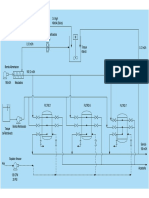
Nominal Pipe Size - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Diunggah oleh
JulioRojasHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nominal Pipe Size - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Diunggah oleh
JulioRojasHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nominal Pipe Size - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Log in / create account
Article Talk Read Edit View history
Nominal Pipe Size
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Main page Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) is a North American set of standard sizes for pipes used for high or low pressures and
Contents temperatures. [1] Pipe size is specified with two non-dimensional numbers: a nominal pipe size (NPS) for diameter based on
Featured content inches, and a schedule (Sched. or Sch.) for wall thickness. NPS is often incorrectly called National Pipe Size, due to confusion
Current events with national pipe thread (NPT). The European designation equivalent to NPS is DN (diamtre nominal/nominal
Random article diameter/Durchmesser nach Norm), in which sizes are measured in millimetres.[2] The term NB (nominal bore) is also
Donate to Wikipedia frequently used interchangeably with NPS.
Interaction Contents [hide]
Help 1 History
About Wikipedia 2 Application
Community portal 3 NPS tables for selected sizes
Recent changes 3.1 NPS to NPS 3
Contact Wikipedia 3.2 NPS 4 to NPS 9
3.3 NPS 10 to NPS 24
Toolbox
3.4 NPS 26 to NPS 36
Print/export 3.5 Additional sizes (NPS)
4 Heading text
Languages
5 See also
Deutsch
6 Notes
Espaol
7 References
Italiano 7.1 Bibliography
Portugus 8 External links
Ting Vit
History [edit]
In March 1927, the American Standards Association authorized a committee to standardize the dimensions of wrought steel
and wrought iron pipe and tubing. At that time only a small selection of wall thicknesses were in use: standard weight (STD),
extra-strong (XS), and double extra-strong (XXS), based on the iron pipe size (IPS) system of the day. However these three
sizes did not fit all applications. The committee surveyed the industry and created a system of schedule numbers that
designated wall thicknesses based on smaller steps between sizes, [3] although IPS and NPS numbers remain equivalent.
The original intent was that each schedule would relate to a given pressure rating, however the numbers deviated so far from
wall thicknesses in common use that this original intent could not be accomplished. [3][note 1] Also, in 1939, it was hoped that
the designations of STD, XS, and XXS would be phased out by schedule numbers, however those original terms are still in
common use today (although sometimes referred to as standard, extra-heavy (XH), and double extra-heavy (XXH),
respectively). Since the original schedules were created, there have been many revisions and additions to the tables of pipe
sizes based on industry use and on standards from API, ASTM, and others.[3]
Stainless steel pipes, which were coming into more common use in the mid 20th century, permitted the use of thinner pipe
walls with much less risk of failure due to corrosion. By 1949 thinner schedules 5S and 10S, which were based on the
pressure requirements modified to the nearest BWG number, had been created, and other "S" sizes followed later. Due to their
thin walls, the smaller "S" sizes can not be threaded together according to ASME code, but must be fusion welded.[4]
Application [edit]
Based on the NPS and schedule of a pipe, the pipe outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness can be obtained from reference
tables such as those below, which are based on ASME standards B36.10M and 5.19M. For example, NPS 14 Sch 40 has an
OD of 14inches and a wall thickness of 0.437inches. However the NPS and OD values are not always equal, which can
create confusion.
For NPS to 12inches, the NPS and OD values are different. For example, the OD of an NPS 12 pipe is actually
12.75inches. To find the actual OD for each NPS value, refer to the tables below. (Note that for tubing, the size is always
the actual OD.)
For NPS 14inches and up, the NPS and OD values are equal. In other words, an NPS 14 pipe is actually 14inches OD.
The reason for the discrepancy for NPS to 12inches is that these NPS values were originally set to give the same inside
diameter (ID) based on wall thicknesses standard at the time. However, as the set of available wall thicknesses evolved, the
ID changed and NPS became only indirectly related to ID and OD.
For a given NPS, the OD stays fixed and the wall thickness increases with schedule. For a given schedule, the OD increases
with NPS while the wall thickness stays constant or increases. Using equations and rules in ASME B31.3 Process Piping, it
can be shown that pressure rating decreases with increasing NPS and constant schedule.[note 1]
Some specifications use pipe schedules called standard wall (STD), extra strong (XS), and double extra strong (XXS),
although these actually belong to an older system called iron pipe size (IPS). The IPS number is the same as the NPS
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nominal_Pipe_Size[13/03/2012 04:50:32 p.m.]
