SCIENCE
Diunggah oleh
羅天佑Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SCIENCE
Diunggah oleh
羅天佑Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
S2 Science Test
Unit 7 Living things and air
Name:____________________________ Time and Marks
Class: ____________________________ Part A: 35 min / 100 marks
Date: ____________________________ Parts A & B: 45 min / 120 marks
Note:
1 Attempt ALL questions.
2 Write your answers in the spaces provided on the Answer Sheets.
Part A (Level 1)
A Ordering (4 marks)
What is the feeding relationship among the following living things? Write a to d in the blanks on the
answer sheets to show the correct order of the food chain formed by them.
a b c d
B True or false questions (6 marks, 1 mark each)
Study each of the following statements. Write T for a true statement and F for a false statement on the
answer sheets.
1 Air contains mainly oxygen.
2 Pouring water onto the burning objects is always the best way to put out the fire because water can lower
the temperature.
3 Both mushroom and grass can obtain light energy directly from the Sun for photosynthesis.
4 Respiration occurs in the lungs only.
5 Green plants take in carbon dioxide in bright light but they give out carbon dioxide in the dark.
6 Every day the Environmental Protection Department reports the latest Air Pollution Index to the public.
Oxford University Press 2005 -1-
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
C Multiple-choice questions (20 marks, 2 marks each)
Choose the correct answer for each of the following questions.
1 Which of the following is a test for carbon dioxide?
A Smelling
B Glowing splint test
C Hydrogencarbonate indicator test
D Using dry cobalt chloride paper
2 Which of the following comparisons between breathed air and fresh air is correct?
Breathed air Fresh air
A Amount of carbon dioxide Less More
B Amount of oxygen More Less
C Temperature Higher Lower
D Amount of water vapour Less More
3 Which of the following is not the condition needed for burning to occur?
A Oxygen
B Fire
C Temperature
D Fuel
4 The figure below shows a small household fire. Which of the following methods is not the right way to put out
the fire?
A Turn off the gas supply.
B Carry the pan of burning oil.
C Cover the pan with a wet cloth to cool the fire.
D Cover the flames with a lid or plate.
Oxford University Press 2005 -2-
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
5 Which of the following activities need energy?
(1) Riding bicycles (2) Walking (3) Sleeping
A (1) and (2) only
B (1) and (3) only
C (2) and (3) only
D (1), (2) and (3)
6 The figure on the right shows a set-up used to collect oxygen produced from
the green plant. What is this method called?
A Collection of oxygen
B Displacement of water
C Photosynthesis
D Respiration
7 The figure on the right shows a balloon-bell jar model which helps simulate the
action of the diaphragm in breathing. Which part of the human breathing system
X
does X represent?
A Diaphragm
B Lung
C Bronchus
D Trachea
8 Which of the following are air pollutants?
(1) Sulphur dioxide (2) Carbon monoxide (3) Lead
A (1) and (2) only
B (1) and (3) only
C (2) and (3) only
D (1), (2) and (3)
9 Which of the following is not the harmful substance found in a cigarette?
A Nicotine
B Tar
C Carbon dioxide
D Carbon monoxide
10 Which of the following substances found in a cigarette causes addiction?
A Nicotine
B Tar
C Cigarette smoke
D Carbon monoxide
Oxford University Press 2005 -3-
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
D Fill in the blanks (20 marks, 2 marks each)
Complete the following sentences.
1 Unbreathed air mainly contains a .
2 Noble gases are also called b . They are a group of very unreactive gases.
3 Food stores c energy which can be released during respiration and converted to other forms of
energy in the body.
4 Only plants which contain d can use light energy to make food.
5 Two sets of muscles control our breathing mechanism. They are the diaphragm and the e .
6 Animals which cannot make their own food but need to feed on plants or other animals are called f
in the food chain.
7 The movement of air into and out of the lungs is called g .
8 We can test for the presence of starch in green leaves with h solution. If the leaves turn to i
colour, it shows the presence of starch.
9 If a certain chemical is present, the test for it will give us the expected result which is called the j
result.
