Rock Candy Lab Introduction
Diunggah oleh
api-3278180230 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
138 tayangan3 halamanJudul Asli
rock candy lab introduction
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
138 tayangan3 halamanRock Candy Lab Introduction
Diunggah oleh
api-327818023Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
Nagavajara, Kanokpon (PLOY)
Rock Candy Lab Introduction
Carbohydrate (saccharide) is a source of energy, which body needs.
Carbohydrates are the most abundant biomolecule on Earth. Living organisms use
carbohydrates as accessible energy to fuel cellular reactions and for structural support inside
cell walls (Dallas Learning Cloud, n.d., para 1). Carbohydrates are used to convert from its
simple form, glucose, into energy in the form that the body could use. Carbohydrates are the
source that are taken to be energy source before other sources, they could be stored in the
body for 1-2 days. If carbohydrates are consumed in the amount that even the liver that has
the function of storing parts of surplus glucose cannot store all of it, the excess would be
stored as fat (Gebel, 2011)
Carbohydrate is classified into monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide.
Monosaccharide or the simple sugar is the monomer of carbohydrate. Two monosaccharides
combine to form disaccharide, and many monosaccharides form polysaccharide. The three
forms of monosaccharide are glucose, fructose, and galactose (Royal Society of Chemistry,
2004). Glucose is the building block of carbohydrate, it is important for the process turning
into energy, or respiration. Other carbohydrate forms also have to change into glucose form
for the process of digestion too. Fructose or fruit sugar is found in fruits. Galactose is found
in mammals milk. One monomer of glucose and glucose form a disaccharide called maltose,
maltose is found in grain, barley, and etc. Glucose and galactose form lactose, which is found
in dairy products. Glucose and fructose form sucrose, which is table sugar (sugar canes and
beets). It also could be found in specific kinds of vegetables and fruits. The main types of
polysaccharide are cellulose, pectin, dextrin, starch, and glycogen (IvyRose Holistic Health,
n.d.)
Because of sugar specific structure, it impacts what property it has. In the range of
sweetness, fructose is considered the sweetest of all sugar and lactose is the least. Some
factors that could affect the sweetness is how that particular sugar cooperate with the taste
buds, pH level, temperature, thickness, and concentration (Mehas and Rogers, 2006). Sugar
also have the property of effecting the flavor of the food by giving off aromas when mixed
with certain foods. For example, sugar and protein interactions result in maillard reaction.
Sugar also effect the texture of food too, especially frozen foods (Kitts, 2010). Sugar
produces the soft, smooth, and airy texture of frozen products like ice cream, by preventing
lactose (milk sugar) crystallization and by lowering the freezing point to facilitate the
production of smaller ice crystals (Kitts, 2010, p. 3). Another property of sugar is preserving
food, this property is related to food industries. Because sugar have the property of taking
moisture from its surroundings, it prevents microorganisms to grow in the water, preserving
food (Kitts, 2010). Caramelization is also one of the properties of sugar. This property cause
the browning of sugar when heated (Mehas and Rogers, 2006). As sugar is heated, some of
the water leaves its molecules in the form of hydrogen and oxygen (Mehas and Rogers,
2006, p. 222). High concentration of carbon dioxide is resulted in the heating process and
created the brown color. Each type of sugar has its own temperature that it would caramelize
(Mehas and Rogers, 2006).
Sugar could easily dissolve in water because they both have hydroxyl groups in their
structures. Each type of sugar also has the different ability to dissolve, how well it dissolves
ordered like the sweetness: fructose is the most soluble and lactose is the least. Temperature
is a factor that effect how much sugar could be in a solution. The higher the heat is, the more
sugar could be dissolved (Mehas and Rogers, 2006). Normally, if the solution is added with
the range of maximum amount of sugar, the extra sugar that added would not dissolve, this
solution is called a saturated solution (Helmenstine, 2016). Adding the heat or increasing
temperature would allow the extra sugar to dissolve, which usually in the normal temperature
it would not, this solution is called a supersaturated solution. Crystal would form in the
supersaturated solution, if that solution reach a specific concentration, tiny crystals would
form. By forming tiny crystals, the other sugar crystals would isolate from the solution and
follow to form bigger crystal (Mehas and Rogers, 2006).
