AnswersAvrinox82% (162)
- Intro To Chem Textbook PDFDokumen795 halamanIntro To Chem Textbook PDFHana Knobel100% (8)
- Curriculum Map Grade 9Dokumen8 halamanCurriculum Map Grade 9api-340406981100% (6)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Topic3 Periodic TableDokumen66 halamanTopic3 Periodic TablenijamBelum ada peringkat
- MotionDokumen10 halamanMotionapi-34040698150% (2)
- VolcanoDokumen8 halamanVolcanoapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Science 9 Rubrics: Health and Fitness Plan Primer RubricsDokumen6 halamanScience 9 Rubrics: Health and Fitness Plan Primer Rubricsapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- 8 Project ProposalDokumen3 halaman8 Project Proposalapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Activity Sheet Body SystemDokumen8 halamanActivity Sheet Body Systemapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Actvity Sheets GeneticsDokumen6 halamanActvity Sheets Geneticsapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Activity Sheet PhotosynthesisDokumen4 halamanActivity Sheet Photosynthesisapi-34040698140% (5)
- ExtinctionsDokumen20 halamanExtinctionsapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Projectile MotionDokumen11 halamanProjectile Motionapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Volcanoes 3 FinalDokumen106 halamanVolcanoes 3 Finalapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Grade 9 Ubd 4th Heat ElectricityDokumen15 halamanGrade 9 Ubd 4th Heat Electricityapi-340406981100% (14)
- 0708 EnergyDokumen42 halaman0708 EnergybittuchintuBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratorysystem 16Dokumen35 halamanRespiratorysystem 16api-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Remodeled Plan 2nd Quarter MoleDokumen23 halamanRemodeled Plan 2nd Quarter Moleapi-340406981100% (1)
- Integration of ValuesDokumen7 halamanIntegration of Valuesapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Remodeled Plan 1st Quarter HeredityDokumen31 halamanRemodeled Plan 1st Quarter Heredityapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Grade 9 Scope and SequenceDokumen2 halamanGrade 9 Scope and Sequenceapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- Remodeled Plan 2nd Quarter Chemical BondingDokumen34 halamanRemodeled Plan 2nd Quarter Chemical Bondingapi-340406981Belum ada peringkat
- AP Chemistry Bonding Help Sheet: 2, (Diamond)Dokumen6 halamanAP Chemistry Bonding Help Sheet: 2, (Diamond)Weiyu TongBelum ada peringkat
- 2013 H2 Chemistry (9647) Syallabus For GCE A Level (Singapore)Dokumen48 halaman2013 H2 Chemistry (9647) Syallabus For GCE A Level (Singapore)Wei Hong HoBelum ada peringkat
- BC10 Examstudy U2Dokumen91 halamanBC10 Examstudy U2Bryant Villarin BaldivicioBelum ada peringkat
- Science 9 PT 2ndQDokumen3 halamanScience 9 PT 2ndQMaria Elaine Feranil100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/43Dokumen11 halamanCambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/43krishaBelum ada peringkat
- Allotropes Research TaskDokumen6 halamanAllotropes Research Taskanonymous1Belum ada peringkat
- OBTL Chemistry I G12 STEMDokumen8 halamanOBTL Chemistry I G12 STEMCelestial Lacambra50% (2)
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDokumen34 halamanChapter 12 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and TechniquesAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry ReviewDokumen15 halamanGeneral Chemistry ReviewPhirun ChengBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 Properties of MatterDokumen40 halamanChapter 11 Properties of MatterWong SunBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding: Pre-AP ChemistryDokumen12 halamanChemical Bonding: Pre-AP ChemistrySaediRisquéBriskeyBelum ada peringkat
- First Periodical Test CONCHEMDokumen5 halamanFirst Periodical Test CONCHEML-lynne NitramBelum ada peringkat
- Versatile Nature of CarbonDokumen26 halamanVersatile Nature of CarbonAashish MenghaniBelum ada peringkat
- 2012 Chemistry Kedah With AnswerDokumen83 halaman2012 Chemistry Kedah With AnswerPei YeeBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Notes (5124) For Senior ClassesDokumen127 halamanChemistry Notes (5124) For Senior ClassesAdrian Robert Mwape100% (3)
- DSE CHEM 2020 必溫重點Dokumen53 halamanDSE CHEM 2020 必溫重點teresa tsoiBelum ada peringkat
- Fred Redmore - ChemistryDokumen12 halamanFred Redmore - ChemistryMark Anthony SantosBelum ada peringkat
- The Walden' InversionDokumen99 halamanThe Walden' InversionsarahBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Paper 1 2009Dokumen7 halamanChemistry Paper 1 2009Robert EdwardsBelum ada peringkat
- AP Chemistry WorkbookDokumen287 halamanAP Chemistry WorkbookVincent Vetter60% (5)
- Practice Test 1 Answer Key AP BioDokumen16 halamanPractice Test 1 Answer Key AP Biotessarox161Belum ada peringkat
- Secondary School Students Misconceptions of Coval PDFDokumen28 halamanSecondary School Students Misconceptions of Coval PDFalfian rosyadiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Matter TGDokumen73 halamanUnit 2 Matter TGGermaine Lajera50% (2)
- Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Test BankDokumen25 halamanMicrobiology With Diseases by Body System 4th Edition Bauman Test BankChadHallwaiy100% (49)
- Question Bank Chemistry 1Dokumen34 halamanQuestion Bank Chemistry 1Karanam.Ramakumar100% (3)
- Bonding, VSEPR, and Intermolecular ForcesDokumen25 halamanBonding, VSEPR, and Intermolecular ForcesKevin Shui Hu100% (2)