Ponstan
Diunggah oleh
You know who0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
123 tayangan5 halamanJudul Asli
Ponstan.docx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
123 tayangan5 halamanPonstan
Diunggah oleh
You know whoHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 5
Drawing
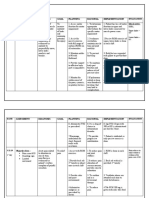
Generic Name Mefenamic Acid
Brand Name Ponstan Forte
Classification Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drug (NSAID)
Blocks a substance in the body called cyclo oxygenase (COX) which is
involved in the production of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are produced in
Action response to injury and certain diseases causing pain, swelling and inflammation.
Mefenamic acid blocks the production of prostaglandins therefore effective at
reducing inflammation and pain.
Dosage 500 mg PRN
Dysmenorrhea, Menorrhagia, Theumatoid arthritis, Juvenile arthritis, Osteoarthritis,
Indication Muscular pain, pain and inflammation due to accidents, toothache, headache, pain
following childbirth and pain following surgery.
People who are taking aspirin or other NSAIDs, Peptic ulcer of bleeding in the gut,
Contraindicatio
Inflammatory bowel disease, Severe heart failure, Kidney Failure, Third trimester of
n
pregnancy.
Should not be used in combination with painkilling doses of aspirin or any other
NSAID taken by mouth as this increases the risk of side effects on the stomach
and intestines.
Drug
Selective inhibitors of COX-2 such as celecoxib or etoricoxib should also be
Interaction
avoided for the same reason.
Increased risk of ulceration or bleeding in the gut if mefenamic acid is taken with
corticosteroids such as prednisolone.
Disturbances of the gut such as indigestion, diarrhoea, constipation, nausea,
vomiting or abdominal pain.
Headache.
Visual disturbances.
Sensation of spinning (vertigo).
Sensation of ringing, or other noise in the ears (tinnitus).
Side Effects and Increased blood pressure.
Adverse Effects Awareness of your heartbeat (palpitations).
Depression.
Hallucinations.
Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
Allergic reactions such as severe skin rashes, swelling of the lips, tongue and
throat (angioedema) or narrowing of the airways (bronchospasm).
Kidney, liver or blood disorders.
Nursing 1. Assess pain and limitation of movement following the administration.
2. Assess fever and associated signs like tachycardia and chills.
3. Monitor periodically in prolonged high dose therapy to assess for GI blood
loss.
4. Instruct to take medication exactly as prescribed.
5. Instruct to take with full glass of water and to remain in an upright position for 1
30 minutes.
6. Advise patient that this may cause drowsiness and blurred vision.
Responsibilities 7. Advise patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol to minimize possible gastric
irritation.
8. Inform patient that most NSAIDs prolong bleeding time due to suppressed
platelet aggregation.
9. Caution patient to avoid taking acetaminophen, salicylates to prevent analgesic
nephropathy.
10. Advise patient to notify health care professional before treatment or surgery or
when adverse effects occur.
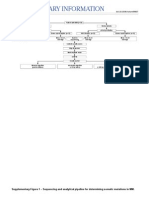
Brain Tumor o Increased intracranial pressure and
- Is a localized intracranial lesion that occupies cerebral edema
space within the skull resulting to:
o Seizure activity and focal neurologic o Arises from the membranes that surround your
signs brain and spinal cord (meninges). Most
o Hydrocephalus meningiomas are noncancerous.
o Altered pituitary function
- Tumor Acoustic neuromas (schwannomas)
o A mass of tissue that is formed by an o Develop on the nerves that control balance and
accumulation of abnormal cells hearing leading from your inner ear to your
o Normally, cells die and replaced by new brain.
cells. With cancer and other tumors,
something disrupts this cycle. Tumor Pituitary adenomas
cells grow and dont die. As this process o Develop in the pituitary gland at the base of the
goes on, the tumor continues to grow as brain.
more and more cells are added to the
mass. Medulloblastomas
- Types o These are the most common cancerous brain
o Primary brain tumors tumors in children. A medulloblastoma starts in
Originate from cells and the lower back part of the brain and tends to
structures within the brain spread through the spinal fluid.
