Year 9 F Jan-Mar 2016-2017
Diunggah oleh
api-344945420Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Year 9 F Jan-Mar 2016-2017
Diunggah oleh
api-344945420Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
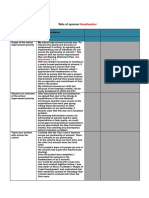
Scheme of Work: Maths Year Group 9
An exceptional environment for learning and discovery
Length of Enquiry (SOL)
3rd January to 10th March
Synopsis Topic / Overview
Students now will work on the Geometry and measures aspect of the curriculum.
Working on Problems involving parallel lines, 2D shapes area and perimeter to 3D
shapes volume and surface area.
Fertile Question
Whats your angle?
Key Concept/s to be learnt this Enquiry
Angles, Regular Polygons, Perimeter, Area and Volume of 2D polygons and 3D
shapes. Surface area using nets, Congruent shapes. Similar shapes
Curriculum Opportunities
SMSC
Students can apply their knowledge learnt from this scheme to Science, design and
technology, computing, IT, construction.
Students will work on how shapes can be used to aid them in life situations such as
construction and interior design. Students will look at the effects of how enlarging a
shape will lead to changes in its surface area and its volume.
See teacher planner
Summative Assessment
End of unit mini tests.
Assessment Point 5 Non-calculator and Calculator paper.
Key Vocabulary
Hypotenuse, Line segment, midpoint, perpendicular, Parallel, congruent, similar,
trapezium. Surface area, prism, volume, capacity. Circumference. Quadrilateral.
Literacy opportunities
To structure mathematical problems and explanations accurately. Students have the
opportunity to discuss the properties of shapes. Discussion of applications of 2D and
3D shapes in real life.
Core Learning Outcomes
Students will be able to solve problems involving 2D and 3D shapes.
Differentiation strategies
Pearson 1-9 Textbook has Strengthen, problem solving and extend sections.
Scheme of Work: Maths Year Group 9
An exceptional environment for learning and discovery
Resources and Texts
Week
1. Angles
2. Angles
Lesson Questions
Pearson 1-9 GCSE Foundation textbook
Learning Objectives
Activation Phase (Learning
Activities)
1. Demonstrate the language of
describing properties with a
square and a rectangle.
Demonstration Phase
Assessment (GEM TASK)
1. Identify quadrilaterals and their
features
H/W
Extension task
What do the 4
angles of
quadrilaterals add
up to?
1. To be able to solve
geometric problems using
the side and angle
properties of quadrilaterals
What is the
mathematical
name for a
diamond?
2. To understand the
difference between
congruent shapes and
similar shapes
2. Review the meaning of the
word congruency and find
concrete examples around the
classroom.
2. Students consider pairs of
congruent and similar shapes.
2.
Translations of
shapes and
enlargement of
shapes on
Cartesian plane.
Is there more than
one method to find
a missing angle?
3. To understand and use
angle properties of straight
and parallel lines (2
lessons)
3. To find missing angles using
corresponding and alternate
angle facts.
3. Students can find missing
angles in parallel lines as well as
give reasons.
3 parallel lines
problems
4. As above
4.
4.
3.
anglesinparallellines
4
1. To know the types of
triangles and solve angle
problems in triangles (2
lessons)
1. Work through the proof that
the angles in a triangle add up to
180 and the proof that the
exterior angle of triangle is equal
to the sum of the two opposite
interior angles.
2.
1. Discuss strategies with
students before they begin this
question.
1. angleproofs
Pythagoras and
Trigonometry.
3. Explain why some polygons fit
together and some others do not
3. Students solve problems
involving the interior and exterior
angles of polygons.
interiorexteriorangles
Solving problems
with 2 or more
polygons
Why do angles in a
triangle add up to
180?
2. As above
What is the sum of
the exterior angles
of any irregular
polygon?
3. To be able to calculate
interior and exterior angles
of regular polygons (3
lessons)
1. linesandquadrilat
erals
2.
Scheme of Work: Maths Year Group 9
3. Solving
Equations with
Angles
4. Area and
Perimeter
If the sum of the
interior angles of a
polygon is 1620,
how many sides
would it have?
Where does the
word perimeter
come from?
An exceptional environment for learning and discovery
4. As above
4.
4.
1. As above
1.
1.
1.
2. To be able to solve
angle problems using
equations (2 lessons)
2. Encourage students, in pairs,
to decide which reason applies
and use it to set up an equation.
2. Students can give a reason to
justify their equations.