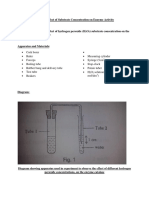
For this experiment, the requirement is to make a rock candy crystal from a
supersaturated solution. We heat up 300 ml of water and slowly dissolve 600 grams of sugar
to form a supersaturated solution. We put a stick that covered in sugar crystals into the
solution, which later on the sugar in the supersaturated solution attach to the previous crystals
to form larger crystals. The purpose of this lab is to understand more about the property of
sugar solubility and crystallization by seeing the process in actions.
References
Royal Society of Chemistry. (2004, November). Carbohydrates. Retrieved from
http://www.rsc.org/Education/Teachers/Resources/cfb/carbohydrates.htm
Dallas Learning Cloud. (n.d.). Biomolecules. Retrieved from https://dlc.dcccd.edu/biology1-
3/carbohydrates
Gebel, E. (2011, March). How the Body Uses Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats. Retrieved
from http://www.diabetesforecast.org/2011/mar/how-the-body-uses-carbohydrates-proteins-
and-fats.html?referrer=https://www.google.co.th/
IvyRose Holistic Health. (n.d.). Types of Sugar. Retrieved from
http://www.ivyroses.com/HumanBiology/Nutrition/Types-of-Sugar.php
Kitts, D. D. (2010). Sucrose: From Field to Table. Retrieved from
http://www.sugar.ca/SUGAR/media/Sugar-Main/PDFs/2010-CHOnews_ENG-LR.pdf
Helmenstine, A. M. (2016, July 7). Saturated Solution Definition and Examples. Retrieved
from https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-saturated-solution-and-examples-605640
Mehas, K. Y., & Rogers, S. L. (2006). Food Science: The Biochemistry of Food and
Nutrition. Columbus, Ohio: McGraw-Hill companies
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Specialized Cells: How Animal and Plant Cells Adapt for Different FunctionsDokumen9 halamanSpecialized Cells: How Animal and Plant Cells Adapt for Different FunctionsJanah Pauline AbunganBelum ada peringkat
- Johniya Cochran - Ionic and Covalent Bonds ActivityDokumen4 halamanJohniya Cochran - Ionic and Covalent Bonds ActivityJohniya CochranBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme ActivityDokumen5 halamanEffect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme ActivityMarc MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Chemical Reactions: I. Purpose: II. MaterialsDokumen4 halamanTypes of Chemical Reactions: I. Purpose: II. MaterialsJerneth Nyka FloresBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 9646 H2 Physics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionDokumen10 halaman2017 9646 H2 Physics Prelim Paper 2 SolutionxiaokiaBelum ada peringkat
- Precipitation ReactionsDokumen3 halamanPrecipitation ReactionsborgiamatriceBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Physics 2023Dokumen30 halamanThermal Physics 2023ishraqtazishraqBelum ada peringkat
- Emission SpectraDokumen4 halamanEmission SpectraKarla Jara Hidalgo GalarionBelum ada peringkat
- IB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisDokumen17 halamanIB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisFinn Bruchet100% (1)
- Carbohydrates Slide-2 PHARM-D, SALUDokumen85 halamanCarbohydrates Slide-2 PHARM-D, SALUShahid AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- List of CPCB Approved Waste Oil Re-ProcessorsDokumen45 halamanList of CPCB Approved Waste Oil Re-Processorsalive2flirtBelum ada peringkat
- Ionic CompoundDokumen16 halamanIonic CompoundLlenzycris SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Dokumen4 halamanChemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Lama DebanaBelum ada peringkat
- Bioprocessing EngineeringDokumen9 halamanBioprocessing EngineeringKuo SarongBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic Table and Periodicity QuizDokumen5 halamanPeriodic Table and Periodicity QuizIzzatiBelum ada peringkat
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDokumen58 halamanAtoms, Molecules and IonsJunaid Alam100% (1)
- Practice Worksheet of Chemical BondingDokumen2 halamanPractice Worksheet of Chemical Bondingch khakanBelum ada peringkat