E Questions (50 marks)
1 The pie chat below shows the relative amounts of gases in the air.
Gas X
(78%) Gas Y
(21%)
Gas Z
(0.03%)
a What are gases X, Y and Z? (3 marks)
b State two tests to distinguish between gases X, Y and Z. (6 marks)
c What is the use of gas X in daily life? Give one example. (2 marks)
Oxford University Press 2005 -4-
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
2 The experiment below shows how to test for the presence of starch in green leaves. Answer the
questions according to the following steps.
boiling liquid A
water
hot
water
bath
liquid B liquid C
a What are liquids A, B and C? (3 marks)
b Write the functions of liquids A, B and C in the experiment. (3 marks)
c The plant below was destarched before placing it under sunlight for three days. A leaf is
then picked for doing the above experiment.
i What is the potted plant shown in the above photo? (1 mark)
ii Draw the appearance of the leaf after the experiment on the answer sheet. (4 marks)
iii Before doing the experiment, why is it necessary to have the plant destarched? (2 marks)
iv Several conditions are necessary for a plant to carry out photosynthesis. What related
conclusion can be drawn from the above experiment? (2 marks)
Oxford University Press 2005 -5-
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
3 The figure below shows the human breathing system.
A C
D
B E
a F
Name parts A to F. (6 marks)
b What are the changes of parts A and F when we breathe in? (3 marks)
c From parts A to F, where does gaseous exchange occur? State one structural feature
of this part. (2 marks)
d During respiration, carbon dioxide is produced by body cells. How can our body get rid of
carbon dioxide? Briefly describe. (3 marks)
e What is the difference between breathing and respiration? (2 marks)
4 The figure below shows three types of equipment used for putting out fires.
A
C
B
a Name equipment A, B and C. (3 marks)
b What does equipment B contain for putting out fires? List two kinds of substances. (2 marks)
c Which side of the fire triangle does each of the above equipment remove in order to
put out fires? (1 mark)
d When a fire is caused by electrical leakage in the electrical equipment, which of the above
equipment is/are better used to put out the fire? We should never pour water on the electrical
equipment. Why? (2 marks)
End of Part A
Oxford University Press 2005 -6-
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
Part B (Level 2) (20 marks)
Know More About SARS
In 2003, the outbreak of SARS severely affected the daily life of Hong Kong people. At this stage, there is
no definitive treatment for SARS. Read the information about SARS below and answer the questions.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is caused by a
coronavirus ( ). The patient will have dry cough and
breathing difficulties. The incubation period ( ) for this
disease ranges from two to ten days.
Some evidence shows that SARS is spread by exhaled
droplets ( of cough or sneezes from infected people.
Besides, when we contact the body secretions from an
infected person, we will be at a high risk of getting SARS.
To protect ourselves from getting SARS, we should build
up a good body immunity. For example, having a balanced
diet, taking adequate rest and regular exercise.
1 SARS patients may have fluid accumulated in the air sacs. How may the accumulation of fluid affect
a the amount of oxygen in the blood of SARS patients? (3 marks)
b the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood of SARS patients? (3 marks)
