Chaebols
Diunggah oleh
Kalathiya Chintan0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan20 halamanChaebols Information
Judul Asli
121942084-chaebols
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
TXT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniChaebols Information
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai TXT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
25 tayangan20 halamanChaebols
Diunggah oleh
Kalathiya ChintanChaebols Information
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai TXT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 20
THE CHAEBOLS OF SOUTH KOREA
Presented byDarshan Bhatt Deepa Khanna Neena Aneja
INTRODUCTION
Chaebols Chaebol is a Korean name meaning a group with a lot of money. It was a la
rge South Korean private business groups. Chaebols were involved in activities r
anging from farming to ship building. The separate companies within Chaebol held
shares in each other. The major contributors to the Countrys economy.
INTRODUCTION
All the financial transactions were subject to Government scrutiny. Decision-mak
ing was top-down with top management exerting strict control. Most Chaebols had
close ties with the government and were involved in policy making. Chaebols had
a support of banks to bail them out of financial crises.
http://www.sjsu.edu/faculty/watkins/chaebol.htm
BACKGROUND
Chaebols was first introduced in 1920s under Japanese rule. It was designed on t
he lines of Japanese Keiretsu. The companies were controlled by Central Governme
nt. Initially designed to meet the requirements of Japanese Government. South Ko
rea became independent in 1945.
BACKGROUND
In 1961 Park Chung became the President. The economy dependence was converted fr
om agrarian economy to industrial one. All banks were nationalized. To encourage
growth of economy a Law was passed Dealing with Illicit Wealth Accumulation. Many
leading businessmen were arrested. Five-year economic plans was implemented rel
ated to export and import. Idea was to make South Korea independent in all manuf
acturing fields.
Goal- Increase wealth and strengthen Political stability. Three 5 year plan were
induced under Economic Planning board since 1962. 1st- 1962-1966 2nd- 1967-1971
3rd- 1972-1976
The Five year Plan
Economic Plan(1960-1966)
Korea was a poor country with inadequate savings. It focused on developing texti
le and light manufacturing industries to make South Korea selfsufficient.
Economic Plan(1967-1971)
It focused on heavy industries such as iron and steel, automobiles, shipping etc
, to make South Korea competitive in world market. 1972, US-China opened for imp
ort gave them more marketplace.
Economic Plan(1972-1976)
The 3rd five year plan was referred as Heavy Chemical Industrialization Plan(HCI
). To fund the plan Government borrowed heavily from foreign countries.
Result of the Economic Plan
Korea is the 11th largest economy in the world. The export-import trade increase
d from 230 million$ from 1948 to 857.84 billion$ in 2008.
Result of Economic Plan
The GDP of Korea increased from 1.3 billion$ to 1,239 billion$. The per capita i
ncome increased from 60 $ to 20,000$. The average income of the workers increase
d from 5990 won to 3.895 million won.
Chaebols post President Park
Civil unrest, labour strikes post assassination of President Park led to Military
rule(1979-1988). By 1988, South Korea adopted democracy and things started falli
ng into places. The Chaebols got the new democratic governments full backing. Cha
ebols started expanding into new industries and markets No fears of risks as the
y had government and banks backing them
Total Government backing totally misused
Chaebols explored new markets and new industries and didnt care about the possibl
e monetary losses Chaebols started new firms instead of new division under the s
ame company. Many ventures of Chaebols started yielding low returns and governme
nt had to divert all available funds with the banks to finance these ventures an
d this led to huge decrease in foreign investments into South Korea. Even fiscal
and monetary Policies were frequently modified as per the needs of the Chaebols
Avoidance of foreign companies in favour of Chaebols
CHAEBOLS IN TROUBLE
Trouble started in late 1990s.Initially the slowdown in international semiconduc
tor, metals and petrochemical businesses. Further with the rise in wages, by thi
s south Korea lost its competitive edge in international markets.
Asian financial crisis played a important role in the downturn of Chaebols.
PROBLEMS
HUGE DEBTS LACK OF TRANCPARENCY IN CHAEBOL CORPORATE GOVERNANCE PROLIFERATION OF
UNPROFITABLE SUBSIDAIRIES THROUGHOUT THE ECONOMY INADEQUATE FINANCIAL REPORTING
AND CONTROLLING WITHIN THE CHAEBOLS ABSENCE OF A FREE MARKET SYSTEM
Restructuring
Improve transparency in management of Chaebols. Cross-Debt gurantees within Chae
bols were banned. Debt to equity ratio to be 2:1) Advised to get rid of unprofit
able subsidiaries. Management instructed to appoint outside director.
