Parts of Speech - Trainer's Manual
Diunggah oleh
DivyaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Parts of Speech - Trainer's Manual
Diunggah oleh
DivyaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PARTS OF SPEECH TRAINER’S MANUAL
short
Trainer’s Manual – exclamat
Objective – To help the participants understand the ion, oh!, Ouch! That
basics of sentence formation through parts of speech. Interject sometim ouch!, hurts! Hi! How are
Duration – 1.5 hrs* ion es hi!, you? Well, I don't
Material – Handout inserted well know.
into a
Summary of Concepts – sentence
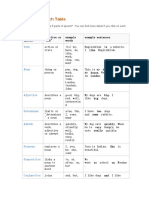
Exampl 1. Noun
Parts of Function Example
e This part of a speech refers to words that are used to
speech or "job" sentences
words name persons, things, animals, places, ideas, or
(to) be, events. Nouns are the simplest among the 8 parts of
have, speech, which is why they are the first ones taught to
do, students in primary school.
EnglishClub is a
action or like,
Verb web site.
state work, Examples:
I like EnglishClub.
sing,
can, Tom Hanks is very versatile.
must The italicized noun refers to a name of a person.
pen, Dogs can be extremely cute.
dog, In this example, the italicized word is considered a
work, noun because it names an animal.
music, This is my dog. He It is my birthday.
thing or
Noun town, lives in my house. The word “birthday” is a noun which refers to an event.
person
Londo We live inLondon. There are different types of nouns namely:
n,
teacher Proper– proper nouns always start with a capital letter
, John and refers to specific names of persons, places, or
good, things.
big, Examples: Volkswagen Beetle, Shakey’s Pizza, Game
Adjectiv describe red, My dogs are big. I of Thrones
e s a noun well, likebig dogs. Common– common nouns are the opposite of proper
interest nouns. These are just generic names of persons,
ing things, or places.
limits or a/an, Examples: car, pizza parlor, TV series
Determi "determi the, 2, I have two dogs Concrete– this kind refers to nouns which you can
ner nes" a some, andsome rabbits. perceive through your five senses.
noun many Examples: folder, sand, board
quickly Abstract- unlike concrete nouns, abstract nouns are
describe , My dog those which you can’t perceive through your five
s a verb, silently eats quickly. senses.
Adverb adjective , well, When he Examples: happiness, grudge, bravery
or badly, is very hungry, he Count– it refers to anything that is countable, and has
adverb very, eats really quickly. a singular and plural form.
really Examples: kitten, video, ball
I, you, Mass– this is the opposite of count nouns. Mass nouns
Tara is are also called non-countable nouns, and they need to
replaces he,
Pronoun Indian. She is have “counters” to quantify them.
a noun she,
beautiful. Examples of Counters: kilo, cup, meter
some
links a Examples of Mass Nouns: rice, flour, garter
to, at, We Collective– refers to a group of persons, animals, or
Preposit noun to
after, went to school on things.
ion another
on, but Monday. Example: faculty (group of teachers), class (group of
word
joins students), pride (group of lions)
I like dogs and I This great list of nouns can help you explore more
clauses
and, like cats. I like nouns.
Conjunc or
but, cats anddogs. I
tion sentence
when like dogs but I 2. Pronoun
s or
don't like cats. A pronoun is a part of a speech which functions as a
words
replacement for a noun. Some examples of pronouns
are: I, it, he, she, mine, his, hers, we, they, theirs, and
ours.
©2016 ETHNUS www.myethnus.com facebook.com/ethnus
PARTS OF SPEECH TRAINER’S MANUAL
Sample Sentences:
Adverb of Place– this tells something about “where”
Janice is a very stubborn child. She just stared at me something happens or ”where” something is done.
and when I told her to stop. Example: Of course, I looked everywhere!
The largest slice is mine. The adverb “everywhere” tells where I “looked.”
We are number one. Adverb of Degree– this states the intensity or the
The italicized words in the sentences above are the degree to which a specific thing happens or is done.
pronouns in the sentence. Example: The child is very talented.
