AnaPhy Lab Exercise 24-41
Diunggah oleh
Angelyka Cabalo50%(2)50% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
588 tayangan6 halaman2A-PH 2016-2017
Seeley's
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Ini2A-PH 2016-2017
Seeley's
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
50%(2)50% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
588 tayangan6 halamanAnaPhy Lab Exercise 24-41
Diunggah oleh
Angelyka Cabalo2A-PH 2016-2017
Seeley's
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
Angelyka Cabalo
2APH
AnaPhy Lab
Exercise 24 ENDOCRINE STRUCTURE AND
FUNCTION
Endocrine System
- composed of glands that release
hormones into the bloodstream
- hormones help maintain homeostasis
- major glands : pineal gland,
hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid
gland, parathyroid glands, thymus
gland, adrenal gland, pancreas,
ovaries and testes
Exercise 25 COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
Blood
- flows and circulates w/in
cardiovascular system
- connective tissue, mesenchymal in
origin
- has liquid matrix
serum clotted blood; w/o
fibrinogen
plasma unclotted blood
Blood Tests
- for clinical evaluation of patients
- blood samples are collected
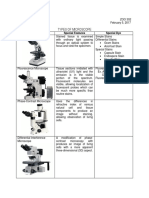
Hemacytometer
- counting the cellular elements of the
blood (RBC,WBC & platelets)
counting chamber
Neubauer improved counting
chamber
~ heavy, colorless glass
~ has 3 parallel platforms
separated by moats
~ central platform : 0.1mm
lower
~ 3x3mm / 9 mm2
~ 4 corner 2o square
(W1,2,3,4) is for WBC
count (16 3o squares)
~ central 2o square
(R1,2,3,4,5) is for RBC (25
3o squares)
~ ordinary cover slip has
uneven surface so it
cannot be used
WBC pipette
RBC pipette
Hematocrit
- volume of packed red cells after
centrifugation of blood samples
packed cell volume (PCV)
simplest & most accurate
more useful than RBC count
measure of the proportion of red cells
to plasma in peripheral blood
- % of erythrocytes in whole blood
Male
47 +/- 7 volume %
Female
42 +/- 5 volume %
At birth
56 +/- volume %
Increase Polycythemia, shock & severe
d in
dehydration
Decreas
Leukemia, anema,
ed in
hyperthyroidism & cirrhosis
Adams Micromethod
- capillary tube filled w/ blood
- cover with sealing clay
- microhematocrit centrifuge
- 10,000 rpm for 4-5 mins
- microhematocrit reader
Hemoglobin
- pigment in RBC that has affinity to O2
- blood : the darker color, the more
hemoglobin
Male
14-16.5 g / 100 mL
Female
12-15 g / 100 mL
Increase High altitudes, obstructive
d in
pulmonary disease, CHF &
polycythemia
Decreas Severe hemorrhage, anemia,
ed in
hyperthyroidism & liver cirrhosis
Acid-Hematin Method
- a. 0.01N HCl : 2 mark : Sahlis tube
- b. 0.02 mL blood : Sahlis pipette
- combine a + b
- adding distilled H2O until the mixture
matches the color of the comparator
block
WBC Count
- no. of WBC in 1 mm3 of blood
- its good diluting fluid is :
hypotonic solution
easily prepared
cheap
readily available
a good preservative
- Blood : 0.5 mark WBC pipette
- Diluting fluid : 11 mark
- 1:20 or 1/20 dilution
- discard first 2-3 drops
- by capillary action : fill the counting
chamber
- angle of pipette : 30-35 degrees
- overcharging : fluid on the moats
undercharging : failure to cover entire
ruled area
- air bubbles = moisture or dirt
- use LPO
RBC Count
- no. of RBC in 1 mm3 of blood
- good diluting fluid :
isotonic solution
has high sp gr
easy to prepare
cheap
good preservative
has buffer action
does not initiate growth of
molds
- blood : 0.5 mark RBC pipette
- diluting fluid : 101 mark
- 1:200 or 1/200 dilution
- discard first 5-6 drops
- by capillary action
- angle of pipette : 30-35 degrees
- HPO for actual counting
Differential White Blood Cell Count
Granulocytes
Eosinophils
2-4 %
Allergic
