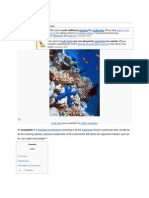
Ecosystem
Diunggah oleh
amol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ecosystem
Diunggah oleh
amol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms (plants, animals and microbes) in conjunction with
the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system.
[2]
These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.
[3]
As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their
environment,[4] they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces [5] (although some
scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem). [6]
Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy
that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system
through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbonfrom the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on
one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They
also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic
matter,decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting
nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes. [7]
Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors.
and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not
themselves influenced by the ecosystem.[8] Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems
are dynamic entitiesinvariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering
from some past disturbance.[9] Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world
can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. [8] Theintroduction of nonnative species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem
processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops.[8] While the resource inputs
are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these
resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading.
[8]
Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist
and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like
climate.[8]
Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems
provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem
management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the
level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step
towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.
History and development
The term "ecosystem" was first used in a publication by British ecology Arthur Tansley.[fn 1][10] Tansley devised the
concept to draw attention to the importance of transfers of materials between organisms and their environment.
[11]
He later refined the term, describing it as "The whole system, ... including not only the organism-complex, but
also the whole complex of physical factors forming what we call the environment". [12] Tansley regarded
ecosystems not simply as natural units, but as mental isolates.[12] Tansley later[13] defined the spatial extent of
ecosystems using the term ecotope.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Introduction to Ecology and Environmental Laws in IndiaDari EverandIntroduction to Ecology and Environmental Laws in IndiaBelum ada peringkat
- The Web of Life: Understanding Ecology and Our Place in ItDari EverandThe Web of Life: Understanding Ecology and Our Place in ItBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem Is A: HistoryDokumen5 halamanEcosystem Is A: HistoryLeoBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystems in 40 CharactersDokumen88 halamanEcosystems in 40 CharactersRDBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDokumen2 halamanEcosystem: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystems and BiodiversityDokumen13 halamanEcosystems and BiodiversityteacherashleyBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen7 halamanEcosystem - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMaria MarqueBelum ada peringkat
- EcosystemDokumen13 halamanEcosystemDinesh33% (3)
- Ecosystem - WikipediaDokumen12 halamanEcosystem - Wikipediavinuveer6379Belum ada peringkat
- Unit Ii Ecosystem and Its ComponentsDokumen22 halamanUnit Ii Ecosystem and Its ComponentsDevraj KhudotiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem: The Concept of The EcosystemDokumen6 halamanEcosystem: The Concept of The EcosystemVinay JainBelum ada peringkat
- Biotic and Abiotic FactorDokumen2 halamanBiotic and Abiotic FactorCharles Hernandez TarogBelum ada peringkat
- Part of SpeechDokumen3 halamanPart of SpeechkcmarianoBelum ada peringkat