The italicized adverb answers the question, “To what
3. Adjective degree is the child talented?”
This part of a speech is used to describe a noun or a
pronoun. Adjectives can specify the quality, the size, 6. Preposition
and the number of nouns or pronouns. This part of a speech basically refers to words that
specify location or a location in time.
Use this link to get a list of adjectives.
Examples of Prepositions: above, below, throughout,
Sample Sentences: outside, before, near, and since
The carvings are intricate. Sample Sentences:
The italicized word describes the appearance of the
noun “carvings.” Micah is hiding under the bed.
I have two hamsters. The italicized preposition introduces the prepositional
The italicized word “two,” is an adjective which phrase “under the bed,” and tells where Micah is
describes the number of the noun “hamsters.” hiding.
Wow! That doughnut is huge! During the game, the audience never stopped
The italicized word is an adjective which describes the cheering for their team.
size of the noun “doughnut.” The italicized preposition introduces the prepositional
phrase “during the game,” and tells when the audience
4. Verb cheered.
This is the most important part of a speech, for without
a verb, a sentence would not exist. Simply put, this is a 7. Conjunction
word that shows an action (physical or mental) or state The conjunction is a part of a speech which joins
of being of the subject in a sentence. words, phrases, or clauses together.
Examples of “State of Being Verbs” : am, is, was, are, Examples of Conjunctions: and, yet, but, for, nor, or,
and were and so
Sample Sentences: Sample Sentences:
As usual, the Stormtroopers missed their shot. This cup of tea is delicious and very soothing.
The italicized word expresses the action of the subject Kiyoko has to start all over again because she didn’t
“Stormtroopers.” follow the professor’s instructions.
They are always prepared in emergencies. Homer always wanted to join the play, but he didn’t
The verb “are” refers to the state of being of the have the guts to audition.
pronoun “they,” which is the subject in the sentence. The italicized words in the sentences above are some
examples of conjunctions.
5. Adverb
Just like adjectives, adverbs are also used to describe 8. Interjection
words, but the difference is that adverbs describe This part of a speech refers to words which express
adjectives, verbs, or another adverb. emotions. Since interjections are commonly used to
convey strong emotions, they are usually followed by
The different types of adverbs are: an exclamation point.
Adverb of Manner– this refers to how something Examples of Interjections:
happens or how an action is done.
Example: Annie danced gracefully. Sample Sentences:
The word “gracefully” tells how Annie danced.
Adverb of Time- this states “when” something happens Ouch! That must have hurt.
or “when” it is done. Hurray, we won!
Example: She came yesterday. Hey! I said enough!
The italicized word tells when she “came.” The bold words attached to the main sentences above
are some examples of interjections.
©2016 ETHNUS www.myethnus.com facebook.com/ethnus
PARTS OF SPEECH TRAINER’S MANUAL
15. Often
Directions: Which of the following option is true? A. I often go there.
B. I go there often.
1. He works hard. C. Both
A. 'Hard' is an adjective.
B. 'Hard' is an adverb. 16. Generally
A. Generally I don't read a newspaper.
2. She's a fast learner. B. I don't read a newspaper generally.
A. 'Fast' is an adjective. C. Both
B. 'Fast' is an adverb.
17. Rarely
3. Go straight down this road till you come to a A. Rarely I go there.
crossing. B. I go there rarely.
