Basic Tissues & Structures - Human Anatomy - Color Atlas and Textbook
Diunggah oleh
Caleb HeJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Basic Tissues & Structures - Human Anatomy - Color Atlas and Textbook
Diunggah oleh
Caleb HeHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Basictissuesandstructures
Skin
Skin(Fig.1.9 )isaprotectivecoveringforthesurfaceofthebodyandcomprisesasuperficial
layer,calledtheepidermis,andadeeperlayer,thedermis.Theepidermisisanepithelium
consistingofasurfacelayerofdeadcellswhicharecontinuallyshedandreplacedbycellsfrom
itsdeepergerminallayer.Thedermisisalayerofconnectivetissuecontainingbloodvessels,
lymphaticsandnerves.Inmostareasofthebodytheskinisthinandmobileovertheunderlying
structures.Specializationsoftheskinincludefingernailsandtoenails,hairfolliclesandsweat
glands.Onthepalmsofthehandsandsolesofthefeet(andcorrespondingsurfacesofthe
digits),hairfolliclesareabsentandtheepidermisisrelativelythick.Theskinintheseregionsis
alsofirmlyanchoredtotheunderlyingstructures,reducingitsmobilityduringgrippingand
standing.Linesoftension(Langerslines)occurwithinskinandareofimportancetosurgeons.
Scarsfollowingsurgicalincisionsmadealongtheselinestendtobenarrowerthanthosemade
acrossthelinesoftension.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b
1/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.9
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Multilevelstepdissectionthroughtherightmidcalftoshowlayersof
Skinisusuallywellvascularizedandreceivesbloodfromnumeroussubcutaneousvessels.
Knowledgeofthisvascularsupplyisimportantwhenoperationsthatinvolvetheuseofskin
flapsareundertaken.Skinhasarichnervesupply,respondingtotouch,pressure,heat,cold,
vibrationandpain.Incertainareas,suchasthefingertips,theskinisespeciallysensitiveto
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b
2/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
touchandpressure.Skinisinnervatedbysuperficial(cutaneous)branchesofspinalorcranial
nerves.Theareaofskinsuppliedbyeachcranialorspinalnerveisknownasadermatome
(seeFigs1.37 &1.38 ).
Subcutaneoustissue(superficialfascia)
Immediatelydeeptotheskinisalayeroflooseconnectivetissue,thesubcutaneoustissue(Fig.
1.9 ),whichcontainsnetworksofsuperficialveinsandlymphaticsandistraversedby
cutaneousnervesandarteries.Italsocontainsfat,whichvariesconsiderablyinthicknessfrom
regiontoregionandbetweenindividuals.Forexample,overthebuttockthefatisparticularly
thickwhilstonthebackofthehanditisrelativelythin.Overthelowerabdomenthistissueis
subdividedintotwolayers,asuperficialfattylayerandadeepermembranouslayer.
Deepfascia
Thedeepfascia(Fig.1.9 )consistsofalayerofdenseconnectivetissueimmediatelybeneath
thesubcutaneoustissue.Althoughthinoverthethoraxandabdomen,itformsasubstantial
layerinthelimbs(forexample,fascialataseep.260 )andneck(forexample,investing
fasciaseep.322 ).Nearthewristandanklejointsthedeepfasciaisthickenedtoform
retinacula,whichmaintainthetendonsinpositionastheycrossthejoints.Deepfasciaalso
providesattachmentformusclesandgivesanchoragetointermuscularsepta,whichseparatethe
musclesintocompartments.Bleedingandswellingwithinmusclecompartmentsdueto
crushinginjuriesorfracturesmayraisethepressuresomuchthatitcompressesbloodvessels
andreducesbloodflow.Theresultingischaemiamaybefollowedbyscarringanddeformitywith
contractureofmuscles.
Muscle
Muscleisatissueinwhichactivecontractioneithershortensitscomponentcellsorgenerates
tensionalongtheirlength.Therearethreebasictypes:smoothmusclecardiacstriatedmuscle
voluntarystriatedmuscle.Striatedandsmoothdescribethemicroscopicappearanceofthe
muscle.
Smoothmuscleispresentintheorgansofthealimentary,genitourinaryandrespiratorysystems
andinthewallsofbloodvessels.Capableofslow,sustainedcontraction,smoothmuscleis
usuallycontrolledbytheautonomicnervoussystem(seep.22 ),and,insomeorgans,by
endocrinesecretions(hormones).
Cardiacstriatedmuscle(myocardium)isconfinedtothewalloftheheartandisabletocontract
spontaneouslyandrhythmically.Itscyclicalactivityiscoordinatedbythespecialized
conductingtissueoftheheartandcanbemodifiedbytheautonomicnervoussystem.
Skeletalmuscle(voluntarystriatedmuscle)isthebasiccomponentofthosemusclesthat
producemovementsatjoints.Theseactionsarecontrolledbythesomaticnervoussystem(seep.
