Fault Analysis
Diunggah oleh
হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Fault Analysis
Diunggah oleh
হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
EEE 306 Power System I Laboratory
Experiment 4
Short Circuit Study for a Test Network
Objectives
In this experiment, fault analysis for a test network will be performed. CYMEPSAF software will be
used for this purpose.
Introduction
The normal operating condition of a power system is balanced three-phase ac. A number of
undesirable but unavoidable incidents might temporarily disrupt this condition. If the insulation of
the system should fail at any point, or if a conducting object should come in contact with a bare
power conductor, a short circuit or fault is said to occur. The causes of faults are many: - they
include lightning, wind damage, trees falling across lines, vehicles colliding with towers or poles,
birds shorting out lines, small animals entering switching gear. Power system faults may be
categorized as one of four types in order of frequency of occurrence: single line to ground (LG), line
to line (LL), double line to ground (LLG), and balanced three phase (LLL) faults. The first three
types constitute severe unbalanced operating conditions.
It is important to determine the system voltages and currents during fault conditions so that
protective devices may be set to detect and minimize the harmful effects of such contingencies.
Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the power system operating in unbalanced conditions. The time
constants of associated transients are such that sinusoidal steady state methods may still be used. The
method of symmetrical component is admirably suited to unbalanced system analysis.
Application of the software CYMEPSAF
Follow the steps described below:
1. Create a new folder in any drive of your PC.
2. Open the software PSAF 2.81. From Database menu, select New Blank Database
Directory to show the path of the folder created in step 1.
3. From File menu, select Preferences to open Preference settings window. Under
Directory tab, select DATABASE under Item and click Browse to show the Path of
the folder created in step 1. Do the same for NETWORK under Item.
4. From File menu, select New Study. In Loading Network Data window, select Use
tabular format for network data presentation and click OK. Next select creating a new
Dept. of EEE, BUET P age |1
EEE 306 Power System I Laboratory
network in New Study Dialog window and Default 1 bus in New Network Dialog
window.
5. Create the network by using tabular format.
G1
1 4 3
G2
6 5 2
Fig. 1: One-line diagram of the network in study
Fault Analysis
1. Using the information given in the following tables, create the network shown in Fig. 1.
Bus
ID Base kV Operating kV
B1 69 69
B2 13.8 13.8
B3 13.8 13.8
B4 69 69
B5 13.8 13.8
B6 69 69
Fixed-tap transformer
From To Primary Secondary Rating Z1 X1/R1 Z0 X0/R0 Standard Connection
Bus Bus kV kV (MVA) (p.u.) (p.u.) Loading
Limit
(MVA)
4 3 69 13.8 100 0.133 13.3 0.133 13.3 100 Yg-D
6 5 69 13.8 100 0.3 30 0.3 30 100 Yg-D
Dept. of EEE, BUET P age |2
EEE 306 Power System I Laboratory
Generator
ID Voltage Rating Active R// X// R/ X/ R X Winding
(kV) (MVA) generation connection
(p.u.) (p.u.) (p.u.) (p.u.) (p.u.) (p.u.)
(MW)
G1 69 100 0 0.01 0.085 0.01 0.12 1.20 0.00005 D
G2 13.8 50 10 0.005 0.075 0.005 0.12 1.20 0.008 Yg
Line
From To kV Loading limit R1 X1 B1 Length
Bus Bus level (Amps) (Ohms/km) (Ohms/km) (.S./km) (km)
1 4 69 800 0.4 2.4 155.5 10
1 6 69 800 0.4 2.4 155.5 5
3 2 13.8 800 0.4 2.4 155.5 5
5 2 13.8 800 0.4 2.4 155.5 7
Load
Bus ID P (MW) Q (MVAR)
B3 10 5
B5 10 2
B6 20 4
2. From Analysis menu, click Select Solver. Select Fault Analysis ANSI in Engine
Selection Dialog window.