reactions
Basophils
0.5-1 % Chronic
infections
Neutrophils
60-70
Acute
%
infections
Aggranulocyt
es
Lymphocytes
20-25 % Antibody
reactions
Monocytes
3-8 %
Chronic
infections
Slide
-
Method
50o angle of another slide
stain the smeared blood
zigzag way of counting
Exercise 26 THE BLOOD GROUPS
Antigens
- on surface of RBC
- agglutinogens
- inherited
Antibodies
- in the plasma
- agglutinins
ABO Grouping
- Anti-A antiserum (blue)
- Anti-B antiserum (yellow)
Rh Grouping
- Anti-D antiserum (colorless)
ABO group
A
B
AB
O
Rh group
Positive
Anti-A
+
+
-
Anti-B
+
+
-
Ab A
+
+
Ab B
+
+
w/
natio
negative
w/o
agglut
i
agglut
i
natio
Exercise 27 COAGULATION TIME
Clotting
- important in arresting hemorrhage
- 3-6 mins
Clot
Drop
-
plugs the opening of the wound
/ Slide Method
30 sec interval
from the moment the blood drops to
the slide until the formation of the
fibrin thread
Exercise 28 BLEEDING TIME
Bleeding time
- refers to the time it takes for a
puncture wound to stop bleeding
- 1-3 mins
- depends upon the depth of the wound
and degree of hyperemia in the finger
Dukes Method
- first drop of blood blotted on a filter
paper
- rough surfaces shorten bleeding time
- appearance of first drop to the time
bleeding stops
Exercise 29 HYPEREMIA OR CONGESTION
Hyperemia / Congestion
- increase of blood flow or an excess
flow of blood in the vessel in a certain
area of the body
Active Hyperemia
- increased blood flow to a specific
area / dilation of blood vessels
Passive Hyperemia
- slowing down of venous return
Exercise 30 CAPILLARY RESISTANCE TEST
Capillary resistance test
measures the ability of the capillary
walls to resist pressure
- arm : 100 mmHg
Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- capillaries will rupture at this pressure
Petechiae / Hemorrhages
- tiny spots
Tourniquet / Rumpel-Leede / Hess Test
No of petechiae
Grade
0-10
1+
11-20
2+
21-50
3+
51 and above
4+
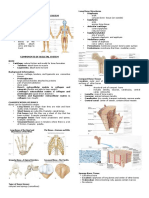
Exercise 31 ANATOMY OF THE HEART
Pericardium
- membrane that surrounds and
protects the heart
Fibrous Pericardium
~ Tough, dense and
inelastic connective
tissue
~ Prevents the
overstretching of the
heart
Serous Pericardium
~ Thinner, more delicate
~ Forms a double layer
around the heart
Parietal layer
Visceral layer
Pericardial space (w/
pericardial fluid) reduces
friction
Heart
- muscular pump
- w/ four chambers (right & left atria &
ventricle)
- contracts continuously
- exhibits auto-rhythmicity
- 5 in long, 3.5 in wide and 2.5 in thick
- female : 250 g while male : 300 g
- rests in the mediastinum and
diaphragm
Apex
- pointed end
Base
- broad opposite end
Musculi Pectinati
- myocardial ridges in right atrium
Interatrial Septum
- separates the atria
Foramen Ovale : hole in infants
blood bypass the lungs and pass from
right to left atrium (Foramen Ovalis)
Trabeculae Carneae
- muscle ridges in ventricles
Interventricular Septum
- separates the ventricles
Chordae Tendineae
- string-like
- attached to papillary muscles
- connected to atrioventricular valves
tricuspid valve (right)
bicuspid/mitral valve (left)
AV and Semilunar Valves
- prevents reflux or backflow of blood
-
Exercise 32 PULSE RATE IN HUMANS
Pulse
- alternate constriction and dilation of
an artery
- all arteries have a pulse
- readily palpable at the wrist (radial
artery)
- number of beats per minute
- 4 beats for every respiration
Exercise 33 HEART SOUNDS IN HUMANS
Auscultation
- process of listening to the sounds w/in
the body
- using stethoscope
Heart Sound
- result of turbulence caused by closure
of the heart valves
One heartbeat = lub dub
Exercise 34 CARDIAC CYCLE IN HUMANS
Cardiac cycle
- 1 Heartbeat = 1 cardiac cycle
- atrial and ventricular systole
(contraction) and diastole (relaxation)
- 60 sec / pulse or heart rate