Begin when normal cells
acquire errors or mutations in Germ cell tumors
their DNA o Germ cell tumors may develop during childhood
These mutations allow cells to where the testicles or ovaries will form. But
grow and divide at increased sometimes germ cell tumors move to other parts
rates and to continue living of the body, such as the brain.
when healthy cells die
o Secondary brain tumors (Metastatic) Craniopharyngiomas
Develop from structures outside o These rare, noncancerous tumors start near the
the brain brain's pituitary gland, which secretes hormones
When cancer begins elsewhere that control many body functions.
and spreads to the brain
- Risk Factors
Breast cancer, colon cancer,
o Age
kidney cancer, lung cancer,
Common in older adults
melanoma
o Exposure to radiation
- Symptoms Increased risk of brain tumors
o Headaches o Family history of brain tumors
o Nausea and vomiting Increased risk of brain tumors
o Vision problems - Diagnosis
o Difficulty with balance o Neurological exam
o Speech difficulties Indicates the areas of the central
o Behaviour changes nervous sytem involve
o Seizures Assist in the precise localization
o Hearing problems of the lesion
o Imaging tests
- Causes MRI and CT scan
o Possible causes may include genetics, Detection of smaller lesions in
defective immune system, heredity, the brain stem and pituitary
regions
viruses and head injury o Biopsy
To remove the brain tumor and
Gliomas determine if it is cancerous or
o These tumors begin in the brain or spinal cord benign
- Treatment
Meningiomas Surgery
Location is accessible, remove as much
as possible
Small and easy to remove, complete
removal
Cannot be separated or located near
sensitive areas, surgery is risky
Radiation Therapy
Treat cancer that has spread to the body
Radiosurgery
Uses multiple beams of radiation
treatment to kill the tumor cells in a very
small area
Chemotherapy
Temozolomide (Temodar)
Targeted Drug Therapy
Bevacizumab (Avastin)
Stops the formation of new blood
vessels, cutting off blood supply to a
tumor and killing the tumor cells
Contraindications
o Hypersensitivity
o Pregnancy (critical to fetus)
Side effects
o Hypertension, hypotension
o Hemoptysis
o GI perforation
o Nephrotic syndrome
o Proteinuria
o Bleeding
o Impaired wound healing
Rehabilitation after treatment
Physical Therapy
Occupational Therapy
Speech Therapy
- Nursing Management
o Teaching patient to direct food and
fluids toward unaffected side
o Eating at upright position, offering
semisoft diet and having suction readily
available
o Neurologic checks
o Monitor vital signs
o Reorient to persons and surroundings
o Assistance to self care
o Prevention to injury
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- AcetylcysteineDokumen2 halamanAcetylcysteineJonah Camille Yap FortunaBelum ada peringkat
- Medications and Nursing Responsibilities for Bone HealthDokumen6 halamanMedications and Nursing Responsibilities for Bone HealthDarla JoyceBelum ada peringkat
- A Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutDari EverandA Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Danger Signs of PregnancyDokumen3 halamanDanger Signs of PregnancyNesly Khyrozz LorenzoBelum ada peringkat
- On Innovation of Treatment of Cancer: Cancer Immune Treatment Combined Chinese with Western MedicineDari EverandOn Innovation of Treatment of Cancer: Cancer Immune Treatment Combined Chinese with Western MedicineBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Nause and Vomiting-Crit-Care-Nurse-2003-Garrett-31-50 PDFDokumen22 halamanManaging Nause and Vomiting-Crit-Care-Nurse-2003-Garrett-31-50 PDFpmuftiaBelum ada peringkat
- A Review On Otitis Media (Karnapaka) : Ayurvedic Aspects and TreatmentDokumen4 halamanA Review On Otitis Media (Karnapaka) : Ayurvedic Aspects and TreatmentEditor_IAIMBelum ada peringkat
- PotassiumDokumen2 halamanPotassiumNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (18)
- Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Therese M. Chapman, Jane K. Mcgavin and Stuart NobleDokumen12 halamanTenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Therese M. Chapman, Jane K. Mcgavin and Stuart NobleBagusHibridaBelum ada peringkat
- Nasopharyngeal Cancer OverviewDokumen31 halamanNasopharyngeal Cancer OverviewMae UsquisaBelum ada peringkat
