Drug Study Metformin
Diunggah oleh
AgronaSlaughterHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Drug Study Metformin
Diunggah oleh
AgronaSlaughterHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Drug Study Metformin
(Glucophage)
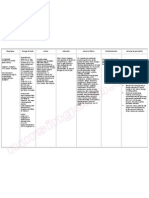
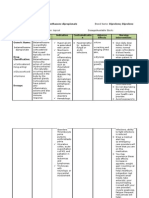
Generic Name:Metformin (met-formin)
Brand Name:Glucophage, Glucophage XR
Classifications: hormone and synthetic substitute; antidiabetic; biguanide
Pregnancy Category: B
Availability :
500 mg, 850 mg tab-lets; 500 mg sustained release
Actions
Biguanide oral hypoglycemic agent. Unlike sulfonylureas, biguanides do not stimulate
the release of insulin from the beta cells of the pancreas. Mechanism of action is
thought to be due to both increasing the binding of insulin to its receptor and
potentiating insulin action.
Therapeutic effects
Improves tissue sensitivity to insulin, increases glucose transport into skeletal muscles
and fat, and suppresses gluconeogenesis and hepatic production of glucose, thus
lowering blood glucose levels.
Uses:
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients not controlled with diet alone. May be
used with an oral sulfonylurea.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to metformin; renal, hepatic, or cardiopulmonary insufficiency;
alcoholism; concurrent infection.
Route & Dosage
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
adult: PO Start with 500 mg q.d. to t.i.d. or 850 mg q.d. to b.i.d. with meals, may
increase by 500850 mg/d every 13 wk (max: 2550 mg/d); or start with 500 mg
sustained release with p.m. meal, may increase by 500 mg/d at p.m. meal q wk (max:
2000 mg/d)
Administration
Oral
Withhold metformin 48 h before and 48 h after receiving IV contrast dye.
Give with or shortly after main meals.
Make dose increment, if needed, at 23-wk intervals.
Consider reduction of dose with concurrent cimetidine therapy.
Store at 1530 C (5986 F).
Adverse effects
CNS:Headache, dizziness, agitation, fatigue.
Nursing implications
Assessment & Drug Effects
Lab tests: Obtain baseline and periodic kidney and liver function tests; drug
contraindicated in the presence of renal or hepatic insufficiency.
Monitor blood glucose and HbA1C, and lipid profile periodically.
Monitor known or suspected alcoholics carefully for decreased liver function.
Monitor cardiopulmonary status throughout course of therapy;
cardiopulmonary insufficiency may predispose to lactic acidosis.
Patient & Family Education
Be aware that hypoglycemia is not a risk when drug is taken in recommended
therapeutic doses unless combined with other drugs which lower blood
glucose.
Report to physician immediately S&S of infection, which increase the risk of
lactic acidosis (e.g., abdominal pains, nausea and vomiting anorexia).