2 As mentioned above, SARS patients suffer from breathing difficulties. Why? (6 marks)
3 Besides those symptoms mentioned above, what other symptoms may SARS patients have?
Give two. (4 marks)
4 Besides those methods mentioned above, give two more ways to protect ourselves from
getting SARS. (4 marks)
End of Part B
Oxford University Press 2005 -7-
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
S2 Science Test
Unit 7 Living things and air
Answer Sheets
Name: ____________________ Class: ____________ Marks: __________________
Total: 100% (Part A) / 120% (Parts A & B)
Section A Total
Part A (Level 1) Do not write in
this box
Ordering (4 marks)
__________ __________ __________ __________
means is eaten by Section B Total
Do not write in
this box
True or false questions (6 marks, 1 mark each)
1 _______ 2 _______ 3 _______ 4 _______ 5 _______ 6 _______
Multiple-choice questions (20 marks, 2 marks each) Section C Total
Do not write in
this box
1 __________ 2 __________ 3 __________ 4 __________ 5 __________
6 __________ 7 __________ 8 __________ 9 __________ 10 __________
Fill in the blanks (20 marks, 2 marks each)
a ______________________ b ______________________ c ______________________
d ______________________ e ______________________ f ______________________ Section D Total
Do not write
in this box
g ______________________ h ______________________ i ______________________
j ______________________
Questions (50 marks)
1 a Gas X: _____________ Gas Y: _____________ Gas Z: _____________
b ___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
c ___________________________________________________________________________
2 a Liquid A: _____________ Liquid B: _____________ Liquid C: _____________
Oxford University Press 2005 -8-
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
b ___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
c i ________________________________________________________________________
ii The appearance of the leaf: iii _________________________________________
_________________________________________
iv _________________________________________
3 a A _____________ B _____________ C _____________
D _____________ E _____________ F _____________
b ___________________________________________________________________________
c ___________________________________________________________________________
d ___________________________________________________________________________
e ___________________________________________________________________________
4 a A _____________ B _____________ C _____________
b ___________________________________________________________________________ Section E Total
Do not write in
this box
c ___________________________________________________________________________
d ___________________________________________________________________________
Part B (Level 2) (20 marks)
1 a ___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
b ___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
2 ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
3 ______________________________________________________________________________ Part B Total
Do not write in
this box
4 ______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Oxford University Press 2005 -9-
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
S2 Science Test (Unit 7 Living things and air)
Answers
Part A (Level 1)
(4%)
cbda 1 m each
B True or false questions (6%)
1F 2F 3F 4F 5T 6T 1 m each
C Multiple-choice questions (20%)
1C 2C 3B 4B 5D 6B 7C 8D 9 C 10 A 2 m each
D Fill in the blanks (20%)
a nitrogen b inert gases c chemical d chlorophyll e intercostal muscles
f consumers g breathing h iodine i blue black j positive 2 m each
E Questions (50%)
1 a Gas X: nitrogen; Gas Y: oxygen; Gas Z: carbon dioxide 1 m each
b Use a burning splint or a glowing splint to test whether gas X, gas Y or gas Z is oxygen; 2m
Use lime water or hydrogencarbonate indicator to test whether gas X, gas Y or gas Z is carbon dioxide; 2m
If the gas shows negative results to the above tests, it should be nitrogen. 2m
c Adding gas X (i.e. nitrogen) into a food package can extend its shelf life. 2m