- Ecological Foundations of Environmental EducationDokumen5 halamanEcological Foundations of Environmental EducationFrqnz AyasivBelum ada peringkat
- NREM 301: 12 Ecological ConceptsDokumen3 halamanNREM 301: 12 Ecological ConceptsAbbas khanBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem: Navigation SearchDokumen12 halamanEcosystem: Navigation Search90614555Belum ada peringkat
- Community Nonliving ComponentsDokumen1 halamanCommunity Nonliving ComponentsJuanitaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 IntroductionDokumen28 halamanUnit 1 IntroductionTris EatonBelum ada peringkat
- EcologyDokumen22 halamanEcologyAnonymous uqBeAy8onBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology (Disambiguation)Dokumen15 halamanEcology (Disambiguation)Joseph PamaongBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystems and Their ServicesDokumen22 halamanEcosystems and Their Servicesstellacfierce_243120Belum ada peringkat
- Environmental Law Renaissance Law College NotesDokumen97 halamanEnvironmental Law Renaissance Law College NotesDesugari ChakriBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology - Reviewer MidtermDokumen7 halamanEcology - Reviewer MidtermMaria Nina Tanedo100% (1)
- Unit-3 ECOSYSTEMDokumen26 halamanUnit-3 ECOSYSTEMSachin SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- The Ecosystem ConceptDokumen7 halamanThe Ecosystem Concepterlina_rachmawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology (from Greek: οDokumen40 halamanEcology (from Greek: οAnonymous E4Rbo2sBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem - Structure and FunctionsDokumen3 halamanEcosystem - Structure and Functions202336 Software DevelopmentBelum ada peringkat
- Komponen EkosistemDokumen13 halamanKomponen EkosistemFadlika HarindaBelum ada peringkat
- Sustainable Design PrinciplesDokumen28 halamanSustainable Design Principlesharai prasadBelum ada peringkat
- Renaissance Notes EnvironmentDokumen98 halamanRenaissance Notes EnvironmentA Aruna Bopche 982Belum ada peringkat
- Subject: Biology Session: 2013-14Dokumen22 halamanSubject: Biology Session: 2013-14prayaasplbBelum ada peringkat
- EcologyDokumen26 halamanEcologyMadhu Mangal KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1 Basic EcologyDokumen7 halamanLesson 1 Basic EcologyEdgardo TangalinBelum ada peringkat
- ZLY 101 Notes-1-1Dokumen11 halamanZLY 101 Notes-1-1abdulmaliqopeyemi04Belum ada peringkat
- Environmental LawDokumen95 halamanEnvironmental LawRastogi RahulBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Bio200 Chapter 31Dokumen20 halaman6 Bio200 Chapter 31api-153638948Belum ada peringkat
- Ecosystems: 4.1 Definition and Concept of EcologyDokumen41 halamanEcosystems: 4.1 Definition and Concept of EcologylibrarianBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 PDFDokumen1 halamanLecture 1 PDFEhsan GujjarBelum ada peringkat
- Ecological Principles and Concepts ScriptDokumen10 halamanEcological Principles and Concepts ScriptJaffy Bustamante0% (1)
- Ecosystem and Their ServicesDokumen22 halamanEcosystem and Their ServicesMauro Valdivia CarterBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - 1 (Ecology PPT) 23-07-2015Dokumen36 halamanLecture - 1 (Ecology PPT) 23-07-2015RAJESH KUMAR BARANWAL33% (3)
- EcologyDokumen26 halamanEcologyAnime LoverBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Module2Dokumen10 halamanEnvironmental Module2maris bitasoloBelum ada peringkat
- Ecology in 40 CharactersDokumen25 halamanEcology in 40 CharactersVaibhav ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Autecology Is The Ecology of A Single SpeciesDokumen23 halamanAutecology Is The Ecology of A Single SpeciesmaygracedigolBelum ada peringkat
- Isu Module For Ee 327 Environmental Science and Engineering Bsee 3Dokumen22 halamanIsu Module For Ee 327 Environmental Science and Engineering Bsee 3Army Joel MarianoBelum ada peringkat
- Interconnected Ecosystem Components and Organism InteractionsDokumen9 halamanInterconnected Ecosystem Components and Organism InteractionsJoris YapBelum ada peringkat
- SUSTAINABLE ARCHITECTURE HISTORIC AND COMMUNITY PERSPECTIVEDokumen5 halamanSUSTAINABLE ARCHITECTURE HISTORIC AND COMMUNITY PERSPECTIVEharai prasadBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Simple EcosystemsDokumen11 halamanStudy of Simple EcosystemsShaunak De60% (5)
- Introduction to Environmental IssuesDokumen10 halamanIntroduction to Environmental Issuesbahru demekeBelum ada peringkat
- ScopeDokumen7 halamanScopemkray0Belum ada peringkat
