Register of Aspect Impact - IMSM 4.3.1 R02
Diunggah oleh
jrpatel18853Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Register of Aspect Impact - IMSM 4.3.1 R02
Diunggah oleh
jrpatel18853Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
DETERMINING PROBABILITY / LIKELIHOOD GUIDANCE CRITERIA
If almost no gap exists in control of the identified Environmental Aspect / impact as technology, operational
1
Highly unlikely (HUL)
control, measurement monitoring, competence in place
2
Unlikely (UL)
If there is any minor gap / weakness in control of the identified Environmental Aspect / impact
Likely (L)
There are unreasonable/ major gaps in the control of the identified Environmental Aspect / impacts with respect
to adoption of technology, operational control, measurement monitoring and competence
Very likely (VL)
There are almost no control in place in controlling the identified Environmental Aspect / Impact
DETERMINING LEVEL OF CONSEQUENCE GUIDANCE CRITERIA
Level of Harm /
Rating
Reference on Controls
Consequence
Effect on Environment
Slightly harmful
No control measure is required
Confined to the equipment / source
area
Harmful
Control measure may be required /
considered
Spread to the section limit
Very harmful
Control measure is certainly required
Spread beyond section limit
urgently
Extremely harmful
Control measures are required
immediately
Spread beyond factory limits / soil
contamination / contamination of
drains
Consumption of Resources
Controls are well established with
effective bench-marking (No
opportunity for further reduction)
Controls are established however yet
an opportunity for improvement
(Random opportunity for further
reduction)
Controls are in place however largely
ineffective (Reasonable opportunity
for further reduction
No Control at all including Huge
Generation of waste (Substantial &
continual opportunity for further
reduction)
DEFINITION OF LEVEL OF IMPACTS
Impact
Level
Impact Level
Action and Time Scale
1,2,3
TRIVIAL
No action is required and no documentary record needs to be kept.
4,6
TOLERABLE
No additional controls are required. Consideration may be given to a more cost-effective solution or improvement
that imposes no additional cost burden. Monitoring is required to ensure that the controls are maintained.
8,9,12
SUBSTANTIAL
Work should not be started until the impact has been reduced. Considerable resources may have to be allocated
to reduce the impact where the impact involves work in progress, urgent action should be taken.
16
INTOLERABLE
Work should not be started or continued until the impact has been reduced. If it is not possible to reduce impact
even with unlimited resources, work has to remain prohibited.
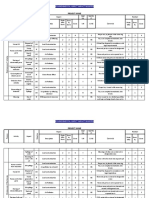
Develop a list of Environmental Aspects and Impacts:
Example:
Condition
Activity / Sub-activity
Environmental Aspect
Adequacy of
N/AN/E
Charging of Raw material in to
day bins
Consumption of electricity
- Operation of dust collector
Consumption of filter bags
Consumption of air
Generation of Hazardous
Waste - Waste mix RMs
Generation of Hazardous
Waste - Waste filter bags
Generation of noise
1. Workplace noise is below 90 dB
2. Regular PM being done
3. Oiling / Greasing is a part of CLIT
Noise Pollution
Dusting from day bins
charging ports
AN
1. PM of ID fan being done regularly
2. Replacement of filter bags every six
month
Air pollution
Fire due to mix of different
RMs
1. Compatibility study conducted
2. Daily frequency of empty out
collected mix RMs from dust collector
Air pollution
CASE: Actual / Normal
Emission from stack within
- No Gap in existing
limits
control
CASE: Actual / Normal Emission from stack within
- Gap in existing control limits
CASE: Potential / Emission from stack
Abnormal beyond limits
AN
CASE: Actual / Emission from stack
Abnormal beyond limits
AN
Existing
Gaps, if any
Impact
D/I
1. Power consumption being