20 )andmaybevoluntaryorreflex.Eachmusclecell(fibre)hasitsownmotornerveending,
whichinitiatescontractionofthefibre.Musclesmaybeattachedtotheperiosteumofbones
eitherdirectlyorbyfibrousconnectivetissueintheformofdeepfascia,intermuscularseptaor
tendons.Directfleshyattachmentcanbeextensivebuttendonsareusuallyattachedtosmall
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b
3/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
areasofbone.Muscleswithsimilaractionstendtobegroupedtogether,andinlimbsthese
groupsoccurincompartments(forinstance,extensorcompartmentofforearm).
Usually,eachendofamusclehasanattachmenttobone.Theattachmentthatremainsrelatively
fixedwhenthemuscleperformsitsprimeactionisknownastheoriginwhereastheinsertionis
themoremobileattachment.However,insomemovementstheoriginmovesmorethanthe
insertiontherefore,thesetermsareofonlylimitedsignificance.
Themusclefibreswithinvoluntarymusclearearrangedindifferingpatternswhichreflectthe
functionofthemuscle.Sometimestheyarefoundasthinflatsheets(asinexternaloblique,Figs
1.10 &1.11 ).Strapmuscles(suchassartorius,Fig.1.12 )havelongfibresthatreach
withoutinterruptionfromoneendofthemuscletotheother.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b
4/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b
5/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.10
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Externalobliqueisaflatmusclewithanextensiveaponeurosis.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b
6/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b
7/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.11
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Externalobliquecuttoshowitsthickness.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b
8/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.12
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Sartoriusisastrapmuscle.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b
9/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Pennatemusclesarecharacterizedbyfibresthatrunobliquely.Unipennatemuscles(for
exampleflexorpollicislongus,Fig.1.13 )havefibresrunningfromtheirorigintoattachalong
onlyonesideofthetendonofinsertion.Inbipennatemuscles(suchasdorsalinterossei,Fig.
1.14 )thefibresareanchoredtobothsidesofthetendonofinsertion.
F IG. 1.13
Flexorpollicislongusisaunipennatemuscle.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
10/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.14
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Dorsalinterosseiarebipennatemuscles.
Multipennatemuscles(forexamplesubscapularis,Fig.1.15 )haveseveraltendonsoforigin
andinsertionwithmusclefibrespassingobliquelybetweenthem.Somemuscles,forinstance
digastric,havetwofleshyparts(bellies)connectedbyanintermediatetendon.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663b 11/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.15
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Subscapularisisamultipennatemuscle.
Mosttendonsarethickandroundorflattenedincrosssection,althoughsomeformthinsheets
calledaponeuroses(seeFig.1.10 ).Whentendonscrossprojectionsortraverseconfined
spacestheyareoftenenvelopedinadoublelayerofsynovialmembranetominimizefriction.
Wheretheycrossjoints,tendonsareoftenheldinplacebybandsofthickfibroustissue,which
preventbowstringingwhenthejointsaremoved.Examplesincludetheretinaculaatthewrist
andanklejoints,andtendonsheathsinthefingersandtoes(Figs1.16 &1.17 ).
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
12/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.16
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Anteriorviewofthelefthand,dissectedtorevealitsfibroussheaths
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
13/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.17
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Posteriorviewofthelefthand,dissectedtoshowtheextensorretin
Thenervesupplytoaskeletalmusclecontainsbothmotorandsensoryfibres,whichusually
enterthefleshypartofthemuscle.Groupsofmuscleswithsimilaractionstendtobesupplied
bynervefibresderivedfromthesamespinalcordsegments.
Asverymetabolicallyactivetissue,musclehasaricharterialbloodsupply,usuallycarriedby
severalseparatevessels.Thecontractionandrelaxationofmusclesinthelimbscompressesthe
veinsineachcompartment.Astheveinscontainunidirectionalvalves,thismusclepumpaction
assiststhereturnofvenousbloodfromthelimbstothetrunk.
Cartilage
Cartilageisavarietyofhardconnectivetissuewhichgainsitsnutritionbydiffusionfromblood
vesselsinthesurroundingtissues.Itisclassifiedbyitshistologicalstructureintohyaline
cartilage,fibrocartilageandelasticcartilage.
Hyalinecartilageoccursincostalcartilages(seeFig.1.11 ),thecartilagesofthelarynxand
trachea,andindevelopingbones.Insynovialjoints(seeFig.1.23 )itformstheglassy,smooth
articularsurfaceswhichreducefrictionduringmovement.Articularcartilageispartlynourished
bydiffusionfromthesynovialfluidinthejointcavity.
Theinclusionoftoughinelasticcollagenfibresinthematrixconstitutesfibrocartilage,whichis
strongerandmoreflexiblethanthehyalinetype.Fibrocartilageisfoundinintervertebraldiscs
(seeFig.1.22 ),thepubicsymphysis,themanubriosternaljoint,andasarticulardiscsinsome
synovialjoints(forexample,kneeandtemporomandibular).
