10 Class Physics Material: Reflection of Light by Different Surfaces
Diunggah oleh
ramprasad0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan1 halamanThe document discusses various concepts related to heat such as:
1. Temperature is defined as a measure of thermal equilibrium.
2. Sweat cools the body through evaporation which removes heat from the skin.
3. Heat is a form of energy that flows from hotter to colder bodies.
4. The factors that affect the rate of evaporation include surface area, temperature, and humidity.
Deskripsi Asli:
1
Judul Asli
---07.02.2017-page-10
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThe document discusses various concepts related to heat such as:
1. Temperature is defined as a measure of thermal equilibrium.
2. Sweat cools the body through evaporation which removes heat from the skin.
3. Heat is a form of energy that flows from hotter to colder bodies.
4. The factors that affect the rate of evaporation include surface area, temperature, and humidity.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan1 halaman10 Class Physics Material: Reflection of Light by Different Surfaces
Diunggah oleh
ramprasadThe document discusses various concepts related to heat such as:
1. Temperature is defined as a measure of thermal equilibrium.
2. Sweat cools the body through evaporation which removes heat from the skin.
3. Heat is a form of energy that flows from hotter to colder bodies.
4. The factors that affect the rate of evaporation include surface area, temperature, and humidity.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
10 B{gZ ty A# $V 7 {2017
10th Class Physics Material
HEAT is called melting point. body is directly proportional to the 3. Dogs try to keep themselves cool during
14. Define the term Latent heat of average kinetic energy of particles hot weather by panting.
1. Define the term temperature?
fusion? of the body. 4. Panting is the process of evaporation
A. Temperature can be defined as the 'degree
A. Latent heat of fusion can be The molecules of the system have that occurs in the mouth and within the
of hotness or coldness'. It is a measure of
defined as the amount of heat different forms of energies. The bronchial tract.
thermal equilibrium.
energy required to convert 1 total energy of the system is called 5. During panting the liquid molecules
2. How does sweat cools our body during
gram of solid completely into internal energy of the system. from the mouth will be evaporated into the
evaporation?
liquid at a constant temperature. When we supply heat energy to air. These molecules carry heat along with
A. When we work our bodies produce heat.
15. Write about freezing? G. Shravan chandra the system, the heat energy given to them resulting in cooling the surface from
As a result the temperature of the skin
A. Freezing: "The process in whi it will be shared by the molecules which liquid is evaporated.
increases and water in the sweat glands Senior Faculty
ch a substance in liquid phase among them. So, when it opens its mouth, its tongue
evaporate from the body. This evaporation
changes to solid phase by losing This sharing will vary from sub- actually expands and it pushes heat out of
cools the body and it regulates the body
some of its energy is called "freezing". stance to substance. the body.
temperature.
16. Why is petrol evaporating in Petri dish The rise in temperature is high for a sub- 26. Draw the apparatus used to determine
3. Define the term heat?
quickly under a fan when compared to stance, if the maximum share of heat ener- specific heat capacity of a substance?
A. Heat is a form of energy that flows from a
that kept in a closed room? gy is utilized for its linear K.E.
body at higher temperature to a body at
A. The petrol in Petri dish evaporates quickly This sharing of heat energy by the mole-
lower temperature.
when compared to that kept in a closed cules also varies with temperature. That is
4. Define the term calorie?
room is because of the following reason. why the specific heat is different for differ-
A. The amount of heat required to raise the
1. The blowing air increases the rate of ent substances.
temperature of 1 gram of water by 1C is
evaporation. 23. Explain the process of evaporation?
called calorie. (Here in calorie 'c' should be
2. This is because any molecule escaping The mole-
in small because it indicates gram calorie.
