2.1 Molecules To Metabolism Worksheet
Diunggah oleh
SayedMuhammadJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2.1 Molecules To Metabolism Worksheet
Diunggah oleh
SayedMuhammadHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IB Biology Chapter 2 Worksheet: Molecules to Metabolism (2.
1) NAME:
Word Definition
Carbon Element that is makes up the backbone of organic molecules.
Carbohydrates One category of organic molecules that are made of C,H, and O and provide energy
and structure.
Lipids One category of organic molecules that are made of C, H and O and dont mix with
water. They provide long term storage, make up membranes and some hormones.
Proteins One category of organic molecules that have an amine and carboxylic acid groups.
They are the most structurally varied and do most of the functions of the body.
Nucleic Acids One category of organic molecules that have C, H, O, N and P. They store
information or store short term chemical energy. These include DNA, RNA, & ATP.
Monomer The small form/unit of an organic molecule
Polymer The large form of an organic molecule. It is made up of many monomers joined
together.
Glucose 6-carbon ring carbohydrate monomer that is the base source of energy for most life.
Ribose 5-carbon ring carbohydrate monomer
Amino Acids Monomer molecule that builds up proteins. There are 20 different types.
Fatty Acids Long carbon-based chains that build up lipids.
Metabolism The set of chemical reactions carried out within organisms.
Anabolism Building-up complex molecules from simpler ones.
Catabolism Breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones.
Hydrolysis A chemical reaction that splits a molecule apart through the addition of water
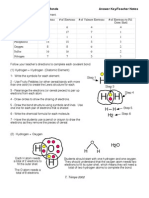
2.1.1 Molecular biology 2.1.2 Carbon atoms can form four bonds allowing a diversity of compounds to exist.
explains living processes in
terms of the chemical 2.1.3 Life is based on carbon compounds including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
substances involved.
2.1.7 Urea as an example of
a compound that is produced
by living organisms but can
also be artificially
synthesized.
It can make 4 covalent bonds
2.1.8 Draw molecular
diagrams of glucose, ribose,
a saturated fatty acid, and a Carbohydrates:
generalized amino acid.
Lipids:
Proteins:
Draw the structure of a Urea
molecule:
Nucleic Acids:
What is the function of
naturally-occurring Urea in
the human body?
Chemical groups:
carrier of waste Name of Group Hydroxyl Amine Carboxyl Methyl
nitrogen R-N-R O=C-OH H
plays a role in the R-O-H R R R-C-H
Full Structure
countercurrent H
exchange system of the
Simplified Notation
nephrons, that allows
for re-absorption of
Common organic molecules:
water and critical ions Name Ribose Glucose Saturated Fatty Acid Amino Acid
from the excreted urine. IN BOOK
What is the function of
artificially-synthesized
Urea? Drawing
Used as fertilizer
Describe why Carbon is an
ideal backbone for building
organic molecules: 2.1.9 Identify biochemicals as carbohydrates, lipids, or proteins from molecular diagrams.
Carbohydrates:
3rd
Proteins:
2nd
Lipids:
1st
Label each molecule as a protein, lipid, or carbohydrate:
2.1.4 Metabolism is the web
of all the enzyme catalyzed
reactions in a cell or
organism.
2.1.5 Anabolism is the
synthesis of complex
molecules from simpler
molecules including the
formation of
macromolecules from
monomers by condensation Describe Anabolism:
reactions.
the synthesis of complex molecules in living organisms from simpler ones together with the storage of
energy; constructive metabolism.
2.1.6 Catabolism is the
breakdown of complex
molecules into simpler
molecules including the Examples of anabolism:
hydrolysis of
macromolecules into synthesizing glucose
monomers.