2 a Liquid A: alcohol; Liquid B: hot water; Liquid C: iodine solution 1 m each
b Liquid A: dissolves the green chlorophyll from the leaf and turns it white. This makes it easier
to observe the result of iodine test. 1m
Liquid B: washes and softens the leaf. 1m
Liquid C: detects the presence of starch in the leaf. 1m
c i It is a variegated plant. 1m
ii
The appearance of the leaf after the experiment:
brown
blue black
correct labels: 2 m; correct distribution of colours: 2 m
iii This shows that any starch found must be newly formed during the experiment. 2m
iv Chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis. 2m
Oxford University Press 2005 - 10 -
Living Science (Second Edition) Unit Test 2 7 Living things and air
3 a A: rib; B: air sac; C: trachea; D: bronchus; E: heart; F: diaphragm 1 m each
b A (i.e. the ribs) move upwards and outwards and F (i.e. the diaphragm) moves down. 1 m each
c Gaseous exchange occurs in B (i.e. the air sacs). 1m
The wall of B (i.e. the air sacs) is very thin. / B are covered with capillaries. (any 1) 1m
d The blood brings carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. Carbon dioxide diffuses from
the blood into the air sacs, then passes through the bronchi, trachea and is breathed out. 3m
e Breathing is a physical process and respiration is a chemical process. 2m
4 a A: fire blanket; B: fire extinguisher; C: sand bucket 1 m each
b Dry powder or carbon dioxide. 1 m each
c All the three equipment puts out fires by cutting down the supply of oxygen. 1m
d B (i.e. fire extinguisher) or C (i.e. sand bucket). 1m
It is because water conducts electricity. 1m
Part B (Level 2) (20%)
1 a Less oxygen diffuses from the air sacs into the capillaries. The amount of oxygen in the blood
of SARS patients will decrease. 3m
b Less carbon dioxide diffuses from the capillaries into the air sacs. The amount of carbon dioxide
in the blood of SARS patients will increase. 3m
2 Breathing is controlled by the respiratory centre in the brain. 3m
When the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood of SARS patients increases, the centre automatically
sends out signals to make them breath faster. 3m
3 Fever / headache / muscular stiffness (any 2) 2 m each
4 Maintain a good personal hygiene. / Make sure the room has good ventilation. / Avoid going to
crowded areas. / Wear a surgical mask when going out. / Clean the home furniture frequently with
diluted bleach. (any 2 or other reasonable answers) 2 m each
Oxford University Press 2005 - 11 -
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- F2 IS Exam 1 (13-14)Dokumen9 halamanF2 IS Exam 1 (13-14)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- KWUN TONG GOVERNMENT SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF YEARLY EXAM 2004-2005 INTEGRATED SCIENCEDokumen9 halamanKWUN TONG GOVERNMENT SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF YEARLY EXAM 2004-2005 INTEGRATED SCIENCE羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 IS Exam 1 (11-12)Dokumen9 halamanF2 IS Exam 1 (11-12)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 IS Exam 1 (10-11)Dokumen7 halamanF2 IS Exam 1 (10-11)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- FIRST-TERM FORM TEST (2020/21) Form Two Integrated Science: Instructions Multiple-Choice Answer SheetDokumen14 halamanFIRST-TERM FORM TEST (2020/21) Form Two Integrated Science: Instructions Multiple-Choice Answer SheetYuki LiBelum ada peringkat
- Sectiona: Multiplechoice (2marks@.24%) : Answer All QuestionsDokumen6 halamanSectiona: Multiplechoice (2marks@.24%) : Answer All QuestionsYuki LiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit TestDokumen11 halamanUnit TestCHUN YIN LEUNGBelum ada peringkat
- F2ISExam1 (01-02) (修復)Dokumen38 halamanF2ISExam1 (01-02) (修復)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)Dokumen10 halamanF2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 7 Living Things and Air (Question)Dokumen7 halamanUnit 7 Living Things and Air (Question)usbdetailsBelum ada peringkat
