Rosie Timmins Resp Case Study
Diunggah oleh
Paolo CarubioDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Rosie Timmins Resp Case Study
Diunggah oleh
Paolo CarubioHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
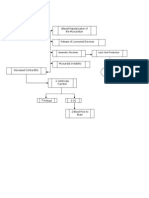
Rosie Timmins is a 60 year old female, asthmatic since she was 15 years of
age. Until age 40 years, she was almost totally asymptotic except for the
spring time when she would become very congested and wheezy with the
fresh pollens in the air. She was allergic to cats. Her ABGs remain normal. At
age 40 she became progressively more symptomatic, having bronchospasms
with any exertion, worsened during cold weather, coughing, audible
wheezing and shortness of breath. Her pulmonary function tests at this time
showed forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1.0) as significantly
reduced. Both her FEV1 and forced vital capacity (FVC) improved following
administration of an inhaled bronchodilator. At this time she started to
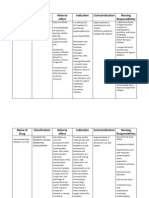
routinely use the following inhalers: ipratropium bromide 2 inhalations, BID,
up to QID prn; salmeterol 1 inhalation BID; budesonide 1 inhalation BID;
montelukast (Singulair) 10 mg daily, HS. As long as she continued to take the
mediations as recommended her symptoms were well under control.
Occasionally when she developed severe bronchospasms she increased her
dosage of inhalers. This increase in dosage was consistently followed by
episodes of palpitations, nervousness and restlessness. She also struggles
with frequent candidal throat infections (opportunistic infections), which she
states is extremely annoying. Every fall she makes sure to get the
recommended flu shot.
A year ago, at age 59 she was diagnosed as having emphysema. Her ABGs
on room air at the time of diagnosis were pH 7.35, pO2 82, pCO2 48, bicarb
29. Now when she is admitted to hospital she is on supplemental oxygen at 2
L/min N/P. Her respiratory rate is 18/min, prolonged expiratory phase,
wheezes present on expiration, using accessory muscles and pursed lip
breathing with and after any exertion. She is beginning to develop an
obvious barrel chest. She has lost some weight and is beginning to appear a
bit emaciated. Pulmonary function tests show increased expiratory reserve
volumes, decreased inspiratory capacity and increased total lung capacity.
On admission to hospital her heart rate is irregular at a rate of 100 beats/min
with ECG showing atrial fibrillation. She was started on propranolol to control
her heart rate and she promptly went into serious life threatening
bronchospasm. Fortunately she did not require artificial ventilation and her
medication was changed to diltiazem without further complications.
1 Why does Rosie become congested and wheezy when exposed to pollens,
cats and later also with exertion and exposure to cold air?
2 Given the mechanisms that cause edema, what is causing edema with
asthma and why/how?
3 People often think that asthma is a problem with getting air in, how do
Rosies pulmonary function tests show that it is an obstructive disease
and therefore primarily a problem with exhalation?
4 What is the purpose of each of the inhalers prescribed for Rosie? Why so
many? How do they work? Any precautions for their use?
Resp Tutorial
5 Which one(s) of Rosies medication is/are not effective in terminating
acute asthma attacks and why is that?
6 What will you teach Rosie about each of the inhalers, use of MDIs, and
about using them in combination?
7 What will you teach Rosie to help reduce the number of candidal throat
infections?
8 Why does Rosie develop palpations, nervousness and restlessness with
increased dosage of the inhalers?
9 Rosies ABGs are significantly altered when she is diagnosed with
emphysema. What are the mechanisms of hypoxemia responsible for her
altered blood gases?
10 What do Rosies symptoms and diagnostic results tell you about the
severity of her emphysema?
11 Why does Rosie have a barrel chest?
12 Why is Rosie doing pursed lip breathing? How is it ultimately helping her
oxygenation?
13 Rosie is given 2 L/min of oxygen, why not 5 or higher levels of oxygen?
14 What is the most likely reason for Rosie developing such severe
bronchospasm when she received propranolol? Explain.
15 Rosie was careful to get her yearly flu shot. Although this is important
for all high risk groups, what in particular places Rosie at high risk for
developing influenza and why is it important for her to prevent getting
the flu? How does the influenza immunization prevent influenza?