from the surface is blown away from the cules of a
Capital C in calorie indicates food Calorie
vicinity of the liquid. This increases the liquid that
which is equal to 1000 gram calories)
rate of evaporation. are kept in
1 calorie = 4.186 Joules
17. Does the temperature of water rise con- a dish
5. What do you mean by evaporation?
tinuously if heat is supplied continuously continu-
A. The process of escaping of molecules from
till 100C? ously 27. Write a table of specific heat capacity of
the surface of a liquid at any temperature is
A. Yes, if heat is supplied to water its temper- move with different substances given below?
called evaporation.
ature rises continuously till it reaches random
6. Write about the factors that affect the
100C. At 100C there will be no further speeds in various directions. As a result
rate of evaporation?
rise of temperature, because heat is steril- these molecules collide with other mole-
A. The factors that affect the rate of evapora-
ized to convert water to water vapour. So, cules.
tion are surface area, temperature and
when heat is supplied beyond 100C, all During this collision they transfer energy
amount of water vapour already present in
the water is converted into vapour. to other molecules. Hence, the molecules at
the surrounding air.
18. How can you say average kinetic energy the surface acquire energy and may fly off
7. Define condensation?
of the molecules is directly proportional from the surface.
A. Condensation can be defined as "The
to absolute temperature? Some of these escaping molecules may be
change of phase from gas to liquid".
A. 1. The average kinetic energy of mole- directed back into liquid when they collide
8. What is humidity?
cules/particles of the hot body is more than with the particles of air. 28. Draw a diagram to show the change of a
A. The amount of water vapour present in air
the colder body. If the number of escaping molecules is gre phase of a substance in solid state?
is called humidity.
2. Temperature of a body acts as an indica- ater than the number returned, then the nu
9. Explain about the formation of dew?
tor in determining the average kinetic ener- mber of molecules in the liquid decreases.
A. During winter nights, the atmospheric tem-
gy of that body. Thus when a liquid is exposed to air, the
perature falls down. The air near to the sur-
3. From the above, we conclude that aver- molecules at the surface keep on escaping
faces will be saturated with vapour and con
age kinetic energy of the molecules is from the surface till the entire liquid disap-
densation begins. The water droplets conde
directly proportional to the absolute tem- pears into air. This process is called evapo-
nsed on such surfaces are known as 'dew'.
perature. ration.
10. Explain the formation of fog?
19. What is the heat energy required to rise 24. Write about the formation of dew on the
A. During winter nights, if the temperature
10 Kg of water from 25C to 75C? surface of a cold soft drink bottle kept in
falls further, the whole atmosphere in that
A. Given m=10 kg = 10,000 gm open air?
region contains a large amount of vapour
t1 = 25C; t2 = 75C A. 1. We know
and the water molecules present in vapour REFLECTION OF LIGHT BY
S = 1 cal/gmC, we know that Q= mST that the tem-
condenses on dust particles in air and form
= 10000 X 1 X (75 - 25) = 10000 X 50; Q perature of DIFFERENT SURFACES
small droplets of water. These droplets
= 500000 calories. surrounding
keep floating in the air and form a thick
20. If you drink 100ml of water at 20C. air is higher 1. A student has three concave mirrors A,
mist which restricts visibility. This thick
What is the heat gained by water from than the tem- B, C of focal lengths 20cm, 15cm and
mist is called as fog.
your body? (Body temperature is 37C). perature of the 10cm respectively. For each concave
11. Distinguish between boiling and boiling
A. m=100g (1ml of water = 1 gm of water) cold soft drink. mirror he performs the experiment of
point?
S=1 cal/gmC; t1 = 20C; t2 = 37C 2. Air contains water molecules in the image formation for three values of
A. Boiling: "Boiling is a process in which the
Q = mST (T=t2 - t1) form of water vapour. object distance of 30cm, 10cm and 20cm.
bulk of the liquid from liquid phase
= 100 X 1 X (37 - 20) = 100 X 17 3. During the motion of the water mole- Answer the following questions:
changes to gaseous phase at a constant
Q = 1700 calories. cules, they strike the surface of the bottle a) For the three object distances identify
temperature and constant pressure".