- S.2 Integrated Science Worksheet Chapter 7 (7.4 - 7.7) : Part A: Concept Checking (10 Marks)Dokumen7 halamanS.2 Integrated Science Worksheet Chapter 7 (7.4 - 7.7) : Part A: Concept Checking (10 Marks)Wong YanBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Exercise For ScienceDokumen13 halamanRevision Exercise For ScienceSumi Vj0% (1)
- 06 Matter As ParticlesDokumen10 halaman06 Matter As ParticlesmahinkamBelum ada peringkat
- KWUN TONG GOVERNMENT SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF-YEARLY EXAMDokumen8 halamanKWUN TONG GOVERNMENT SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF-YEARLY EXAM羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 IS Exam 2 (15-16)Dokumen10 halamanF2 IS Exam 2 (15-16)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- Part A (Level 1) A: True or False QuestionsDokumen10 halamanPart A (Level 1) A: True or False Questionsshirley wongBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Starting Science: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokumen20 halamanUnit 1 Starting Science: Multiple-Choice QuestionsVincent NG100% (1)
- F1 Sci - Living Things BDokumen29 halamanF1 Sci - Living Things BYuenHei KwokBelum ada peringkat
- Making efficient use of electricityDokumen40 halamanMaking efficient use of electricityYuenHei Kwok100% (1)
- Scicent AB TE U8 eDokumen40 halamanScicent AB TE U8 erayckng2Belum ada peringkat
- QB - Ch7 - Eng (Living Things and AirDokumen88 halamanQB - Ch7 - Eng (Living Things and Air羅天佑100% (1)
- Scicent AB TE U11 eDokumen26 halamanScicent AB TE U11 eYuenHei KwokBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokumen8 halamanChapter 2 Multiple-Choice QuestionsDavid LouBelum ada peringkat
- WW1 History Exam PrepDokumen86 halamanWW1 History Exam PrepVincent NGBelum ada peringkat
- S1 Is First Term ExamDokumen8 halamanS1 Is First Term ExamNicole Yau100% (1)
- 09 Space Travel PDFDokumen9 halaman09 Space Travel PDFTAi Man Chan100% (1)
- Making Use of Electricity: Conditions Necessary For Current FlowDokumen12 halamanMaking Use of Electricity: Conditions Necessary For Current FlowOli Leung100% (1)
- 10 Common Acids and Alkalis PDFDokumen10 halaman10 Common Acids and Alkalis PDFTAi Man ChanBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Major Conflicts and The Quest For Peace Data-Based QuestionsDokumen129 halaman4 Major Conflicts and The Quest For Peace Data-Based QuestionsDai Sinatra'sBelum ada peringkat
- Ch5 Food and Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokumen5 halamanCh5 Food and Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsYing Hei NgBelum ada peringkat
- CHP 1 Suggested AnswerDokumen10 halamanCHP 1 Suggested AnswerRachel Wong74% (31)
- Nms Utest04 L2 Trial eDokumen11 halamanNms Utest04 L2 Trial eHugo CheungBelum ada peringkat
- Questions: World History Express 3Dokumen108 halamanQuestions: World History Express 3Vincent NGBelum ada peringkat
- Oxford Mastering Science 2a Unit 7Dokumen17 halamanOxford Mastering Science 2a Unit 7cocBelum ada peringkat
- S1 Is YE Term Exam 2022 - Final VersionDokumen19 halamanS1 Is YE Term Exam 2022 - Final VersionTimmy SzeBelum ada peringkat
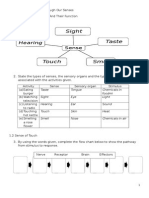
- Sensing the environment: Sight 視覺Dokumen3 halamanSensing the environment: Sight 視覺Winnie ChanBelum ada peringkat
- S1 Science Exam 2021-22 (W Ans)Dokumen15 halamanS1 Science Exam 2021-22 (W Ans)Lorraine TsoiBelum ada peringkat
- S3 Geography Mock PaperDokumen12 halamanS3 Geography Mock Paperharis Rehman100% (1)
- 03 Cells and Human ReproductionDokumen10 halaman03 Cells and Human ReproductionYan WongBelum ada peringkat
- Is Unit 9 RevisionDokumen8 halamanIs Unit 9 RevisionwingBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Sensing The Environment PDFDokumen12 halaman11 Sensing The Environment PDFTAi Man Chan100% (4)
- HKDSE Chemistry Bridging Programe 1CDokumen76 halamanHKDSE Chemistry Bridging Programe 1Cthe222Belum ada peringkat
- Suggested Answers: The Cell As A Basic Unit of LifeDokumen2 halamanSuggested Answers: The Cell As A Basic Unit of Lifeapi-3841068100% (1)
- 10 Sensing the Environment: Detecting Stimuli with Our SensesDokumen30 halaman10 Sensing the Environment: Detecting Stimuli with Our SensesYuenHei Kwok100% (1)
- F3 Final Exam 11-12Dokumen23 halamanF3 Final Exam 11-12jonas hoBelum ada peringkat
