Orange Sa
Diunggah oleh
Jon West0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
20 tayangan2 halamanorange sa
Judul Asli
orange sa
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
TXT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniorange sa
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai TXT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
20 tayangan2 halamanOrange Sa
Diunggah oleh
Jon Westorange sa
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai TXT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
range S.A.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the corporation formerly known as France Tlcom. For the UK m
obile phone operator, see Orange (UK).
Orange S.A.
Orange logo.svg
Type
Socit Anonyme
Traded as Euronext: ORA
NYSE: ORAN
BIT: ORA
Industry Telecommunications
Founded 1988; 29 years ago (Privatization)
Headquarters 15th arrondissement, Paris, France
Area served
Worldwide
Key people
Stphane Richard
(Chairman and CEO)
Products Landline telephony, Mobile telephony, Fixed internet, Mobile int
ernet, IP television, IT services, Livebox
Revenue Increase 40.236 billion (2015)[1]
Operating income
Increase 12.426 billion (2015)[1]
Profit Increase 2.652 billion (2015)[1]
Total assets Decrease 89.980 billion (2012)
Total equity Decrease 24.306 billion (2012)
Owner Public float (86.6%)
Government of France (13.4%)[2]
Number of employees
157,000 (2015)[3]
Subsidiaries Orange Marine
Website www.orange.com
Orange S.A., formerly France Tlcom S.A., is a French multinational telecommunicati
ons corporation. It has 256 million customers worldwide and employs 95,000 peopl
e in France, and 59,000 elsewhere.[3] In 2015, the group had revenue of 40 billio
n.[4] The company's head office is located in the 15th arrondissement of Paris.
The current CEO is Stphane Richard. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx
50 stock market index.[5]
Orange has been the company's main brand for mobile, landline, internet and IPTV
services since 2006. It originated in 1994 when Hutchison Whampoa acquired a co
ntrolling stake in Microtel Communications during the early 1990s and rebranded
it as "Orange." It became a subsidiary of Mannesmann in 1999 and was acquired by
France Tlcom in 2000. The company was rebranded as Orange in July 2013.[6]
Contents [hide]
1 History
1.1 Nationalised service (1970s 1980s)
1.2 Creation of France Tlcom (1988 1997)
1.3 'Roaring Nineties' (1997 2000)
1.4 Acquisition of Orange and privatization
1.5 NeXT scheme and rebranding to Orange (2006 present)
2 Shareholders
3 Operations
3.1 Mobile
3.2 Landline and Internet
3.3 Broadcasting
3.4 Music
4 Subsidiaries, joint ventures and holdings
4.1 Orange Business Services
4.2 BT Group
4.3 Globecast
4.4 Viaccess Orca
4.5 Orange Labs
4.6 Dailymotion
4.7 Deezer
4.8 Studio 37
4.9 Cityvox
4.10 Cloudwatt
5 Controversy
5.1 Staff suicides
5.2 Access to some sites limited
5.3 Accusations of false advertising in France
5.4 Corruption in Tunisia
5.5 Anticompetitive practices in French overseas departments
5.6 SMS and MMS propagation of 1 January 2011 in France
5.7 Controversies in UK regarding the quality of service
5.8 Accusations of antisemitism and calls for boycott
6 Governance
6.1 Overview of governance
6.2 Chairmen
6.3 Chief executive officers
6.4 Board of directors
6.5 Executive committee
6.6 Head office
7 Orange Foundation
8 Sponsorship
9 See also
10 References
11 External links
History[edit]
Nationalised service (1970s 1980s)[edit]
In 1792, under the French Revolution, the first communication network was develo
ped to enable the rapid transmission of information in a warring and unsafe coun
try. That was the optical telegraphy network of Claude Chappe.
In 1878, after the invention of the electrical telegraph and then the invention
of the telephone, the French State created a Ministry of Posts and Telegraphs. T
elephone Services were added to the ministry when they were nationalised in 1889
. However, it was not until 1923 that the second 'T' (for 'telephones') appeared
and the department of P&T became PTT.