3. For analyzing fault on bus:
a. From Analysis menu, select Study. In Short Circuit ANSI Study Dialog window
under the Fault Analysis Parameters tab, select Fault Selected Bus(es) under
Shunt Fault. Select LLL, LG, LL, LLG under Fault type. Click Ok.
b. From Analysis menu, select Solve. In Solving for Fault Analysis window, select
B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6 under Select Bus(es). Click Solve!.
For analyzing sliding fault on lines:
a. From Analysis menu, select Study. In Short Circuit ANSI Study Dialog window
under the Fault Analysis Parameters tab, select Sliding fault on selected Line and
specify the fault location (as % of line length) under Shunt Fault. Select LLL,
LG, LL, LLG under Fault type. Click Ok.
b. From Analysis menu, select Solve. In Solving for Fault Analysis window, select
L14, L16, L32, L52 under Select Line(s) or Cable(s). Click Solve!.
Dept. of EEE, BUET P age |3
EEE 306 Power System I Laboratory
4. From Report menu, select Show Text Report. Reports will appear on the bottom part of
the window.
Study:
1. Perform fault analysis for LLL, LG, LL, and LLG faults on different buses and observe the
system voltages and currents.
2. Perform fault analysis for sliding fault at different locations on different lines. Study the
faults given in the following table. Observe the system voltages and currents.
Line ID Fault location, Length (%) Fault type
L14 5 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L14 50 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L14 95 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L16 5 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L16 50 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L16 95 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L32 5 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L32 50 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L32 95 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L52 5 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L52 50 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
L52 95 LLL, LG, LL, LLG
Note:
First ring contribution
The first ring contributions are fault currents from links adjacent to the fault bus.
1st ring bus 1st ring bus
1st ring bus
Fault
Fig. 2: First ring contribution
Report:
1. Draw the positive, negative and zero sequence networks of the system in Fig. 1.
Dept. of EEE, BUET P age |4
EEE 306 Power System I Laboratory
2. Determine the fault currents for (i) LG, (ii) LL, (iii) LLG, and (iv) LLL faults on bus 5 of the
network analytically. Compare your results with the output of CYMEPSAF. For which type
of fault is the fault current maximum?
3. Choose the rating of circuit breakers for the lines connected to bus 5.
4. Eliminate the loads connected at buses 3, 5 and 6 and repeat the analysis. What is the effect
of eliminating the loads on the results of fault analysis? Explain.
Reference:
1. Elements of Power System Analysis - William D. Stevenson, Jr.
Dept. of EEE, BUET P age |5
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- PTEE7403 April 2019Dokumen3 halamanPTEE7403 April 2019imman46920Belum ada peringkat
- Contingency Analysis of Power SystemsDokumen16 halamanContingency Analysis of Power SystemsAnish PoudelBelum ada peringkat
- Service Manual JIK-6 V1 ENGDokumen25 halamanService Manual JIK-6 V1 ENGIvan PeeBelum ada peringkat
- Service Manual Jik 6Dokumen25 halamanService Manual Jik 6aldo100% (1)
- Slvu 274 eDokumen21 halamanSlvu 274 eMohammad HBBelum ada peringkat
- Assignments - AB - PSA - S220222023Dokumen6 halamanAssignments - AB - PSA - S220222023HermyraJ RobertBelum ada peringkat