- Msci Lssws02 eDokumen9 halamanMsci Lssws02 efishyueBelum ada peringkat
- Water Purification and the Water CycleDokumen20 halamanWater Purification and the Water CycleYuki LiBelum ada peringkat
- 2020-21-S2 EnglishDokumen12 halaman2020-21-S2 EnglishYuen Ying SzeBelum ada peringkat
- Scicent AB TE U3 eDokumen28 halamanScicent AB TE U3 erayckng2100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Temperature and ThermometersDokumen4 halamanChapter 1 Temperature and ThermometersZhu JiankunBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrition in Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokumen54 halamanNutrition in Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsRyanBelum ada peringkat
- Scicent QRN U1 Final BilingualDokumen17 halamanScicent QRN U1 Final BilingualLo karenBelum ada peringkat
- 1920 F3 Chem First Exam Question PaperDokumen6 halaman1920 F3 Chem First Exam Question PaperElsaaaBelum ada peringkat
- F3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - WT Ans - Final - 110526Dokumen14 halamanF3 - Bio - Final Exam - MCQs - WT Ans - Final - 110526jonas hoBelum ada peringkat
- Ws ch05 eDokumen10 halamanWs ch05 eJoesy ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Answer SchemeDokumen10 halamanChapter 1 - Answer Schemehm100% (1)
- (Unit 2) Water 水Dokumen14 halaman(Unit 2) Water 水Lai Chuen Chan100% (2)
- STFALKKC F2IS1stTermDokumen5 halamanSTFALKKC F2IS1stTermVic KyBelum ada peringkat
- S.2 Integrated Science Worksheet Chapter 7 (7.1 - 7.3) : Part A: Multiple Choice (10 Marks)Dokumen7 halamanS.2 Integrated Science Worksheet Chapter 7 (7.1 - 7.3) : Part A: Multiple Choice (10 Marks)elephantn63Belum ada peringkat
- F2ISExam1 (01-02) (修復)Dokumen38 halamanF2ISExam1 (01-02) (修復)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 IS Exam 1 (12-13)Dokumen8 halamanF2 IS Exam 1 (12-13)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 2ndtest ISDokumen10 halamanF2 2ndtest IS羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 - IS - 1213 - 1st Exam 20.0 PDFDokumen8 halamanF2 - IS - 1213 - 1st Exam 20.0 PDF羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 2ndtest IS PDFDokumen10 halamanF2 2ndtest IS PDF羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2ISExam1 (01 02)Dokumen9 halamanF2ISExam1 (01 02)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- QB Ch7 EngDokumen12 halamanQB Ch7 Eng羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 - IS - 1213 - 1st Exam 20.0 PDFDokumen8 halamanF2 - IS - 1213 - 1st Exam 20.0 PDF羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 - IS - 1314 - 2nd Exam PDFDokumen10 halamanF2 - IS - 1314 - 2nd Exam PDF羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 - IS - 1213 - 2nd Exam PDFDokumen9 halamanF2 - IS - 1213 - 2nd Exam PDF羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 IS Exam1 (03-04)Dokumen9 halamanF2 IS Exam1 (03-04)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 2ndtest ISDokumen10 halamanF2 2ndtest IS羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- KWUN TONG GOVERNMENT SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF-YEARLY EXAMDokumen8 halamanKWUN TONG GOVERNMENT SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF-YEARLY EXAM羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 IS Exam 2 (15-16)Dokumen10 halamanF2 IS Exam 2 (15-16)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)Dokumen10 halamanF2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- PpsDokumen38 halamanPps羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- F1 - IS - 1213 - 2nd ExamDokumen15 halamanF1 - IS - 1213 - 2nd ExamWong WingyeeBelum ada peringkat
- F2 IS Exam 1 (09-10)Dokumen8 halamanF2 IS Exam 1 (09-10)羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- Interactive Science Ch. 8 Question BankDokumen79 halamanInteractive Science Ch. 8 Question Bank羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- Abp - Electric Current Circuits Multiple ChoiceDokumen11 halamanAbp - Electric Current Circuits Multiple Choice羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- PpsDokumen38 halamanPps羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- QB - Ch7 - Eng (Living Things and AirDokumen88 halamanQB - Ch7 - Eng (Living Things and Air羅天佑100% (1)