Resp Tutorial
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Leo Weber Cirrhosis Case StudyDokumen2 halamanLeo Weber Cirrhosis Case StudyPaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Best Practice Tools and Guidelines Health Maintenance ContinenceDokumen25 halaman12 Best Practice Tools and Guidelines Health Maintenance ContinencePaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- Leo Weber Cirrhosis Case StudyDokumen2 halamanLeo Weber Cirrhosis Case StudyPaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- Competency Appraisal 1 Reviewer-1Dokumen53 halamanCompetency Appraisal 1 Reviewer-1Paolo Carubio100% (1)
- Pathophy MIDokumen3 halamanPathophy MIPaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular Accident Hypothetical CaseDokumen1 halamanCerebrovascular Accident Hypothetical CasePaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- MI QuestionsDokumen4 halamanMI QuestionsPaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular Accident Hypothetical CaseDokumen1 halamanCerebrovascular Accident Hypothetical CasePaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- HepabDokumen5 halamanHepabPaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology AlterationsDokumen10 halamanHematology AlterationsPaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- NCP UEDokumen2 halamanNCP UEPaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- NCP UEDokumen2 halamanNCP UEPaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- Drugstudy KPDokumen5 halamanDrugstudy KPPaolo CarubioBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Presentation of Influenza in Children 6.22Dokumen7 halamanClinical Presentation of Influenza in Children 6.22akreditasi rsunhBelum ada peringkat
- Equine Influenza VirusDokumen10 halamanEquine Influenza Virusraul hernandezBelum ada peringkat
- MPS Quick Reference Chart 1Dokumen3 halamanMPS Quick Reference Chart 1caseynolanBelum ada peringkat
- End of Season 2022-2023 Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness in Preventing Influenza in Primary Care in PortugalDokumen5 halamanEnd of Season 2022-2023 Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness in Preventing Influenza in Primary Care in PortugalSofiaBelum ada peringkat
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 18. Viral InfectionsDokumen20 halamanBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 18. Viral Infectionsmirai desu100% (1)
- Health FinalDokumen11 halamanHealth Finalbernadeth magtibayBelum ada peringkat
- Tabel SKDR 2022Dokumen4 halamanTabel SKDR 2022Basroni FaizalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 67Dokumen1 halamanChapter 67James Gabriel SalardaBelum ada peringkat
- Blush 2012 Acute Bronchitis PDFDokumen7 halamanBlush 2012 Acute Bronchitis PDFMarimar FilardoBelum ada peringkat
- MEHLMANMEDICAL Microbiology Assessment 1 1Dokumen75 halamanMEHLMANMEDICAL Microbiology Assessment 1 1Feroz RaZa SoomrOoBelum ada peringkat
- Western Mindanao State University COLLEGE OF NURSING MIDTERM EXAMDokumen8 halamanWestern Mindanao State University COLLEGE OF NURSING MIDTERM EXAMDa DungBelum ada peringkat
- Davainea Proglottina - A Potentially Underestimated PDFDokumen3 halamanDavainea Proglottina - A Potentially Underestimated PDFryan100% (1)
- Home Remedies For PneumoniaDokumen15 halamanHome Remedies For PneumoniaAljunBaetiongDiazBelum ada peringkat
- EVS UNIT 5 Notes CBCS For ERPDokumen12 halamanEVS UNIT 5 Notes CBCS For ERPBrindha SBelum ada peringkat
- Pract 4Dokumen9 halamanPract 4Інга Гаврилюк100% (1)
- Paket 4 Soal2 Pra UN Untuk B. IngDokumen11 halamanPaket 4 Soal2 Pra UN Untuk B. Ingricky setiawan civilGBelum ada peringkat
- Influenza Vaccine Medical Exemption FormDokumen1 halamanInfluenza Vaccine Medical Exemption FormSatine EvansBelum ada peringkat
- Bacteria and VirusesDokumen48 halamanBacteria and VirusesSamKris Guerrero MalasagaBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd MAPEH 3Dokumen2 halaman2nd MAPEH 3Edmar MejiaBelum ada peringkat
- ICAR JRF PG Entrance Exam Questions 2011 - Veterinary ScienceDokumen3 halamanICAR JRF PG Entrance Exam Questions 2011 - Veterinary Sciencemadheshvet33% (3)
- On The Road AgainDokumen20 halamanOn The Road AgainmooraboolBelum ada peringkat
- Health Security As A Public Health Concept - A Critical AnalysisDokumen10 halamanHealth Security As A Public Health Concept - A Critical AnalysisViorentina YofianiBelum ada peringkat
- Alternative Healing: Reiki Over MedicineDokumen16 halamanAlternative Healing: Reiki Over MedicineSamy RajooBelum ada peringkat
- Texts Pau 2013 201412Dokumen19 halamanTexts Pau 2013 201412Helena SanzBelum ada peringkat
- Mold Toxins Richard Loyd MDDokumen4 halamanMold Toxins Richard Loyd MDOliver QueenBelum ada peringkat
- NLE Exam Drill 2 (Q Only 100)Dokumen13 halamanNLE Exam Drill 2 (Q Only 100)Epaphras Joel MilitarBelum ada peringkat
- 1respiratory System DisordersDokumen10 halaman1respiratory System DisordersArvin MalondrasBelum ada peringkat
- Mock 10031 Explanation Answer KeyDokumen13 halamanMock 10031 Explanation Answer KeyKavya PunjabiBelum ada peringkat
- Global ConspiracyDokumen196 halamanGlobal ConspiracymohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Public Health MODULE 7 - Pharmacists, Vaccines, and Public HealthDokumen13 halamanPublic Health MODULE 7 - Pharmacists, Vaccines, and Public HealthEmerson John TallodBelum ada peringkat