Do not breast feed while taking this drug without consulting physician.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Drug Study CaptoprilDokumen2 halamanDrug Study CaptoprilLyza Pamela T. Vinluan0% (1)
- Drug Study MetforminDokumen2 halamanDrug Study MetforminRez Apego94% (16)
- Lantus (Insulin Glargine)Dokumen3 halamanLantus (Insulin Glargine)EBelum ada peringkat
- Sodium ChlorideDokumen1 halamanSodium ChlorideMark Christian M. GonzagaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug Studymike_steven12Belum ada peringkat
- Humulin RDokumen1 halamanHumulin RZyrah Ziska ZafraBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)Dokumen3 halamanDrug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Metformin GlucophageDokumen2 halamanMetformin GlucophageCassie100% (4)
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug StudyKristine Joy A. AniBelum ada peringkat
- Name of Drug FinalDokumen7 halamanName of Drug FinalJaessa FelicianoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study MetforminDokumen3 halamanDrug Study MetforminAgronaSlaughter0% (1)
- Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanDrug StudyLee JennyBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study MetforminDokumen3 halamanDrug Study MetforminCalimlim Kim33% (3)
- Metformin Drug StudyDokumen1 halamanMetformin Drug StudyRose Echevarria67% (3)
- Gliclazide - Diamicron (Anti-Diabetics, Sulfonylureas - Insulin Production)Dokumen1 halamanGliclazide - Diamicron (Anti-Diabetics, Sulfonylureas - Insulin Production)Danielle Marie Samblaceno100% (1)
- Ipratropium BromideDokumen2 halamanIpratropium Bromideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug-Study-Metformin 1Dokumen2 halamanDrug-Study-Metformin 1Caroline Cha100% (1)
- AlprazolamDokumen3 halamanAlprazolamapi-3797941100% (1)
- GliclazideDokumen2 halamanGliclazideReinell GoBelum ada peringkat
- Epinephrine (DrugStudy)Dokumen4 halamanEpinephrine (DrugStudy)Axl Rose R. ArnejoBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationDokumen5 halamanHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdBelum ada peringkat
- BisoprololDokumen2 halamanBisoprololNovi YulianaBelum ada peringkat
- Glimepiride Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanGlimepiride Drug StudydyndzBelum ada peringkat
- LantusDokumen10 halamanLantusShanta100% (2)
- Drug StudyDokumen6 halamanDrug StudyMa R DyBelum ada peringkat
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDokumen1 halamanClonidine HydrochlorideLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezBelum ada peringkat
- AspirinDokumen1 halamanAspirinrhieyanBelum ada peringkat
- DRUG STUDY MetoprololDokumen1 halamanDRUG STUDY MetoprololSymone Jay Lapiz100% (2)
- Drug Study - InsulinDokumen1 halamanDrug Study - InsulinYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study LosartanDokumen2 halamanDrug Study LosartanKirsty Marie Supranes0% (1)
- SimvastatinDokumen3 halamanSimvastatinLonnieAllenVirtudes100% (1)
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDokumen4 halamanGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsBelum ada peringkat
- ClopidogrilDokumen2 halamanClopidogrilAkocmeme Sanchez100% (1)
- Tolvaptan-Drug StudyDokumen1 halamanTolvaptan-Drug Studykaycelyn jimenez100% (2)
- AmilorideDokumen1 halamanAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadBelum ada peringkat
- Brand Name: Aprovel Generic Name: Irbesartan Indications: For The TreatmentDokumen2 halamanBrand Name: Aprovel Generic Name: Irbesartan Indications: For The TreatmentianecunarBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen23 halamanDrug StudyEdward Baes33% (3)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaBelum ada peringkat
- NootropilDokumen2 halamanNootropilianecunar100% (4)
- Doxazosin MesylateDokumen2 halamanDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941Belum ada peringkat
- PrevacidDokumen2 halamanPrevacidianecunar100% (2)
- Atenolol Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanAtenolol Drug StudyFranz.thenurse6888100% (2)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanFurosemide Drug StudyYanna N. Cuaki100% (2)
- Drug Study ProglinDokumen2 halamanDrug Study ProglinChris Denver BancaleBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokumen1 halamanGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study DiclofenacDokumen4 halamanDrug Study DiclofenacFielMendoza89% (9)
- GlimepirideDokumen3 halamanGlimepirideapi-3797941100% (1)
- 18 Drug Study Drug Name Classificati ON Dosage Indicatio N Action Side Effects Contraindica Tion Nursing Consideratio NSDokumen2 halaman18 Drug Study Drug Name Classificati ON Dosage Indicatio N Action Side Effects Contraindica Tion Nursing Consideratio NSKhrycys Olairez RN100% (1)
