Anaphysio
Diunggah oleh
Thea GonzalesJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Anaphysio
Diunggah oleh
Thea GonzalesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Thea Izza T.
Gonzales
MLS 2-D
1. Plot a table regarding on the Tissues Description, Site/ Locations, Distinct
Features/ Function
Tissue
Description
Site/Locations
EPITHELIAL TISSUE It covers internal and Found in the lining
Features/Functions
Protecting
external surfaces
of the digestive tract
underlying structures.
throughout the body.
organs.
Acting as a barrier.
Consist of a single
Permitting the
layer of cells or
passage of substances.
multiple layers of
Secreting substances.
epithelial cells between
Absorbing
the free surface and the
substances.
basement membrane
CONNECTIVE
It is characterized by Found throughout the Enclosing and
TISSUE
large amounts of
body.
separating other
extracellular material
tissues.
that separates cells
Connecting tissues to
from one another.
one another.
Supporting and
moving parts of the
body.
Storing compounds.
Cushioning and
insulating.
Thea Izza T. Gonzales
MLS 2-D
Transporting
NERVOUS TISSUE
Protecting
It is responsible for
Nervous tissue is the Found in the brain,
main component of the spinal cord and nerves. coordinating and
two parts of the
controlling many body
nervous system; the
activities.
brain and spinal cord of
the central nervous
system (CNS), and the
branching peripheral
nerves of the peripheral
MUSCLE TISSUE
nervous system (PNS).
is a soft tissue found Found in Muscles
Ability to contract or
in most animals.
attached to the bones.
shorten, making
Muscle cells contain
Muscles of the heart.
movement possible.
protein filaments of
actin and myosin that
slide past one another,
producing a contraction
that changes both the
length and the shape of
the cell.
3. Plot a table regarding on the Stages of Cell Division, give its distinct features and
physiologic mechanism towards the cellular production/ reproduction.
Stages of Cell Division
Features
Physiological mechanism
towards the cellular
Thea Izza T. Gonzales
MLS 2-D
production/ reproduction.
INTERPHAS
Is the "resting" or non-
The interphase continuum
mitotic portion of the cell
of stages, G1, S, and G2,
cycle.
begins the process in which
It is comprised of G1, S,
the cell grows and matures
and G2 stages of the cell
(G1), followed by the S phase
cycle.
in which the DNA is copied.
Finally, the G2 phase is when
the cell prepares for
division. Mitosis occurs when
the nucleus of the cell
divides into two identical
nuclei with the same number
and type of chromosomes,
followed by cytokinesis when
the cytoplasm, for both plant
and animal cells, divides,
thus creating two daughter
cells that are genetically
equal and approximately
PROPHASE
identical in size.
The chromatin condenses The centrosomes move to
and become visible into
opposite poles of the cell,
Thea Izza T. Gonzales
MLS 2-D
chromosomes.
forming a bridge of spindle
The centrioles form and
fibers. At the end of
move toward opposite ends prophase,
of the cell ("the poles").
the nucleolus disperses. In
The nuclear membrane
prometaphase, the next
dissolves.
step of mitosis, the nuclear
membrane breaks apart
and the chromosomes are
captured by the
microtubules which are
METAPHASE
attached to centromeres.
The chromosomes align in During metaphase, the cell's
the center of the cell in
chromosomes align
association with the spindle themselves in the middle of
fibers.
the cell through a type of
cellular "tug of war." The
chromosomes, which have
been replicated and remain
joined at a central point
called the centromere, are
ANAPHASE
The chromatids separate
called sister chromatids.
During anaphase, each pair
to form two sets of identical of chromosomes is
chromosomes. The
separated into two identical,
Thea Izza T. Gonzales
MLS 2-D
chromosomes, assisted by
independent chromosomes.
the spindle fibers, move
The chromosomes are
toward the centrioles at
separated by a structure
each end of the cell.
called the mitotic spindle.
The mitotic spindle is made
of many long proteins called
microtubules, which are
attached to a chromosome at
one end and to the pole of a
TELOPHASE
The chromosomes
cell at the other end.
Telophase begins once the
decondense.
replicated, paired
The nuclear envelope
chromosomes have been
forms.
separated and pulled to
Cytokinesis reaches
opposite sides, or poles, of
completion, creating two
the cell. During telophase, a
daughter cells.
nuclear membrane forms
around each set of
chromosomes to separate
the nuclear DNA from the
cytoplasm
Thea Izza T. Gonzales
MLS 2-D
5. Give the relevance of tissue identification (in all aspects) as a Medical Laboratory
Science Student.