- HIV and Its TreatmentDokumen24 halamanHIV and Its Treatmentaathira_kBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Nursing Management in Uterine (Endometrial) CancerDokumen17 halaman11 Nursing Management in Uterine (Endometrial) Cancerclaire yowsBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Presentation - Management of Preclamplsia, Mild and ModerateDokumen22 halaman1 - Presentation - Management of Preclamplsia, Mild and ModeratesharonBelum ada peringkat
- Enzymes-Lactose 20intoleranceDokumen2 halamanEnzymes-Lactose 20intoleranceapi-323374257Belum ada peringkat
- Bipolar Affective Disorder, Current Manic Episode With Symptoms of Psychotic and Care in NursingDokumen4 halamanBipolar Affective Disorder, Current Manic Episode With Symptoms of Psychotic and Care in NursingKit LaraBelum ada peringkat
- FoscarnetDokumen2 halamanFoscarnetTandri JuliantoBelum ada peringkat
- DM Case StudyDokumen21 halamanDM Case StudyBern TolentinoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokumen1 halamanDrug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJeyser T. GamutiaBelum ada peringkat
- Cancer NursingDokumen53 halamanCancer Nursingfairwoods100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal DrugsDokumen45 halamanGastrointestinal DrugsCindy MaslagBelum ada peringkat
- Kwashiorkor AND Marasmus: Group 6Dokumen18 halamanKwashiorkor AND Marasmus: Group 6Christian De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Chymoral PlusDokumen3 halamanChymoral PlusNeha SureshBelum ada peringkat
- Kaposi's SarcomaDokumen6 halamanKaposi's SarcomaveremkovichBelum ada peringkat
- Filipino Culture, Values, and Practices in Relation To Difficult Childbearing and ChildrearingDokumen8 halamanFilipino Culture, Values, and Practices in Relation To Difficult Childbearing and ChildrearingRheeanne AmilasanBelum ada peringkat
- Esophageal CancerDokumen40 halamanEsophageal Cancerapi-282115150Belum ada peringkat
- Paracetamol Dosage For ChildrenDokumen14 halamanParacetamol Dosage For Childrenkevinhabakuk_88Belum ada peringkat
- KetoconazoleDokumen9 halamanKetoconazolePradeep BhimaneniBelum ada peringkat
- Epilepsy in Pregnancy JatuDokumen57 halamanEpilepsy in Pregnancy Jatuninjahattori1Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan for ClubfootDokumen6 halamanNursing Care Plan for ClubfootMarzie LugtuBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanDrug StudyJay-ar Batara SorianoBelum ada peringkat
- EvistaDokumen18 halamanEvistaBrankoPopovićBelum ada peringkat
- Case 16 Pediatric t1dmDokumen12 halamanCase 16 Pediatric t1dmapi-501730091Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Implementation Objective DataDokumen8 halamanNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Implementation Objective DataMoonBelum ada peringkat
- Discharge Discharge Summary AlzheimerDokumen10 halamanDischarge Discharge Summary Alzheimermp1757Belum ada peringkat
- Phenobarbital Risk For Injury EAMCDokumen4 halamanPhenobarbital Risk For Injury EAMCkeitacBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Order: Lonsurf (Trifluridine/TipiracilDokumen3 halamanDrug Order: Lonsurf (Trifluridine/TipiracilKristine AcasioBelum ada peringkat
- Biliary DyskinesiaDokumen1 halamanBiliary DyskinesiaYolotl Hilario Sanchez CarrilloBelum ada peringkat
- Ketorolac PI PDFDokumen2 halamanKetorolac PI PDFintan kusumaningtyasBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokumen1 halamanDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesJohnrick VenturaBelum ada peringkat
- Myasthenia Gravis PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanMyasthenia Gravis PathophysiologyRyan Daet0% (1)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Dokumen3 halamanAcute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- GRP 20 Final Abscess Case StudyDokumen14 halamanGRP 20 Final Abscess Case StudyBorja, Kimberly GraceBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Management Pancreatic CancerDokumen2 halamanNursing Management Pancreatic CancerKit NameKo100% (2)
- RP-Case History of A Child With Sickle Cell Anemia in IndiaDokumen5 halamanRP-Case History of A Child With Sickle Cell Anemia in IndiaMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigBelum ada peringkat