- Solubility Rules: Name - Chem Worksheet 15-1Dokumen1 halamanSolubility Rules: Name - Chem Worksheet 15-1Mohamed El-sherbinyBelum ada peringkat
- Flame TestDokumen9 halamanFlame TestChristopher YepmoBelum ada peringkat
- Naming Ionic Compounds WorksheetDokumen3 halamanNaming Ionic Compounds Worksheetgowrimanohar1975Belum ada peringkat
- Solubility and Solubility CurveDokumen39 halamanSolubility and Solubility CurveSymon Alonzo VersozaBelum ada peringkat
- B1.1 - Carbohydrates and LipidsDokumen4 halamanB1.1 - Carbohydrates and LipidslittleianlauBelum ada peringkat
- ENSYN RTP Description (2011)Dokumen25 halamanENSYN RTP Description (2011)iboukis100% (1)
- Enzymatic Starch HydrolysisDokumen107 halamanEnzymatic Starch HydrolysisManuel Rojas100% (1)
- Flame TestDokumen2 halamanFlame Testtompet8Belum ada peringkat
- How To Measure Dietary Fibres CorrectlyDokumen5 halamanHow To Measure Dietary Fibres CorrectlyLSBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Test 5Dokumen10 halamanChem Test 5Alejandro AristizabalBelum ada peringkat
- Titration LabDokumen15 halamanTitration Labapi-387944893Belum ada peringkat
- Waste Oil GujaratDokumen4 halamanWaste Oil GujaratLalit NagarBelum ada peringkat
- Rock Candy ExperimentDokumen4 halamanRock Candy ExperimentsamBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of Purification TechniquesDokumen43 halamanMethods of Purification Techniquespriya sundaramBelum ada peringkat
- Chie p6 Descriptive Essay ModelsDokumen10 halamanChie p6 Descriptive Essay Modelsapi-170611830Belum ada peringkat
- Christian Lara Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanChristian Lara Lab ReportLeslieBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report Rock CandyDokumen2 halamanLab Report Rock Candyapi-350496922Belum ada peringkat
- Investigatory Project - Rock CandyDokumen9 halamanInvestigatory Project - Rock CandyChing Lising0% (1)
- STOICHIOMETRYDokumen5 halamanSTOICHIOMETRYGadde Gopala KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 5 Flame Tests and Electron ConfigurationDokumen7 halamanExp 5 Flame Tests and Electron ConfigurationJean OlbesBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Spa Skill 3 Planning OutlineDokumen3 halamanPhysics Spa Skill 3 Planning OutlinexeonzwongBelum ada peringkat
- Test4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedDokumen13 halamanTest4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedEga SukmaBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Lab ReportDokumen10 halamanBio Lab ReportMariamBelum ada peringkat
- Nano and The Environment: Potential Risks, Real Uncertainties & Urgent IssuesDokumen12 halamanNano and The Environment: Potential Risks, Real Uncertainties & Urgent IssuesGeorgina Catacora V.Belum ada peringkat
- Group 1 and 17 Elements Properties and ReactionsDokumen5 halamanGroup 1 and 17 Elements Properties and ReactionsLeong Kit WaiBelum ada peringkat
- Notes and Questions: Aqa GcseDokumen12 halamanNotes and Questions: Aqa Gcseapi-422428700Belum ada peringkat
- JC H2 Chemistry Prelim PapersDokumen13 halamanJC H2 Chemistry Prelim Paperschong56Belum ada peringkat
- 16 - Flat vs. Fizzy Soda CompleteDokumen9 halaman16 - Flat vs. Fizzy Soda CompleteAli AlzarooniBelum ada peringkat
- Tataquara Lodge Eco Tourism in Brazilian RainforestDokumen2 halamanTataquara Lodge Eco Tourism in Brazilian RainforesthhfjyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Assessment The Periodic Table and Periodic Law Student EditableDokumen8 halamanChapter Assessment The Periodic Table and Periodic Law Student Editableanon_789010972Belum ada peringkat
- F321 Group 7Dokumen5 halamanF321 Group 7Doc_CrocBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank of Chapter 1Dokumen4 halamanQuestion Bank of Chapter 1lovika malhotraBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Classifying Matter NotesDokumen5 halaman3.1 Classifying Matter NotesJam Uly GastyBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Topic 2: Inorganic ChemistryDokumen4 halamanEdexcel IGCSE Chemistry Topic 2: Inorganic ChemistryVenant HakizimanaBelum ada peringkat