monitored
2. Regular PM of ID fan / blower
Approved standard make filter bags
being used. Life expetency is 6 month
as per OEM
PM of ID fan being done regularly
1. Waste mix RMs extracted from
dust collector being tracked
2. Hazardous waste being disposed
off as per defined SOP
1. Approved standard make filter
bags being used. Life expetency is 6
month as per OEM
2. Hazardous waste being disposed
off as per defined SOP
1. Monitoring of stack emission being
done on month basis by MoEF
approved laboratory
2. Filter bags being replaced every six
month during PM
1. Monitoring of stack emission being
done on month basis by MoEF
Filter bags not
approved laboratory
replaced in last PM
2. Filter bags being replaced every six
month during PM
1. Monitoring of stack emission being
done on month basis by MoEF
approved laboratory
2. Filter bags being replaced every six
month during PM
1. Monitoring of stack emission being
done on month basis by MoEF
approved laboratory
2. Filter bags being replaced every six
month during PM
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Disposal of Hazardous
Waste by Incineration
Disposal of Hazardous
Waste by Incineration
Air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution
Likelihood - Consequen Total = L x
L
ces - C
C
Classification
of Impact
Over-riding factor
(LC)
Control Measures
Develop a list of Environmental Aspects and Impacts:
Exercise: 05
Condition
Activity / Sub-activity
Environmental Aspect
D/I
N/AN/E
Adequacy of
Existing
Gaps, if any
Impact
Likelihood - Consequen
Classification of
Total = L x C
L
ces - C
Impact
Over-riding factor
(LC)
Control Measures
Evaluate & Prioritize Environmental Aspects and Impacts:
Example:
Activity / Sub-activity
Environmental Aspect
Condition
D/I
N/AN/E
Charging of Raw material in to
day bins
Consumption of electricity
- Operation of dust collector
Consumption of filter bags
Consumption of air
Generation of Hazardous
Waste - Waste mix RMs
Generation of Hazardous
Waste - Waste filter bags
Generation of noise
Dusting from day bins
charging ports
Fire due to mix of different
RMs
Likelihood - Consequen
Classification of
Total = L x C
L
ces - C
Impact
2
Trivial
Resource Depletion
Trivial
Resource Depletion
Trivial
Disposal of Hazardous
Waste by Incineration
12
Substantial
Disposal of Hazardous
Waste by Incineration
Trivial
1. Workplace noise is below 90 dB
2. Regular PM being done
3. Oiling / Greasing is a part of CLIT
Noise Pollution
Trivial
AN
1. PM of ID fan being done regularly
2. Replacement of filter bags every six
month
Air pollution
Tolerable
1. Compatibility study conducted
2. Daily frequency of empty out
collected mix RMs from dust collector
Air pollution
Tolerable
Air pollution
Tolerable
Air pollution
Substantial
Air pollution
Tolerable
CASE: Actual / Normal Emission from stack within
- Gap in existing control limits
AN
1. Power consumption being
monitored
2. Regular PM of ID fan / blower
Impact
CASE: Actual / Emission from stack beyond
Abnormal limits
Gaps, if any
Resource Depletion
CASE: Actual / Normal
Emission from stack within
- No Gap in existing
limits
control
CASE: Potential / Emission from stack beyond
Abnormal limits
Adequacy of
Existing
AN
Approved standard make filter bags
being used. Life expetency is 6 month
as per OEM
PM of ID fan being done regularly
1. Waste mix RMs extracted from dust
collector being tracked
2. Hazardous waste being disposed off
as per defined SOP
1. Approved standard make filter bags
being used. Life expetency is 6 month
as per OEM
2. Hazardous waste being disposed off
as per defined SOP
1. Monitoring of stack emission being
done on month basis by MoEF
approved laboratory
2. Filter bags being replaced every six
month during PM
1. Monitoring of stack emission being
done on month basis by MoEF
Filter bags not
approved laboratory
replaced in last PM
2. Filter bags being replaced every six