Describe Catabolism:
the breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones, together with the
release of energy; destructive metabolism
Examples of catabolism:
Muscle tissue growth
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- AP Chemistry Summer AssignmentDokumen6 halamanAP Chemistry Summer AssignmentDavina MarstonBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Dokumen3 halamanGas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Nikhil Singh100% (1)
- 07 - IB Biology (2020) - 2.1 - Molecules To MetabolismDokumen29 halaman07 - IB Biology (2020) - 2.1 - Molecules To MetabolismSamuel French RojasBelum ada peringkat
- AS Chemistry Unit 1 Class Test Jan 2015 QuestionsDokumen26 halamanAS Chemistry Unit 1 Class Test Jan 2015 Questionsecs90603Belum ada peringkat
- C 1 2 2025 Topic Test MsDokumen4 halamanC 1 2 2025 Topic Test MsRawanMazen SharifBelum ada peringkat
- Limiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetDokumen1 halamanLimiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetFandy ArdyBelum ada peringkat
- AP Chem CH 3 Practice QuizAP Chemistry Practice TestDokumen5 halamanAP Chem CH 3 Practice QuizAP Chemistry Practice TesthydrocrackermanBelum ada peringkat
- Rates Review Questions (HL)Dokumen8 halamanRates Review Questions (HL)nadia sykesBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Structure QuizDokumen7 halamanElectromagnetic Radiation and Atomic Structure QuizKinal PatelBelum ada peringkat
- C 1 1 2025 Topic Test MsDokumen4 halamanC 1 1 2025 Topic Test MsRawanMazen SharifBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganic Chemistry Practice QuestionsDokumen7 halamanInorganic Chemistry Practice QuestionskitoniumBelum ada peringkat
- Ib PPT 3 SL PDFDokumen24 halamanIb PPT 3 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Ecology TestDokumen7 halaman04 Ecology TestFrancisBelum ada peringkat
- Electron Affinity and Ionization EnergiesDokumen251 halamanElectron Affinity and Ionization Energiesgkawsar22Belum ada peringkat
- B1.1 - Carbohydrates and LipidsDokumen4 halamanB1.1 - Carbohydrates and LipidslittleianlauBelum ada peringkat
- Back TitrateDokumen16 halamanBack Titratepicket1019Belum ada peringkat
- Topic 10 HLQDokumen21 halamanTopic 10 HLQPipen 5Belum ada peringkat
- U3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT WatermarkDokumen45 halamanU3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT Watermarkapi-125934329Belum ada peringkat
- Redox ReactionsDokumen4 halamanRedox Reactionsmahika gaurBelum ada peringkat
- AP Chem CH 6 Practice Quiz Heat Capacity ReactionsDokumen3 halamanAP Chem CH 6 Practice Quiz Heat Capacity Reactionsprin ppBelum ada peringkat
- Apch3.1 Problems-Equilibrium AnsDokumen5 halamanApch3.1 Problems-Equilibrium AnsQueenQiBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Equilibrium TutorialDokumen3 halamanChemical Equilibrium TutorialNavine NavBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrocarbons: K. Atkins IB Chemistry Pensacola High SchoolDokumen31 halamanHydrocarbons: K. Atkins IB Chemistry Pensacola High Schoollianchen251110Belum ada peringkat
- H2 Bio Paper 2 Glycogen and Transport ProteinsDokumen10 halamanH2 Bio Paper 2 Glycogen and Transport ProteinsSamuel TeohBelum ada peringkat
- CHE 160 Semester Review Zumdahl CH 5-7Dokumen20 halamanCHE 160 Semester Review Zumdahl CH 5-7Kinal PatelBelum ada peringkat
- AP Chem CH 15 Practice QuizDokumen8 halamanAP Chem CH 15 Practice QuizHussain MerchantBelum ada peringkat
- Chem12 C120Dokumen4 halamanChem12 C120MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- AP Chapter 13 MC Practice Questions With MC AnswersDokumen9 halamanAP Chapter 13 MC Practice Questions With MC AnswersapantollanoBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Paper 3 SampleDokumen3 halamanChemistry Paper 3 Samplerihdus2100% (2)