Nominal Pipe Size - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
number. STD is identical to SCH 40S, and 40S is identical to 40 for NPS 1/8 to NPS 10, inclusive. XS is identical to SCH 80S,
and 80S is identical to 80 for NPS 1/8 to NPS 8, inclusive. XXS wall is thicker than schedule 160 from NPS 1/8" to NPS 6"
inclusive, and schedule 160 is thicker than XXS wall for NPS 8" and larger.
The "S" designation, for example "NPS Sch 10S", most often indicates stainless steel pipes. However some stainless steel
pipes are available in steel designations, so strictly speaking the "S" designation only differentiates B36.19M pipe from
B36.10M pipe. [1]
Both polyvinyl chloride pipe (PVC) and chlorinated polyvinyl chloride pipe (CPVC) are made in NPS sizes.
NPS tables for selected sizes [edit]
NPS to NPS 3 [edit]
Wall thickness
[in (mm)]
DN OD
NPS [5] [2] SCH SCH
[in (mm)] SCH
SCH 5 SCH 30 40s/40 80s/80 SCH 120 SCH 160 XXS
10s/10
/STD /XS
0.405 0.035 0.049 0.057 0.068 0.095
6
(10.29) (0.889) (1.245) (1.448) (1.727) (2.413)
0.540 0.049 0.065 0.073 0.088 0.119
8
(13.72) (1.245) (1.651) (1.854) (2.235) (3.023)
0.675 0.049 0.065 0.073 0.091 0.126
10
(17.15) (1.245) (1.651) (1.854) (2.311) (3.200)
0.840 0.065 0.083 0.095 0.109 0.147 0.188 0.294
15
(21.34) (1.651) (2.108) (2.413) (2.769) (3.734) (4.775) (7.468)
1.050 0.065 0.083 0.095 0.113 0.154 0.219 0.308
20
(26.67) (1.651) (2.108) (2.413) (2.870) (3.912) (5.563) (7.823)
1.315 0.065 0.109 0.114 0.133 0.179 0.250 0.358
1 25
(33.40) (1.651) (2.769) (2.896) (3.378) (4.547) (6.350) (9.093)
1.660 0.065 0.109 0.117 0.140 0.191 0.250 0.382
1 32
(42.16) (1.651) (2.769) (2.972) (3.556) (4.851) (6.350) (9.703)
1.900 0.065 0.109 0.125 0.145 0.200 0.281 0.400
1 40
(48.26) (1.651) (2.769) (3.175) (3.683) (5.080) (7.137) (10.160)
2.375 0.065 0.109 0.125 0.154 0.218 0.250 0.343 0.436
2 50
(60.33) (1.651) (2.769) (3.175) (3.912) (5.537) (6.350) (8.712) (11.074)
2.875 0.083 0.120 0.188 0.203 0.276 0.300 0.375 0.552
2 65
(73.03) (2.108) (3.048) (4.775) (5.156) (7.010) (7.620) (9.525) (14.021)
3.500 0.083 0.120 0.188 0.216 0.300 0.350 0.438 0.600
3 80
(88.90) (2.108) (3.048) (4.775) (5.486) (7.620) (8.890) (11.125) (15.240)
4.000 0.083 0.120 0.188 0.226 0.318 0.636
3 90
(101.60) (2.108) (3.048) (4.775) (5.740) (8.077) (16.154)
NPS 4 to NPS 9 [edit]
Wall thickness
OD [in (mm)]
DN
NPS [5] [2] [in SCH SCH
SCH SCH SCH SCH SCH SCH SCH SCH SCH
(mm)] 40s/40 80s/80 XXS[5]
5 10s/10 20 30 60 100 120 140 160
/STD /XS
4.500 0.083 0.120 0.188 0.237 0.281 0.337 0.437 0.531 0.674
4 100
(114.30) (2.108) (3.048) (4.775) (6.020) (7.137) (8.560) (11.100) (13.487) (17.120)
5.000 0.247 0.355 0.710
4 115
(127.00) (6.274) (9.017) (18.034)
5.563 0.109 0.134 0.258 0.375 0.500 0.625 0.750
5 125
(141.30) (2.769) (3.404) (6.553) (9.525) (12.700) (15.875) (19.050)
6.625 0.109 0.134 0.280 0.432 0.562 0.718 0.864
6 150
(168.28) (2.769) (3.404) (7.112) (10.973) (14.275) (18.237) (21.946)
7.625 0.301 0.500 0.875
7[5]
(193.68) (7.645) (12.700) (22.225)
8.625 0.109 0.148 0.250 0.277 0.322 0.406 0.500 0.593 0.718 0.812 0.906 0.875
8 200
(219.08) (2.769) (3.759) (6.350) (7.036) (8.179) (10.312) (12.700) (15.062) (18.237) (20.625) (23.012) (22.225)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nominal_Pipe_Size[13/03/2012 04:50:32 p.m.]