Elasticcartilage,whichoccursintheexternalearandepiglottis,isthemostflexibleformof
cartilage.Itcontainspredominantlyelasticfibresandhasayellowishappearance.
Cartilagemaybecomecalcifiedinoldage,becomingharderandmorerigid.
Bone
Boneformsthebasisoftheskeletonandischaracterizedbyahard,calcifiedmatrixwhichgives
rigidity.Inmostbonestwozonesarevisible.Nearthesurfacetheoutercorticallayerofbone
appearssolidandiscalledcompactbone,whereascentrallytheboneisknownasspongy
(cancellous)bone.Manybonescontainacavity(medulla)occupiedbythebonemarrow,a
potentialsiteofbloodcellproduction(Fig.1.18 ).
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
14/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
15/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.18
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Longitudinalsectionofanadulttibia.
Thenumerousbonescomprisingthehumanskeletonvaryconsiderablyinshapeandsize,and
areclassifiedintolongbones(forexample,femur),shortbones(bonesofthecarpus),flatbones
(parietalboneofskull),irregularbones(maxillaofskull)andsesamoidbones(patella).
Sesamoidbonesdevelopintendons,generallywherethetendonpassesoverajointorbony
projection.Somebonesaredescribedaspneumatizedbecauseoftheirairfilledcavities(for
instance,ethmoid).
Boneisenvelopedbyathinlayeroffibroustissuecalledperiosteum(seeFig.1.9 )which
providesanchorageformuscles,tendonsandligaments.Periosteumisasourceofcellsforbone
growthandrepairandisrichlyinnervatedandexquisitelysensitivetopain.
Bonehasaprofusebloodsupplywhichisprovidedpartlyviatheperiostealvesselsandpartlyby
nutrientarteries,whichenterbonesvianutrientforaminaandalsosupplythemarrow.
Fracturedbonesoftenbleedprofuselyfromdamagedmedullaryandperiostealvessels.
Severalnamesaregiventothedifferentpartsofalongboneinrelationtoitsdevelopment(Fig.
1.19 ).Theshaft(ordiaphysis)ossifiesfirstandisseparatedbygrowthplatesfromthe
secondarycentresofossification(orepiphyses)whichusuallylieattheextremitiesofthebone.
Thepartofadiaphysisnexttoagrowthplateiscalledametaphysisandhasaparticularlyrich
bloodsupply.Whenincreaseinbonelengthceases,thegrowthplatesdisappearandthe
epiphysesfusewiththediaphysis.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
16/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
17/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.19
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Anteriorviewofachildstibia.
Skeleton
Theskeleton(Fig.1.20 )iscomposedofbonesandcartilagesheldtogetherbyjoints,and
givesrigidityandsupporttothebody.Ithasaxialandappendicularcomponents.Theaxial
componentincludestheskull,vertebralcolumn,ribs,costalcartilagesandsternum.The
appendicularskeletoncomprisesthebonesoftheupperandlowerlimbsandtheirassociated
girdles.Inthisbook,individualbonesaredescribedintheappropriateregions.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
18/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.20
Joints
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Anteriorandposteriorviewsoftheskeleton.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
19/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Joints
Jointsareclassifiedaccordingtotheirstructureintofibrous,cartilaginousandsynovialtypes.In
fibrousjoints(Fig.1.21 )whicharerelativelyimmobile,thetwobonesarejoinedbyfibrous
tissue(forexample,suturesseenbetweenthebonesoftheskull).
F IG. 1.21
Theinferiortibiofibularjointisanexampleofafibrousjoint.
Cartilageisinterposedbetweenboneendsincartilaginousjoints.Primarycartilaginousjoints
containhyalinecartilage,areusuallycapableofonlylimitedmovement,andaredescribed
betweentheribsandsternum.Insecondarycartilaginousjoints(Fig.1.22 ),fibrocartilage
unitestheboneends.Thesejoints,whichgenerallyallowmoremovementthanthoseofthe
primarytype,alllieinthemidline.Examplesincludetheintervertebraldiscs,the
manubriosternaljointandthepubicsymphysis.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
20/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.22
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Sagittalsectiontoshowanintervertebraldisc,asecondarycartilagi
Synovialjoints
Themostcommontypeofjointisthesynovialjoint,whichiscomplexandusuallyhighlymobile.