- Chapter 4 Practice Test 4u1Dokumen4 halamanChapter 4 Practice Test 4u1helloblargBelum ada peringkat
- Electrons in Atoms QuestionsDokumen1 halamanElectrons in Atoms QuestionsAmrutha Lakshmi67% (3)
- SL & HL Answers To Questions On Acid Deposition: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingDokumen1 halamanSL & HL Answers To Questions On Acid Deposition: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, Inthinkingzarna nirmal rawalBelum ada peringkat
- Topical Test 5: Chemical Bonds: Ujian Topikal 5: Ikatan KimiaDokumen6 halamanTopical Test 5: Chemical Bonds: Ujian Topikal 5: Ikatan KimiaManiArasiChandranBelum ada peringkat
- BondingDokumen52 halamanBondingArian CoenBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Kinetics SlidesDokumen87 halamanChemical Kinetics SlidesFarith AfifiBelum ada peringkat
- Oxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsDokumen19 halamanOxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsGian Paolo GerzonBelum ada peringkat
- IB Biology 3ED PEQ AnswersDokumen110 halamanIB Biology 3ED PEQ AnswersGeorge KoukouvesBelum ada peringkat
- A1.2 Nucleic AcidsDokumen83 halamanA1.2 Nucleic AcidsGhenwa DimachkiBelum ada peringkat
- Alkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsDokumen83 halamanAlkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsG M Ali KawsarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionDokumen63 halamanChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionSiti Nursyafiqah100% (7)
- Buffers&titrationsquestions ReviewDokumen6 halamanBuffers&titrationsquestions Reviewapi-279595789Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 ENZYMES Crossword Puzzle (Teacher)Dokumen2 halamanChapter 4 ENZYMES Crossword Puzzle (Teacher)api-3728508100% (3)
- Redox WKSHTDokumen4 halamanRedox WKSHTMarco ConopioBelum ada peringkat
- Bonding Basics CovalentDokumen2 halamanBonding Basics Covalentwosli350% (2)
- Gas Laws Practice Test: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen8 halamanGas Laws Practice Test: Multiple Choice Questionsanj pianoBelum ada peringkat
- WEEK3 ModuleLec (BIO101)Dokumen10 halamanWEEK3 ModuleLec (BIO101)Maricris GatdulaBelum ada peringkat
- Chem NotesDokumen300 halamanChem NotesTeejay MakazhuBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic Structure Review QuestionsDokumen11 halamanAtomic Structure Review Questionsoc100% (1)
- Chapter 13 Nervous System in Mammals - Worksheet (Answers)Dokumen2 halamanChapter 13 Nervous System in Mammals - Worksheet (Answers)api-3728508100% (2)
- Practice Problems on Net Ionic EquationsDokumen3 halamanPractice Problems on Net Ionic EquationsZainabBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 MC 1Dokumen68 halamanTopic 1 MC 1senpaiBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Organic Chemistry Introduction 2Dokumen126 halaman03 Organic Chemistry Introduction 2Hamid Hussain HamidBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 Data Interpretation Practice Questions & AnswersDokumen17 halamanPaper 2 Data Interpretation Practice Questions & AnswersHanna “Hannaboo” YunBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Cellular Respiration NotesDokumen22 halaman3 - Cellular Respiration Notesapi-375285021Belum ada peringkat
- Biophysical Chemistry: Thermodynamics, Electrostatics, and the Biological Significance of the Properties of MatterDari EverandBiophysical Chemistry: Thermodynamics, Electrostatics, and the Biological Significance of the Properties of MatterBelum ada peringkat
- Albert PikeDokumen6 halamanAlbert Pikeapi-302575383Belum ada peringkat