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificDokumen1 halamanVii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificnuraBelum ada peringkat
- DiovanDokumen2 halamanDiovanianecunar100% (1)
- Drug Study - NitroglycerinDokumen1 halamanDrug Study - Nitroglycerinchriscustodio100% (1)
- Drug Study MetforminDokumen5 halamanDrug Study MetforminSabita PaudelBelum ada peringkat
- Metformin Hydrochloride PDFDokumen4 halamanMetformin Hydrochloride PDFHannaBelum ada peringkat
- PharmaDokumen2 halamanPharmaContrerasBelum ada peringkat
- Glyburide PDFDokumen3 halamanGlyburide PDFHannaBelum ada peringkat
- FR H 6788 001 FinalSPCDokumen28 halamanFR H 6788 001 FinalSPCabenezer g/kirstosBelum ada peringkat
- CKD Case StudyDokumen8 halamanCKD Case StudyEspiridionBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes Pancreatitis: J. Urquiza Z. M.C. F.CDokumen42 halamanDiabetes Pancreatitis: J. Urquiza Z. M.C. F.CgianmarcoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Analysis Table FormDokumen3 halamanDrug Analysis Table FormadjnglakaBelum ada peringkat
- Antidiabetic Medications: Pharm 585 February 15, 2011 Hy N DangDokumen36 halamanAntidiabetic Medications: Pharm 585 February 15, 2011 Hy N DangILa B Alwi ShahabBelum ada peringkat
- Atorvastatin Dosage 02Dokumen9 halamanAtorvastatin Dosage 02AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Atorvastatin Side Effects 01Dokumen7 halamanAtorvastatin Side Effects 01AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Atorvastatin Dosage 02Dokumen9 halamanAtorvastatin Dosage 02AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Atorvastatin 0Dokumen7 halamanAtorvastatin 0AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Atorvastatin Side Effects 01Dokumen7 halamanAtorvastatin Side Effects 01AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Atorvastatin 0Dokumen7 halamanAtorvastatin 0AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Metformin (Met For Min)Dokumen16 halamanMetformin (Met For Min)AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Atorvastatin Side Effects 01Dokumen7 halamanAtorvastatin Side Effects 01AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Metformin - Oral, GlucophageDokumen6 halamanMetformin - Oral, GlucophageAgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders of The Nervous System 2Dokumen2 halamanDisorders of The Nervous System 2AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Atorvastatin 0Dokumen7 halamanAtorvastatin 0AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Metformin, Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Glumetza, Fortamet, RiometDokumen5 halamanMetformin, Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Glumetza, Fortamet, RiometAgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- The Origin of 'Inaugurate': What Does 'Inaugurate' Have To Do With Interpreting Omens?Dokumen2 halamanThe Origin of 'Inaugurate': What Does 'Inaugurate' Have To Do With Interpreting Omens?AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen40 halamanDrug Studyapi-374468390% (61)
- Lactulose (Constulose, Enulose, Enerlac, Cholac, Constilac)Dokumen4 halamanLactulose (Constulose, Enulose, Enerlac, Cholac, Constilac)AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- LactuloseDokumen2 halamanLactuloseNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (1)
- Lactulose (LAK Tyoo Lose)Dokumen6 halamanLactulose (LAK Tyoo Lose)AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- LactuloseDokumen2 halamanLactuloseGrace Iloreta RN82% (11)
- Cavalry' or The Calvary'Dokumen2 halamanCavalry' or The Calvary'AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Lactulose Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanLactulose Drug StudyAgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Inaugurate 1Dokumen2 halamanInaugurate 1AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: ND RDDokumen5 halamanDrug Study: ND RDBinky Gozun100% (1)
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDokumen5 halamanDisorders of The Nervous SystemAgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Bible Printables - Creation Coloring Pages - Bible Creation Day 6Dokumen4 halamanBible Printables - Creation Coloring Pages - Bible Creation Day 6AgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Heredity: Genetic MutationsDokumen2 halamanHeredity: Genetic MutationsAgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- TrussesDokumen1 halamanTrussesAgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat
- Acs NCPDokumen4 halamanAcs NCPAgronaSlaughterBelum ada peringkat