Brake g120
Diunggah oleh
KnjigescribdJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Brake g120
Diunggah oleh
KnjigescribdHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
FAQ about Drive Technology
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Low Voltage motors
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Item-ID: 29108503
PDF_Air_gap_of_ 2008 All rights
Siemens AG
reserved
Copyright
Warranty, liability and support
brakes_en_V2.do
tech bremse
120918
We do not accept any liability for the information contained in this
document.
Any claims against us - based on whatever legal reason - resulting from the
use of the examples, information, programs, engineering and performance
data etc., described in this example shall be excluded. Such an exclusion
shall not apply in the case of mandatory liability, e.g. under the German
Product Liability Act (Produkthaftungsgesetz), in case of intent, gross
negligence, or injury of life, body or health, guarantee for the quality of a
product, fraudulent concealment of a deficiency or breach of a condition
which goes to the root of the contract (wesentliche Vertragspflichten).
However, claims arising from a breach of a condition which goes to the root
of the contract shall be limited to the foreseeable damage which is intrinsic
to the contract, unless caused by intent or gross negligence or based on
mandatory liability for injury of life, body or health The above provisions
does not imply a change in the burden of proof to your detriment.
Copyright 2008 Siemens A&D. It is not permissible to transfer or
copy these examples or excerpts of them without first having prior
authorization from Siemens A&D in writing.
Version 2 issue September 2012 2/10
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Item-ID: 29108503
PDF_Air_gap_of_ 2008 All rights
Siemens AG
reserved
Copyright
Table of Contents
Table of Content3
brakes_en_V2.do
tech bremse
120918
1 Overview ........................................................................................................ 4
1.1 Brake types used ............................................................................................ 4
1.2 Spring-operated 2LM8 disk-type brake ............................................................ 7
Principle of operation .................................................................................. 7
1.3 3. Spring-operated KFB disk-type brakes ........................................................ 8
Principle diagram ........................................................................................ 8
2 Appendix ...................................................................................................... 10
2.1 History ........................................................................................................... 10
This entry is from the Internet offer of Siemens AG, Automation and Drives,
Service & Support. Clicking the link below directly displays the download
page of this document.
http://support.automation.siemens.com/WW/view/en/29108503
Version 2 issue September 2012 3/10
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Item-ID: 29108503
PDF_Air_gap_of_ 2008 All rights
Siemens AG
reserved
Copyright
1 Overview
brakes_en_V2.do
Low-voltage motors are equipped with a brake when motor option G26 is
tech bremse
120918
specified when the motor is ordered.
The air gap between the coil and the armature increases as a result of
brake pad wear (brake frictional surface). In order to ensure that the brake
reliably functions, this air gap must be re-adjusted. This is described in the
following text.
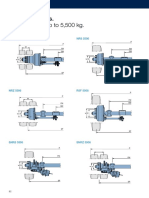
1.1 Brake types used
The spring-operated 2LM8 disk-type brakes are mounted as standard on
1LA5 and 1LA7 motors, frame sizes 63 to 225. These spring-operated
brakes are also mounted onto 1LG motors, frame sizes 180 to 225.
The KFB spring-operated disk-type brake is the standard brake for 1LG
motors in frame sizes 250 to 315.
The individual brake types and detailed technical data are subsequently
listed below:
Version 2 issue September 2012 4/10
Copyright Siemens AG 2008 All rights reserved
tech bremse 120918 PDF_Air_gap_of_brakes_en_V2.doc
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Item-ID: 29108503
Version 2 issue September 2012 5/10
Copyright Siemens AG 2008 All rights reserved
tech bremse 120918 PDF_Air_gap_of_brakes_en_V2.doc
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Item-ID: 29108503
1)
The standard brake for frame size 180 und 225 is the 2LM8 brake. A KFB brake on request.
2)
The standard brake for frame size 250 bis 315 is the KFB brake.
Version 2 issue September 2012 6/10
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Item-ID: 29108503
PDF_Air_gap_of_ 2008 All rights
Siemens AG
reserved
Copyright
1.2 Spring-operated 2LM8 disk-type brake
brakes_en_V2.do
tech bremse
120918
Principle of operation
When in the no-current condition, the brake is electromagnetically released. When
braking operation starts, the rotor - that can axially move along the shaft - is
pressed onto the mating frictional surfaces using springs that act on the armature
disk. In the braked state there is a defined air gap between the armature disk and
the solenoid assembly. This air gap can increase as the brake pads wear.
For normal applications, this disk-type brake is practically maintenance-free. The
air gap only has to be checked at certain time intervals for those applications where
considerable amount of frictional work takes place does. A check should be made
at the latest when the maximum permissible air gap is reached. The air gap should
then be reset back to the nominal air gap.
Please refer to the table above for the values for the nominal air gap and the
maximum permissible air gap.
The air gap is checked using a feeler gauge.
Version 2 issue September 2012 7/10
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Item-ID: 29108503
PDF_Air_gap_of_ 2008 All rights
Siemens AG
reserved
Copyright
For deviations, the adjustment is made as folllows:
brakes_en_V2.do
Disconnect the power, the brake must then go into a no-torque
tech bremse
120918
condition.