Nominal Pipe Size - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
9.625 0.342 0.500
9[5]
(244.48) (8.687) (12.700)
NPS 10 to NPS 24 [edit]
Wall thickness
DN OD [in (mm)]
NPS [5] [2]
[in (mm)] SCH
SCH 5s SCH 5 SCH 10s SCH 10 SCH 20 SCH 30
40s/STD
10.75 0.134 0.134 0.165 0.165 0.250
10 250 0.307 (7.798) 0.365 (9.271)
(273.05) (3.404) (3.404) (4.191) (4.191) (6.350)
12.75 0.156 0.165 0.180 0.180 0.250
12 300 0.330 (8.382) 0.375 (9.525)
(323.85) (3.962) (4.191) (4.572) (4.572) (6.350)
14.00 0.156 0.156 0.188 0.250 0.312
14 350 0.375 (9.525) 0.375 (9.525)
(355.60) (3.962) (3.962) (4.775) (6.350) (7.925)
16.00 0.165 0.165 0.188 0.250 0.312
16 400 0.375 (9.525) 0.375 (9.525)
(406.40) (4.191) (4.191) (4.775) (6.350) (7.925)
18.00 0.165 0.165 0.188 0.250 0.312 0.437
18 450 0.375 (9.525)
(457.20) (4.191) (4.191) (4.775) (6.350) (7.925) (11.100)
20.00 0.188 0.188 0.218 0.250 0.375 0.500
20 500 0.375 (9.525)
(508.00) (4.775) (4.775) (5.537) (6.350) (9.525) (12.700)
24.00 0.218 0.218 0.250 0.250 0.375 0.562
24 600 0.375 (9.525)
(609.60) (5.537) (5.537) (6.350) (6.350) (9.525) (14.275)
Wall thickness
[in (mm)]
NPS[5]
SCH
SCH 40 SCH 60 SCH 80 SCH 100 SCH 120 SCH 140 SCH 160
80s/XS
0.500 0.500 0.593 0.718 0.843 1.000 1.125
10 0.365 (9.271)
(12.700) (12.700) (15.062) (18.237) (21.412) (25.400) (28.575)
0.406 0.562 0.500 0.687 0.843 1.000 1.125 1.312
12
(10.312) (14.275) (12.700) (17.450) (21.412) (25.400) (28.575) (33.325)
0.437 0.593 0.500 0.750 0.937 1.093 1.250 1.406
14
(11.100) (15.062) (12.700) (19.050) (23.800) (27.762) (31.750) (35.712)
0.500 0.656 0.500 0.843 1.031 1.218 1.437 1.593
16
(12.700) (16.662) (12.700) (21.412) (26.187) (30.937) (36.500) (40.462)
0.562 0.750 0.500 0.937 1.156 1.375 1.562 1.781
18
(14.275) (19.050) (12.700) (23.800) (29.362) (34.925) (39.675) (45.237)
0.593 0.812 0.500 1.031 1.280 1.500 1.750 1.968
20
(15.062) (20.625) (12.700) (26.187) (32.512) (38.100) (44.450) (49.987)
0.687 0.968 0.500 1.218 1.531 1.812 2.062 2.343
24
(17.450) (24.587) (12.700) (30.937) (38.887) (46.025) (52.375) (59.512)
NPS 26 to NPS 36 [edit]
Wall thickness
DN OD [in (mm)]
NPS [5] [2]
[in (mm)] SCH SCH
SCH 5s SCH 10s SCH 10 SCH 20 SCH 30 SCH 40
40s/STD 80s/XS
26.000 0.312 0.500 0.375 0.500
26 650
(660.400) (7.925) (12.700) (9.525) (12.700)
28.000 0.312 0.500 0.625 0.375
28 700
(711.200) (7.925) (12.700) (15.875) (9.525)
30.000 0.250 0.312 0.312 0.500 0.625 0.375 0.500
30 750
(762.000) (6.350) (7.925) (7.925) (12.700) (15.875) (9.525) (12.700)
32.000 0.312 0.500 0.625 0.375 0.688 0.500
32 800
(812.800) (7.925) (12.700) (15.875) (9.525) (17.475) (12.700)
34.000 0.312 0.500 0.625 0.375 0.688
34 850
(863.600) (7.925) (12.700) (15.875) (9.525) (17.475)
36.000 0.312 0.625 0.375 0.750 0.500
36 900
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nominal_Pipe_Size[13/03/2012 04:50:32 p.m.]