Theyareclassifiedaccordingtotheshapeofthejointsurfaces(suchasplane,saddle,balland
socket)orbythetypeofmovementtheypermit(suchassliding,pivot,hinge).Inatypical
synovialjoint(Fig.1.23 )thearticulatingsurfacesarecoatedwithhyalinecartilageandthe
bonesarejoinedbyafibrouscapsule,atubularsleevewhichisattachedaroundtheperipheryof
theareasofarticularcartilage.Ineverysynovialjoint,alloftheinterior(exceptforintra
articularcartilage)islinedwithsynovialmembrane.Thisthinvascularmembranesecretes
synovialfluidintothejointspace,providingnutritionforthecartilageandlubricationforthe
joint.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
21/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.23
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Coronalsectionthroughametacarpophalangealjoint,asynovialjoi
Thecapsuleisusuallythickenedtoformstrengtheningbandsknownascapsularligaments(for
example,thepubofemoralligament).Inaddition,fibrousbands,discretefromthecapsule,may
formextracapsularligaments(suchasthecostoclavicularligament).Insomejointsthereare
intracapsularligaments(forinstance,theligamentoftheheadofthefemur)whicharecovered
bysynovialmembrane.Tendonssometimesfusewiththecapsule(asintherotatorcuff)orthey
mayrunwithinthejoint,coveredbysynovialmembrane,beforegainingtheirbonyattachment
(forexample,bicepsbrachiiattheshoulderjointFig.1.24 ).
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
22/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.24
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Removalofpartoftheshoulderjointcapsulerevealstheintracapsul
Fluidcontainingsacsofsynovialmembranecalledbursae(Fig.1.25 )separatesometendons
andmusclesfromotherstructures.Bursaewhichlieclosetojointsmaycommunicatewiththe
cavityofthejointthroughasmallopeninginthecapsule(asdoesthesubscapularisbursa).
F IG. 1.25
Sagittalsectionthroughtheelbowjoint.Theolecranonbursadoesn
Insomejoints(forexample,theknee)adiscofcartilageisinterposedbetweenthearticular
cartilagecoveringtheboneends(Fig.1.26 ).Thisprovidesamatchedshapeforeachbone
end,thusallowingfreermovementwithoutcompromisingstability.Inaddition,differenttypes
ofmovementarepermittedineachhalfofthejoint.
F IG. 1.26
Disarticulatedkneejointtoshowthemenisci.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
23/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Stabilityvariesconsiderablyfromonesynovialjointtoanother,asseveralfactorslimitexcessive
movementandcontributetothestabilityofthejoint.Theseincludetheshapeofthearticulating
surfaces,thestrengthofthecapsuleandassociatedligaments,thetoneofthesurrounding
musclesand,wherepresent,intraarticulardiscsandligaments.Atthehipjointtheligaments
andtheshapeofthebonesprovidethemainstability,whereasthetoneofthesurrounding
musclesismoreimportantinstabilizingtheshoulderjoint.Lackofstabilityassociatedwith
muscleweaknessortraumamayresultindislocationsothatthecartilagecoveredsurfacesno
longerarticulate.Dislocationmaydamageadjacentbloodvesselsandnerves.
Joints,particularlytheircapsules,receivearichsensoryinnervationderivedfromthenerves
supplyingthemusclesthatactonthejoint.Forinstance,theaxillarynervesuppliestheshoulder
jointanddeltoid.
Bloodvesselsaroundjointsfrequentlytakepartinrichanastomoses,whichallowalternative
pathwaysforbloodflowwhenthejointhasmovedtoadifferentpositionandensurean
adequatesupplytothesynovialmembrane(suchasinthekneejointFig.1.27 ).
F IG. 1.27
Branchesofthepoplitealarteryanastomosearoundthekneejoint.
Serousmembranesandcavities
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
24/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Serousmembranesandcavities
Pericardium,pleuraandperitoneumcomprisetheserousmembranesliningthecavitiesthat
separatetheheart,lungsandabdominalviscera,respectively,fromtheirsurroundingstructures.
Wherethemembranelinestheouterwallofthecavityitiscalledparietal,andwhereitcovers
theappropriateorganitiscalledvisceral.Theparietalandvisceralpartsareincontinuity
aroundtherootoftheviscusandareseparatedfromeachotherbyacavity,whichnormally
containsonlyathinfilmofserousfluid.Themembranesareinclosecontactbutarelubricated
bytheinterveningfluid,whichpermitsmovementbetweentheviscusanditssurroundings(Fig.
1.28 ).
F IG. 1.28
TransversesectionthroughthethoraxatthelevelofT5showingth
Bloodvessels
Bloodvesselsconveybloodaroundthebodyandareclassifiedintothreemaintypes:arteries,
capillariesandveins.