month during PM
1. Monitoring of stack emission being
done on month basis by MoEF
approved laboratory
2. Filter bags being replaced every six
month during PM
1. Monitoring of stack emission being
done on month basis by MoEF
approved laboratory
2. Filter bags being replaced every six
month during PM
Air pollution
12
Substantial
Over-riding factor
(LC)
Control Measures
SOP/EMP:
1. QIP to be taken for
chemical scrap reduction
OSEP
LC
SOP/EMP:
Filter bag to be replaced eery
six month and noted in log
book
LC
SOP/EMP:
1. Filter bags replacement
frequency to be revised to 03
months
2. Improved dust collector
bfilter bags to be explored
3. Improved design of dust
collector to be procured
Evaluate & Prioritize Environmental Aspects and Impacts:
Exercise: 06
Date of Aspect Impact Study:
Risk Assessment Carried out by:
Version No.:
Activity / Sub-activity
Environmental Aspect
IDENTIFICATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL
ASPECTS AND EVALUTAION OF IMPACTS
Condition
D/I
N/AN/E
Adequacy of
Existing
Gaps, if any
Impact
Likelihood - Consequen
Classification of
Total = L x C
L
ces - C
Impact
IMSM 4.3.1/R01
Over-riding factor
(LC)
Control Measures
List of Aspect Imapct:
Aspect Category
Resource Use
Material Use
Air Emissions
Release to Air /
Water / Land
Aspect List
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Consumption of Engineering Material -*
Consumption of Chemical - *
Air Emission: Dust
Air Emission: Fumes
Air Emission: Vapours
Air Emission: Flue gas from stack
Air Emission: Vehicular emissions
Resource Depletion
Resource Depletion
Air Pollution
Air Pollution
Air Pollution
Air Pollution
Air Pollution
Generation of Condensate
Fire
Water Pollution
Land Pollution
Reuse of condensate (+ve)
Water Pollution
Land Pollution
Recycle of treated effluent in gardening (+ve)
Air Pollution
Water Pollution
Land Pollution
Air Pollution
Water Pollution
Land Pollution
Environmental Damage
Generation of Noise
Generation of Heat
Generation of Radiations
Generation of Vibrations
Generation of Odour
Environmental Nuisance
Environmental Nuisance
Environmental Nuisance
Environmental Nuisance
Environmental Nuisance
Generation of Effluent
Spillage
Leakage
Environmental
Nuisance
Impact List
Use of Electricity
Use of Water
Use of Natural Gas
Use of Diesel
Use of Furnace Oil
Use of Coal
Use of Steam
Use of Air
Use of Nitrogen
Consumption of Raw Material - *
Waste Management Generation of Hazardouse Waste - *
Generation of Bio-medical Waste
Generation of e-waste
Generation of Waste Lead Acid Batteries
Generation of Non-Hazardous Waste - *
Generation of Food Waste
Disposal of Hazardous Waste to Landfill
Disposal of Hazardous Waste by Incineration
Disposal of Hazardous Waste to Authorised Recycler
(+ve)
Disposal of Bio-medical Waste to Common BMW
Incineration
Final Impact for Waste Disposal
Land Pollution
Air Pollution
Conservation of Resources (+ve)
Air Pollution
Disposal of e-waste to Authorised Recycler (+ve)
Conservation of Resources (+ve)
Disposal of Waste Lead Acid Batteries to Authorised
Recyclers (+ve)
Conservation of Resources (+ve)
Reuse / Recycle of Non-Hazadrous Waste to Authorised
Traders (+ve)
Conservation of Resources (+ve)
Recycle of Non-Hazardous Waste by Re-work
Conservation of Resources (+ve)
Disposal of Food Waste by Cattle Feed (+ve)
Conservation of Resources (+ve)
List of RMs, HW, Non-HW:
Consumption of Raw Material - *
Generation of Non-Hazardouse Waste *
Bladder
Rubber
Carbon Black
Silica
Oil
Sulphur
Other Chemicals
Others - Indirect Material
Textile
Steel Cord
Generation of Hazardouse Waste - *
33.3-Discarded containers - empty containers / drums
Compound
Conveyor Belt
Electrical Scrap
Fabric
Flaps
33.3-Discarded containers - empty liners bags
34.3-ETP Sludge
5.1-Used Spent oil
3.3-Sludge and filters contaminated with oil
Garbage
Green Tyre
Liner bags
Liner MS drums
21.1-Waste / residue - Dust collector bags