- Hand3 I PDFDokumen11 halamanHand3 I PDFankit pandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Ecosystem: Reliable Sources Challenged RemovedDokumen12 halamanEcosystem: Reliable Sources Challenged RemovedSailaja Sankar SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Law Document Explains Key ConceptsDokumen95 halamanEnvironmental Law Document Explains Key ConceptssubhashcmBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Test 2 P-5 Envirnmental ManagementDokumen13 halamanUnit Test 2 P-5 Envirnmental Managementpankajsharma130Belum ada peringkat
- Crop Ecology and Cropping SystemsDokumen252 halamanCrop Ecology and Cropping SystemsBirhanu GebeyehuBelum ada peringkat
- Es Digital NotesDokumen27 halamanEs Digital NotesInstagramBelum ada peringkat
- Insect Ecology (Fourth Edition), 2016 - Timothy SchowalterDokumen12 halamanInsect Ecology (Fourth Edition), 2016 - Timothy SchowalterJefferson SepúlvedaBelum ada peringkat
- EcologyDokumen2 halamanEcologyZel's FieldBelum ada peringkat
- Types of EcologyDokumen8 halamanTypes of EcologypriyaBelum ada peringkat
- Full BookletDokumen28 halamanFull BookletMukesh ManwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical FertilizerDokumen3 halamanChemical Fertilizeramol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Project On Study of Antacids For Class 12 CBSEDokumen13 halamanChemistry Project On Study of Antacids For Class 12 CBSEJunaid Khan75% (4)
- Online Complaint Management SystemDokumen67 halamanOnline Complaint Management Systemamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)88% (65)
- Wireless Seminar ReportDokumen36 halamanWireless Seminar Reportamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)0% (1)
- Soil BiodiversityDokumen14 halamanSoil Biodiversityamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Nursery ManagementDokumen59 halamanNursery Managementamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)50% (2)
- Bus ReservationDokumen26 halamanBus ReservationPrashant Jachak0% (1)
- Employee Management SystemDokumen35 halamanEmployee Management Systemravikumar_ch33% (6)
- 11 Cells and BatteriesDokumen21 halaman11 Cells and BatteriesSok SinBelum ada peringkat
- Determinatio of Acid Contents in Sour FruitsDokumen12 halamanDeterminatio of Acid Contents in Sour Fruitsamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)70% (20)
- Winemaking: ProcessDokumen8 halamanWinemaking: Processamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Science Chemistry Teaching Resources Documents POTENTIOMETRYDokumen60 halamanScience Chemistry Teaching Resources Documents POTENTIOMETRYamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Determinatio of Acid Contents in Sour FruitsDokumen12 halamanDeterminatio of Acid Contents in Sour Fruitsamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)70% (20)
- Types of Fuel and Their CharacteristicsDokumen13 halamanTypes of Fuel and Their CharacteristicsjacopanyBelum ada peringkat
- Study On Biodiversity of Soil FungiDokumen8 halamanStudy On Biodiversity of Soil Fungiamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Early Life: Vasco Da Gama, 1stDokumen1 halamanEarly Life: Vasco Da Gama, 1stamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- What Is PersonalityDokumen3 halamanWhat Is Personalityamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)100% (1)
- Vedic Method of MathDokumen3 halamanVedic Method of Mathamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Vikram Ambalal SarabhaiDokumen2 halamanVikram Ambalal Sarabhaiamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- The PH of Various Water SamplesDokumen4 halamanThe PH of Various Water Samplesamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- What Is Land Pollution by Chemical ResedueDokumen4 halamanWhat Is Land Pollution by Chemical Resedueamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- No Smoking PhotoDokumen5 halamanNo Smoking Photoamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Festivals of IndiaDokumen4 halamanFestivals of Indiaamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Policies Unauthorized Computer Network: Network Security Consists of TheDokumen19 halamanPolicies Unauthorized Computer Network: Network Security Consists of Theamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Early Life: Research in Nuclear PhysicsDokumen2 halamanEarly Life: Research in Nuclear Physicsamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Homi Jehangir Bhabha: हहोममी भभाभभा 30 October 1909, (present-day India)Dokumen2 halamanHomi Jehangir Bhabha: हहोममी भभाभभा 30 October 1909, (present-day India)amol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- What Is Floriculture?: ChrysanthemumDokumen4 halamanWhat Is Floriculture?: Chrysanthemumamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Tree Fruit Crops: Apples . Apples AreDokumen5 halamanTree Fruit Crops: Apples . Apples Areamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Belum ada peringkat