A. 'Straight' is an adjective. C. Both
B. 'Straight' is an adverb.
18. Soon
4. That's pretty. A. I'll do it soon.
A. 'Pretty' is an adjective. B. I'll do soon it.
B. 'Pretty' is an adverb. C. Both
5. It was pretty expensive. 19. Frequently
A. 'Pretty' is an adjective. A. I am frequently late for work.
B. 'Pretty' is an adverb. B. I frequently am late for work.
C. Both
6. It's a straight road.
A. 'Straight' is an adjective. 20. Always
B. 'Straight' is an adverb. A. I am on always time.
B. I am always on time.
7. She's a hard worker. C. Both
A. 'Hard' is an adjective.
B. 'Hard' is an adverb. 21. Yet
A. I haven't finished yet it.
8. Hold tight. B. I haven't finished it yet.
A. 'Tight' is an adjective. C. Both
B. 'Tight' is an adverb.
22. Now
9. I'm not well. A. I want now it.
A. 'Well' is an adjective. B. I want it now.
B. 'Well' is an adverb. C. Both
10. She did well. 23. Tomorrow
A. 'Well' is an adjective. A. Tomorrow I'll go there.
B. 'Well' is an adverb. B. I'll go there tomorrow.
C. Both
11. My shoes are tight.
A. 'Tight' is an adjective. 24. Yesterday
B. 'Tight' is an adverb. A. I yesterday went there.
B. I went there yesterday.
12. Please don't drive so fast. C. Both
A. 'Fast' is an adjective.
B. 'Fast' is an adverb. 25. Today
A. She arrives today.
Directions: Which of the following option is correct? B. She today arrives.
C. Both
13. Never
A. I never go there. 26. Yet
B. I go never there. A. I haven't done it yet.
C. Never I go there. B. I haven't yet done it.
C. Both
14. Usually
A. I usually get up at six-thirty. 27. Still
B. I get usually up at six-thirty. A. I still haven't finished.
B. I haven't finished still.
©2016 ETHNUS www.myethnus.com facebook.com/ethnus
PARTS OF SPEECH TRAINER’S MANUAL
C. Both 41. Mouse
A. Mouse's B. Mouses
C. Mice
Directions: Which option indicates the plural of the
word given? Explanation - Mutated Plurals
The second group of plurals we’ll talk about are
28. Child mutants, which also have Old English roots (4).
A. Childs B. Child's Examples are “foot,” “goose,” “woman,” and “louse,”
C. Children which become “feet,” “geese,” “women,” and “lice.”
Again we turn to German for an explanation of why
29. Half they're pluralized this way.
A. Halfs B. Halves
You form these mutated plurals simply by changing the
30. Potato vowel sound of the singular, in a process called
A. Potatos B. Potatoes “umlaut” (5). An umlaut is that little two-dot symbol you
C. Either sometimes see on German vowels, but what we’re
talking about here is a different meaning of the word.
31. Fish The process of umlaut is a technical linguistics concept
A. Fish B. Fishes (6). All we need to know for our purposes is that
C. Either mutated plurals are in fact quite rare in modern
English. Other examples are “man” and “men,”
32. Goose “mouse” and mice,” and “tooth” and “teeth.”
A. Geeses B. Geese
C. Gooses D. Goose Directions: Use the correct form of the verb to fill the
blanks in the sentences that follow:
33. Aircraft
A. Aircraft B. Aircrafts 42. It ____ easy.
A. am B. is
34. Church C. are
A. Churchs B. Church
C. Churches 43. There ____ some people waiting to see you.
A. am B. is
35. Woman C. are
A. Women B. Womans
44. There ____ some money to pay into the bank.
36. Fly A. am B. is
A. Flys B. Flies C. are
37. Sheep 45. They ____ coming.
A. Sheep B. Sheep's A. am B. is
C. Sheeps C. are
38. Foot 46. We ____ nearly ready.
A. Foot B. Foots A. am B. is
C. Feet C. are
39. Ox 47. It ____ impossible.
A. Ox B. Oxes A. am B. is
C. Oxen - C. are
Explanation - The s-form plurals became dominant in 48. He ____ unfriendly.
northern England first, while the en-form hung on in A. am B. is
southern England. By the 14th century the s-form C. are
became dominant everywhere, but people didn't let go
49. You ____ not to blame.
of the en-form completely; as late as the 16th century A. am B. is
the plural of eye was eyen and the plural of hose was C. are
hosen. Today only a few en-forms survive; the most
common are oxen and children. 50. How much ____ it?