In 1941, a General Direction of Telecommunications was created within this minis
try. Then, in 1944, the National Centre of Telecommunications Studies (CNET) was
created to develop the telecommunications industry in France.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- "Raphy" PinaDokumen34 halaman"Raphy" PinaMetro Puerto RicoBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- San Antonio Police Department Police Report On The Arrest of Daniel Pentkowski.Dokumen2 halamanSan Antonio Police Department Police Report On The Arrest of Daniel Pentkowski.David ClarkBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Chapter 10 State and Local Government ExpendituresDokumen34 halamanChapter 10 State and Local Government ExpendituresGabriel RegoBelum ada peringkat
- QNNPJG lSUK0kSccrTSStqeIPoUAJF27yLdQCcaJFO0Dokumen1 halamanQNNPJG lSUK0kSccrTSStqeIPoUAJF27yLdQCcaJFO0Viktoria PrikhodkoBelum ada peringkat
- Invoice: VAT No: IE6364992HDokumen2 halamanInvoice: VAT No: IE6364992HRajBelum ada peringkat
- Federal Lawsuit Against Critchlow For Topix DefamationDokumen55 halamanFederal Lawsuit Against Critchlow For Topix DefamationJC PenknifeBelum ada peringkat
- Clado-Reyes V LimpeDokumen2 halamanClado-Reyes V LimpeJL A H-DimaculanganBelum ada peringkat
- Harvey Vs Defensor Santiago DigestDokumen5 halamanHarvey Vs Defensor Santiago DigestLeo Cag0% (1)
- App A For PrintingDokumen28 halamanApp A For PrintingJon WestBelum ada peringkat
- Ise690 Catalog TopicsDokumen1 halamanIse690 Catalog TopicsJon WestBelum ada peringkat
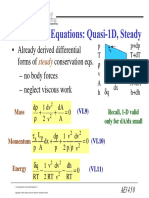
- Already Derived Differential Forms of Conservation Eqs. - No Body Forces - Neglect Viscous WorkDokumen3 halamanAlready Derived Differential Forms of Conservation Eqs. - No Body Forces - Neglect Viscous WorkJon WestBelum ada peringkat
- Solar EngineeringDokumen1 halamanSolar EngineeringJon WestBelum ada peringkat
- CocaineDokumen3 halamanCocaineJon WestBelum ada peringkat
- And Prescribed by The National Office." (Italics and Emphasis Supplied)Dokumen2 halamanAnd Prescribed by The National Office." (Italics and Emphasis Supplied)Ckey ArBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Counseling Notice Jexpo Voclet17Dokumen2 halamanPre Counseling Notice Jexpo Voclet17Shilak BhaumikBelum ada peringkat
- About Dhanalaxmi Bank KarthikDokumen4 halamanAbout Dhanalaxmi Bank KarthikYkartheek GupthaBelum ada peringkat
- Public +Private+PartnershipsDokumen18 halamanPublic +Private+PartnershipsNuha MansourBelum ada peringkat
- Test I - TRUE or FALSE (15 Points) : College of Business Management and AccountancyDokumen2 halamanTest I - TRUE or FALSE (15 Points) : College of Business Management and AccountancyJamie Rose AragonesBelum ada peringkat
- ARTADokumen1 halamanARTAAron Paul Morandarte RulogBelum ada peringkat
- VDC: The Weekly Statistical ReportDokumen8 halamanVDC: The Weekly Statistical ReportimpunitywatchBelum ada peringkat
- AWS QuestionnaireDokumen11 halamanAWS QuestionnaireDavid JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Hernandez Vs Go - A.C. No. 1526Dokumen4 halamanHernandez Vs Go - A.C. No. 1526Kevin GalegerBelum ada peringkat
- 23 September Paula Stratton - Has Received Documents For PID - Notification of Decision Not To Allocate A Disclosure SECOFFICIALSensitive ACCESSPersonalPrivacyDokumen20 halaman23 September Paula Stratton - Has Received Documents For PID - Notification of Decision Not To Allocate A Disclosure SECOFFICIALSensitive ACCESSPersonalPrivacyricharddrawsstuffBelum ada peringkat
- Final Managerial AccountingDokumen8 halamanFinal Managerial Accountingdangthaibinh0312Belum ada peringkat
- Second Semester of Three Year LL.B. Examination, January 2011 CONTRACT - II (Course - I)Dokumen59 halamanSecond Semester of Three Year LL.B. Examination, January 2011 CONTRACT - II (Course - I)18651 SYEDA AFSHANBelum ada peringkat
- Stevens V University of Birmingham (2016) 4 All ER 258Dokumen25 halamanStevens V University of Birmingham (2016) 4 All ER 258JYhkBelum ada peringkat
- Please Return This Form To:: Brill - Nl/rightsDokumen1 halamanPlease Return This Form To:: Brill - Nl/rightslimetta09Belum ada peringkat
- Improving Indonesia's Competitiveness: Case Study of Textile and Farmed Shrimp IndustriesDokumen81 halamanImproving Indonesia's Competitiveness: Case Study of Textile and Farmed Shrimp IndustriesadjipramBelum ada peringkat
- FCI Recruitment NotificationDokumen4 halamanFCI Recruitment NotificationAmit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Controlled Parking Zones Within Tower HamletsDokumen1 halamanControlled Parking Zones Within Tower Hamletsmoshkur.chowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Bank Reconciliation StatementDokumen5 halamanBank Reconciliation StatementjithaBelum ada peringkat
- Flash Cards & Quiz: Berry Creative © 2019 - Primary PossibilitiesDokumen26 halamanFlash Cards & Quiz: Berry Creative © 2019 - Primary PossibilitiesDian CiptaningrumBelum ada peringkat
- Certification: Barangay Development Council Functionality Assessment FYDokumen2 halamanCertification: Barangay Development Council Functionality Assessment FYbrgy.sabang lipa city100% (4)
- Rosalina Buan, Rodolfo Tolentino, Tomas Mercado, Cecilia Morales, Liza Ocampo, Quiapo Church Vendors, For Themselves and All Others Similarly Situated as Themselves, Petitioners, Vs. Officer-In-charge Gemiliano c. Lopez, JrDokumen5 halamanRosalina Buan, Rodolfo Tolentino, Tomas Mercado, Cecilia Morales, Liza Ocampo, Quiapo Church Vendors, For Themselves and All Others Similarly Situated as Themselves, Petitioners, Vs. Officer-In-charge Gemiliano c. Lopez, JrEliza Den DevilleresBelum ada peringkat
- September PDFDokumen402 halamanSeptember PDFNihal JamadarBelum ada peringkat