- The Ionic Product For WaterDokumen6 halamanThe Ionic Product For WaterPrince SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Anions and CationsDokumen10 halamanAnions and CationsKeerthy VenthenBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Arithmetic and Reactions: ObjectivesDokumen24 halamanChemical Arithmetic and Reactions: Objectivesgoputs6386Belum ada peringkat
- Environment Ecology PDFDokumen163 halamanEnvironment Ecology PDFmadhan10aeroBelum ada peringkat
- Balancing Equations PDFDokumen6 halamanBalancing Equations PDFFeli CiaBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFDokumen4 halamanTypes of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFStefanie CorcoranBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Kinetics Part 1Dokumen46 halamanChapter 1 - Chemical Kinetics Part 1NUR DINI MAISARAH BINTI HEZAL / UPMBelum ada peringkat
- Ian Chow - Biology IA First DraftDokumen3 halamanIan Chow - Biology IA First DraftIanBelum ada peringkat
- In-Class Worksheet AnswersDokumen6 halamanIn-Class Worksheet AnswersalgonzBelum ada peringkat
- 0620 w10 QP 31Dokumen16 halaman0620 w10 QP 31Mennatallah Mohamed HamedBelum ada peringkat
- H2 Chemical Kinetics and EnergeticsDokumen12 halamanH2 Chemical Kinetics and EnergeticskitoniumBelum ada peringkat
- 2011wksht Heating Curve - CalcsDokumen3 halaman2011wksht Heating Curve - Calcsapi-2982478730% (2)
- SNC1D Exam Review CHEMISTRYDokumen4 halamanSNC1D Exam Review CHEMISTRYSwae LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Chemistry 2: Phase Equilibria and Distribution LawsDokumen33 halamanPhysical Chemistry 2: Phase Equilibria and Distribution LawsCatriona BlackBelum ada peringkat
- q4 Module 2 CompressedDokumen4 halamanq4 Module 2 CompressedFELIX ROBERT VALENZUELABelum ada peringkat
- CarbohydratesDokumen5 halamanCarbohydratesSurbhi JainBelum ada peringkat
- Biology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDokumen15 halamanBiology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson On CarbohydratesDokumen5 halamanLesson On CarbohydratesTweenieSumayanMapandiBelum ada peringkat
- The Outsiders EssayDokumen3 halamanThe Outsiders Essayapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Labreport2 5Dokumen6 halamanLabreport2 5api-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- History Newspaper PloyDokumen3 halamanHistory Newspaper Ployapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Echinoderm ConservationDokumen7 halamanEchinoderm Conservationapi-347898112Belum ada peringkat
- The Biology Really Really Real Lab IntroductionDokumen2 halamanThe Biology Really Really Real Lab Introductionapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Food Science 2-Recovered With A GraphDokumen1 halamanFood Science 2-Recovered With A Graphapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Real Outsiders Essay 1Dokumen4 halamanThe Real Outsiders Essay 1api-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Thai DressDokumen4 halamanThai Dressapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Food Science 2-Recovered With A GraphDokumen1 halamanFood Science 2-Recovered With A Graphapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Lab ReportDokumen9 halamanLab Reportapi-387944893Belum ada peringkat
- General Biology: Osmosis LabDokumen11 halamanGeneral Biology: Osmosis Labapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- ProcedureDokumen1 halamanProcedureapi-327713634Belum ada peringkat
- Ling Nutrition1Dokumen16 halamanLing Nutrition1api-295691633Belum ada peringkat
