UTM System Intro PDF
Diunggah oleh
AngelHernandez0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
35 tayangan2 halamanJudul Asli
UTM_system_intro.pdf
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
35 tayangan2 halamanUTM System Intro PDF
Diunggah oleh
AngelHernandezHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Brief Introduction to the UTM coordinate system
The Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system is an international
locational reference system that depicts the Earth's three-dimensional
surface in a relatively-accurate, two-dimensional manner.
It relies on the meter unit of measure, and allows users to accurately
and unambiguously identify geographical locations anywhere on the
Earth's surface between the northern limits of North America (84
degrees north latitude) and the southern limits of continent of
Antarctica (80 degrees south latitude).
The remaining north and south polar regions are not included in the
UTM coordinate system due to extreme projection distortions in the
UTM grid.
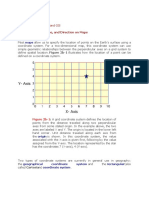
The UTM zones and grid
The UTM system depicts the Earth's
three-dimensional surface as a flat,
two-dimensional plane by dividing
its surface into 60 equally-spaced
vertical planes known as zones, or
world zones. Sequentially-
numbered 1 through 60, from west
to east, the starting point for the
zones (and the common border
between Zone 1 and Zone 60) is the
180-degree meridian of longitude,
or International Date Line.
British Columbia occupies 5 UTM
zones: 7 through 11.
The world-wide grid for the UTM
coordinate system consists of
parallel-running vertical (easting)
lines and parallel-running horizontal
(northing) lines, each of which is
spaced exactly 1,000 meters (1
kilometer) apart, to form 1,000-
meter squares.
Brief Introduction to the UTM coordinate system
Easting: UTM grid coordinates
are always written or
conveyed with the easting
data string appearing first,
before the northing data
string. By common
convention, easting
coordinates output from GPs
units are typically followed by
the letter "E".
Vertical lines are measured
from a separate point for each
zone, namely, an imaginary
line lying 500,000 metres west
of the zone's central meridian.
Actually, zones never attain
the full width of 1,000,000
metres which such a
measurement suggests; in
fact, in northern Canada, zone
widths shrink to as little as
80,000 metres (40,000 metres
on either side of the central meridian).
In practice, this means that in BC the actual distance between equal zone points is approx. 425km in the
South and 350km in the North (see illustration below for the importance of the UTM zone; all 4 points
have the same Easting and Northing, but a different zone!)
Northing: In the northern
hemisphere, a zone's southern
boundary (and point of origin) is the
equator, and it assumes the value of
zero meters. Horizontal lines are
designated by their distance from
the equator in metres. Because
Canada's southernmost point is
about 4,620,000 metres from the
equator, all horizontal lines in
Canada have a "northing" value
above that figure.
Note: While easting coordinates are
only six digits in length, convention
often adds a leading zero to make
them seven digits long so they
correspond lengthwise with seven-
digit northing coordinates.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Land Navigation With Map and CompassDokumen56 halamanLand Navigation With Map and CompassAngelHernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Hong Kong - Guide To Soil Nail Design and ConstructionDokumen100 halamanHong Kong - Guide To Soil Nail Design and Constructionvramirezm100% (1)
- Hydraulic Calculation Report - PSDokumen289 halamanHydraulic Calculation Report - PSAob AprilBelum ada peringkat
- Map ProjectionDokumen45 halamanMap ProjectionKhenny25Belum ada peringkat
- Manual of Cadastral Map Standards, Concepts & Cartographic ProceduresDokumen907 halamanManual of Cadastral Map Standards, Concepts & Cartographic ProceduresMariaAzevedoBelum ada peringkat