Nominal Pipe Size - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(914.400) (7.925) (15.875) (9.525) (19.050) (12.700)
Additional sizes (NPS) [edit]
DN OD
NPS Wall thickness [in (mm)]
[2] [in (mm)]
22 550 22.000 (558.800) 0.375
40 1000 40.000 (1,016.000) ?
42 1050 42.000 (1,066.800) ?
44 1100 44.000 (1,117.600) ?
48 1200 48.000 (1,219.200) ?
52 1300 52.000 (1,320.800) ?
56 1400 56.000 (1,422.400) ?
60 1500 60.000 (1,524.000) ?
64 1600 64.000 (1,625.600) ?
68 1700 68.000 (1,727.200) ?
72 1800 72.000 (1,828.800) ?
76 1900 76.000 (1,930.400) ?
80 2000 80.000 (2,032.000) ?
88 2200 88.000 (2,235.200) ?
Heading text [edit]
See also [edit]
British standard pipe thread sizes
Copper tubing sizes
National pipe thread sizes
Pipe (fluid conveyance)
Pipe thread sizes
Notes [edit]
1. ^ a b This is contrary to the McGraw Hill Piping Handbook, which says that the schedule number can be converted to pressure by
dividing the schedule by 1000 and multiplying by the allowable stress of the material. [Nayyar and Mohinder, 2000.]
References [edit]
1. ^ a b ASME B36.10M-2004, p. 1
2. ^ a b c d e f NPS - "Nominal Pipe Size" and DN - "Diamtre Nominale" , EngineeringToolbox.com
3. ^ a b c ASME B36.10M-2004, p. iv
4. ^ ASME Standard 36.19M-2004, p. iv
5. ^ a b c d e f g h Table of Pipe Schedules from EngineersEdge.com.
Bibliography [edit]
Nayyar, P.E., Mohinder L. (2000). "A1". In Mohinder L. Nayyar, P.E.. Piping Handbook (7th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
ISBN0-07-047106-1.
ASME B36.10M - Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe.
ANSI/ASME Standard 36.19M - Stainless Steel Pipe.
External links [edit]
Notes on Pipe -- PVC Pipe weights and max PSI
Quick calculator to determine standard pipe dimensions For Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel pipes as per ANSI.
[1] - Online Pipe Schedule Calculator
Categories: Piping Mechanical standards
This page was last modified on 20 February 2012 at 08:19.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. See Terms of use for details.
Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
Contact us
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nominal_Pipe_Size[13/03/2012 04:50:32 p.m.]
Nominal Pipe Size - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Mobile view
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nominal_Pipe_Size[13/03/2012 04:50:32 p.m.]