Heart rate
- number of beats per minute
- not necessarily equal to pulse rate
Systole = 0.04 seconds
Exercise 36 BLOOD PRESSURE
Heartbeat
- forces blood into the aorta
Systolic pressure
- peak pressure obtained during cardiac
cycle
measure of the force of myocardial
contraction
Diastolic pressure
- lowest pressure reach just before the
next beat
- measure of the peripheral resistance +
elastic recoil of blood vessels
Sphygmomanometry
- measure arterial blood pressure
- sphygmomanometer
Palpation Method
- palpate the pulse at the radial artery
Auscultation Method
- on antecubital fossa in the brachial
artery region
Exercise 37 ANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY
SYSTEM
Respiratory System
- composed of the nose, pharynx,
larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs
- upper and lower respiratory system
- composed of tubes and cavities that
interconnect outside and w/in the
lungs and respiratory portion
Otorhinolaryngology
- branch of medicine that deals w/ the
diagnosis and treatment of disorders
associated w/ nose, ears and throat
Pulmonology
- concerned w/ diseases associated w/
the lungs
Exercise 38 PULMONARY VOLUMES AND
CAPACITIES
Spirometry
- lab procedure
- determines the strength of the lungs
- tool to diagnose the nature of
respiratory defects
- aid in the selection of the most
specific and effective therapy for diff.
respiratory disorders
Respiratory cycle
- 2 phases : inhalation & exhalation
Ventilation
- movement of air into & out of the
respiratory tract
- critical for normal body functions
Spirometer
- instrument used to measure volume of
air that moves into & out of the lungs
Wet Spirometer
inverted drum in a tank of water
suspended from a pulley &
counterbalanced by a weight
- w/ a corrugated tube
Spirogram
- record of pulmonary volumes using
spirometer
Tidal
Amt. of air during
500
Volume / Air
normal respiration
mL
(TV)
Inspiratory
Max. vol. of air that
3,10
Reserve
can be inhaled
0 mL
Volume (IRV)
(normal inhalation)
Expiratory
Vol. of air that can
1,20
Reserve
be exhaled
0 mL
Volume (ERV) forcefully (normal
inhalation)
Residual
Vol. of air that
1,20
Volume (RV)
remains in the lungs 0 mL
after a most forceful
exhalation
Inspiratory
Capacity (IC)
Functional
Residual
Capacity
(FRC)
Vital Capacity
(VC)
Total Lung
Capacity
(TLC)
Cannot be
measured by
spirometry
TV + IRV
RV + ERV
IRV + TV + ERV
TV + RV + IRV +
ERV
3,60
0 mL
2,40
0 mL
4,80
0 mL
6,00
0 mL
Residual Volume
Gender
Age Equation (in L)
Male/Fe
<1 (0.020 x height in inches)
male
9
0.91092
Female
19- (0.0813 x ht in) + 0.009 x
99
age in yrs (3.9)
Male
19- (0.0686 x ht in) + (0.017
99
x age in yrs (3.45)
Exercise 39 BREATH-HOLDING TIME
Hyperventilation
- fast, deep breathing
- brought by anxiety attacks
may lead to brief periods of apnea or
cessation of breathing
- build-up of CO2 in blood
- may experience dizziness or may faint
(alkalosis constrict cerebral blood
vessels)
- breathe into a paper bag
Hypoventilation
- slow, shallow breathing
Carbonic Acid
- greatly increases during
hypoventilation
- decreases in hyperventilation
Acidosis / Alkalosis
- result of affected buffering ability of
the blood
Cyanosis
- breathing stops for an extended period
of time
- insufficient oxygen in the blood
Exercise 40 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM STRUCTURE
AND FUNCTION
Digestive System
- organs of gastrointestinal Tract (GI
tract)
mouth
pharynx
esophagus
stomach
small intestine ( duodenum,
jejunum, ileum)
large intestine
colon
anus
and accessory structures
teeth
tongue
salivary glands
liver
gallbladder
pancreas
- for ingestion of food, secretion of
digestive juices, mixing, digestion,
absorption and elimination of waste
products
Digestion
- mechanical and chemical digestion of