- Bio-Diversity Uses Threats and ConservationDokumen32 halamanBio-Diversity Uses Threats and ConservationRoshin VargheseBelum ada peringkat
- Aquaponics ProjectDokumen5 halamanAquaponics Projectキャベ ジョセルBelum ada peringkat
- Rankem SolventsDokumen6 halamanRankem SolventsAmmar MohsinBelum ada peringkat
- Phyllodes Tumors of The Breast UpToDateDokumen22 halamanPhyllodes Tumors of The Breast UpToDateSean SialanaBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Powder Technology: Kandasamy Saravanakumar, Myeong-Hyeon WangDokumen9 halamanAdvanced Powder Technology: Kandasamy Saravanakumar, Myeong-Hyeon WangsilviaBelum ada peringkat
- Quantitative Analysis of The Relative Effectiveness of 3 Iliotibial Band StretchesDokumen4 halamanQuantitative Analysis of The Relative Effectiveness of 3 Iliotibial Band Stretchessalthill01Belum ada peringkat
- CIP Annual Report 2007Dokumen96 halamanCIP Annual Report 2007cip-libraryBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Stress Fact SheetDokumen3 halamanHeat Stress Fact SheetjacquestsBelum ada peringkat
- Birds of Prey PDFDokumen24 halamanBirds of Prey PDFPaula MatosBelum ada peringkat
- Karakterisasi Koleksi Plasma Nutfah Tomat Lokal Dan IntroduksiDokumen7 halamanKarakterisasi Koleksi Plasma Nutfah Tomat Lokal Dan IntroduksiAlexanderBelum ada peringkat
- Competitive Intelligence AcceraDokumen29 halamanCompetitive Intelligence AcceranarenebiowebBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study On Dengue FeverDokumen76 halamanCase Study On Dengue FeverMary Rose Silva Gargar0% (1)
- Water Indices For Water UsesDokumen12 halamanWater Indices For Water UsesWayaya2009Belum ada peringkat
- Pone 0097013 s001Dokumen400 halamanPone 0097013 s001Nomeda PetrauskaiteBelum ada peringkat
- biology_at_ease Scientists and Their Discoveries in BiologyDokumen7 halamanbiology_at_ease Scientists and Their Discoveries in BiologySomya Kataria0% (1)
- Allplex SARS-CoV-2 Variant I AssaysDokumen1 halamanAllplex SARS-CoV-2 Variant I AssaysadibyanBelum ada peringkat
- Cultivo de CianobacteriasDokumen35 halamanCultivo de CianobacteriasArmando Chiclla SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Embryo RescueDokumen8 halamanEmbryo RescuesathyaBelum ada peringkat
- Erl mf2 PDFDokumen2 halamanErl mf2 PDFJorgeBelum ada peringkat
- Microfossils Description Paper: Palaeontology Practical: KalpanadekakalitaDokumen32 halamanMicrofossils Description Paper: Palaeontology Practical: Kalpanadekakalitarikalave ramanBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of Florfenicol Following Intravenous, Intramuscular and Oral Administrations in RabbitsDokumen10 halamanPharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of Florfenicol Following Intravenous, Intramuscular and Oral Administrations in RabbitsJohanna Valentina López CortesBelum ada peringkat
- Study Guide Lecture Exam 1 Use This Handout With Your Video Review Possible Essay QuestionsDokumen4 halamanStudy Guide Lecture Exam 1 Use This Handout With Your Video Review Possible Essay QuestionsBrandice BradleyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 Physical Development BerkDokumen14 halamanChapter 8 Physical Development BerkMARIAH HOLLETTBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On Hydration PDFDokumen17 halamanPresentation On Hydration PDFManuel CastroBelum ada peringkat
- TATIANADokumen8 halamanTATIANAKaizer NdoloBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Drug Targets-1Dokumen75 halamanMolecular Drug Targets-1Phoebe Llamelo100% (1)
- Effects of Air Pollutants On Mediterranean and Temperate Forest EcosystemsDokumen263 halamanEffects of Air Pollutants On Mediterranean and Temperate Forest EcosystemsPACIFIC SOUTHWEST RESEARCH STATION REPORTBelum ada peringkat
- DocumentDokumen7 halamanDocumentDébàshis Dash50% (2)
- Menthae Piperitae FoliumDokumen2 halamanMenthae Piperitae FoliumartemBelum ada peringkat
- Cell SignalingDokumen1 halamanCell SignalingNathan Stuart The Retarded idiotBelum ada peringkat