- Side Effects of Pregabalin DrugDokumen20 halamanSide Effects of Pregabalin DrugtulipcatcherBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Cholecystitis SeminarDokumen42 halamanAcute Cholecystitis SeminarNatnaelBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study FUROSEMIDE (Eugene San)Dokumen2 halamanDrug Study FUROSEMIDE (Eugene San)Ana LanticseBelum ada peringkat
- Amlodipine Captopril MetronidazoleDokumen5 halamanAmlodipine Captopril Metronidazolekhrysty1506Belum ada peringkat
- Example of Health GenogramDokumen1 halamanExample of Health Genogramapi-322059527Belum ada peringkat
- Tetanus PathophysiologyDokumen7 halamanTetanus PathophysiologyWahyu Adhitya PrawirasatraBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen16 halamanDrug StudyMonica Luz FajardoBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma CardsDokumen5 halamanPharma CardsazancheBelum ada peringkat
- The Breasts & The AxillaeDokumen26 halamanThe Breasts & The AxillaeMark Villarmea AlforqueBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study-Med WardDokumen2 halamanDrug Study-Med WardErnest Brian FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Addison's Disease: An Overview of Etiology, Pathogenesis and Clinical PresentationDokumen11 halamanAddison's Disease: An Overview of Etiology, Pathogenesis and Clinical PresentationKertiasihwayanBelum ada peringkat
- Levothyroxine - WikipediaDokumen9 halamanLevothyroxine - WikipediaRoxana FrincuBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanDrug StudyJohn Ronald P. RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Radio PharmaceuticalsDokumen48 halamanRadio PharmaceuticalsKris Joy EbonBelum ada peringkat
- MedicationsDokumen23 halamanMedicationsYou know whoBelum ada peringkat
- Loop Diuretic Furosemide Guide: Uses, Dosage, Side EffectsDokumen2 halamanLoop Diuretic Furosemide Guide: Uses, Dosage, Side EffectsYou know whoBelum ada peringkat
- AminolebanDokumen2 halamanAminolebanYou know who0% (1)
- Vitamin KDokumen7 halamanVitamin KYou know whoBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen4 halamanBrain Anatomy and PhysiologyYou know whoBelum ada peringkat
- Pon StanDokumen5 halamanPon StanYou know whoBelum ada peringkat
- Norepinephrine Drug CardDokumen2 halamanNorepinephrine Drug CardYou know who100% (9)
- Peptic Ulcer Disease PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanPeptic Ulcer Disease PathophysiologyYou know whoBelum ada peringkat
- Enlarged Vestibular Aqueducts and Childhood Deafness PDFDokumen20 halamanEnlarged Vestibular Aqueducts and Childhood Deafness PDFNics GanoBelum ada peringkat
- Cervical CancerDokumen5 halamanCervical Cancerjinoop100% (1)
- Initial Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Multiple Myeloma - SuppDokumen75 halamanInitial Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Multiple Myeloma - SuppShantanu KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Transport SystemDokumen22 halamanTransport Systemredditor1276Belum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho Physiology of Liver Cirrhosis - MercyDokumen7 halamanPa Tho Physiology of Liver Cirrhosis - Mercymersenie_TheovercomerBelum ada peringkat
- Endo FinalDokumen52 halamanEndo Finalspamboy6464Belum ada peringkat
- Biologics Immunogenicity Causes and ConsequencesDokumen12 halamanBiologics Immunogenicity Causes and ConsequencesWei Sheng ChongBelum ada peringkat
- Gmo - PPT BiotechDokumen16 halamanGmo - PPT BiotechGerwyn Gervacio CBelum ada peringkat
- Analyzing a Family's Risk for Huntington's DiseaseDokumen3 halamanAnalyzing a Family's Risk for Huntington's DiseaseMark KimBelum ada peringkat
- Kanha: Important InstructionsDokumen24 halamanKanha: Important InstructionsHARIKRISHNA PRASAD R KBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory System in Animals: Regents BiologyDokumen37 halamanCirculatory System in Animals: Regents Biologyapi-285078865Belum ada peringkat
- Action Potentials and Saltatory ConductionDokumen21 halamanAction Potentials and Saltatory ConductionrkblsistemBelum ada peringkat
- Mr. Abhishek Sharma-1Dokumen3 halamanMr. Abhishek Sharma-1Abhishek SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Osamu Mizukami's Health Promotion Clinic in TokyoDokumen40 halamanDr. Osamu Mizukami's Health Promotion Clinic in TokyoLuckner Jr. Jean-BaptisteBelum ada peringkat