food
Mechanical Digestion
- starts when mouth does the
perfunctory functions of chewing &
masticating
segmentation contractions : churning
of food by smooth muscle movements
Chemical Digestion
- enzymes break down macromolecules
of carbs, lipids & proteins
~ Amylase -- digests starch
~ Lipase digests lipids
~ Pepsin digests proteins
Digestion of Starch by Amylase
- Loefflers test tubes
- 37oC water bath
Determination of the Amt of Starch
- spot place
- lugols iodine solution
Brown or other color
Light blue
+
Medium blue
++
Dark blue
+++
Black
++++
Determination of Sugar
- Benedicts reagent
- Hot water for 3 mins
Blue
Green
+
Yellow
++
Orange
+++
Red
++++
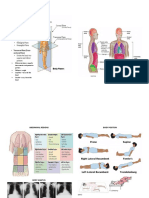
Exercise 41 EXCRETORY SYSTEM
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
Excretory System
- kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder &
urethra
Urine
- forms in the kidney
- flows through the ureters
- temporarily stored in the urinary
bladder
- eliminated through the urethra
Kidneys
- bean-shaped retroperitoneal organs
- found between T12 and L3
~ Renal Hilus vertical fissure in
the concave surface
~ Renal Fascia attaches the
kidney to the abdominal wall
~ Renal Capsule covers the
outer surface of the kidney
~ Adipose Capsule padding &
protection
- has 3 main regions
Renal Cortex smooth area
which extends as the renal
column in bet. renal pyramids
(cone-shaped; deep in renal
medulla; apex points into renal
sinus as renal papilla)
Renal Medulla
Renal Sinus contains the minor
calyces, drain into major
calyces which drain into renal
pelvis ; expansion of ureter
Ureter
- measures 25-30cm long
Urinary Bladder
- hollow, pear shaped organ
- collection & disposal of urine
- male : anterior to rectum, posterior to
symphysis pubis
female : anterior to vagina, posterior
to pubic symphysis, inferior to uterus
Urethra
- carries urine from bladder
- process of micturition
- female : 4cm
- male : 15-20cm
- prostatic (along prostate gland),
membranous (bet. prostate & penis) &
spongy (along penis)
Urine
- formed by 1 million nephrons
- removal of nitrogenous waste products
of metabolism
- urinalysis (study of physical, chemical
& microscopic characteristics)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Head Eyes: Head To Toe AssessmentDokumen2 halamanHead Eyes: Head To Toe AssessmentVijungco88% (8)
- Lab 6 Tissue Answers PDFDokumen9 halamanLab 6 Tissue Answers PDFJameson Ephisson Ferguson Forson100% (3)
- Anatomy Chapter 2 Test Answer KeyDokumen4 halamanAnatomy Chapter 2 Test Answer KeyOlalekan Oyekunle100% (1)
- 242c33f8 A8d5 9ab6 F6ac A366ee824b75 Wecan DancinghandDokumen160 halaman242c33f8 A8d5 9ab6 F6ac A366ee824b75 Wecan DancinghandTourya Morchid100% (1)
- Thyroid & Parathyroid GlandsDokumen21 halamanThyroid & Parathyroid GlandsAzizan HannyBelum ada peringkat
- Medico-Legal Aspects of Death DeterminationDokumen19 halamanMedico-Legal Aspects of Death DeterminationTIPAY, EMELIE L.100% (1)
- Shapes of Bacterial Cell.Dokumen17 halamanShapes of Bacterial Cell.Galaxina BraileyBelum ada peringkat
- MicroscopeDokumen4 halamanMicroscopeBryan PaulBelum ada peringkat
- The Resident's Guide To LMCC II (And MCC Qualifying Exam II)Dokumen56 halamanThe Resident's Guide To LMCC II (And MCC Qualifying Exam II)bobsherif86% (7)
- Respiratory Physiology OverviewDokumen7 halamanRespiratory Physiology OverviewMac Vince HipolitoBelum ada peringkat
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesDokumen9 halamanClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesAngelyka Cabalo100% (1)
- Assessing The Thorax and LungsDokumen4 halamanAssessing The Thorax and LungsLorenz Jude Cańete100% (2)
- PharDose Lab Prep 19-30Dokumen4 halamanPharDose Lab Prep 19-30Angelyka Cabalo100% (1)