21.2-Filler residues - Spent slurry from mixing
23.1-Waste / residue - Waste chemicals from mixing
Bead Wire
Liner Paper drums
Liner PVC Can
Liner PVC drum
MS Scrap
Non-Ferrous Scrap
Paper
Plastic
Rubber
Steel
Tubes
Tyre
Wooden Scrap
5.2-Waste/residue containing oil - Cotton waste / Used PPEs
33.1-Chemical containing residue from decontamination Chemicals from spillage / floor cleaning
34.1-Flue gas cleaning residue - Boiler / DG stacks
34.2-Residue from used ion exchange material in water
purification
34.5-Sludge from cooling water treatment
15.2-Discarded asbestos
Class D-Waste / residue containing sulphur (>50000 mg/kg)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Environmental Impact PrioritiesDokumen3 halamanEnvironmental Impact Prioritiespak-ksa lifeBelum ada peringkat
- EMS - Sample Environmental Aspects & Impacts RegisterDokumen7 halamanEMS - Sample Environmental Aspects & Impacts RegisterBalaji_Rajaman_22800% (2)
- Register of Environmental Aspects & Impacts: Business Standards SystemDokumen4 halamanRegister of Environmental Aspects & Impacts: Business Standards SystemguliBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Management System Risk RegisterDokumen6 halamanEnvironmental Management System Risk Registersjmpak100% (7)
- Register of Environmental Objectives and Targets SAMPLEDokumen1 halamanRegister of Environmental Objectives and Targets SAMPLERamasubramanian Sankaranarayanan0% (1)
- Aspect Impact RegisterDokumen4 halamanAspect Impact Registermark_vyz100% (7)
- Environmental Aspects and ImpactsDokumen9 halamanEnvironmental Aspects and Impactssharif khan100% (3)
- 200-74195 Aspect & Impacts Register RevDokumen484 halaman200-74195 Aspect & Impacts Register RevCandice100% (2)
- Environmental Management System, Aspect Impact RegisterDokumen2 halamanEnvironmental Management System, Aspect Impact RegisterBhagavat PatilBelum ada peringkat
- 02 General Aspect Impact StudyDokumen1 halaman02 General Aspect Impact StudymakdelBelum ada peringkat
- Sample SOP For Legal and Other Requirements PDFDokumen2 halamanSample SOP For Legal and Other Requirements PDFanoushia alviBelum ada peringkat
- PLT - H&S - Project HIRA - (R 13) 191125Dokumen115 halamanPLT - H&S - Project HIRA - (R 13) 191125soubhagyaBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Legal RegisterDokumen13 halamanEnvironmental Legal Registermuthuswamy77Belum ada peringkat
- Environmental Aspects and Impacts Evaluation REV-003Dokumen12 halamanEnvironmental Aspects and Impacts Evaluation REV-003sunthu100% (1)
- Aspects and Impacts Register 160415Dokumen1 halamanAspects and Impacts Register 160415Roselyn SharronBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Aspects & Impact AssessmentDokumen12 halamanEnvironmental Aspects & Impact AssessmentNida ArshadBelum ada peringkat
- Procedure For Objectives and TargetsDokumen2 halamanProcedure For Objectives and TargetsSAKTHIVEL A100% (1)
- Environmental Aspect Impact RegisterDokumen17 halamanEnvironmental Aspect Impact Registersyahir et0% (1)
- Environmental Risk RegisterDokumen3 halamanEnvironmental Risk RegisterSiyad SubairBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Aspect Impact RegisterDokumen10 halamanEnvironmental Aspect Impact Registernikhilearat100% (7)
- Operational ControlDokumen3 halamanOperational ControlAjas Aju50% (2)
- Aspects & Impacts Register Evaluates Company Environmental EffectsDokumen1 halamanAspects & Impacts Register Evaluates Company Environmental EffectsRASHEED YUSUFBelum ada peringkat
- GS - RA Gulfstar - Environmental Aspect and ImpactDokumen6 halamanGS - RA Gulfstar - Environmental Aspect and Impactsajin100% (1)
- 1-Mock Drill Report of Aegis Gas On 16-01-2018Dokumen3 halaman1-Mock Drill Report of Aegis Gas On 16-01-2018Parth PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Aspect Impact Evaluation Procedure.Dokumen3 halamanAspect Impact Evaluation Procedure.harshar2100% (1)
