Scan 0008
Diunggah oleh
ilias19730 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan1 halamanII
Judul Asli
97426797 Scan 0008
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniII
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan1 halamanScan 0008
Diunggah oleh
ilias1973II
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
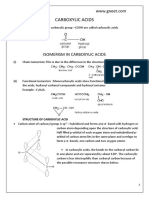
SOLUTION (GIST POINTS)
Concentration of Solutions: es 7
‘wiw'h Composition: | Mass of solute present per 100 a. of solution ]
Siti 3a 100
| w/w Composition = eres
Molarity (Mi: " Wo. of moies of solute present per iter of solution in called ‘molarity of solution It
is temperature dependent M= No. of Moles of solute / Volume of solution in litre
| Molality (mj: 'No. of moles of solute present per kg. of solvent is called molality. Itis temperature
| independent_m= No. of Moles of solute / Mass of Solvent in Kg
| NormaiityiNi: 'No, of gram equivalent of solute present per ier of solution is called normality of
solution
'N-= No, of gm equivalent of solute / Volume of solution in ire |
Parts Per Million It is used for very dilute solutions, Parts of solute in per million parts of solution |
sa Dr = Part of solute x10° / Part of solution
| Mole Fraction: Ratio of moles of components to total no. of moles of all the components of |
| iat solution is called mole fraction (x) of the component.
Henry's law :- “The partial pressure of the gas in vapour phase p is proportional to the mole fraction of the
gas x in the solution.” P=Kyx
Applications of Henery Law(1) In Packing of soda/ Soft drinks(2) In Deep see diving( He = 11.7% , No=
156.2% and, 2 =32.1% )(3) Functions of lungs (4)At high altitudes pressure is low there for breathing
problems lead to ANOXIA (unable to think and weak)
Vapour Pressure: The pressure exerted by vapours over the liquid surface at equilibrium is called vapour
pressure of the liquid
Raoult’s Law: The V.P. of any volatle component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction”.
Raoult Law for Solutions Containing Non-Volatile Solute | Raoult's Law for Solution Containing Volatile Solute
Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions:
Ideal Solution Non Ideal Solution
Follows Raoults law at all temperature and Does not follow Raoutt’s law at all
concentrations. P = Pa + Ps temperature and pressure. P # P, + Pp
Intermolecular forces in resulting solution are same as | Intermolecular forces in resulting solution
in pure components. are different from the inter molecular force
|A-8 senrasneen #A-A,B
|/No change in volume while mixing components. CChange in volume while mixing components.
AVmix=0
'No heat change take place while mixing
‘components. 4H mix = 0
Eg: n— hexane + n— heptanes & benzene + toluene
__Non Ideal Solution ae
‘Showing Positive elevation from Raoult’s Law _| Showing Negative Deviation from Raoult’s Law
Vapour pressure of resulting solution is greater | Vapour pressure of resulting solution is less than |
than sum of partial pressure of components. P > | sum of the partial pressure of pure components. _
| components. A H mix # 0
| Eg: Acetone + Water &Acetone + CHCl,
Pa Po a P< Pat Pp |
| Resulting intermolecular force is weaker than pure | Resulting intermolecular force is stronger than
components. pure components. Fe
eS AV mix = He AV mix
Volume of solution > Sum of volume of ‘Volume of solution < Sum of volume of
pure compor Se _pure components
[BHimix = #ve —Endothermic mi DH mix=-ve Exothermic process i
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 18 GroupDokumen3 halaman18 Groupilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- Basics of Reaction Mechanism PDFDokumen22 halamanBasics of Reaction Mechanism PDFilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- Carboxylic AcidsDokumen14 halamanCarboxylic Acidsilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- XI Chemistry Chapterwise Topicwise With Solution PDFDokumen227 halamanXI Chemistry Chapterwise Topicwise With Solution PDFilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- 12 Chemistry Revision Book Chapter 3 PDFDokumen49 halaman12 Chemistry Revision Book Chapter 3 PDFDeepak PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch07 The Pblock ElementsDokumen10 halaman12 Chemistry Notes Ch07 The Pblock ElementsSwaroop SurendraBelum ada peringkat
- 2014 12 Lyp Chemistry Compt 04 Outside DelhiDokumen12 halaman2014 12 Lyp Chemistry Compt 04 Outside Delhiilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- 4.3 Rates A Levels ChemistryDokumen18 halaman4.3 Rates A Levels ChemistrychwalidBelum ada peringkat
- RevisionChemistryQPAK PDFDokumen5 halamanRevisionChemistryQPAK PDFilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Solid StateDokumen36 halaman1.1 Solid Stateilias1973100% (1)
- Scan 0005Dokumen1 halamanScan 0005ilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class XII SyllabusDokumen5 halamanCBSE Class XII Syllabusilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- Question Bank Chemistry-Xii The Solid State CHAPTER - 1 (Weightage 4 Marks) Very Short Answer Type Questions (Of 1 Mark Each)Dokumen63 halamanQuestion Bank Chemistry-Xii The Solid State CHAPTER - 1 (Weightage 4 Marks) Very Short Answer Type Questions (Of 1 Mark Each)Shiv GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 LogarithmDokumen1 halaman2 Logarithmilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- Particles Equations Past Paper QuestionsDokumen10 halamanParticles Equations Past Paper Questionsilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- SBI PO Exam 2013 Previous Year Question Paper 1Dokumen19 halamanSBI PO Exam 2013 Previous Year Question Paper 1umaannamalaiBelum ada peringkat
- 11 ChemDokumen3 halaman11 Chemilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Igcse 1 PDFDokumen35 halamanChemistry Igcse 1 PDFRohit MITTALBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch07 The Pblock ElementsDokumen10 halaman12 Chemistry Notes Ch07 The Pblock ElementsSwaroop SurendraBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Chemistry Impq Ch08 Redox ReactionDokumen6 halaman11 Chemistry Impq Ch08 Redox Reactionilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- 11 Chemistry NcertSolutions Chapter 7 Exercises 2 PDFDokumen14 halaman11 Chemistry NcertSolutions Chapter 7 Exercises 2 PDFilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- Synonyms PDFDokumen3 halamanSynonyms PDFilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- U12 Redox ElectrochemDokumen4 halamanU12 Redox Electrochemilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- Chemsheets A2 009 (Acids & Bases)Dokumen21 halamanChemsheets A2 009 (Acids & Bases)ilias197380% (5)
- Transition Metals: REVISIONDokumen11 halamanTransition Metals: REVISIONAmeenIbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- CH 13 AminesjDokumen2 halamanCH 13 Aminesjilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- 11 Chemistry NcertSolutions Chapter 7 Exercises 2 PDFDokumen14 halaman11 Chemistry NcertSolutions Chapter 7 Exercises 2 PDFilias1973Belum ada peringkat
- IbchkineticsDokumen16 halamanIbchkineticsapi-293306937Belum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)