Arteriesarerelativelythickwalledvesselswhichconveybloodinabranchingsystemof
decreasingcalibreawayfromtheheart(Fig.1.31 ).Somearteriesarenamedaftertheregion
throughwhichtheypass(suchasthefemoralartery),whileothersarenamedaccordingtothe
structurestheysupply(forinstance,therenalartery).Thelargestvessels,suchastheaorta,have
elasticwallsandthereforearecalledelasticarteries.Theygiverisetoarterieswhosewallsare
moremuscular(musculararteries),suchastheradialarteryintheforearm.Aparticularlythick
smoothmusclecoatisalsoafeatureofthewallsofthemicroscopicarterioles.Thetoneof
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
25/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
arteriolarsmoothmuscleisunderthecontroloftheautonomicnervoussystemandhormones,
andisanimportantfactorinthemaintenanceofpressureinthearterialsystem.Ingeneral,
therearefewalternativepathwaysforarterialbloodtoreachitsdestination.However,insome
regions(forexample,jointsandatthebaseofthebrain),arterialsupplyisprovidedbymore
thanonevessel(seeFig.1.27 ).Sucharteriesmaycommunicatedirectlywitheachotherat
sitesknownasarterialanastomoses.Arterialpulsesmaybefelteasilyinsuperficialarteriessuch
astheradialarteryatthewrist.Identifyingpulsesindeeplylocatedarteriessuchasthe
abdominalaortamayrequirefirmpressure.
Capillarieslinkthesmallestarteriesandthesmallestveinsandconveybloodatlowpressure
throughthetissues.Collectively,thesethinwalledmicroscopicvesselshaveaveryextensive
surfacearea,facilitatinggaseousandmetabolicexchangebetweenthebloodandtissues.
Veinscarrybloodatlowpressurefromthecapillarybedbacktotheheart(seeFig.1.32 ).
Theymaybedeep(accompanyingarteries)orsuperficial(lyinginthesuperficialfascia)(Fig.
1.29 )andareusuallylinkedbyvenousanastomoses.Veinsaccompanyingarteriesareoften
arrangedasseveralinterconnectingvesselscalledvenaecomitantes.Inthelimbsthedeepveins
canbecompressedbylocalmuscularaction,thusassistingvenousreturn.Manyveins
(excludingthevenaecavae,thosedrainingvisceraandthosewithinthecranium)contain
unidirectionalvalveswhichdirecttheflowofbloodtowardstheheart(Fig.1.30 ).Thevenous
patternisoftenvariable,andnumerousanastomoticconnectionsprovidealternativepathways
forvenousreturn.Insomeregions,numerousintercommunicatingveinsformmeshworks
calledplexuses(suchasthepelvicvenousplexus).Inthecranialcavity,venousbloodiscarried
inspecialvesselsformedbytheduramaterliningtheinterioroftheskull.Theseduralsinuses
receivebloodfromthebrain.
F IG. 1.29
Multilevelstepdissectionthroughtherightlegshowingthebloodv
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
26/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.30
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Portionofsaphenousveinopenedlongitudinallyandincrosssection.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
27/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.31
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Principalsystemicarteries.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
28/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.32
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Principalsystemicveins.
Lymphaticvesselsandnodes
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
29/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Lymphaticvesselsandnodes
Tissuefluidiscollectedbymicroscopicopenendedchannelscalledlymphatics.Froma
particularregionororgan,thesevalvedlymphaticvesselsdrainintoaggregationsoflymphoid
tissue(calledlymphnodesFig.1.33 )whichfilterlymph.Groupsoflymphnodesareoften
foundclosetoanorgan(forexample,hilarnodes)orattherootofalimb(forexample,axillary
lymphnodes).Ultimately,lymphdrainsintothevenoussystemintherootoftheneckthrough
largerlymphchannelscalledthethoracicductandtherightlymphatictrunk(Fig.1.34 ).
F IG. 1.33
Inguinallymphnode.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
30/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.34
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Themainlymphaticnodesandvessels.
Becausetheyfilterthefluidpassingthroughthem,lymphnodesmaybecomeinvolvedinthe
spreadofinfectionormalignancy(forexample,cancer).Thus,thesurgeonremovinga
cancerousorganmayalsoexcisethelymphnodesdrainingthatorgan.
Nervoustissue
Nervoustissuecontainstwotypesofcell:neuronesandneuroglia.Theneuroneisthefunctional
unitresponsiblefortheconductionofnerveimpulses.Itconsistsofacellbodyandits
associatedprocesses.Onetypeofprocess,ofwhichthereisonlyoneperneurone,istheaxon.
Thismayberelativelyshortbutsometimesisverylong,asinperipheralnerveswhereaxons
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
31/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
comprisetheindividualnervefibres.Theneurogliaundertakesupportingrolesandinclude
Schwanncells,whichprovidethemyelinsheathsaroundaxons.Thesesheathsinsulatethe
axons,increasingtheirspeedsofconduction.
Thenervoussystemconsistsofcentralandperipheralparts.Thebrainandspinalcordcomprise
thecentralnervoussystem.
Theperipheralnervoussystemconsistsofspinal,cranialandautonomicnerves,andtheir
associatedganglia.BundlesofnervecellprocessesandtheirsupportingSchwanncellsform
peripheralnerves.Severalnerveprocesses,boundtogetherbyconnectivetissue,formanerve
bundlenumerousbundles,surroundedbyafibroussheath(epineurium),constitutethe
completeperipheralnerve.Nervecellbodiesalsoformpartoftheperipheralnervoussystem
andareusuallygroupedtogetherintoganglia.Theperipheralnervoussystemisdividedinto
somaticandautonomicparts.