2.
3. As above
3.
3.
3.
4. Mini-assessment - end
of chapter test
4.
4.
4.
1. To be able to calculate
area and perimeter of
simple quadrilaterals (2
Lessons)
1. Show how the area of a
rectangle can be used to find the
areas of parallelograms and
triangles.
1. Students know and learn the
formulae for areas of rectangles,
parallelograms and triangles.
Solving
Inequalities.
1.
areaofrecta
ngles
area-ofaparallelo
gram
How can a farmer
work out how
much area he
needs to give his
sheep in order to
meet health and
safety standards?
How can a farmer
area-ofa-triangle
2.
2. As above
2. To be able to calculate a
missing length given areas
2.
3. To be able to calculate
the area and perimeter of
trapezia
3. Using cut-out trapezia to
demonstrate may help students
visualise how two trapezia
always make a parallelogram
when put together.
3. Students derive the formula for
the area of a trapezium.
area-ofatrapeziu
m
4. To be able to find
4. To be able to calculate a
4.
4.
Area and
perimeter of
circles
Scheme of Work: Maths Year Group 9
An exceptional environment for learning and discovery
work out how
much fencing is
required to cover
the area his cows
need to roam?
How many mm is
there in 1cm?
missing lengths of a
trapezium given its area
missing length given areas
1. To be able to convert
between measures
1. Converting between area
measures. Cm squared and m
squared
1. Students use their knowledge
of converting between lengths
and apply to area.
What two well
known shapes can a
trapezium be split in
to?
2. To be able to calculate
area and perimeter of
compound shapes (2
lessons)
2. Make sure students see how
the missing lengths are worked
out using the fact that opposite
sides are equal lengths.
2. Students can divide a shape
into smaller shapes in any way
the area is still the same.
3. As above
3.
3.
4. To be able to calculate
the surface area of prisms
by considering their nets (2
lessons)
4. Make sure students see how
the lengths on the net are taken
from the cuboid. Encourage
students to look for identical
faces as a shortcut when finding
surface areas.
4. Use the symmetry of the
cuboid, the faces are in pairs.
Work out the area of the three
different rectangles, then double
the total to find the surface area.
1. As above
1.
1.
2. To be able to calculate
volume of prisms
2. Point out that if you cut a slice
anywhere along the length of a
prism, at right angles to the
length, the slices will all be the
same shape and size.
2. Students can find cross
sections of prisms and use to
calculate the volume of any
prism.
How much coke
fits in a can?
3. To solve problems
involving surface are and
volume (2 lessons)
3. Remind students about the
difference between area and
volume.
3. Students solve problems
involving 3D shapes.
Tracy pours melted
chocolate into
moulds, what
volume of
chocolate does
4. As above
4.
4.
5. Area and
Perimeter
A central heating
tank is in the
shape of a cuboid.
How can we work
out the total area
that needs to be
painted?
6. 3D - Surface
area and
Volume
Similar shapes
and enlargement
effects on
measures.
Compound
shapes involving
circles
netssurfacearea
volumeofcuboids
volumeof-prisms
Compound 3D
shapes volume
and surface area.
Spheres and
Pyramids
Surface area and
Volume
Scheme of Work: Maths Year Group 9
An exceptional environment for learning and discovery
she need?
7. Rich Task
Week
1. Mini-assessment - end
of chapter test
2.
3.
4.
1.
1.
2.
3.
4.
2.
3.