- EE008 Load Flow Analysis of IEEE-14 Bus Using E-TAP SoftwareDokumen9 halamanEE008 Load Flow Analysis of IEEE-14 Bus Using E-TAP SoftwareJULFANRI SIRAITBelum ada peringkat
- Bucky C-TSDokumen33 halamanBucky C-TSPablo RosasBelum ada peringkat
- ADDAD 5, DatasheetDokumen17 halamanADDAD 5, Datasheetpb21Belum ada peringkat
- Electrical System AnalysisDokumen6 halamanElectrical System AnalysisSolarMaxBelum ada peringkat
- CEP Complete ReportDokumen23 halamanCEP Complete ReportHassan ZiaBelum ada peringkat
- Specification for BTHQ 128064AVG-FFEMN-06 LED02WHITE-COG LCD ModuleDokumen31 halamanSpecification for BTHQ 128064AVG-FFEMN-06 LED02WHITE-COG LCD Modulerogeriop1986Belum ada peringkat
- Determination of Voltage DropDokumen6 halamanDetermination of Voltage DropFahmi CumiBelum ada peringkat
- B 30Dokumen4 halamanB 30free123456789Belum ada peringkat
- Digital Photo Frame TF-108 Service ManualDokumen32 halamanDigital Photo Frame TF-108 Service ManualТеодор ТодоровBelum ada peringkat
- Open Ended ProjectDokumen3 halamanOpen Ended ProjectMd. HarunBelum ada peringkat
- Load Flow Analysis of IEEE-14 Bus Using E-TAP SoftwareDokumen9 halamanLoad Flow Analysis of IEEE-14 Bus Using E-TAP SoftwareAshwini UdgaveBelum ada peringkat
- Complete The Following Sentences.: Question#1Dokumen4 halamanComplete The Following Sentences.: Question#1Huấn PhanBelum ada peringkat
- Transmission and Distribution Design Old QuestionsDokumen10 halamanTransmission and Distribution Design Old QuestionsHarry ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Fast Cell Balancing Using External MOSFETDokumen7 halamanFast Cell Balancing Using External MOSFETranjitheee1292Belum ada peringkat
- hITACHI AP8X TrainPackDokumen70 halamanhITACHI AP8X TrainPackJames Jackson100% (1)
- ADDAD-5 Preliminary DatasheetDokumen16 halamanADDAD-5 Preliminary Datasheetbhuvan16Belum ada peringkat
- Brief 42Dokumen2 halamanBrief 42Ahmed EsamBelum ada peringkat
- Case Studies With Test Systems: 8.1 Four Machine SystemDokumen3 halamanCase Studies With Test Systems: 8.1 Four Machine SystemAbhishek KushwahaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 4 - DC Motor Tachometer: ObjectiveDokumen8 halamanLab 4 - DC Motor Tachometer: Objectiveswagato deyBelum ada peringkat
- ULQ200xA-Q1 High-Voltage High-Current Darlington Transistor ArraysDokumen26 halamanULQ200xA-Q1 High-Voltage High-Current Darlington Transistor ArraysDanny Alexander Bodegas pinedaBelum ada peringkat
- P343 Relay Testing ReportDokumen8 halamanP343 Relay Testing ReportUsman MughalBelum ada peringkat
- SC60 - 120 Sme ADokumen59 halamanSC60 - 120 Sme ARicardo Ribeiro da SilveiraBelum ada peringkat
- Tesedoutorado 1Dokumen15 halamanTesedoutorado 1rogeriocorrea601Belum ada peringkat
- Fault in Power System 212160218Dokumen15 halamanFault in Power System 212160218Muhammad AkidBelum ada peringkat
- Solis BrochureDokumen56 halamanSolis BrochureSyndicate boxBelum ada peringkat
- Data Sheet RSTDokumen4 halamanData Sheet RSTIndra Hans AditiyaBelum ada peringkat
- General: (Parallel and Multidrop Systems Only - Not Required Where Slot Modem Is Used)Dokumen27 halamanGeneral: (Parallel and Multidrop Systems Only - Not Required Where Slot Modem Is Used)Carlos Eduardo AlvesBelum ada peringkat
- Power Loss Heat Dissipation Watts Per PoleDokumen2 halamanPower Loss Heat Dissipation Watts Per PoleKhaideer AmirBelum ada peringkat
- 18 BL PDFDokumen6 halaman18 BL PDFRichard RegidorBelum ada peringkat
- Claa061la0bcw Chunghwapicturetubes PDFDokumen17 halamanClaa061la0bcw Chunghwapicturetubes PDFFrancisco MataBelum ada peringkat
- Strain Gauge Signal Acquisition SystemDokumen5 halamanStrain Gauge Signal Acquisition SystemNB Instrument Pvt LtdBelum ada peringkat