21. Write about the principle of method of which is cool. During this process water the mirror which will form an image
Boiling point: The temperature at which
mixtures? molecules lose their kinetic energy and equal in size to that of object. Find at
the liquid boils is called the boiling point
A. When two (or) more bodies at different form dew by condensing slowly on the sur- least one value of object distance.
of the liquid.
temperatures are mixed with each other, face of the cold soft drink bottle. b) Out of the three mirrors identify the
12. Define the term latent heat of vaporization.
then net heat lost by the hot bodies is equal 25. Why dogs pant during hot summer days? mirror which would be preferred to be
A. Latent heat of vaporization can be defined
to net heat gained by the cold bodies until A. 1. Dogs used for shaving purpose.
as the amount of heat energy required to
they attain thermal equilibrium (or) equal pant to reg- c) For the mirror B draw ray diagram for
change 1 gram of liquid to gas at constant
temperature. ulate their image formation for any two given val-
temperature.
Net heat lost = Net heat gain body tem- ues of object distance.
Its CGS units: cal/gm and SI units: J/Kg.
This is known as principle of method of perature A. a) Mirror B of focal length 15cm this is
13. Distinguish between melting and melting
mixture. during hot because an image equal in size to that of
point?
22. "Specific heat is different for different summer object is formed if object placed at C.
A. Melting: "The process in which solid
substances." Comment on the statement? days. b) For shaving purpose object is placed
phase changes to liquid phase at a constant
The statement "Specific heat is different 2. They have fewer sweat glands between between f and O so that magnified virtual
temperature is called melting".
for different substances" is a true state- the toes, which prevent them to lose heat
Melting point: This constant temperature
ment. We know that the temperature of a through sweating. $V {$, *$ MP iZ.. .
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Heat NotesDokumen105 halamanHeat NotesNuan Ting NgBelum ada peringkat
- Astm A 131 - A 131M - 14Dokumen7 halamanAstm A 131 - A 131M - 14Nguyễn Như ThếBelum ada peringkat
- PHYSICS Chapter21 - Temperature, Heat and Expansion PDFDokumen24 halamanPHYSICS Chapter21 - Temperature, Heat and Expansion PDFAanya gupta100% (1)
- WLP-Week 6Dokumen15 halamanWLP-Week 6Justin Abad Fernandez100% (1)
- MCQs Suface Tension & Interficial TensionDokumen15 halamanMCQs Suface Tension & Interficial Tensionmukul sidhque100% (1)
- Thermal Properties of MatterDokumen79 halamanThermal Properties of MatterHafiza JaweriaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterDari EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Wall-Thickness-Calculation-ASME B31.8-2016-API5LGRBDokumen1 halamanWall-Thickness-Calculation-ASME B31.8-2016-API5LGRBtitir bagchiBelum ada peringkat
- ME3122E - Tutorial Solution 3Dokumen8 halamanME3122E - Tutorial Solution 3LinShaodun100% (3)
- Product List: Additives and Resins For Liquid CoatingsDokumen12 halamanProduct List: Additives and Resins For Liquid CoatingsAPEX SONBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of Dental MaterialsDokumen8 halamanProperties of Dental MaterialsSatya Asatya100% (1)
- The Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseDari EverandThe Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseBelum ada peringkat
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialDokumen32 halamanScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialMar Angelo TangcangcoBelum ada peringkat
- HeatDokumen7 halamanHeatkrushnakadam0029Belum ada peringkat
- Science 8 Q1 Week 6 7Dokumen13 halamanScience 8 Q1 Week 6 7Rachelle Mitch R. TamparongBelum ada peringkat