- Chart Projections ExplainedDokumen19 halamanChart Projections ExplainedNyan Min Htet100% (1)
- Radar Fundamentals 2Dokumen56 halamanRadar Fundamentals 2Chandan MishraBelum ada peringkat
- #### Biophotonics and Coherent Systems in Biology by Beloussov Voeikov Martynyuk 314pDokumen314 halaman#### Biophotonics and Coherent Systems in Biology by Beloussov Voeikov Martynyuk 314pwealth10Belum ada peringkat
- Supercritical Fluid Chromatography and ExtractionDokumen20 halamanSupercritical Fluid Chromatography and ExtractionHenny Casanova100% (2)
- Dynamic Positioning c12Dokumen28 halamanDynamic Positioning c12S D100% (1)
- Latitude & Longitude: Geography 2nd Grade for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionDari EverandLatitude & Longitude: Geography 2nd Grade for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences Books EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate SystemDokumen7 halamanUniversal Transverse Mercator Coordinate SystemNanang SantosaBelum ada peringkat
- UTM coordinate system explainedDokumen6 halamanUTM coordinate system explainedNguyen Van LongBelum ada peringkat
- 1coordenadas Del Tubo Conductor y ObjetivoDokumen36 halaman1coordenadas Del Tubo Conductor y ObjetivoJason PinzonBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Coordinate Systems and Map ProjectionsDokumen24 halamanReview of Coordinate Systems and Map ProjectionsPrince SanjiBelum ada peringkat
- Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinate system explainedDokumen7 halamanUniversal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinate system explainedanon_114803412Belum ada peringkat
- Unit II Coordinate SystemsDokumen76 halamanUnit II Coordinate SystemsRashkv428 kvBelum ada peringkat
- Coordinate System - SamiDokumen15 halamanCoordinate System - SamiAfzal PansuviBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 5 - PRS Handling - UTMDokumen32 halamanMODULE 5 - PRS Handling - UTMgavin.vedder1980Belum ada peringkat
- Coordinate System and Map ProjectionsDokumen27 halamanCoordinate System and Map ProjectionsAmbachew AlitahBelum ada peringkat
- Longitude, Latitude and DatumsDokumen24 halamanLongitude, Latitude and DatumsTATAVARTHYCH HANUMANRAOBelum ada peringkat
- The Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Grid: Map ProjectionsDokumen2 halamanThe Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Grid: Map ProjectionsJessica KingBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic declination and other compass-related conceptsDokumen17 halamanMagnetic declination and other compass-related conceptsKarl Luis RagmaBelum ada peringkat
- Vertical Position: Pattern Seen Is That Distortion of Scale Increases To 1.0010 at The Zone BoundariesDokumen2 halamanVertical Position: Pattern Seen Is That Distortion of Scale Increases To 1.0010 at The Zone BoundariesMayankJainBelum ada peringkat
- Coordinate Reference Systems - Bench PartnerDokumen3 halamanCoordinate Reference Systems - Bench PartnerSonu BhaiBelum ada peringkat
- LCC & UtmDokumen5 halamanLCC & Utmali_bse2301Belum ada peringkat
- Field Geology (Lec.2)Dokumen9 halamanField Geology (Lec.2)cm4pt45hkvBelum ada peringkat
- INTRO MWD MODULE-UTM ZONESDokumen19 halamanINTRO MWD MODULE-UTM ZONEShilmiBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 Concept of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Map Projections and Map TypeDokumen64 halamanLecture 3 Concept of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Map Projections and Map TypeJunaid Afzal100% (1)
- Geographic Information System (GIS) : TrainingDokumen13 halamanGeographic Information System (GIS) : TrainingArenPrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Active Sensors Are Instruments That Emit EMDokumen12 halamanActive Sensors Are Instruments That Emit EMAbebawBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4: 4.0. Coordinate System and Global Positioning System (GPS)Dokumen10 halamanUnit 4: 4.0. Coordinate System and Global Positioning System (GPS)sly gotoBelum ada peringkat