Somaticnerves
Ingeneral,thesomaticnervesinnervateskeletalmuscleandtransmitsensationfromallpartsof
thebodyexcepttheviscera.Twelvepairsofcranialnervesareattachedtothebrainandare
named:olfactory(I),optic(II),oculomotor(III),trochlear(IV),trigeminal(V),abducens(VI),
facial(VII),vestibulocochlear(VIII),glossopharyngeal(IX),vagus(X),accessory(XI),
hypoglossal(XII).Mostofthesenervessupplystructuresintheheadandneck,butthevagus
nervealsosuppliesthoracicandabdominalviscera.
Spinalnervesarealsoinpairsandeachisattachedtoaspecificsegmentofthespinalcordby
anteriorandposteriorroots.Thereareeightcervical(C1C8),twelvethoracic(T1T12),five
lumbar(L1L5),fivesacral(S1S5),andoneortwococcygeal(Co)spinalnerves(seeFig.
1.35 ).
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
32/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
33/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.35
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Lateralviewofthedistributionoftheanteriorramiofthespinalner
Thoracicspinalnervesillustratethetypicalsegmentalpatternofdistributiontothebodywall
(Fig.1.36 ).Theareaofskinsuppliedbyonespinal(orcranial)nerveiscalledadermatome
(Figs1.37 &1.38 ).Inthetrunkthedermatomepatterninvolvessubstantialoverlap
betweenadjacentareas.Similarly,allthemusclessuppliedbyasinglespinal(orcranial)nerve
compriseamyotome.
F IG. 1.36
Courseanddistributionofatypicalthoracicspinalnerve.Inferioras
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
34/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.37
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Dermatomesofthetrunk.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
35/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.38
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Dermatomesofthelimbs.
Theregularpatternofinnervationinthetrunkismodifiedinthelimbs,eachbeingsuppliedby
severalspinalnervesthroughacomplexnetwork,aplexus(suchasthebrachialplexusofthe
upperlimbFig.1.39 ).Plexusformationmodifiesthepatternofmyotomessothatspinalcord
segmentsinnervatemusclesaccordingtotheirprimeactions.Forexample,flexorsoftheelbow
jointaresuppliedbythespinalcordsegmentsC5andC6.Sensorycellbodiesarelocatedin
gangliaonperipheralnervesnearthecentralnervoussystem(forinstance,trigeminalganglion,
posteriorrootganglia).However,thecellbodiesofsomaticmotornervesarelocatedinthe
centralnervoussystem.
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
36/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.39
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Theaxillahasbeendissectedtoshowthebrachialplexus.
Autonomicnerves
Theautonomicnervoussysteminnervatessmoothandcardiacmuscle,andglands.Itisdivided
intotwoparts,sympatheticandparasympathetic,whoseeffectsforthemostpartareanta
gonistic(forexample,sympatheticstimulationincreaseswhileparasympatheticstimulation
reducesheartrate).Inbothsympatheticandparasympatheticcomponents,preganglionic
myelinatedaxonsleavethecentralnervoussystemandsynapseonneuronesinperipheral
gangliadistributedthroughoutthebody.Thepostganglionicaxonsthatpasstotheeffector
organsarenonmyelinated.Autonomicsensoryfibresaccompanyautonomicefferentfibresin
peripheralnervesbuttheircellbodiesarelocatedintheposteriorrootgangliaincompanywith
somaticsensoryneurones.
Thepartsofthecentralnervoussystemfromwhichtheautonomicnervesemergedifferforthe
sympatheticandparasympatheticcomponents(Fig.1.40 ).
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
37/39
12/5/2016
F IG. 1.40
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Patternofinnervationintheparasympatheticandsympatheticauto
Sympatheticnerves
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
38/39
12/5/2016
Basictissues&structures|HumanAnatomy:ColorAtlasandTextbook
Preganglionicsympatheticfibresleavethecentralnervoussysteminthespinalnervesofallthe
thoracicandtheuppertwolumbarsegments(thoracolumbaroutflow)andenterthe
ganglionatedsympathetictrunksviawhiteramicommunicantes.Thetwosympathetictrunkslie
oneithersideofthevertebralcolumnandextendthroughoutmostofitslength.Eachtrunk
consistsofsympatheticgangliaandinterconnectingnervetrunks.
Unmyelinatedpostganglionicaxonsdestinedforthebloodvesselsandsweatglandsofthebody
wall,includingthelimbs,leavethegangliabygreyramicommunicantesandaredistributedby
thespinalnerves.Specialvisceralbranchespassdirectlyfromthetrunkstoreachthe
appropriateorgan.
Postganglionicsympatheticnervefibresareoftenconveyedtotheirdestinationsasplexuses
intimatelyrelatedtothewallsofarteries.