- Heat As Energy TransferDokumen22 halamanHeat As Energy TransferNiño Gerard JabagatBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 5Dokumen5 halamanActivity 5Yani CenaBelum ada peringkat
- Heat and TemperatureDokumen2 halamanHeat and TemperatureDhana AryalBelum ada peringkat
- Practice IV: Specific Heat of The MetalDokumen6 halamanPractice IV: Specific Heat of The MetalMaria Jose CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 11 General Physics LaboratoryDokumen4 halamanExp 11 General Physics LaboratoryKhrisha TindoyBelum ada peringkat
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDokumen13 halamanHeating Substances COMPLETEMaliq MorrisBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Nibqis PKEZpp FDPWDUqDokumen24 halaman8 Nibqis PKEZpp FDPWDUqmrockzedzBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6 Heat & TemperatureDokumen18 halamanLesson 6 Heat & TemperatureRonnie AbsalonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 IGCSE - ActualDokumen7 halamanChapter 2 IGCSE - ActualNajia UmarBelum ada peringkat
- Latent HeatDokumen6 halamanLatent HeatVjayan DharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 2 - Methods of MixturesDokumen6 halamanExperiment 2 - Methods of MixturesAngelica UyBelum ada peringkat
- CDI 108 Main Topic 3Dokumen5 halamanCDI 108 Main Topic 3maulionaronbokBelum ada peringkat
- Energy of Phase Changes: Chemistry 135Dokumen9 halamanEnergy of Phase Changes: Chemistry 135Guen Min ShitiBelum ada peringkat
- 2 2water 2Dokumen30 halaman2 2water 2Zeineb AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDokumen13 halamanHeating Substances COMPLETEMariah CampbellBelum ada peringkat
- 2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 NotesDokumen21 halaman2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 NotesAhmad RaghebBelum ada peringkat
- Week 9 Phys LabDokumen3 halamanWeek 9 Phys LabJacob JohnsonBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Properties of Matter - 23-24Dokumen9 halamanThermal Properties of Matter - 23-24smodi6545Belum ada peringkat
- Subject: Science Class - VII Chapter - 4 Heat (Module) : Question - AnswerDokumen3 halamanSubject: Science Class - VII Chapter - 4 Heat (Module) : Question - AnswerAzib KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 Lesson Plan - Heat and TemperatureDokumen5 halamanScience 8 Lesson Plan - Heat and TemperatureAnchelle MelendresBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Sheet No. 5 Temperature, Heat, and ExpansionDokumen1 halamanActivity Sheet No. 5 Temperature, Heat, and ExpansionKirene mae BoniaoBelum ada peringkat
- Heat TemperatureDokumen67 halamanHeat TemperatureSean Joaquin AlcoyBelum ada peringkat
- Study Guide - ThermodynamicsDokumen9 halamanStudy Guide - ThermodynamicsEj ParañalBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 5 HeatDokumen26 halamanTopic 5 HeatAnthonyDomBelum ada peringkat
- 4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatDokumen6 halaman4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatkhodijahaminBelum ada peringkat
- Matter in Our Surroundings: Session 3Dokumen10 halamanMatter in Our Surroundings: Session 3swarup.kadam17Belum ada peringkat
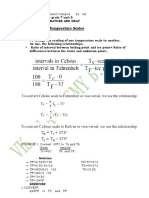
- Conversion of Temperature Scales: ExerciseDokumen6 halamanConversion of Temperature Scales: Exercisekidanemariam HabtemariamBelum ada peringkat
- HVAC Chapter 03Dokumen22 halamanHVAC Chapter 03gmusama1Belum ada peringkat
- Most Essential Learning Competency: S8FE-Ig-29: Differentiate Heat and Temperature at The Molecular LevelDokumen3 halamanMost Essential Learning Competency: S8FE-Ig-29: Differentiate Heat and Temperature at The Molecular LevelLenie MateoBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 New - X STDDokumen6 halamanLesson 3 New - X STDkratosthegodkiller51Belum ada peringkat