As a Medical Laboratory Science student, we studied and trained to become
highly professionals who work in a hospital or a laboratory as soon as we finish this
college degree. As a future Medical Technologist, we should be familiarize and analyze
sample of blood, tissue and body fluids to determine blood count, blood type, and
microorganisms like bacteria or parasites because this is our job duties. In biology,
tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete
organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells from the same origin that together carry
out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of
multiple tissues.
The study of tissue is known as histology or, in connection with disease,
histopathology (study of tissues). Its one of the branches of medical technology and a
duty of a MedTech to prepare cultures of a tissue samples.
Thea Izza T. Gonzales
MLS 2-D
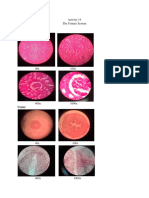
2. Draw the microscopic presentation of the different tissue found in our body. Observe
the relativity on its colour, shape and cytoplasmic/ nuclear ratio of size.
Epithelial Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Connective Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Thea Izza T. Gonzales
MLS 2-D
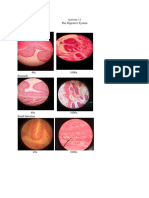
4. Draw the microscopic presentation of every cell division stages, observe relativity.
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
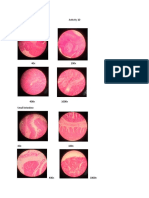
2. Draw the microscopic presentation of the different tissue found in our body. Observe
the relativity on its colour, shape and cytoplasmic/ nuclear ratio of size.
Thea Izza T. Gonzales
Epithelial Tissue
Nervous Tissue
MLS 2-D
Connective Tissue
Muscle Tissue
4. Draw the microscopic presentation of every cell division stages, observe relativity.
Interphase
Prophase
Thea Izza T. Gonzales
MLS 2-D
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- BB NotesDokumen15 halamanBB NotesThea Gonzales100% (3)
- Part2MICRO (COMPILED)Dokumen9 halamanPart2MICRO (COMPILED)Thea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: Ascariasis. Infections Most Often Seen in Young Children byDokumen7 halamanAscaris Lumbricoides: Ascariasis. Infections Most Often Seen in Young Children byThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Part2MICRO (COMPILED)Dokumen9 halamanPart2MICRO (COMPILED)Thea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- "Arrowhead" ("Bowtie"/"butterfly-Like: Pin Head Colonies", Soft Butter-Like, Oil Paint, Grapelike ClustersDokumen3 halaman"Arrowhead" ("Bowtie"/"butterfly-Like: Pin Head Colonies", Soft Butter-Like, Oil Paint, Grapelike ClustersThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Sisig PDFDokumen44 halamanSisig PDFThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- AR-THEA Aug1-15Dokumen1 halamanAR-THEA Aug1-15Thea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- New Drugs PDF HighlightedDokumen11 halamanNew Drugs PDF HighlightedThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Fornt PageDokumen1 halamanFornt PageThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- StainDokumen5 halamanStainThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Bacte 3RD QeeDokumen2 halamanBacte 3RD QeeThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Gonzales - Toxic Granulation Hema ReportDokumen5 halamanGonzales - Toxic Granulation Hema ReportThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- ImmunoSero QE 1stDokumen7 halamanImmunoSero QE 1stThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Humble and Generous ServiceDokumen5 halamanHumble and Generous ServiceThea Gonzales100% (1)
- Activity 15 The Endocrine System Thyroid: Capayan, Mer Conrad L. Mls 3-CDokumen5 halamanActivity 15 The Endocrine System Thyroid: Capayan, Mer Conrad L. Mls 3-CThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Form:: Form and Matter Ministers EffectsDokumen9 halamanForm:: Form and Matter Ministers EffectsThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Augustinian ChurchesDokumen2 halamanAugustinian ChurchesThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Gonzales, Thea Izza T. Mls IiicDokumen6 halamanGonzales, Thea Izza T. Mls IiicThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Heart and Layers of The Heart Purkinje Fiber EndocardiumDokumen2 halamanHeart and Layers of The Heart Purkinje Fiber EndocardiumThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- PhilLit MidtermsDokumen49 halamanPhilLit MidtermsThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Categories: Staphylococcus Aureus Escherichia ColiDokumen2 halamanCategories: Staphylococcus Aureus