4.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Visual Grammar - Princeton Architectural Press (2006)Dokumen96 halamanVisual Grammar - Princeton Architectural Press (2006)Long ZauBelum ada peringkat
- Congruence of TrianglesDokumen33 halamanCongruence of Trianglesptv7105Belum ada peringkat
- Sample - Primary - Intro of Standards To Assess WritingDokumen17 halamanSample - Primary - Intro of Standards To Assess Writingapi-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Sample - T L Good To OutstandingDokumen11 halamanSample - T L Good To Outstandingapi-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Sample - Raise Achievement of Yr 11Dokumen20 halamanSample - Raise Achievement of Yr 11api-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Eysiadimpactreport2016 1Dokumen3 halamanEysiadimpactreport2016 1api-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Maths Sig Poster - June 2017 ProgDokumen2 halamanMaths Sig Poster - June 2017 Progapi-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Impactreport-Ccah 1Dokumen3 halamanImpactreport-Ccah 1api-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Year 9 H Jan-Mar 2016-2017Dokumen18 halamanYear 9 H Jan-Mar 2016-2017api-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Y8 Physics 2 SolDokumen25 halamanY8 Physics 2 Solapi-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Year 8 Sol Biology 2Dokumen46 halamanYear 8 Sol Biology 2api-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Year 8 Jan-Mar 2016-2017 RevisedDokumen7 halamanYear 8 Jan-Mar 2016-2017 Revisedapi-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- Year 7 Jan-Mar 2016-2017Dokumen9 halamanYear 7 Jan-Mar 2016-2017api-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- How To Use Hegarty MathsDokumen10 halamanHow To Use Hegarty Mathsapi-344945420Belum ada peringkat
- 2020-21 G12 Mock AA-HL Calculator Practice Questions ANSWERSDokumen23 halaman2020-21 G12 Mock AA-HL Calculator Practice Questions ANSWERS0010048Belum ada peringkat
- CircleDokumen13 halamanCirclevanessa mendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1Dokumen21 halamanUnit 1Gwen Geraldine L. QuinteBelum ada peringkat
- LinesDokumen27 halamanLinesicynitrogen9087Belum ada peringkat
- The AFLOW Library of Crystallographic PrototypesDokumen831 halamanThe AFLOW Library of Crystallographic PrototypesJulian BriceñoBelum ada peringkat
- Maths Mock 8, Paper 2 (3008)Dokumen13 halamanMaths Mock 8, Paper 2 (3008)Yongcheng LiuBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Dokumen15 halamanUNIT 1 - Lesson 1 & 2Celina MarraBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering MechanicsDokumen41 halamanEngineering MechanicsAditya SutarBelum ada peringkat
- 2701 Mathematics Paper With Answer EveningDokumen6 halaman2701 Mathematics Paper With Answer Eveningalachno17Belum ada peringkat
- Name: Teacher: Date: Score:: Triangle Angle SumDokumen2 halamanName: Teacher: Date: Score:: Triangle Angle SumMohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Imotc: Circumcircle-ExcircleDokumen8 halamanImotc: Circumcircle-ExcircleSimple.comINDIA OFFICIALBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematcs 2-dDokumen11 halamanKinematcs 2-dALI RIZVIBelum ada peringkat
- Math 8th Class WorksheetDokumen38 halamanMath 8th Class WorksheetAnuradha SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- 3rdqunit TestDokumen5 halaman3rdqunit TestPatrice Del MundoBelum ada peringkat
- PX KX X X K: Important Questions MathematicsDokumen3 halamanPX KX X X K: Important Questions MathematicsNishant RaoBelum ada peringkat
- RMO 2013 Paper 2Dokumen1 halamanRMO 2013 Paper 2Himansu MookherjeeBelum ada peringkat
- DaringDokumen4 halamanDaringIsnania Auliya HikmaBelum ada peringkat
- Table of Specifications 3 Quarter Examination in Grade 10 MathematicsDokumen3 halamanTable of Specifications 3 Quarter Examination in Grade 10 MathematicsJoseph S. Palileo Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Pre CalDokumen17 halamanPre CalNatalie GaidBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes, M261-004, Conic Sections: 1 ParabolasDokumen4 halamanLecture Notes, M261-004, Conic Sections: 1 Parabolasaerogem618Belum ada peringkat
- Lines and AnglesDokumen63 halamanLines and AnglesthinkiitBelum ada peringkat
- 2.kinematics of MachineryDokumen14 halaman2.kinematics of MachineryJegan ParamasivamBelum ada peringkat
- ReviewerDokumen2 halamanReviewerFloribel OleBelum ada peringkat
- Path Planning of Multiple UAVs Using Dubins PDFDokumen17 halamanPath Planning of Multiple UAVs Using Dubins PDFcesarBelum ada peringkat
- Las 3.5 Constructing Polygons Solving Problems Involving Sides and Angles of A PolygonDokumen2 halamanLas 3.5 Constructing Polygons Solving Problems Involving Sides and Angles of A PolygonAngelo Rey NavaBelum ada peringkat
- Combined First and Second Semester B.Tech. Degree Examination, May 2009 (2008 Scheme) 08-104: Engineering Graphics (Cerpuf)Dokumen2 halamanCombined First and Second Semester B.Tech. Degree Examination, May 2009 (2008 Scheme) 08-104: Engineering Graphics (Cerpuf)Salim Saifudeen SaifudeenBelum ada peringkat
- Sat Maths FormulasDokumen83 halamanSat Maths FormulasJayati MehtaBelum ada peringkat