- ThermochemDokumen29 halamanThermochemNash MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 4 SummaryDokumen6 halamanChap 4 SummaryAzaizulAhmadBelum ada peringkat
- IB Diploma Programme Physics Standard Level Internal AssessmentDokumen11 halamanIB Diploma Programme Physics Standard Level Internal Assessmentmaxwell210592Belum ada peringkat
- Physics ReviewDokumen159 halamanPhysics ReviewSinned ArgalesBelum ada peringkat
- Theme: Heat Chapter 4: Heat: of WaterDokumen11 halamanTheme: Heat Chapter 4: Heat: of WaterJasbir SidhuBelum ada peringkat
- Science Conclusion - States of MatterDokumen2 halamanScience Conclusion - States of Matterapi-287882693Belum ada peringkat
- Heat Measuring Heat - : From To Fahrenheit To Celsius To KelvinDokumen2 halamanHeat Measuring Heat - : From To Fahrenheit To Celsius To KelvinJeravem OrtiyasBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration: Learning Objective: Describe The Stages of Heat Theory and The Principles InvolvedDokumen98 halamanRefrigeration: Learning Objective: Describe The Stages of Heat Theory and The Principles Involvedgopinathan_karuthedaBelum ada peringkat
- How Hurricanes Pick Up EnergyDokumen23 halamanHow Hurricanes Pick Up EnergyAhanaBelum ada peringkat
- Heating and Air-Conditioning Principles: Learning ObjectivesDokumen11 halamanHeating and Air-Conditioning Principles: Learning ObjectivesMubarek TeshomeBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal ExpansionDokumen5 halamanThermal ExpansiongospakopaBelum ada peringkat
- ThermodynamicsDokumen63 halamanThermodynamicsJerome JavierBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen19 halamanChapter 1raghu ramBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal PropertiesDokumen6 halamanThermal PropertiesMordecai ChimedzaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Secondary - Homework Sheet: H Oh Academy For ChemistryDokumen7 halaman1 Secondary - Homework Sheet: H Oh Academy For ChemistryMark FahimBelum ada peringkat
- Calorimetry SynopsisDokumen4 halamanCalorimetry Synopsissreevaishnava01Belum ada peringkat
- Module 13 Transit EnergiesDokumen37 halamanModule 13 Transit EnergiesMelvin Cabonegro100% (2)
- 9.5heat and TemperatureDokumen12 halaman9.5heat and Temperaturebugrahankilic13Belum ada peringkat
- HeatDokumen163 halamanHeatSrMoonSengChoo100% (1)
- First LawDokumen23 halamanFirst Lawnoah.sibulo2014Belum ada peringkat
- Deposits Borrowings Average Cost of Funds: Financial Margin 1.81Dokumen2 halamanDeposits Borrowings Average Cost of Funds: Financial Margin 1.81ramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 1Dokumen1 halamanPresentation 1ramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- System Bus Structure: Minimum Mode 8086 Pin ConfigurationsDokumen89 halamanSystem Bus Structure: Minimum Mode 8086 Pin ConfigurationsramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Deposits Borrowings Average Cost of Funds: Financial Margin 1.81Dokumen2 halamanDeposits Borrowings Average Cost of Funds: Financial Margin 1.81ramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Service Report 84416096361 20210225Dokumen1 halamanService Report 84416096361 20210225ramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- PACS Shall Issue Deposit Receipts To MembersDokumen5 halamanPACS Shall Issue Deposit Receipts To MembersramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation1 Legal ActionDokumen1 halamanPresentation1 Legal ActionramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation New - 019Dokumen1 halamanPresentation New - 019ramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Developing PACS As Multi Service Center Workshop OnDokumen6 halamanDeveloping PACS As Multi Service Center Workshop OnramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 13333Dokumen7 halamanPresentation 13333ramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Importance