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Malt - A Practical Guide From Field To Brewhouse - John Mallett - Cicerone Certification ProgramDokumen1 halamanMalt - A Practical Guide From Field To Brewhouse - John Mallett - Cicerone Certification ProgramJulioRojas0% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Pipe Caps - McMaster-CarrDokumen1 halamanPipe Caps - McMaster-CarrJulioRojasBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hiller 1 Problems Current Situation: We Reconnected The Same MPI Connector We Removed The MPI Network CablesDokumen4 halamanHiller 1 Problems Current Situation: We Reconnected The Same MPI Connector We Removed The MPI Network CablesJulioRojasBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- PID ModelDokumen1 halamanPID ModelJulioRojasBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grammar Pit Stop Grammar Pit StopDokumen9 halamanGrammar Pit Stop Grammar Pit StopJulioRojasBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Bel Pesce - 5 Maneras de ... ND Transcript - TEDDokumen5 halamanBel Pesce - 5 Maneras de ... ND Transcript - TEDJulioRojasBelum ada peringkat
- Oil Water Separator DrawingDokumen1 halamanOil Water Separator DrawingHazem Esam100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Ncma Tek: Concrete Masonry Bond Patterns TEK 14-6Dokumen4 halamanNcma Tek: Concrete Masonry Bond Patterns TEK 14-6MarioleRouxBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Technicalinfo 6066670Dokumen2 halamanTechnicalinfo 6066670petriBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- 17-4 Architectural Metal WorksDokumen4 halaman17-4 Architectural Metal WorksZuberYousufBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Flyover FormworkDokumen13 halamanFlyover FormworkvrushankshahBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Luxury Living Personified: 3-Storey Bungalow at Bukit JelutongDokumen18 halamanLuxury Living Personified: 3-Storey Bungalow at Bukit JelutongMohd KhairulazharBelum ada peringkat
- Img 0001Dokumen1 halamanImg 0001Harish RanaBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- COLORBOND® Steel For Insulated Panel (XIP) Datasheet May 2023Dokumen4 halamanCOLORBOND® Steel For Insulated Panel (XIP) Datasheet May 2023Ramiro RivasBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Welder HandbookDokumen7 halamanWelder Handbooksandeepkumar63Belum ada peringkat
- High Performance Butterfly Valves: Corrosion ResistantDokumen3 halamanHigh Performance Butterfly Valves: Corrosion ResistantMina MagdyBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Quonset Hut Product Steel MasterDokumen8 halamanQuonset Hut Product Steel Masterhedi.chaouch007Belum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Metals 12 01421 v2Dokumen16 halamanMetals 12 01421 v2Juan BonottiBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- 0344 90 9220 C02 0051 01 A 1Dokumen526 halaman0344 90 9220 C02 0051 01 A 1Afranio de Melo FrancoBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Sika PDS - E - Sika MultiSeal APDokumen2 halamanSika PDS - E - Sika MultiSeal APJahidul IslamBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- American Girl Dollhouse - Fits 18 Dolls Ana WhiteDokumen1 halamanAmerican Girl Dollhouse - Fits 18 Dolls Ana WhiteSchindler JoanieBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 Notes 3 Strengthening MechanismDokumen89 halamanLecture 3 Notes 3 Strengthening Mechanismrony16novBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Details - 3 BranchDokumen10 halamanLab Details - 3 BranchDevdoot SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Atmospheric Corrosion Behavior of 6xxx Al Alloys in Qatar StateDokumen2 halamanAtmospheric Corrosion Behavior of 6xxx Al Alloys in Qatar Statekssn1981Belum ada peringkat
- SPBG PLBG - Kalkulasi Tebal Pipa-ASME B31.3 - High PressureDokumen1 halamanSPBG PLBG - Kalkulasi Tebal Pipa-ASME B31.3 - High PressureAris KancilBelum ada peringkat
- Flat Plate Skillet Calculation From B31.3 Section 304.5.3Dokumen2 halamanFlat Plate Skillet Calculation From B31.3 Section 304.5.3Abu AkhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Failure of A Vertical Ammonia Transfer Pump ShaftDokumen3 halamanFailure of A Vertical Ammonia Transfer Pump ShaftWendi JunaediBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Diaphragm Valve: G2K Rising HW Type, Flanged EndsDokumen1 halamanDiaphragm Valve: G2K Rising HW Type, Flanged EndsHARSHABelum ada peringkat
- Anexo 4 IDO-L.18.001-1212-EBD-3000 Rev.0 - Mechanical-Piping Design CriteriaDokumen64 halamanAnexo 4 IDO-L.18.001-1212-EBD-3000 Rev.0 - Mechanical-Piping Design CriteriaRusBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Fiber Reinforced High Performance SCC at Elevated Temperatures - Khaliq, Kodur PDFDokumen11 halamanThermal and Mechanical Properties of Fiber Reinforced High Performance SCC at Elevated Temperatures - Khaliq, Kodur PDFMauricio GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- Concrete Repair Scope of WorkDokumen4 halamanConcrete Repair Scope of WorkAnonymous uTEAEbug0% (1)
- DIN 17100 Steels For General Structural Purposes (DIN17100)Dokumen7 halamanDIN 17100 Steels For General Structural Purposes (DIN17100)tiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Sieve Analysis of Fine AggregateDokumen7 halamanSieve Analysis of Fine Aggregatemcdonald jumaBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion Protection of Tanks FRPDokumen5 halamanCorrosion Protection of Tanks FRPaarmasp100% (1)
- Catalog DuctingDokumen9 halamanCatalog DuctingchristiadiargaBelum ada peringkat
- PlumDokumen15 halamanPlumChristian ConsignaBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)