- Satellite CommunicationDokumen3 halamanSatellite CommunicationNuuradiin Xasan DhaqaneBelum ada peringkat
- GPS MappingDokumen34 halamanGPS MappingAnonymous itBHhEuBelum ada peringkat
- UTM Coordinate SystemDokumen13 halamanUTM Coordinate SystemErick JumaBelum ada peringkat
- Let's Get Started (Diagnostic Test)Dokumen10 halamanLet's Get Started (Diagnostic Test)kathBelum ada peringkat
- Dana Tutorial On Coordinate SystemsDokumen14 halamanDana Tutorial On Coordinate SystemsSurvey_easyBelum ada peringkat
- (B) - Location, Distance, and Direction On MapsDokumen12 halaman(B) - Location, Distance, and Direction On MapsprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Universal Polar Stereographic Co-Ordinate SystemDokumen19 halamanUniversal Polar Stereographic Co-Ordinate SystemUzair UllahBelum ada peringkat
- Measurement of AnglesDokumen5 halamanMeasurement of AnglesVerlyn Kate Pang-ayBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of MapDokumen45 halamanFundamentals of MapPamela WashingtonBelum ada peringkat
- USGS How To Use Map & CompassDokumen2 halamanUSGS How To Use Map & CompassDana WillsonBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Electronic Communication Systems Lecture 5 Satellite CoordinatesDokumen26 halamanAdvanced Electronic Communication Systems Lecture 5 Satellite Coordinatesndeshmukh83Belum ada peringkat
- Conformal Mapping of A Surface Onto A PlaneDokumen14 halamanConformal Mapping of A Surface Onto A PlaneMark Jeric UbiasBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah 3 - Coordinate System - Map ProjectionDokumen33 halamanKuliah 3 - Coordinate System - Map ProjectionKevin aryaBelum ada peringkat
- Coordinate SystemsDokumen22 halamanCoordinate SystemsBilal KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Cooesinte SystemDokumen35 halamanCooesinte SystemUNNATI AGRAWALBelum ada peringkat
- Transportation System - Distance CalculationDokumen14 halamanTransportation System - Distance CalculationRaluca AndreeaBelum ada peringkat
- Duhok Polytechnic University: Global Position System (GPS)Dokumen7 halamanDuhok Polytechnic University: Global Position System (GPS)Xogr BargarayBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Maps of EarthDokumen4 halamanUnderstanding Maps of EarthKalyana AyyaswamyBelum ada peringkat
- EarthKAM GeoUnderstandingMaps PDFDokumen4 halamanEarthKAM GeoUnderstandingMaps PDFKalyana AyyaswamyBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 4 Sistem Koordinat - Proyeksi PetaDokumen40 halamanPertemuan 4 Sistem Koordinat - Proyeksi PetaKevin aryaBelum ada peringkat
- Surveying 2 Practical 3Dokumen15 halamanSurveying 2 Practical 3Huzefa AliBelum ada peringkat
- Map Scale Coordinate System: Two Common Systems of Coordinate ReferencingDokumen2 halamanMap Scale Coordinate System: Two Common Systems of Coordinate ReferencingAngel TsuiBelum ada peringkat
- Angle Measurements GuideDokumen47 halamanAngle Measurements GuideKhiel Yumul100% (1)
- Geography Skills (Mapwork)Dokumen2 halamanGeography Skills (Mapwork)Marina RamharackBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 5Dokumen7 halamanLesson 5t8ktwrcvj4Belum ada peringkat
- Geographic Location SystemsDokumen16 halamanGeographic Location SystemsSyed Jabed Miadad AliBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - 4 - Basic Concepts - ProjectionsDokumen34 halamanLecture - 4 - Basic Concepts - ProjectionsSai KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Look at The Picture and Answer These Questions. Suggested AnswerDokumen7 halamanLook at The Picture and Answer These Questions. Suggested AnswerKamolpan JammapatBelum ada peringkat
- Carthography 1&2 1Dokumen40 halamanCarthography 1&2 1warkisa0Belum ada peringkat
- Projections Examples of Different Projections Coordinate Systems DatumsDokumen53 halamanProjections Examples of Different Projections Coordinate Systems DatumsRajBelum ada peringkat
- The Earth As A Sphere - 025327Dokumen8 halamanThe Earth As A Sphere - 025327Baraka LoibangutiBelum ada peringkat