- Environmental Aspects Register (Iso 14001)Dokumen6 halamanEnvironmental Aspects Register (Iso 14001)Naba majeadBelum ada peringkat
- Hazard identification and risk assessment formDokumen8 halamanHazard identification and risk assessment formRaghulal ThalappalaBelum ada peringkat
- Register Environmental ImpactsDokumen7 halamanRegister Environmental ImpactsArmand LiviuBelum ada peringkat
- ISO-14001-2015 EA And-Procedure-SampleDokumen7 halamanISO-14001-2015 EA And-Procedure-SampleFaisal0% (1)
- Environmental AspectsDokumen31 halamanEnvironmental AspectsNachar A N100% (4)
- Incident Reports and Non-ConformancesDokumen12 halamanIncident Reports and Non-Conformancesvictor100% (1)
- Risks in Canteen and Office AreasDokumen8 halamanRisks in Canteen and Office Areasjoshisunil2Belum ada peringkat
- Condition Control or Influence Liklehood Severity Risk Rating Notes Controls Controlled Impact Rating ID No. Date Raised Activity Aspect ImpactDokumen2 halamanCondition Control or Influence Liklehood Severity Risk Rating Notes Controls Controlled Impact Rating ID No. Date Raised Activity Aspect ImpactnabilBelum ada peringkat
- Context of Org, Expectation of Interested Parties, Risk and OpporDokumen3 halamanContext of Org, Expectation of Interested Parties, Risk and OpporRAHUL SINGHBelum ada peringkat
- M/S Kaushal Prasad Patel: Excavation Permit-To-WorkDokumen2 halamanM/S Kaushal Prasad Patel: Excavation Permit-To-WorkAkhilesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Risk & Opportunities EMS 14001: 2015Dokumen23 halamanRisk & Opportunities EMS 14001: 2015Sukhdeep0% (1)
- EHS Induction Training ModuleDokumen19 halamanEHS Induction Training ModuleBhaskar ShuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Ims Manual 2019 FinalDokumen58 halamanIms Manual 2019 Finalaneesh awasthi100% (7)
- AJCI Hazard Identification ProcedureDokumen4 halamanAJCI Hazard Identification ProcedureEldhose Varghese100% (1)
- 1.1 Emergency Preparedness & Responce PlanDokumen29 halaman1.1 Emergency Preparedness & Responce PlanRavikant PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Aspect & Impact Assessment FinalDokumen7 halamanAspect & Impact Assessment FinalArsh Alam100% (2)
- Environmental Aspects and Impact Register TemplateDokumen5 halamanEnvironmental Aspects and Impact Register TemplateCarlosBelum ada peringkat
- Procedure For Accident Incident and Near MissDokumen2 halamanProcedure For Accident Incident and Near MissrgmBelum ada peringkat
- IMS Procedures Table of ContentsDokumen2 halamanIMS Procedures Table of Contentsaadwitya0% (2)
- Env Aspect Impact Register DAICEC ProjectDokumen16 halamanEnv Aspect Impact Register DAICEC Projectberat cilvezoğluBelum ada peringkat
- Aspect Impact RegisterDokumen17 halamanAspect Impact RegisterVi KraBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Aspects and Impacts RegisterDokumen1 halamanEnvironmental Aspects and Impacts Registerkev24580% (5)
- Aspects & Impacts Register v8.2 January 2015: S I G N I F I C A N C eDokumen5 halamanAspects & Impacts Register v8.2 January 2015: S I G N I F I C A N C eShashank SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Legal Register and Compliance TableDokumen34 halamanLegal Register and Compliance Tableheikal hajazie100% (1)
- Legal RegisterDokumen13 halamanLegal RegisterVictor Thembinkosi Makhubele50% (2)
- Legal Register 1Dokumen51 halamanLegal Register 1VictorBelum ada peringkat
- HIRADokumen57 halamanHIRAAnonymous Uc25fP83% (6)
- Identify and evaluate environmental impactsDokumen7 halamanIdentify and evaluate environmental impactsmanBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 14001 2015 Upgrade ChecklistDokumen10 halamanISO 14001 2015 Upgrade ChecklistDariush Rumi100% (1)
- Environmental Aspect Evaluation FormDokumen4 halamanEnvironmental Aspect Evaluation Form逍逾Belum ada peringkat