of PAN CardDokumen1 halamanImportance of PAN CardramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- QbankDokumen15 halamanQbankramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Total Advances: Impaired AdvancesDokumen4 halamanTotal Advances: Impaired AdvancesramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 1987456Dokumen1 halamanPresentation 1987456ramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 1Dokumen1 halamanPresentation 1ramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- Milk CostDokumen1 halamanMilk CostramprasadBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Electrostatics - Theory - PDF Module-4Dokumen28 halaman1 - Electrostatics - Theory - PDF Module-4Raju SinghBelum ada peringkat
- BUFAB BUMAX Brochyre 2013 PDFDokumen30 halamanBUFAB BUMAX Brochyre 2013 PDFalbertofgvBelum ada peringkat
- Zona PanelDokumen7 halamanZona PanelrobertBelum ada peringkat
- CM2018 - Smart ConnectionsDokumen24 halamanCM2018 - Smart ConnectionsVincenzo PilusoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 2 UpdatedDokumen43 halamanChapter - 2 UpdatednorazifahBelum ada peringkat
- Note 4 - Composition Structure and Mechanical Properties of Bone TissueDokumen37 halamanNote 4 - Composition Structure and Mechanical Properties of Bone Tissuejoyonize08Belum ada peringkat
- 8084 Resin Tech. DataDokumen3 halaman8084 Resin Tech. Dataamir53Belum ada peringkat
- N40SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDokumen1 halamanN40SH Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuBelum ada peringkat
- Experimental Data and Modelling of Thermal Properties of Ice CreamsDokumen11 halamanExperimental Data and Modelling of Thermal Properties of Ice CreamsSUMIT SHINDEBelum ada peringkat
- 2024 04 08 6613e5b9e7e4a 1712580025Dokumen19 halaman2024 04 08 6613e5b9e7e4a 1712580025BALDEV CHOUDHARYBelum ada peringkat
- Minor LossesDokumen8 halamanMinor LossesshieferBelum ada peringkat
- Static AnalysisDokumen13 halamanStatic AnalysisVictoryBelum ada peringkat
- Mosfet Equivalencias Con DataDokumen51 halamanMosfet Equivalencias Con DataJose BenavidesBelum ada peringkat
- Rr310802 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics IIDokumen8 halamanRr310802 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics IISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Junoon e JEE (3.0) Wave Optics IIDokumen186 halamanJunoon e JEE (3.0) Wave Optics IIkisuisoffbeatBelum ada peringkat
- BS 2561carbon Fibre Reinforced Plastics UnidirecionalDokumen16 halamanBS 2561carbon Fibre Reinforced Plastics UnidirecionalDamian GilBelum ada peringkat
- Twins and Dislocations in HCPDokumen46 halamanTwins and Dislocations in HCPthuronBelum ada peringkat
- Figure UCS-66 Impact Test Exemption Curves (Cont'd) : ASME BPVC - VIII.1-2019 UCS-66Dokumen2 halamanFigure UCS-66 Impact Test Exemption Curves (Cont'd) : ASME BPVC - VIII.1-2019 UCS-66MechanicalBelum ada peringkat
- Cundall - Et - El - 2008 - Quantifying The Size Effect of Rock Mass StrengthDokumen15 halamanCundall - Et - El - 2008 - Quantifying The Size Effect of Rock Mass StrengthrBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of Crystal Structures Among CAAC-InGaZnO, nc-InGaZnO, and Solution-Processed InGaZnODokumen4 halamanComparison of Crystal Structures Among CAAC-InGaZnO, nc-InGaZnO, and Solution-Processed InGaZnORabbi HasnatBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 8: Exact Solutions To Energy Equation Example 1: Energy Dissipation in Poiseuille FlowDokumen4 halamanExercise 8: Exact Solutions To Energy Equation Example 1: Energy Dissipation in Poiseuille FlowRafael DalmauBelum ada peringkat
- Transport Phenomena Quiz 1 SolutionDokumen2 halamanTransport Phenomena Quiz 1 SolutionAyman Al Kafrawy100% (1)
- ASTM B265 - 13aDokumen10 halamanASTM B265 - 13areza acbariBelum ada peringkat