A. am B. is
40. Box C. are
A. Box B. Boxes
C. Boxen 51. Who ____ on the phone?
A. am B. is
©2016 ETHNUS www.myethnus.com facebook.com/ethnus
PARTS OF SPEECH TRAINER’S MANUAL
C. are
52. Each week ____ worse.
A. am B. is
C. are
53. Everybody ____ leaving now.
A. am B. is
C. are
54. ____ anybody there?
A. Am B. Is
C. Are
©2016 ETHNUS www.myethnus.com facebook.com/ethnus
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 108.108. Sentence Pattern and Verb Form Egyptian Grammar Since Polotsky - Pdfpolotsky PDFDokumen10 halaman108.108. Sentence Pattern and Verb Form Egyptian Grammar Since Polotsky - Pdfpolotsky PDFsychev_dmitryBelum ada peringkat
- Alphabet Coloring PagesDokumen26 halamanAlphabet Coloring PagesPepepereirasBelum ada peringkat
- Birthday BannerDokumen9 halamanBirthday BannerKatie Waltemeyer100% (1)
- Thank You: For Downloading My FREE - at Family Reader From !Dokumen9 halamanThank You: For Downloading My FREE - at Family Reader From !Angelia PattersonBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Grade Curriculum MapDokumen1 halaman2nd Grade Curriculum Mapapi-261817938Belum ada peringkat
- Leaf IdialDokumen1 halamanLeaf IdiallolaBelum ada peringkat
- 1st Grade Units of StudyDokumen2 halaman1st Grade Units of Studyapi-472927063Belum ada peringkat
- CuteClassroomPostersSet5 1Dokumen28 halamanCuteClassroomPostersSet5 1Hariz shahBelum ada peringkat
- Leaders Guide Winter 2016 One Room School House Deep BlueDokumen100 halamanLeaders Guide Winter 2016 One Room School House Deep BlueBen Ondrak100% (1)
- NB Basics GuideDokumen43 halamanNB Basics GuideJulio Vicencio PonceBelum ada peringkat
- Placement Test 02Dokumen18 halamanPlacement Test 02Jennifer SouzaBelum ada peringkat
- Classroom Rules: ©pauley 2016Dokumen8 halamanClassroom Rules: ©pauley 2016Mercedes Marín RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Paper BAG Book: Made By:The Creative ClassroomDokumen19 halamanPaper BAG Book: Made By:The Creative ClassroomMartha Gotes TamayoBelum ada peringkat
- Through The Phonics BarrierDokumen64 halamanThrough The Phonics BarriersankahouseBelum ada peringkat
- Directory of Children's Illustration: Edition #16Dokumen82 halamanDirectory of Children's Illustration: Edition #16myalaura100% (1)
- A Silly Phonogram Review GameDokumen18 halamanA Silly Phonogram Review GameEkaterina DatsenkoBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4Dokumen11 halamanUnit 4Diego Nolasco OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- BloggingProcessMap PDFDokumen8 halamanBloggingProcessMap PDFDante Lau Jing Teck0% (1)
- Skills Builder BookDokumen24 halamanSkills Builder BookRodrigo Gonzalez GamboaBelum ada peringkat
- Build-a-Word Booklets: PrimerDokumen12 halamanBuild-a-Word Booklets: PrimerSiew Funn ChinBelum ada peringkat
- Independent Study Packet 1st Grade Week 8Dokumen25 halamanIndependent Study Packet 1st Grade Week 8Jennandco PrintsBelum ada peringkat
- Ps 7 Nov 2019 Cns 2Dokumen162 halamanPs 7 Nov 2019 Cns 2RutchelBelum ada peringkat
- Cut Apart Predictable SentencesDokumen28 halamanCut Apart Predictable SentencesakrichtchrBelum ada peringkat
- Grocery ListDokumen1 halamanGrocery ListHirra PervaizBelum ada peringkat
- About This ResourceDokumen10 halamanAbout This ResourceSanel Kriel KrielBelum ada peringkat
- Search EnginesDokumen3 halamanSearch EnginesSathya PrakashBelum ada peringkat
- Wiggle Like A WormDokumen12 halamanWiggle Like A Wormapi-537172848Belum ada peringkat
- Social and Political Issues Debate TopicsDokumen8 halamanSocial and Political Issues Debate Topicscaimacan.tundeBelum ada peringkat