- Computer Python Poster-RecoveredDokumen1 halamanComputer Python Poster-Recoveredapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Lab Crystal Introduction PloyyyyyyyyDokumen1 halamanLab Crystal Introduction Ployyyyyyyyapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Printing Reading PortfolioDokumen5 halamanThe Printing Reading Portfolioapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Biology ProjectDokumen1 halamanBiology Projectapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Biology ProjectDokumen1 halamanBiology Projectapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Printing Reading PortfolioDokumen5 halamanThe Printing Reading Portfolioapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Please Print CorrectlyDokumen6 halamanPlease Print Correctlyapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Biology ProjectDokumen1 halamanBiology Projectapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Printing Reading PortfolioDokumen5 halamanThe Printing Reading Portfolioapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Printing Reading PortfolioDokumen5 halamanThe Printing Reading Portfolioapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Printing Reading PortfolioDokumen5 halamanThe Printing Reading Portfolioapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Printing Reading PortfolioDokumen5 halamanThe Printing Reading Portfolioapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Printing Reading PortfolioDokumen5 halamanThe Printing Reading Portfolioapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Printing Reading PortfolioDokumen5 halamanThe Printing Reading Portfolioapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- The Printing Reading PortfolioDokumen5 halamanThe Printing Reading Portfolioapi-327818023Belum ada peringkat
- Determination of Sugars in Soft Drinks by PDFDokumen5 halamanDetermination of Sugars in Soft Drinks by PDFSAINT TDOHBelum ada peringkat
- 05-30-15 SatDokumen32 halaman05-30-15 SatSan Mateo Daily JournalBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus 8Dokumen1 halamanSyllabus 8harrypaswan87Belum ada peringkat
- Biological Losses in Milling TandemDokumen6 halamanBiological Losses in Milling TandemMaydolBelum ada peringkat
- Carbohidraţii Sunt Clasificaţi Astfel 1. Simple CarbohydratesDokumen3 halamanCarbohidraţii Sunt Clasificaţi Astfel 1. Simple CarbohydratesMonica CreangaBelum ada peringkat
- Global Warming Consensus Among ScientistsDokumen121 halamanGlobal Warming Consensus Among ScientistsAtraSicariusBelum ada peringkat
- Carbohydrates II NEW JaiDokumen10 halamanCarbohydrates II NEW JaiNur SanaaniBelum ada peringkat
- Sbt1102 - Biochemistry Unit 1 CarbohydratesDokumen22 halamanSbt1102 - Biochemistry Unit 1 CarbohydratesJeremy CorrenBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Technology Product List 2 July 2015 PDFDokumen630 halamanEnergy Technology Product List 2 July 2015 PDFerwin ktaBelum ada peringkat
- Molasses - 68476-78-8Dokumen5 halamanMolasses - 68476-78-8Ria angrainiBelum ada peringkat
- CARBOHYDRATE NAMES AND SYMBOLS TABLEDokumen2 halamanCARBOHYDRATE NAMES AND SYMBOLS TABLEnelaojBelum ada peringkat
- 5 6100500212126580750 PDFDokumen94 halaman5 6100500212126580750 PDFRizziel NemesBelum ada peringkat
- Carbohydrates Classification and FunctionsDokumen2 halamanCarbohydrates Classification and FunctionsANGELA DENISSE AMAT100% (1)
- Maltose - WikipediaDokumen9 halamanMaltose - WikipediaSANKAR VBelum ada peringkat
- CarbohydrateDokumen36 halamanCarbohydrateAmit Raje JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 1Dokumen6 halamanWorksheet 1Arista_rafifBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Activity 1 CarbohydratesDokumen59 halamanLearning Activity 1 CarbohydratesMaxine Danielle AlmeroBelum ada peringkat
- Carbohydrates: Biological MoleculesDokumen50 halamanCarbohydrates: Biological MoleculesRalph FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Potential and Constraints of Cassava Bioenergy Development in IndonesiaDokumen20 halamanPotential and Constraints of Cassava Bioenergy Development in IndonesiaNova hardiantyBelum ada peringkat
- BIOMOLECULES: KEY COMPONENTS OF LIFEDokumen17 halamanBIOMOLECULES: KEY COMPONENTS OF LIFElyaffleBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Modeling of CarbohydratesDokumen4 halamanMolecular Modeling of CarbohydratesPhuc DangBelum ada peringkat
- Biomolecules - DPP 01 - DPP - 1 - Biomolecues - Chemistry Vishal Sir - 08112021 - HussainDokumen2 halamanBiomolecules - DPP 01 - DPP - 1 - Biomolecues - Chemistry Vishal Sir - 08112021 - Hussainanurag palBelum ada peringkat