Parasympatheticnerves
Intheparasympatheticsystem,myelinatedpreganglionicfibresleavethecentralnervous
systemaspartofcranialnervesIII,VII,IXandXandaspartofsacralspinalnervesS2,S3and
S4toformthecraniosacralautonomicoutflow.Thesepreganglionicfibressynapseinganglia
lyingclosetoorinthewallofthetargetorgan.Relativelyshortnonmyelinatedpostganglionic
axonsemergefromthesegangliatoinnervatetheappropriatetissue.Intheheadtherearefour
pairedganglia(ciliary,pterygopalatine,submandibularandotic)thatreceivepreganglionic
parasympatheticfibresfromcranialnervesIII,VIIandIX.Thepostganglionicfibresfromthese
gangliasupplytheeye,andlacrimal,nasalandsalivaryglands.Preganglionicfibresfromthe
vagus(X)nervesynapsewithpostganglionicneuronesthatinnervatecervical,thoracicand
abdominalviscera.Preganglionicfibresfromthesacralnerves(pelvicsplanchnicnervesornervi
erigentes)supplythepelvicorgans.Theparasympatheticgangliaassociatedwiththevagusand
sacralnervesusuallycomprisesmallclustersofcellsinthewallsoftheinnervatedorgans(Fig.
1.40 ).
https://studentconsult.inkling.com/read/goslinghumananatomycoloratlastextbook5th/chapter1/basictissuesandstructures#2c517cd116eb46f191cef663
39/39
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hierholzer - 1992 - Adenoviruses in The Immunocompromised Host.Dokumen13 halamanHierholzer - 1992 - Adenoviruses in The Immunocompromised Host.Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Baker Et Al. - 2022 - Acute Hepatitis and Adenovirus Infection Among ChiDokumen3 halamanBaker Et Al. - 2022 - Acute Hepatitis and Adenovirus Infection Among ChiCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Ethnographic Field School in Isla MujeresDokumen2 halamanEthnographic Field School in Isla MujeresCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 22 11-17-22Dokumen19 halamanLecture 22 11-17-22Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Sun Et Al. - 2022 - Does Adenovirus Cause The Acute Hepatitis of UnknoDokumen1 halamanSun Et Al. - 2022 - Does Adenovirus Cause The Acute Hepatitis of UnknoCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 23 11-22-22Dokumen17 halamanLecture 23 11-22-22Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 21 11-15-22Dokumen16 halamanLecture 21 11-15-22Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 16 10-25-22Dokumen19 halamanLecture 16 10-25-22Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Immigration EssayDokumen12 halamanImmigration EssayCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 24 11-29-22Dokumen21 halamanLecture 24 11-29-22Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Immigration PowerpointDokumen18 halamanImmigration PowerpointCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 17 10-27-22Dokumen14 halamanLecture 17 10-27-22Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Taxonomy and Systematics ActivitiesDokumen12 halamanTaxonomy and Systematics ActivitiesCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- BIOL 329 Cellular and Molecular Biology Collaborate Session 3 - 08/25Dokumen23 halamanBIOL 329 Cellular and Molecular Biology Collaborate Session 3 - 08/25Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 12 10-6-22Dokumen15 halamanLecture 12 10-6-22Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 15 10-20-22Dokumen16 halamanLecture 15 10-20-22Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 11 9-29-22Dokumen20 halamanLecture 11 9-29-22Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Genes 13 00532Dokumen12 halamanGenes 13 00532Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Thalassemia Intermedia ArticleDokumen8 halamanThalassemia Intermedia ArticleCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 329 Cellular and Molecular Biology Proteins - Structure and FunctionsDokumen39 halamanBIO 329 Cellular and Molecular Biology Proteins - Structure and FunctionsCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 - IntroductionDokumen36 halamanUnit 1 - IntroductionCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Histogram Worksheet KeyDokumen3 halamanHistogram Worksheet KeyCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Respiration and Photosynthesis: Plants Do Both!Dokumen11 halamanRespiration and Photosynthesis: Plants Do Both!Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- African Library Project Book Drive Summary: For Internal UseDokumen1 halamanAfrican Library Project Book Drive Summary: For Internal UseCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Absorbance Spectrum ActivityDokumen2 halamanAbsorbance Spectrum ActivityCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Organelles Worksheet: Stroma Intermembrane Space Grana Outer MembraneDokumen1 halamanOrganelles Worksheet: Stroma Intermembrane Space Grana Outer MembraneCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Mitosis WorksheetDokumen3 halamanMitosis WorksheetCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- The Gilded Age Was A Period of Economic Prosperity and Political Equality For All AmericansDokumen1 halamanThe Gilded Age Was A Period of Economic Prosperity and Political Equality For All AmericansCaleb He100% (1)