- American AlligatorsDokumen11 halamanAmerican Alligatorsapi-394440828Belum ada peringkat
- Ps 5 Oct 2016 NCDokumen154 halamanPs 5 Oct 2016 NCmarian fae MallariBelum ada peringkat
- Family Home Budget Planner PDFDokumen8 halamanFamily Home Budget Planner PDFVikaBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech: A Concise GuideDokumen20 halamanParts of Speech: A Concise GuideMayla Lei PabloBelum ada peringkat
- GRAMMAR Fresh BeginningDokumen33 halamanGRAMMAR Fresh BeginningRitesh PoojaryBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech Table: Examples More Than One Job QuizDokumen5 halamanParts of Speech Table: Examples More Than One Job QuizlanrrayBelum ada peringkat
- EC Second Semester FinalsDokumen10 halamanEC Second Semester Finalschrisbel.simonBelum ada peringkat
- The Summary of Grammatical Patterns in TOEFL-OKDokumen53 halamanThe Summary of Grammatical Patterns in TOEFL-OKMur SyidahBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of SpeechDokumen10 halamanParts of SpeechKaung HeinBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech TableDokumen4 halamanParts of Speech TableVisnudaran NaIRBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech TableDokumen3 halamanParts of Speech TableNurul Hildayanti ILyasBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of SpeechDokumen6 halamanParts of SpeechjaquelineBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 Parts of SpeechDokumen23 halamanTopic 1 Parts of SpeechTuan Badarina T JusohBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech Table: A/an, The SomeDokumen3 halamanParts of Speech Table: A/an, The SomeMazlin MuratBelum ada peringkat
- Pel All NotesDokumen153 halamanPel All NotesAakrati JainBelum ada peringkat
- Bus Com 10Dokumen19 halamanBus Com 10Elijah ManzanoBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of SpeechDokumen8 halamanParts of SpeechMuhammad NeuerBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech, Phrase and ClauseDokumen16 halamanParts of Speech, Phrase and ClauseImam Syafi'iBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech: Tom Hanks Is Very VersatileDokumen5 halamanParts of Speech: Tom Hanks Is Very VersatileNorcena DaytoBelum ada peringkat
- 9 Parts of Speech ExplainedDokumen2 halaman9 Parts of Speech ExplainedM TBelum ada peringkat
- English For Faculty AgricultureDokumen70 halamanEnglish For Faculty AgricultureDelfrida KarlaniBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of SpeechDokumen13 halamanParts of SpeechDaniellina MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- 1.english Grammar Parts of SpeechDokumen39 halaman1.english Grammar Parts of Speechankamgude100% (1)
- KURANGDokumen55 halamanKURANGAdeluh KristantiBelum ada peringkat
- Group 1 - Cdi 302 Technical Report WritingDokumen47 halamanGroup 1 - Cdi 302 Technical Report WritingNiña Grace AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Winch 9780195529098 SCDokumen37 halamanWinch 9780195529098 SCArti SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech TheoryDokumen5 halamanParts of Speech TheoryJustoBelum ada peringkat
- 0 Parts of Speech IntroDokumen7 halaman0 Parts of Speech IntroMSQ GamingBelum ada peringkat
- English For EconomicsDokumen81 halamanEnglish For Economicskhun agnesBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of SpeechDokumen37 halamanParts of SpeechMuhammad Umar NaheedBelum ada peringkat
- The Parts of Speech: Part of Speech Function or "Job" Example Words Example SentencesDokumen3 halamanThe Parts of Speech: Part of Speech Function or "Job" Example Words Example SentencesYaser8Belum ada peringkat