Escherichia ColiThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney: Activity 14 The Urinary SystemDokumen3 halamanKidney: Activity 14 The Urinary SystemThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Histo PuzzleDokumen2 halamanHisto PuzzleThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 13Dokumen2 halamanActivity 13Thea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial Activity and Synergism of Cefuroxime On Anaerobic BacteriaDokumen3 halamanAntimicrobial Activity and Synergism of Cefuroxime On Anaerobic BacteriaThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 10 HistoDokumen3 halamanActivity 10 HistoThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 11 The Digestive System EsophagusDokumen2 halamanActivity 11 The Digestive System EsophagusThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Olfactory Mucosa: Activity 12 The Respiratory SystemDokumen3 halamanOlfactory Mucosa: Activity 12 The Respiratory SystemThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Material ManagementDokumen37 halamanMaterial ManagementThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 10 HistoDokumen3 halamanActivity 10 HistoThea GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Simplify Type1 1Dokumen2 halamanSimplify Type1 1parmeilaBelum ada peringkat
- Development of Dermal Ridges Fetus : in TheDokumen9 halamanDevelopment of Dermal Ridges Fetus : in TheIsmail FadlurrohmanBelum ada peringkat
- Micro GliaDokumen335 halamanMicro GliaHelena QuintBelum ada peringkat
- Examination of Body FluidsDokumen14 halamanExamination of Body Fluidskiedd_04100% (11)
- Dairy 2 PDFDokumen23 halamanDairy 2 PDFSariful IslamBelum ada peringkat
- English Skills BookDokumen49 halamanEnglish Skills BookAngela SpadeBelum ada peringkat
- Pipiolo and The Roof Dogs Organizer - MCDDokumen8 halamanPipiolo and The Roof Dogs Organizer - MCDMichelle Peloquin McDonaldBelum ada peringkat
- Picture Book of Poultry DiseasesDokumen24 halamanPicture Book of Poultry Diseasesanirbanpal4400Belum ada peringkat
- Fauna Paraguay Handbook of The Mammals of Paraguay IIDokumen120 halamanFauna Paraguay Handbook of The Mammals of Paraguay IIportalguaraniBelum ada peringkat
- TKT Module 1 Describing Language Phonology PDFDokumen9 halamanTKT Module 1 Describing Language Phonology PDFRachel Maria Ribeiro100% (1)
- The Axial Skeleton PDFDokumen9 halamanThe Axial Skeleton PDFElvin EzuanBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge English YLE Staters 1Dokumen13 halamanCambridge English YLE Staters 1kobelynnBelum ada peringkat
- Latest KSSR Year Four WritingDokumen38 halamanLatest KSSR Year Four WritingMurely Ponnusamy50% (2)
- "Human Sexual Response"-A Discussion of The Work of Masters and Johnson PDFDokumen11 halaman"Human Sexual Response"-A Discussion of The Work of Masters and Johnson PDFPetar DimkovBelum ada peringkat
- Katia Crochet MagazineDokumen159 halamanKatia Crochet MagazineMaria Louisa Wessels100% (5)
- Rad Ana Handouts Feb 4 2022Dokumen13 halamanRad Ana Handouts Feb 4 2022danlen faye flojoBelum ada peringkat
- Gram Negative BacilliDokumen15 halamanGram Negative BacilliFabasyira JamalBelum ada peringkat
- Beary Bearnita. Winnie Pooh. WinnieDokumen22 halamanBeary Bearnita. Winnie Pooh. Winniejosita100% (12)
- Non-Reproductive Sexual Behavior in AnimalsDokumen8 halamanNon-Reproductive Sexual Behavior in AnimalsLeokadia ŻukowskaBelum ada peringkat
- Brioche Cat Hat by Natasha SillsDokumen4 halamanBrioche Cat Hat by Natasha SillsMythili SHIVKUMARBelum ada peringkat
- Reflexes and Special SensesDokumen66 halamanReflexes and Special SensesPamela Agatha PunoBelum ada peringkat
- Organisation of Living Things Study PresentationDokumen26 halamanOrganisation of Living Things Study PresentationRUIZ CANO EnriqueBelum ada peringkat
- ESL Trivia Game - Beginner 2 PDFDokumen1 halamanESL Trivia Game - Beginner 2 PDFjoshuabaezBelum ada peringkat
- The Dulce Battle ReportDokumen11 halamanThe Dulce Battle ReportHdv Mal100% (1)
- Our Masterpiece 1961Dokumen160 halamanOur Masterpiece 1961FraterPrieriusBelum ada peringkat
- PPOK Jurnal NewDokumen8 halamanPPOK Jurnal NewjihanBelum ada peringkat
- 7th Grade Considering Cockroaches Text - QuestionsDokumen3 halaman7th Grade Considering Cockroaches Text - QuestionsSubhash_iimaBelum ada peringkat
- Afropop DiscographyDokumen4 halamanAfropop DiscographyThe Neverending Story100% (2)
- To Be Accomplished by The Licensed Manning Agency.: Repatriation Information Sheet 2Dokumen1 halamanTo Be Accomplished by The Licensed Manning Agency.: Repatriation Information Sheet 2ian clark MarinduqueBelum ada peringkat
- AdenoiditisDokumen4 halamanAdenoiditisApurbBelum ada peringkat