- Catalogue MinicenterDokumen36 halamanCatalogue Minicentermohamed mahdiBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment No.7Dokumen2 halamanAssignment No.7queen estevesBelum ada peringkat
- PMMC ExperimentDokumen2 halamanPMMC ExperimentShyam ShankarBelum ada peringkat
- LaQshya Labour Room Quality Improvement InitiativeDokumen2 halamanLaQshya Labour Room Quality Improvement InitiativeHimanshu SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Anginal DrugsDokumen39 halamanAnti-Anginal Drugspoonam rana100% (1)
- Prperman 2016 14 3 (Spec. 14Dokumen8 halamanPrperman 2016 14 3 (Spec. 14celia rifaBelum ada peringkat
- Graphs & Charts SummariesDokumen20 halamanGraphs & Charts SummariesMaj Ma Salvador-Bandiola100% (1)
- Cat IQ TestDokumen3 halamanCat IQ TestBrendan Bowen100% (1)
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan ElementaryDokumen3 halamanSemi Detailed Lesson Plan ElementaryJinky JunioBelum ada peringkat
- معامل الاسفلتDokumen32 halamanمعامل الاسفلتMohammed AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Media LiteracyDokumen33 halamanMedia LiteracyDo KyungsooBelum ada peringkat
- Roxas Avenue, Isabela City, Basilan Province AY: 2018-2019: Claret College of IsabelaDokumen2 halamanRoxas Avenue, Isabela City, Basilan Province AY: 2018-2019: Claret College of IsabelaJennilyn omnosBelum ada peringkat
- Ukraine and Russia E IRDokumen287 halamanUkraine and Russia E IRtatgirBelum ada peringkat
- Painter CardDokumen1 halamanPainter CardPraveen RANABelum ada peringkat
- Balajit Nath Pandita-Specific Principles of Kashmir Saivism-Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers (1998) PDFDokumen228 halamanBalajit Nath Pandita-Specific Principles of Kashmir Saivism-Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers (1998) PDFvramaniitkBelum ada peringkat
- Why Leaders Should Look in the “MirrorDokumen4 halamanWhy Leaders Should Look in the “MirrorCaryl Baylon EstreraBelum ada peringkat
- Transistor Amplifier Operating ParametersDokumen21 halamanTransistor Amplifier Operating ParametersReddyvari VenugopalBelum ada peringkat
- Quantitative Aptitude-More Exercise Questions Updated On Jul 2019Dokumen4 halamanQuantitative Aptitude-More Exercise Questions Updated On Jul 2019SANAMGI BHAVYABelum ada peringkat
- Liugong 938 Wheel Loader Parts ManualDokumen20 halamanLiugong 938 Wheel Loader Parts Manualjonathan100% (49)
- 341SAM Ethical Leadership - Alibaba FinalDokumen16 halaman341SAM Ethical Leadership - Alibaba FinalPhoebe CaoBelum ada peringkat
- System Software Module 3: Machine-Dependent Assembler FeaturesDokumen28 halamanSystem Software Module 3: Machine-Dependent Assembler Featuresvidhya_bineeshBelum ada peringkat
- Case Briefing and Case SynthesisDokumen3 halamanCase Briefing and Case SynthesisKai RaguindinBelum ada peringkat
- Automated Crime Reporting SystemDokumen101 halamanAutomated Crime Reporting SystemDeepak Kumar60% (10)
- Vsip - Info - Ga16de Ecu Pinout PDF FreeDokumen4 halamanVsip - Info - Ga16de Ecu Pinout PDF FreeCameron VeldmanBelum ada peringkat
- Differentiation SS2Dokumen88 halamanDifferentiation SS2merezemenike272Belum ada peringkat
- Key Elements of Participation and Conflict Resolution in a DemocracyDokumen6 halamanKey Elements of Participation and Conflict Resolution in a DemocracyAbhinayBelum ada peringkat
- JC Metcalfe - The Power of WeaknessDokumen3 halamanJC Metcalfe - The Power of Weaknesschopin23Belum ada peringkat
- Chime Primary School Brochure TemplateDokumen1 halamanChime Primary School Brochure TemplateNita HanifahBelum ada peringkat
- Literature Review Marketing StrategyDokumen4 halamanLiterature Review Marketing Strategyc5td1cmc100% (1)