- Parts of Speech in EnglishDokumen23 halamanParts of Speech in EnglishNina fauziah100% (1)
- Biru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000Dokumen24 halamanBiru Hijau Imut Ceria Tugas Presentasi Kelompok - 20240317 - 230007 - 0000saputsaput251Belum ada peringkat
- Socio LectDokumen3 halamanSocio LectChristelle Jean Arellano-PamanBelum ada peringkat
- Verb To Be: Affirmative and Negative FormDokumen8 halamanVerb To Be: Affirmative and Negative FormLuisa Fernanda RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Forming Comparative and Superlative AdverbsDokumen1 halamanForming Comparative and Superlative AdverbsMaryBelum ada peringkat
- Rhymes and RhythmDokumen30 halamanRhymes and Rhythmclaualexandra12100% (1)
- Fonologia NevalainenDokumen16 halamanFonologia Nevalainenireneireneirene24Belum ada peringkat
- Sanskrit Full PDFDokumen209 halamanSanskrit Full PDFSahaj Agarwal25% (4)
- Word Stress DictionaryDokumen17 halamanWord Stress DictionaryTwinkle Soni100% (1)
- Best Way To Learn Spanish PDFDokumen151 halamanBest Way To Learn Spanish PDFshahjitu100% (1)
- Subject Verb AgreementDokumen78 halamanSubject Verb Agreementanniedream80% (5)
- Communicative EnglishDokumen64 halamanCommunicative Englishkarthika4aBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar Awareness - QuipperDokumen6 halamanGrammar Awareness - QuipperShenron InamoratoBelum ada peringkat
- PT's ROLL NO.:230 DATE: 14-02-2011 Class: Vi Topic: Adjectives Subject: English Duration: 40 MinutesDokumen26 halamanPT's ROLL NO.:230 DATE: 14-02-2011 Class: Vi Topic: Adjectives Subject: English Duration: 40 MinutesKathryn BrownBelum ada peringkat
- Language q1 w3 10-23-17Dokumen1 halamanLanguage q1 w3 10-23-17api-366863515Belum ada peringkat
- Subject-Verb Agreement RulesDokumen3 halamanSubject-Verb Agreement RulesEl Gio EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Conditional Sentences: 1. First Conditional A. StructureDokumen2 halamanConditional Sentences: 1. First Conditional A. StructureBelén RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Personal PronounDokumen9 halamanPersonal PronounYamson MillerJrBelum ada peringkat
- Language VariationDokumen21 halamanLanguage VariationdanishBelum ada peringkat
- Alphabet Letter SoundsDokumen3 halamanAlphabet Letter Soundsapi-464640818Belum ada peringkat
- Ful and LessDokumen1 halamanFul and LessMed ChaibBelum ada peringkat
- Articles Unit 10Dokumen10 halamanArticles Unit 10Vicky SaezBelum ada peringkat
- English Grammar LessonsDokumen15 halamanEnglish Grammar LessonsVivek Kumar ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Norwegian Tutorial: Basic Phrases, Vocabulary and GrammarDokumen12 halamanNorwegian Tutorial: Basic Phrases, Vocabulary and GrammarolicluBelum ada peringkat
- Tajweed Rules of Stopping (Waqf) WorkshopDokumen9 halamanTajweed Rules of Stopping (Waqf) WorkshopArabic CacheBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges 2 (8. Razred)Dokumen2 halamanChallenges 2 (8. Razred)Jasna HadžićBelum ada peringkat
- Validity of Blends in Arabic and Jordanian Colloquial ArabicDokumen15 halamanValidity of Blends in Arabic and Jordanian Colloquial ArabicAla'a OmairatBelum ada peringkat
- Serbian Personal PronounsDokumen4 halamanSerbian Personal PronounsmyrmomBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Written ExpressionDokumen16 halamanStructure and Written ExpressionRizka Amelia IstyBelum ada peringkat
- Madjarska GramatikaDokumen184 halamanMadjarska GramatikaAlexandra Weiss100% (1)
- Summerof42Perusal PDFDokumen228 halamanSummerof42Perusal PDFAlberto KuryBelum ada peringkat