- Demonstration of The Reflex Pathway in FrogsDokumen12 halamanDemonstration of The Reflex Pathway in FrogsRuwiniRajakarunaBelum ada peringkat
- Phlebotomy in A NutshellDokumen131 halamanPhlebotomy in A Nutshellgreen_archerBelum ada peringkat
- Pdose Lab 8-15Dokumen2 halamanPdose Lab 8-15Angelyka Cabalo100% (1)
- Clinical 20manual 20for 20oral 140206021148 Phpapp02 PDFDokumen561 halamanClinical 20manual 20for 20oral 140206021148 Phpapp02 PDFAnca MartinoviciBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionsDokumen9 halamanQuestionsDennis Dane AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Lymphatic SystemDokumen22 halamanLymphatic SystemArnab GuinBelum ada peringkat
- PAHS ED Protocol Edition ThreeDokumen315 halamanPAHS ED Protocol Edition ThreeNeha Shrestha100% (3)
- (Chapter 1 and 2) : Anaphy Quiz Reviewer (Chapters 1-3)Dokumen20 halaman(Chapter 1 and 2) : Anaphy Quiz Reviewer (Chapters 1-3)Mariam GamosBelum ada peringkat
- Vital SignsDokumen97 halamanVital SignsPrincess Mariscotes100% (1)
- Human Respiratory System ExperimentDokumen6 halamanHuman Respiratory System ExperimentRohan Saste100% (1)
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 1Dokumen29 halamanHealth Optimizing Physical Education 1Julie Anne Tolentino70% (27)
- Lab 2 Nursing Skill - Vital Sings 2021Dokumen10 halamanLab 2 Nursing Skill - Vital Sings 2021PHOEBE Ci100% (1)
- Heart Dissection WorksheetDokumen5 halamanHeart Dissection Worksheetapi-237875296100% (1)
- Peripheral Vascular and Lymphatic System AssessmentDokumen37 halamanPeripheral Vascular and Lymphatic System AssessmentSuzanne Rush100% (3)
- 6 Microbial ControlDokumen36 halaman6 Microbial ControlGladish RindraBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphy Free Sample ExamDokumen5 halamanAnaphy Free Sample ExamNurse UtopiaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Review Group Analytical Chemistry Solubility and Volumetric AnalysisDokumen8 halamanChemistry Review Group Analytical Chemistry Solubility and Volumetric AnalysisLouisiana SollestreBelum ada peringkat
- The Cardiovascular System: The HeartDokumen16 halamanThe Cardiovascular System: The HeartNicoleTrishiaDeparineBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDokumen8 halamanAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerMildred Santos AnchetaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is PeritonitisDokumen9 halamanWhat Is PeritonitisArsitoBelum ada peringkat
- Post Lab. Exs. 8-35 PhyanaDokumen33 halamanPost Lab. Exs. 8-35 PhyanaChesmar Macapala100% (7)
- Phyana Lab Ex. 8-15, 35Dokumen4 halamanPhyana Lab Ex. 8-15, 35Raul Mangrobang100% (1)
- Biochem Lec ReviewerDokumen8 halamanBiochem Lec ReviewerHelen Mari PublicoBelum ada peringkat
- Analec Reviewer MichieDokumen9 halamanAnalec Reviewer MichieMichieBelum ada peringkat
- Physiological ApparatusDokumen4 halamanPhysiological ApparatusRenai MaticBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 2 FORMAL REPORT DraftDokumen11 halamanExperiment 2 FORMAL REPORT DraftChristine Danica Bitera100% (1)
- STUDY QUESTIONS - Digestive SystemDokumen3 halamanSTUDY QUESTIONS - Digestive SystemValenz AbrugarBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Halide Classification TestsDokumen3 halamanOrganic Halide Classification TestsROSEMARIE ONGBelum ada peringkat
- BIO024 Session-1 IGDokumen6 halamanBIO024 Session-1 IGKenny McCormickBelum ada peringkat
- STOICHIOMETRYDokumen4 halamanSTOICHIOMETRYKrisjohn Paul Flores0% (1)