- AgeLOC Dermatic EffectsDokumen28 halamanAgeLOC Dermatic EffectsAulia CandraBelum ada peringkat
- Determinants of Human BehaviorDokumen31 halamanDeterminants of Human BehaviorFe Malanum GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Cancerous Profiles Using Machine LearningDokumen6 halamanClassification of Cancerous Profiles Using Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- A Combinatorial Approach To Hybrid Enzymes Independent of DNA HomologyDokumen5 halamanA Combinatorial Approach To Hybrid Enzymes Independent of DNA HomologyArdiellaputriBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology - Guyton BLOODDokumen6 halamanPhysiology - Guyton BLOODIsra K. SoomroBelum ada peringkat
- AsdfDokumen15 halamanAsdfdwBelum ada peringkat
- Millor Silva Coelho Savino TadeuDokumen6 halamanMillor Silva Coelho Savino TadeuBafowethu Sibanda MavuleBelum ada peringkat
- Schilder's Disease: EpidemiologyDokumen4 halamanSchilder's Disease: EpidemiologyUky SuGoyBelum ada peringkat
- Bio4 6Dokumen17 halamanBio4 6HarmonyChui100% (1)
- Sleep Disorders in Myopathy 3.10.19Dokumen16 halamanSleep Disorders in Myopathy 3.10.19Nitesh DahiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Syndactyly and ClinodactylyDokumen47 halamanSyndactyly and ClinodactylychlondBelum ada peringkat
- Base Excision Repair and CancerDokumen17 halamanBase Excision Repair and CancerIonela Petronela Tarabuta BocanceaBelum ada peringkat
- Myopathy: By: Rey MartinoDokumen16 halamanMyopathy: By: Rey Martinorey martinoBelum ada peringkat
- Interpretation of Gram Stains and Other Common Microbiologic Slide Preparations - LibraryDokumen4 halamanInterpretation of Gram Stains and Other Common Microbiologic Slide Preparations - Libraryfabriclive15Belum ada peringkat
- GE7 - Pre-Final ExamDokumen2 halamanGE7 - Pre-Final ExamRojean TinggasBelum ada peringkat
- Msds Kalium Iodida (Ki)Dokumen6 halamanMsds Kalium Iodida (Ki)FajarSholikhin100% (2)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDari EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (402)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDari EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDari EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (13)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingDari EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearDari EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (23)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDari EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBelum ada peringkat
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDari EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDari EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDari EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDari EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDari EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBelum ada peringkat
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDari EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (169)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesDari EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (34)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsDari EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsBelum ada peringkat
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDari EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (31)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementDari EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (40)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Dari EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (110)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDari EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDari EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (253)
- Secure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeDari EverandSecure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (17)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDari EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (327)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDari EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (44)