- ETAP PS 7 Arc Flash Calculation MethodologyDokumen29 halamanETAP PS 7 Arc Flash Calculation MethodologyhenriquezrsBelum ada peringkat
- Ap0806010 - v1 0 - CanmotionDokumen18 halamanAp0806010 - v1 0 - CanmotionasASasASBelum ada peringkat
- SERVICE GUIDE FOR PANASONIC AG-AC90P CAMCORDERDokumen40 halamanSERVICE GUIDE FOR PANASONIC AG-AC90P CAMCORDEREdward CapmariBelum ada peringkat
- Ger 4654Dokumen44 halamanGer 4654nooralhuda007Belum ada peringkat
- SC60 SC120 Service ManualDokumen60 halamanSC60 SC120 Service Manualemilio gustavo saez duroBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 of RTDS 2020Dokumen13 halamanAssignment 1 of RTDS 2020kalinath41Belum ada peringkat
- YPP110A APC Application Controller Hardware ManualDokumen19 halamanYPP110A APC Application Controller Hardware ManualEguinaldo da Silva VieiraBelum ada peringkat
- c2f69f1ab3d1ffb5fef91cc4718bb741Dokumen23 halamanc2f69f1ab3d1ffb5fef91cc4718bb741JulioBelum ada peringkat
- Power Flow 2 1. ObjectiveDokumen3 halamanPower Flow 2 1. ObjectiveBotlhe SomolekaeBelum ada peringkat
- ECE4205 Design Problem 3Dokumen17 halamanECE4205 Design Problem 3Yasser JrBelum ada peringkat
- Ger 4654aDokumen50 halamanGer 4654anooralhudBelum ada peringkat
- Improved High-Voltage Resonant Controller: FeaturesDokumen31 halamanImproved High-Voltage Resonant Controller: FeaturesДмитрий КопышевBelum ada peringkat
- Ensuring selectivity between CVS circuit breakers and downstream protectionDokumen19 halamanEnsuring selectivity between CVS circuit breakers and downstream protectionalejo8623Belum ada peringkat
- Simulating An Evolving FaultDokumen12 halamanSimulating An Evolving FaultRonny CruzBelum ada peringkat
- UCC39421 3.3-V SEPIC Evaluation Board: User's GuideDokumen7 halamanUCC39421 3.3-V SEPIC Evaluation Board: User's GuidebensumbbBelum ada peringkat
- XT2235-x (Devon 4G - Moto g32)_ L3 Troubleshooting GuideDokumen29 halamanXT2235-x (Devon 4G - Moto g32)_ L3 Troubleshooting GuideluumBelum ada peringkat
- KD600S-Newest-Manual-Book MANUAL EN ESPAÑOL (001-091)Dokumen91 halamanKD600S-Newest-Manual-Book MANUAL EN ESPAÑOL (001-091)armando valle durantesBelum ada peringkat
- Kikusui Cos5020 Cos5021 Service Manual OcrDokumen128 halamanKikusui Cos5020 Cos5021 Service Manual OcrNilson Konrad100% (1)
- ABO QP1000Manual Complete - CompressedDokumen180 halamanABO QP1000Manual Complete - CompressedRoohollah TavassoliBelum ada peringkat
- L&T MB34 Model Isolator PDFDokumen20 halamanL&T MB34 Model Isolator PDFAnonymous lFFnnXmjUuBelum ada peringkat
- CAN AT89C51 KitDokumen23 halamanCAN AT89C51 KitEnkhbaatar TumenjargalBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding and Servicing Alarm SystemsDari EverandUnderstanding and Servicing Alarm SystemsPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignDari EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Brac Bank ACCountDokumen1 halamanBrac Bank ACCountহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Circular 16172Dokumen2 halamanCircular 16172হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Tft0'lb (Ql-Cn. - : FrffiDokumen1 halamanTft0'lb (Ql-Cn. - : Frffiহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Construction of All Basic Gates Using Universal (NAND/NOR) Gates and Verify Its.Dokumen4 halamanConstruction of All Basic Gates Using Universal (NAND/NOR) Gates and Verify Its.হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- E-GP Registration and Tendering Process enDokumen3 halamanE-GP Registration and Tendering Process enহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Constructs Ex-OR Gate Using Basic Gates and Verify Its/ Constructs Ex-NOR Gate Using Basic Gates and Verify Its.Dokumen4 halamanConstructs Ex-OR Gate Using Basic Gates and Verify Its/ Constructs Ex-NOR Gate Using Basic Gates and Verify Its.হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- PGCB Officials Nomination for Tower Design TrainingDokumen4 halamanPGCB Officials Nomination for Tower Design Trainingহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- 2019 04 11 17 21 44 PPA 2006, PPR 2008 With All Amendments Up To January, 2019 PDFDokumen274 halaman2019 04 11 17 21 44 PPA 2006, PPR 2008 With All Amendments Up To January, 2019 PDFMd Shamim HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Annexure 1Dokumen3 halamanAnnexure 1হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Megger Multifunctional Transformer DiagnosisDokumen3 halamanMegger Multifunctional Transformer Diagnosisহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Construction of All Basic Gates Using Universal (NAND/NOR) Gates and Verify Its.Dokumen4 halamanConstruction of All Basic Gates Using Universal (NAND/NOR) Gates and Verify Its.হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
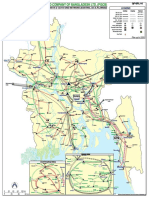
- Transmission Network Map MainDokumen1 halamanTransmission Network Map Mainহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Class9 Part1Dokumen5 halamanChemistry Class9 Part1হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Verify The Truth Table For Basic Gates and Others Logic Gates.Dokumen2 halamanVerify The Truth Table For Basic Gates and Others Logic Gates.হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Differentiation Test: Marks:100 Time:1.30 HoursDokumen2 halamanDifferentiation Test: Marks:100 Time:1.30 Hoursহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Higher K Value or Lower PK Valu Indicates Strong AcidDokumen3 halamanHigher K Value or Lower PK Valu Indicates Strong Acidহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- EQEDITOR Use the Equation EditorDokumen11 halamanEQEDITOR Use the Equation EditorpanchopanzaBelum ada peringkat
- Uncertainty of ElectronDokumen1 halamanUncertainty of Electronহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- EQEDITOR Use the Equation EditorDokumen11 halamanEQEDITOR Use the Equation EditorpanchopanzaBelum ada peringkat
- Word Collection by MEDokumen2 halamanWord Collection by MEহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- PSP Lab 1Dokumen5 halamanPSP Lab 1হাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্য0% (1)
- Load Flow Study in BuetDokumen4 halamanLoad Flow Study in Buetহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- AP Electron Config U ExceptionsDokumen8 halamanAP Electron Config U Exceptionsহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 PDFDokumen5 halamanExperiment 1 PDFJarin TasnimBelum ada peringkat
- Prepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power PlantDokumen26 halamanPrepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power Plantহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Short Circuit Study For A Test NetworkDokumen32 halamanShort Circuit Study For A Test Networkহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Wind by PSSEDokumen31 halamanGeneric Wind by PSSEহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Some Information About PointerDokumen1 halamanSome Information About Pointerহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যBelum ada peringkat
- Editable - Application For Learner's Driving LicenseDokumen2 halamanEditable - Application For Learner's Driving LicenseFoisul AlamBelum ada peringkat
- GD32F130xx Datasheet Rev2.1Dokumen41 halamanGD32F130xx Datasheet Rev2.1Moez MizouBelum ada peringkat