Result of Sever Measures
Out of 50 Chaebols, 16 underwent radical transformation. Early 2000 unemployment
rate was 3.1% and foreign exchange currency reserve $107 billion.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Pest Analysis For AustraliaDokumen2 halamanPest Analysis For AustraliaKalathiya Chintan50% (2)
- Social Media Has Improve Human Communication (FOR AND DEBATE)Dokumen2 halamanSocial Media Has Improve Human Communication (FOR AND DEBATE)Abdul Raheman89% (9)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Agriculture in NigeriaDokumen216 halamanAgriculture in Nigeriakingkumar5Belum ada peringkat
- Agriculture in NigeriaDokumen216 halamanAgriculture in Nigeriakingkumar5Belum ada peringkat
- Agriculture in NigeriaDokumen216 halamanAgriculture in Nigeriakingkumar5Belum ada peringkat
- Asia Pacific BusinessDokumen6 halamanAsia Pacific BusinessKalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- Definition of ChaebolDokumen1 halamanDefinition of ChaebolKalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- Intercultural 5Dokumen5 halamanIntercultural 5Kalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- Hotel Marketing Plan 120125224706 Phpapp01Dokumen33 halamanHotel Marketing Plan 120125224706 Phpapp01Kalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- Definition of ChaebolDokumen1 halamanDefinition of ChaebolKalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- Scope of BusinessDokumen3 halamanScope of BusinessKalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- Pestle PDFDokumen26 halamanPestle PDFabubakarBelum ada peringkat
- Project Management: DefinitionDokumen3 halamanProject Management: DefinitionKalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- Assesment-1: Name: Chintan Vinodbhai Kalathiya ID Number: 14095054BDokumen3 halamanAssesment-1: Name: Chintan Vinodbhai Kalathiya ID Number: 14095054BKalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- Interview On NZ TourismDokumen6 halamanInterview On NZ TourismKalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- MGT250 - Assign 1 SampleDokumen2 halamanMGT250 - Assign 1 SampleKalathiya ChintanBelum ada peringkat
- USA v. William Gazafi Plea Letter To Judge TitusDokumen13 halamanUSA v. William Gazafi Plea Letter To Judge TitusSouthern Maryland OnlineBelum ada peringkat
- IEM Notes Unit-2Dokumen2 halamanIEM Notes Unit-2Ashish YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Full Download Discovering Gis and Arcgis Rental Only 2nd Edition Shellito Solutions ManualDokumen35 halamanFull Download Discovering Gis and Arcgis Rental Only 2nd Edition Shellito Solutions Manualaidenbnyoung100% (35)
- BM AssignmentDokumen7 halamanBM AssignmentAntony LawrenceBelum ada peringkat
- 08 Subsurface Sucker-Rod Pumps PDFDokumen10 halaman08 Subsurface Sucker-Rod Pumps PDFBanda ClaretBelum ada peringkat
- Extreme Sports TestDokumen3 halamanExtreme Sports TesttrigtrigBelum ada peringkat
- SCK MagazinDokumen27 halamanSCK Magazinadmin_sckriensBelum ada peringkat
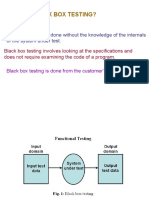
- What Is Black Box Testing?: Black Box Testing Is Done Without The Knowledge of The Internals of The System Under TestDokumen127 halamanWhat Is Black Box Testing?: Black Box Testing Is Done Without The Knowledge of The Internals of The System Under TestusitggsipuBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economy: Chapter 6: Comparison and Selection Among AlternativesDokumen25 halamanEngineering Economy: Chapter 6: Comparison and Selection Among AlternativesBibhu R. TuladharBelum ada peringkat
- President Uhuru Kenyatta's Speech During The Kenya@50 Celebrations at Uhuru Gardens, Nairobi On The Mid-Night of 12th December, 2013Dokumen3 halamanPresident Uhuru Kenyatta's Speech During The Kenya@50 Celebrations at Uhuru Gardens, Nairobi On The Mid-Night of 12th December, 2013State House KenyaBelum ada peringkat
- Past Simple PDFDokumen4 halamanPast Simple PDFderlinBelum ada peringkat
- Report Why EvolveDokumen11 halamanReport Why EvolveMirela OlarescuBelum ada peringkat
- Item Analysis Third QuarterDokumen4 halamanItem Analysis Third Quarterwhite valeBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal Analisis Stabilitas Lidokain HCLDokumen11 halamanJurnal Analisis Stabilitas Lidokain HCLMusfira Dewy SuardiBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 1Dokumen15 halamanPresentation 1Ashish SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Corrective Action Report (CAR) : Form1001 CAR-KMR - e Page 1 of 1 Revision: 6 Reference: Organizational Instruction 8.5.01Dokumen1 halamanCorrective Action Report (CAR) : Form1001 CAR-KMR - e Page 1 of 1 Revision: 6 Reference: Organizational Instruction 8.5.01JOECOOL67Belum ada peringkat
- Gentle Genitty UnderstandingDokumen8 halamanGentle Genitty UnderstandingANDREW ROBERT BASCUGUINBelum ada peringkat
- Purification and Detection of Linamarin From Cassava Root Cortex by HPLCDokumen5 halamanPurification and Detection of Linamarin From Cassava Root Cortex by HPLCJohn Eiver BelalcazarBelum ada peringkat
- EconomicsDokumen19 halamanEconomicsTooba NoushadBelum ada peringkat
- Concept PaperDokumen3 halamanConcept PaperDan Reynald Domingo SomeraBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial MATLAB Matrix NotationDokumen10 halamanTutorial MATLAB Matrix NotationgeorgesmaccarioBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Dementia On The ClinicalDokumen8 halamanThe Impact of Dementia On The ClinicalihsansabridrBelum ada peringkat
- Literature ReviewDokumen5 halamanLiterature ReviewRochelle CampbellBelum ada peringkat
- Num PyDokumen46 halamanNum Pyytmusik4Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - Modes of ExtinguishmentDokumen19 halamanChapter 4 - Modes of ExtinguishmentcartyeolBelum ada peringkat
- English Grammar Book-Final - 2-5-21Dokumen42 halamanEnglish Grammar Book-Final - 2-5-21Manav GaurBelum ada peringkat
- Ed 2 Module 8 1Dokumen5 halamanEd 2 Module 8 1Jimeniah Ignacio RoyoBelum ada peringkat
- Boast 1 - Fragility Hip Fractures PDFDokumen1 halamanBoast 1 - Fragility Hip Fractures PDFSam BarnesBelum ada peringkat
- EDEL453 Spring2013 MelanieHADJES Unit 4 Economic Day1Dokumen6 halamanEDEL453 Spring2013 MelanieHADJES Unit 4 Economic Day1Melanie HadjesBelum ada peringkat