- QB Ch10 EngDokumen217 halamanQB Ch10 Eng羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- IS QB09 ENG p.156 211Dokumen59 halamanIS QB09 ENG p.156 211羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- QB Ch10 EngDokumen217 halamanQB Ch10 Eng羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- QB - Ch10 - Eng 222Dokumen196 halamanQB - Ch10 - Eng 222羅天佑Belum ada peringkat
- M H Case SolutionDokumen1 halamanM H Case SolutionSai Dinesh UniqueBelum ada peringkat
- Mortality Review - ppt2Dokumen27 halamanMortality Review - ppt2mohamad ashmuniBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Wives One Husband 2Dokumen508 halaman3 Wives One Husband 2relebohilelehasa2Belum ada peringkat
- Botox 2017 PDFDokumen244 halamanBotox 2017 PDFDyah Ayu Putri Midiantari50% (2)
- Professional AdjustmentDokumen12 halamanProfessional AdjustmentNikkie Salazar100% (1)
- Breast LumpDokumen2 halamanBreast Lumplentini@maltanet.netBelum ada peringkat
- Firstaid ModuleDokumen143 halamanFirstaid Moduleretni wulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg InterpretationDokumen3 halamanEcg Interpretationman0billi0% (1)
- Pain Myocardial: Review Treatment of in InfarctionDokumen5 halamanPain Myocardial: Review Treatment of in InfarctionAlifah ChoBelum ada peringkat
- AutohalerDokumen51 halamanAutohalerLinto JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Pharyngitis Laryngitis TonsillitisDokumen10 halamanPharyngitis Laryngitis Tonsillitisapi-457923289Belum ada peringkat
- Diuretics in States of Volume Overload Core Curriculum 2022Dokumen13 halamanDiuretics in States of Volume Overload Core Curriculum 2022Fercho MedBelum ada peringkat
- Sickle Cell Diet and NutritionDokumen30 halamanSickle Cell Diet and NutritiondaliejBelum ada peringkat
- 11th Zoology EM Practical NotesDokumen11 halaman11th Zoology EM Practical NotesBhavana Gopinath100% (1)
- Case StudyDokumen5 halamanCase StudyHomework PingBelum ada peringkat
- Fphar 12 768268Dokumen25 halamanFphar 12 768268Araceli Anaya AlvaradoBelum ada peringkat
- Healthcare Financing in IndiADokumen86 halamanHealthcare Financing in IndiAGeet Sheil67% (3)
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Clinical PracticeDokumen10 halamanSocial Anxiety Disorder: Clinical PracticeMarcelo Falcão BarrosBelum ada peringkat
- INTERN-3 Community Pharmacy ProfileDokumen34 halamanINTERN-3 Community Pharmacy ProfilejadeBelum ada peringkat
- FCPS Ii Major Tentative Schedule 2a Feb 2024Dokumen1 halamanFCPS Ii Major Tentative Schedule 2a Feb 2024haseeb ur rehmanBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Treatment For BREAST CANCERDokumen5 halamanSurgical Treatment For BREAST CANCERJericho James TopacioBelum ada peringkat
- Obama Mind ControlDokumen68 halamanObama Mind Controlkdnkgljfg67% (3)
- Desai - Palliative Medicine in Myelodysplastic Syndromes - Patients and Caregivers - A Qualitative StudyDokumen5 halamanDesai - Palliative Medicine in Myelodysplastic Syndromes - Patients and Caregivers - A Qualitative StudyRafael TerceiroBelum ada peringkat
- CefepimeDokumen2 halamanCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonBelum ada peringkat
- Vidas Troponin High Sensitive Ref#415386Dokumen1 halamanVidas Troponin High Sensitive Ref#415386Mike GesmundoBelum ada peringkat
- Radiographic EvaluationDokumen12 halamanRadiographic EvaluationLuis Gerardo Castillo MendozaBelum ada peringkat
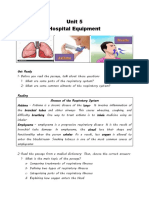
- Unit 5 Hospital EquipmentDokumen3 halamanUnit 5 Hospital EquipmentALIFIABelum ada peringkat
- As 5013.2-2007 Food Microbiology Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs - Horizontal Method For The eDokumen10 halamanAs 5013.2-2007 Food Microbiology Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs - Horizontal Method For The eSAI Global - APAC100% (1)
- Jan Marc Bulatao 10-Einstein BiologyDokumen3 halamanJan Marc Bulatao 10-Einstein BiologyNomer SenadorBelum ada peringkat
- Severe Gastric ImpactionDokumen4 halamanSevere Gastric ImpactionNanda Ayu Cindy KashiwabaraBelum ada peringkat