- cbhf2 NaDokumen8 halamancbhf2 NaStefan CorjucBelum ada peringkat
- Service Manual FSHTV-Z60Dokumen30 halamanService Manual FSHTV-Z60Armamndo RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- Peripheral Series: Frequency Measurement CardDokumen2 halamanPeripheral Series: Frequency Measurement CardSohail ABelum ada peringkat
- DB 3Dokumen11 halamanDB 3You LookBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 25Dokumen57 halamanChapter 25Rawan Z NemerBelum ada peringkat
- RF Integrated Circuits Mid-Term ExamDokumen1 halamanRF Integrated Circuits Mid-Term Examsreekanth2728Belum ada peringkat
- BUBT Lab Report on Performance Analysis of Half-Wave & Full-Wave RectifiersDokumen5 halamanBUBT Lab Report on Performance Analysis of Half-Wave & Full-Wave Rectifiers23 - 017 - Md. Imran HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Ultravox - Distriaudio catalog with PA speaker models and pricesDokumen2 halamanUltravox - Distriaudio catalog with PA speaker models and pricesFabian MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Generator HVP-80Dokumen1 halamanManual Generator HVP-80kiran kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Talexxengine Stark Lle Guide enDokumen53 halamanTalexxengine Stark Lle Guide enMihai ConstantinescuBelum ada peringkat
- FTTH Drop and Indoor CablesDokumen8 halamanFTTH Drop and Indoor Cablesvijay_786Belum ada peringkat
- MS Progress Presentation M Ejaz MalikDokumen8 halamanMS Progress Presentation M Ejaz Malikijaz sajjadBelum ada peringkat
- Stator-Flux-Based Vector Control of Induction Machines in Magnetic SaturationDokumen9 halamanStator-Flux-Based Vector Control of Induction Machines in Magnetic SaturationjalalhBelum ada peringkat
- Product Sheet: Nibp100D Noninvasive Blood Pressure Monitoring SystemDokumen3 halamanProduct Sheet: Nibp100D Noninvasive Blood Pressure Monitoring SystemSadegh ShebaniBelum ada peringkat
- eNB-MCE Functions, Parameters & Statistics - 20140626 PDFDokumen64 halamaneNB-MCE Functions, Parameters & Statistics - 20140626 PDFanupwadhwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Electric Bike Controller with Regen BrakingDokumen23 halamanElectric Bike Controller with Regen Brakingabhignyan nayak ?Belum ada peringkat
- Chap 03Dokumen22 halamanChap 03AmandaBelum ada peringkat
- 1176 PDFDokumen169 halaman1176 PDFJoshua PalizaBelum ada peringkat
- SunPower 305Dokumen2 halamanSunPower 305kalabala8Belum ada peringkat
- Operating Systems From 0 To 1 PDFDokumen311 halamanOperating Systems From 0 To 1 PDF3charlie52Belum ada peringkat
- EQ3 SynScan INSTALLATION guideDokumen1 halamanEQ3 SynScan INSTALLATION guideOscar MalamudBelum ada peringkat
- Cascaded Schwarz converters for high-frequency power distributionDokumen8 halamanCascaded Schwarz converters for high-frequency power distributionozoemena29Belum ada peringkat
- SCANIA CoordInator PinoutDokumen10 halamanSCANIA CoordInator Pinoutnicamarcos83% (12)
- AgentInstallGuide enDokumen56 halamanAgentInstallGuide enshikhanirankariBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Instruction Sheet DOP B07S410Dokumen2 halaman10 Instruction Sheet DOP B07S410Nisar AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Sony MZ-B50 Service ManualDokumen72 halamanSony MZ-B50 Service ManualDavid PiçarraBelum ada peringkat
- DFFHMDokumen9 halamanDFFHMyaswanthBelum ada peringkat
- 1sdc210033d0204 TC Tmax XT Iec enDokumen348 halaman1sdc210033d0204 TC Tmax XT Iec enBolivar MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Low Cost PCO Billing Meter PDFDokumen1 halamanLow Cost PCO Billing Meter PDFShrivlsi RamBelum ada peringkat