- Coordinates SystemsDokumen27 halamanCoordinates Systemsshayma190852Belum ada peringkat
- Active Microwave RSDokumen77 halamanActive Microwave RSChikutokiBelum ada peringkat
- Real-Time Earthquake Tracking and Localisation: A Formulation for Elements in Earthquake Early Warning Systems (Eews)Dari EverandReal-Time Earthquake Tracking and Localisation: A Formulation for Elements in Earthquake Early Warning Systems (Eews)Belum ada peringkat
- ELEM Activity Moon Rise SetDokumen15 halamanELEM Activity Moon Rise SetLinus MungerBelum ada peringkat
- UTM System IntroDokumen2 halamanUTM System IntroAngelHernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Solution - Manual - Fundamentals - o 83Dokumen1 halamanSolution - Manual - Fundamentals - o 83Lit Pao WongBelum ada peringkat
- Order of ReactionDokumen11 halamanOrder of ReactionBadar RizwanBelum ada peringkat
- 9702 w11 QP 43Dokumen24 halaman9702 w11 QP 43Hubbak KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Soal GeotekDokumen12 halamanSoal GeotekNurafni Nugroho PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Magneto Abrasive Flow MachiningDokumen11 halamanMagneto Abrasive Flow MachiningBhuvnesh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Low Power-Consumption CO2 Sensor: (Model NO:MG-812)Dokumen6 halamanLow Power-Consumption CO2 Sensor: (Model NO:MG-812)Nguyen Vu Hoang ThachBelum ada peringkat
- Xapp1301 Mechanical Thermal Design GuidelinesDokumen88 halamanXapp1301 Mechanical Thermal Design GuidelinesJogirek VekturBelum ada peringkat
- Production of BioemulsifierDokumen4 halamanProduction of BioemulsifierSwateja MangleBelum ada peringkat
- RooftankDokumen1 halamanRooftankwennycantikBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4-9: Bonding in Ceramics and Structure of Ceramics: MM 362 Ceramics and Glasses Spring Semester 2020, FMCE, GIKIDokumen70 halamanLecture 4-9: Bonding in Ceramics and Structure of Ceramics: MM 362 Ceramics and Glasses Spring Semester 2020, FMCE, GIKIUsamaBelum ada peringkat
- Forces and Motion WSDokumen5 halamanForces and Motion WSMohammed Aamir YasirBelum ada peringkat
- Outcome 2 T 1Dokumen14 halamanOutcome 2 T 1R ASTUSBelum ada peringkat
- F 2013 - 00 - RjiwmtmtmdaDokumen9 halamanF 2013 - 00 - RjiwmtmtmdaAndres Camilo BenitezBelum ada peringkat
- Submittal FCQ24MVJU - RZQ24MVJU 07-06 - DaikinDokumen1 halamanSubmittal FCQ24MVJU - RZQ24MVJU 07-06 - Daikinedward sabedraBelum ada peringkat
- MD2 - HBW Set 2Dokumen1 halamanMD2 - HBW Set 2BenBelum ada peringkat
- Unsteady Heat Transfer Experiment ResultsDokumen16 halamanUnsteady Heat Transfer Experiment ResultssukhmaniBelum ada peringkat
- Electro ChemistryDokumen5 halamanElectro ChemistrySush ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- WELDINGDokumen94 halamanWELDINGharshaBelum ada peringkat
- Water-Injected Flare Tips Reduce Radiated Heat, Noise: Rilling RoductionDokumen4 halamanWater-Injected Flare Tips Reduce Radiated Heat, Noise: Rilling RoductionAnonymous cuOIjrLIBelum ada peringkat
- 2005 Gelder 1 PHDDokumen320 halaman2005 Gelder 1 PHDMaxel Abe DamuagBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis of Pan Hui 2006 University of Singapo PHDDokumen219 halamanThesis of Pan Hui 2006 University of Singapo PHDWeiwei SunBelum ada peringkat
- Aerodynamics-II Questions BankDokumen6 halamanAerodynamics-II Questions Bankae00505Belum ada peringkat
- Review On Fused Deposition ModelingDokumen11 halamanReview On Fused Deposition ModelingM Ali HaiderBelum ada peringkat
- High-performance industrial gear oilsDokumen5 halamanHigh-performance industrial gear oilsKeshab ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Finite Element Analysis of Laminated Composite Pressure VesselsDokumen6 halamanFinite Element Analysis of Laminated Composite Pressure VesselssrivatsanBelum ada peringkat
- Advantages & Disadvantages of Glass As A Building MaterialDokumen9 halamanAdvantages & Disadvantages of Glass As A Building MaterialRohithBelum ada peringkat