- Environmental Aspects & ImpectsDokumen25 halamanEnvironmental Aspects & ImpectsAldrinBelum ada peringkat
- OHSAS Objectives and Targets PA Rev2Dokumen3 halamanOHSAS Objectives and Targets PA Rev2ShirleyBelum ada peringkat
- Procedure Manual - IMS: Locomotive Workshop, Northern Railway, LucknowDokumen3 halamanProcedure Manual - IMS: Locomotive Workshop, Northern Railway, LucknowMarjorie Dulay Dumol67% (3)
- IVRCL IMS Audit ChecklistDokumen9 halamanIVRCL IMS Audit ChecklistAkd DeshmukhBelum ada peringkat
- Safe Handling of Haz SubstancesDokumen7 halamanSafe Handling of Haz Substancesjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- UndertakingDokumen1 halamanUndertakingjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Safe Handling of Haz SubstancesDokumen7 halamanSafe Handling of Haz Substancesjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Warehouse Inventory ReportDokumen4 halamanWarehouse Inventory Reportjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Lifting EquipmentsDokumen31 halamanLifting Equipmentsjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Hardner MachineDokumen1 halamanHardner Machinejrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Booklet For Road Safety For StudentsDokumen4 halamanBooklet For Road Safety For Studentsjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- AssertivenessDokumen16 halamanAssertivenesssaadiqbalBelum ada peringkat
- M5 Chapter2Dokumen32 halamanM5 Chapter2jrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- NET Payment Receipt: PCB ID: 33407-Ceat LimitedDokumen1 halamanNET Payment Receipt: PCB ID: 33407-Ceat Limitedjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Service Voucher: Josco Gsa Travel Pte LTDDokumen2 halamanService Voucher: Josco Gsa Travel Pte LTDjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- M5 Chapter3Dokumen11 halamanM5 Chapter3jrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- EHS Induction Record for CEAT Limited ContractorsDokumen5 halamanEHS Induction Record for CEAT Limited Contractorsjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Bbs PDFDokumen27 halamanBbs PDFjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Economic Evaluation of Pollution Prevention ProjectsDokumen18 halamanEconomic Evaluation of Pollution Prevention Projectsjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Nutrients Content of Sewage SludgeDokumen5 halamanNutrients Content of Sewage Sludgejrpatel18853100% (1)
- M5 Chapter1Dokumen64 halamanM5 Chapter1jrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- M5 Chapter1Dokumen64 halamanM5 Chapter1jrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- PDIS Practical BookDokumen16 halamanPDIS Practical Bookjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Silica CristalinaDokumen12 halamanSilica CristalinaRaul EvertonBelum ada peringkat
- Road Safety QuizDokumen4 halamanRoad Safety Quizjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Answer IIIDokumen1 halamanAnswer IIIjrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Worksheet - Impact Diagram (EMIQ) PDFDokumen2 halamanWorksheet - Impact Diagram (EMIQ) PDFjrpatel188530% (1)
- Gujarat Motor Vehicles Rules 1989 Amended909090919191Dokumen236 halamanGujarat Motor Vehicles Rules 1989 Amended909090919191Vishnu Prajapati100% (1)
- Preventing Sulphur Fires and ExplosionsDokumen40 halamanPreventing Sulphur Fires and Explosionsliveconnectionz2820% (1)
- Behavior Based Safety & You!!! Part IDokumen19 halamanBehavior Based Safety & You!!! Part Ijrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- R 22Dokumen7 halamanR 22Anggraeni DianBelum ada peringkat
- Gujarat State Eligibility Test (Gujarat Set)Dokumen2 halamanGujarat State Eligibility Test (Gujarat Set)jrpatel18853Belum ada peringkat
- Syllabus For Isat - 2011: PhysicsDokumen11 halamanSyllabus For Isat - 2011: PhysicsGulshan JhaBelum ada peringkat