- Freezing Point DepressionDokumen4 halamanFreezing Point DepressionJuan Agustin Garcia TancoBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 11 LAB REVIEW: MICROSCOPY, CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONSDokumen6 halamanBIO 11 LAB REVIEW: MICROSCOPY, CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONSJewelle Anne Estanilla LimenBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Exam Papers Cover Anatomy and Physiology TopicsDokumen15 halamanNursing Exam Papers Cover Anatomy and Physiology TopicsAnubhav ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 10Dokumen4 halamanExercise 10aker39Belum ada peringkat
- Pharchem Lecture Chap 6Dokumen12 halamanPharchem Lecture Chap 6Charm MatiasBelum ada peringkat
- Carroll Lab Chap 3Dokumen8 halamanCarroll Lab Chap 3Aya Karlmela LangresBelum ada peringkat
- Which of The Following Statements About The Equivalence Point of An AcidDokumen10 halamanWhich of The Following Statements About The Equivalence Point of An AcidCorrine PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Ymphatic Ystem: Natomy AND HysiologyDokumen7 halamanYmphatic Ystem: Natomy AND Hysiologydlneisha61Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry of Ribonucleic AcidDokumen10 halamanChemistry of Ribonucleic AcidPrince DannBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 Determination of PHDokumen5 halamanExperiment 1 Determination of PHRoselle AbrazaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Column and Thin Layer Chromatography: Malunggay (Moringa Oleifera)Dokumen3 halamanColumn and Thin Layer Chromatography: Malunggay (Moringa Oleifera)Rico RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- ANAPHY REVIEWER (MDL+QSTNS)Dokumen170 halamanANAPHY REVIEWER (MDL+QSTNS)Jewell Nivera CarpioBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Chemistry Exam ReviewDokumen4 halamanAnalytical Chemistry Exam ReviewBernard Jomari Blancada RazoteBelum ada peringkat
- Calorimetry: Heat of Solution of Ammonium NitrateDokumen4 halamanCalorimetry: Heat of Solution of Ammonium Nitratebk1234567Belum ada peringkat
- The Isolation of Plant Pigments by Column and Paper ChromatographyDokumen4 halamanThe Isolation of Plant Pigments by Column and Paper ChromatographyholyfelipeBelum ada peringkat
- ZOO302 HW1 Types of MicroscopeDokumen3 halamanZOO302 HW1 Types of MicroscopeNini CioconBelum ada peringkat
- The Same Results Happened With The Oil of Wintergreen. The Translucent Spot Did Not DisappearDokumen3 halamanThe Same Results Happened With The Oil of Wintergreen. The Translucent Spot Did Not DisappearZerimar Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Frog Skeletal Muscle Student HandoutDokumen6 halamanFrog Skeletal Muscle Student HandoutJasper AdonisBelum ada peringkat
- Action PlanDokumen2 halamanAction PlanThalia PacamalanBelum ada peringkat
- Cyst I Nuria Nature Reviews 2010Dokumen12 halamanCyst I Nuria Nature Reviews 2010joshBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphy Lab ReviewerDokumen7 halamanAnaphy Lab ReviewerJoice Bundang Maningo100% (1)
- Fibrinolysis Laboratory TestDokumen2 halamanFibrinolysis Laboratory TestMark Vincent SahagunBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry Reactions of CarbohydratesDokumen13 halamanBiochemistry Reactions of CarbohydratesBridgette JuarezBelum ada peringkat
- Ti Tri Metric Analysis of Amino Acids and PeptidesDokumen4 halamanTi Tri Metric Analysis of Amino Acids and PeptidesSharm Jarin-AlonzoBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary SystemDokumen2 halamanUrinary SystemCharlayne AnneBelum ada peringkat
- ANAPHY Lec Session #14 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Dokumen8 halamanANAPHY Lec Session #14 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaBelum ada peringkat
- CH 4 & 5 Quiz Q & A From Site PDFDokumen35 halamanCH 4 & 5 Quiz Q & A From Site PDFJeanette SalibBelum ada peringkat
- Phyana Postlab Ex 8-35Dokumen38 halamanPhyana Postlab Ex 8-35shairaorqueta71% (7)