- Compound Microscope Worksheet: Insert A Text Box To Fill in The DiagramDokumen2 halamanCompound Microscope Worksheet: Insert A Text Box To Fill in The DiagramCaleb HeBelum ada peringkat
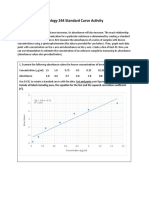
- Biology 244 Standard Curve Activity: 6 F (X) 3.24 X + 0.71 R 0.93Dokumen2 halamanBiology 244 Standard Curve Activity: 6 F (X) 3.24 X + 0.71 R 0.93Caleb HeBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Apollo Root Cause AnalysisDokumen20 halamanApollo Root Cause AnalysisMohd Fakhruddin Basar100% (2)
- Schleip Fascia As A Sensory OrganDokumen28 halamanSchleip Fascia As A Sensory Organignacio camposBelum ada peringkat
- Degeneration & Regeneration of Nerve FibreDokumen29 halamanDegeneration & Regeneration of Nerve FibreSana Fatima100% (2)
- Nervous Control of Body MovementDokumen24 halamanNervous Control of Body MovementKanwal KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Biomo306 Quiz One QuestionsDokumen5 halamanBiomo306 Quiz One QuestionsAdrianBelum ada peringkat
- INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY (Carticiano) PDFDokumen93 halamanINTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY (Carticiano) PDFJas John100% (2)
- Nervous System - Cabil (G6)Dokumen96 halamanNervous System - Cabil (G6)Lady Ann CabilBelum ada peringkat
- Neurotrophic KeratopathyDokumen25 halamanNeurotrophic KeratopathyJavier Infantes MolinaBelum ada peringkat
- Sidney Ochs - A History of Nerve Functions - From Animal Spirits To Molecular Mechanisms-Cambridge University Press (2004) PDFDokumen450 halamanSidney Ochs - A History of Nerve Functions - From Animal Spirits To Molecular Mechanisms-Cambridge University Press (2004) PDFRaphael ResendeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture On The Histology of Peripheral Nerve and Ganglia by Dr. RoomiDokumen15 halamanLecture On The Histology of Peripheral Nerve and Ganglia by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiBelum ada peringkat
- 001 Wk01b Tools For Exploring The WorldDokumen63 halaman001 Wk01b Tools For Exploring The WorldJames DboyBelum ada peringkat
- (Current Topics in Membranes 72) Vann Bennett (Eds.) - Functional Organization of Vertebrate Plasma Membrane-Academic Press (2013) PDFDokumen364 halaman(Current Topics in Membranes 72) Vann Bennett (Eds.) - Functional Organization of Vertebrate Plasma Membrane-Academic Press (2013) PDFSankarshan talluriBelum ada peringkat
- AI Chapter - OneDokumen42 halamanAI Chapter - OnemkBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook For Brain-Based EducationDokumen31 halamanHandbook For Brain-Based EducationABCDirekt-InternationalBelum ada peringkat
- Ion ChannelsDokumen6 halamanIon ChannelsNicolas IsformermynameBelum ada peringkat
- Neural Network PPT PresentationDokumen23 halamanNeural Network PPT PresentationNihal Sharma67% (3)
- (Computational Neuroscience) Christof Koch - Biophysics of Computation - Information Processing in Single Neurons-Oxford University Press, USA (2004) PDFDokumen587 halaman(Computational Neuroscience) Christof Koch - Biophysics of Computation - Information Processing in Single Neurons-Oxford University Press, USA (2004) PDFayan849100% (1)
- The Nervous System-Final PDFDokumen57 halamanThe Nervous System-Final PDFCarlo Makiling100% (1)
- Disorders of The Nervous System2Dokumen20 halamanDisorders of The Nervous System2Ian Rizavi Villamor AntopinaBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System WorksheetDokumen2 halamanNervous System WorksheetRoda Aranquez RabinoBelum ada peringkat
- Class 10th Biology - Maha Marathon (Prashant Kirad)Dokumen183 halamanClass 10th Biology - Maha Marathon (Prashant Kirad)yashuummachgiBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic Test SolutionDokumen2 halamanPeriodic Test SolutionBabluBelum ada peringkat
- Sri Bhavishya Educational Academy: SyllabusDokumen4 halamanSri Bhavishya Educational Academy: SyllabusAnonymous A6Jnef04Belum ada peringkat
- Animal PhysiologyDokumen104 halamanAnimal PhysiologyClara MaeBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen3 halamanChapter 5Nona PeriarceBelum ada peringkat
- Max BrainDokumen240 halamanMax Brainyonnuma0% (1)
- Philosophical Perspective of The Self Understanding The SelfDokumen16 halamanPhilosophical Perspective of The Self Understanding The Selfmarie parfanBelum ada peringkat
- Science BiologyCompleteDokumen11 halamanScience BiologyCompleteJohanis Galaura EngcoBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet - I: Biology XDokumen5 halamanWorksheet - I: Biology XDharmendra SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Development of Nervous SystemDokumen71 halamanDevelopment of Nervous SystemAbdimalik AliBelum ada peringkat