- Eco Waste ManagementDokumen9 halamanEco Waste ManagementJhonny WankyBelum ada peringkat
- B. Wastewater TreatmentDokumen55 halamanB. Wastewater Treatmentelynah mistiola100% (1)
- Pollution Emitting From Guernsey Power Plant/PEH Incinerator and Proposed EtWDokumen6 halamanPollution Emitting From Guernsey Power Plant/PEH Incinerator and Proposed EtWchastyaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding the Air Quality Index (AQIDokumen13 halamanUnderstanding the Air Quality Index (AQIGilbert LBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Report On PollutionDokumen50 halamanSeminar Report On PollutionRanjuSingla100% (1)
- Logistics Company in SingaporeDokumen7 halamanLogistics Company in SingaporeAlex christenBelum ada peringkat
- Supply Chain AssignmentDokumen2 halamanSupply Chain AssignmentSounak81% (16)
- Improper Waste Disposal Threatens PhilippinesDokumen3 halamanImproper Waste Disposal Threatens PhilippinesAly TuzonBelum ada peringkat
- Official List of Registered Individual Preparers For Posting REVISED 9-19-2018Dokumen19 halamanOfficial List of Registered Individual Preparers For Posting REVISED 9-19-2018PHAU LIMITEDBelum ada peringkat
- Sunspot BeveragesDokumen6 halamanSunspot BeveragesDeep GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- TranspsDokumen27 halamanTranspsShariq KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Solid Waste Management in Guwahati CityDokumen42 halamanSolid Waste Management in Guwahati CityGirindra Konwar0% (1)
- Waste Generation and Characterization: Lesson 2 Week 2Dokumen52 halamanWaste Generation and Characterization: Lesson 2 Week 2Jennyrose AmigoBelum ada peringkat
- Waste Management in Selected Hotels in GoaDokumen11 halamanWaste Management in Selected Hotels in GoaSyna SoaresBelum ada peringkat
- Ecological Solid Waste Management NotesDokumen10 halamanEcological Solid Waste Management NotessantiagofayeBelum ada peringkat
- Pollution and Environment Lesson for Class 5Dokumen2 halamanPollution and Environment Lesson for Class 5Rakesh Agarwal57% (7)
- Environmental Quality Report (EQR) 2006Dokumen73 halamanEnvironmental Quality Report (EQR) 2006aubar67% (3)
- Clean Air ActDokumen48 halamanClean Air ActEphraim Gieronymus Esteban80% (10)
- Improper Waste ManagementDokumen10 halamanImproper Waste Managementapi-244392203Belum ada peringkat
- Table of Contents Report LiDokumen5 halamanTable of Contents Report LiSalihin FhooziBelum ada peringkat
- Book 1Dokumen7 halamanBook 1udinBelum ada peringkat
- Appendix A11: List of China's LNG Satellite StationsDokumen4 halamanAppendix A11: List of China's LNG Satellite StationsarapublicationBelum ada peringkat
- Marine PollutionDokumen18 halamanMarine PollutionPrem KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Environmental Pollution and Its Impacts On The EarthDokumen11 halamanEnvironmental Pollution and Its Impacts On The EarthnagarajanBelum ada peringkat
- SFZRFVHBJNKDokumen363 halamanSFZRFVHBJNKFazila KhanBelum ada peringkat
- List of Valid Mtos: in Charge For Export. (As On 24.08.2016)Dokumen269 halamanList of Valid Mtos: in Charge For Export. (As On 24.08.2016)tejasBelum ada peringkat
- Logistics Management of Indonesia's Livestock IndustryDokumen39 halamanLogistics Management of Indonesia's Livestock IndustrySofyan Wahidjul AdhzharruuBelum ada peringkat
- Role of Freight Forwarder in Import Export Business at PT - Jasa Trans Samudera Sulut Vinnita Laloma Johny. R.E. Tampi Danny D.S MukuanDokumen8 halamanRole of Freight Forwarder in Import Export Business at PT - Jasa Trans Samudera Sulut Vinnita Laloma Johny. R.E. Tampi Danny D.S MukuanFudjia YanBelum ada peringkat
- Water Pollution: Effects and SolutionsDokumen3 halamanWater Pollution: Effects and SolutionsJeremy EdBelum ada peringkat
- Landfills: What Is A Landfill?Dokumen4 halamanLandfills: What Is A Landfill?princekamutikanjoreBelum ada peringkat