- Heart Anatomy ReviewDokumen6 halamanHeart Anatomy ReviewfailinBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To PharmacognosyDokumen12 halamanIntroduction To PharmacognosyMayuri Chaudhari50% (2)
- Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory SystemDokumen9 halamanFunctional Anatomy of the Respiratory SystemKat ArriolaBelum ada peringkat
- Hemodialysis: Dangers of Inappropriate UfDokumen11 halamanHemodialysis: Dangers of Inappropriate UfSTEFFANIE VALE BORJABelum ada peringkat
- Prep 16-18Dokumen1 halamanPrep 16-18Angelyka CabaloBelum ada peringkat
- PharDose Appendix BDokumen5 halamanPharDose Appendix BAngelyka CabaloBelum ada peringkat
- PharDose Appendix ADokumen4 halamanPharDose Appendix AAngelyka CabaloBelum ada peringkat
- PharDose Chapter 3Dokumen2 halamanPharDose Chapter 3Angelyka Cabalo100% (1)
- PharDose Chapter 1Dokumen4 halamanPharDose Chapter 1Angelyka CabaloBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 - Endocrine SystemDokumen4 halamanChapter 10 - Endocrine SystemAngelyka CabaloBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12 - HeartDokumen3 halamanChapter 12 - HeartAngelyka CabaloBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - TissuesDokumen3 halamanChapter 4 - TissuesAngelyka CabaloBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanChapter 8 Nervous SystemAngelyka CabaloBelum ada peringkat
- Pe ReviewerDokumen11 halamanPe ReviewerJohn Arsen AsuncionBelum ada peringkat
- Immersion Physical Exam Final - ChecklistDokumen2 halamanImmersion Physical Exam Final - ChecklistElizalde HusbandBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Monitor and Pulse OximeterDokumen14 halamanCardiac Monitor and Pulse OximeterYanna Habib-MangotaraBelum ada peringkat
- I. LESSON 5/melcs 4: Analyzes Physiological Indicators Such As Heart Rate, Rate ofDokumen5 halamanI. LESSON 5/melcs 4: Analyzes Physiological Indicators Such As Heart Rate, Rate ofIssabhel Neyn DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- 5.vital Signs-1Dokumen89 halaman5.vital Signs-1Abdella UmerBelum ada peringkat
- Review: Ediatric NursingDokumen142 halamanReview: Ediatric NursingBuRiO03Belum ada peringkat
- Hemodynamics - New Diagnostic and The Rape Uric ApproachesDokumen164 halamanHemodynamics - New Diagnostic and The Rape Uric Approachesa_artışBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Grade Heart Rate Lesson Plan: Guiding ObjectivesDokumen4 halaman2 Grade Heart Rate Lesson Plan: Guiding ObjectivesYeshua YeshaBelum ada peringkat
- NURSING CARE PLANDokumen81 halamanNURSING CARE PLANKaye CorBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAADokumen2 halamanNursing Care for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAASheryn ShahwanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 09 Vital SignsDokumen36 halamanChapter 09 Vital SignsAnnie PriscillaBelum ada peringkat
- Danger Signs of LaborDokumen13 halamanDanger Signs of LaborBenj Villanueva50% (2)
- Bed Making: Learning OutcomesDokumen88 halamanBed Making: Learning OutcomesTJPlayzBelum ada peringkat
- Kinns The Medical Assistant An Applied Learning Approach 13Th Edition Proctor Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokumen49 halamanKinns The Medical Assistant An Applied Learning Approach 13Th Edition Proctor Test Bank Full Chapter PDFsiliquavexinglygmnfo100% (9)
- Assignment 3: PharmacologyDokumen6 halamanAssignment 3: PharmacologyHanif JaisBelum ada peringkat
- KMDICAPost Market Surveillance Report 작성사례집Dokumen150 halamanKMDICAPost Market Surveillance Report 작성사례집Suna KimBelum ada peringkat
- Heart and Neck Vessels AssessmentDokumen8 halamanHeart and Neck Vessels Assessmentfatimafaith1129Belum ada peringkat
- Pulse Rate LabDokumen4 halamanPulse Rate LabTishana ThompsonBelum ada peringkat