Slightly release the outer/external retaining screws of the brake flange.
Uniformly rotate the adjusting screws for the air gap using an open-
ended wrench.
1/6 of a revolution changes the air gap by approx. 0.15 mm.
Re-tighten the retaining screws and carefully check the new air gap.
Repeat the re-adjustment until the nominal air gap has been reached.
1.3 3. Spring-operated KFB disk-type brake
Principle diagram
Version 2 issue September 2012 8/10
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Item-ID: 29108503
PDF_Air_gap_of_ 2008 All rights
Siemens AG
reserved
Copyright
The electro-magnet (solenoid) two-surface KFB spring-operated disk brake
brakes_en_V2.do
is a safety brake. When the current is disconnected, the armature disk and
tech bremse
120918
the support for the friction pads are pressed against the mating frictional
surface. This is what causes the braking effect.
In order to guarantee correct operation of the brake, the air gap between
the coil assembly group and the armature disk must have the specified
size. The minimum and maximum air gap size is stamped on the type plate
of the brake. When shipped from the factory the brake is set to the
minimum air gap.
Check the air gap through the open thread holes as follows:
Unscrew the screws together with sealing rings (sealing gaskets) from
the housing.
Introduce the feeler gauge at three locations around the open thread
holes.
Measure the air gap between the armature disk and the coil assembly
group.
If the air gap does not correspond to the specified values then adjust the air
gap as follows:
Disconnect the power, the brake must then go into a no-torque
condition.
Remove the housing.
Slightly release the retaining screws of the brake flange.
Turn the adjusting screws uniformly using an open-ended wrench.
Reduce the air gap: Rotate the adjusting screws clockwise (when
viewing the brake flange).
Increase the air gap: Rotate the adjusting screws in an anti-clockwise
direction (when viewing the brake flange).
Re-tighten the retaining screws of the brake flange.
Re-check the air gap and if required, continue to adjust as described
above.
The air gap can be continuously re-adjusted several times.
If this is no longer possible then the friction pad support assembly can be
simply replaced after opening the housing ( three screws ). It is not
necessary to disassembly the complete brake.
Version 2 issue September 2012 9/10
Adjusting the air gap of motor brakes
Item-ID: 29108503
PDF_Air_gap_of_ 2008 All rights
Siemens AG
reserved
Copyright
2 Appendix
brakes_en_V2.do
tech bremse
120918
2.1 History
Table 2-1 History
Version Datum nderung
V1.0 March 2008 First issue
V2.0 September 2012 Correction in chapter 1.1 Brake types used
Version 2 issue September 2012 10/10
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Acti9 Ic60 - A9F75104Dokumen3 halamanActi9 Ic60 - A9F75104KnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Acti9 Ic60 - A9F75104Dokumen3 halamanActi9 Ic60 - A9F75104KnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Technical Guide No. 8: Electrical BrakingDokumen30 halamanTechnical Guide No. 8: Electrical BrakingKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- 3KC03440QE000AA0 Datasheet enDokumen6 halaman3KC03440QE000AA0 Datasheet enKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Technical Guide No. 8: Electrical BrakingDokumen30 halamanTechnical Guide No. 8: Electrical BrakingKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Harmony Timer Relays - RE17RMMWDokumen17 halamanHarmony Timer Relays - RE17RMMWKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Acti 9 Ic60 - A9F74120Dokumen3 halamanActi 9 Ic60 - A9F74120KnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Technical Guide No. 8: Electrical BrakingDokumen30 halamanTechnical Guide No. 8: Electrical BrakingKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Fiedbus Interfaces FaqDokumen17 halamanFiedbus Interfaces FaqLeonardoAcevedo100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Drives For Motion 2Dokumen39 halamanDrives For Motion 2KnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Guide No. 8: Electrical BrakingDokumen30 halamanTechnical Guide No. 8: Electrical BrakingKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Feeder Protection and Control REF615Dokumen8 halamanFeeder Protection and Control REF615KRISH kmsBelum ada peringkat
- Fiedbus Interfaces FaqDokumen17 halamanFiedbus Interfaces FaqLeonardoAcevedo100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Drives For Motion 1Dokumen40 halamanDrives For Motion 1KnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- DSU Manual PDFDokumen204 halamanDSU Manual PDFCarlos Alberto RuedaBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Feeder Protection and Control REF615Dokumen8 halamanFeeder Protection and Control REF615KRISH kmsBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Motion Control DrivesDokumen44 halamanMotion Control DrivesKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Firmware Manual ACS800 Standard Control Program 7.xDokumen284 halamanFirmware Manual ACS800 Standard Control Program 7.xjunfa100% (1)
- Fund Mech Eng SiemensDokumen150 halamanFund Mech Eng SiemensRafael Pacheco100% (2)
- Motion Control DrivesDokumen44 halamanMotion Control DrivesKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Firmware Manual ACS800 Standard Control Program 7.xDokumen284 halamanFirmware Manual ACS800 Standard Control Program 7.xjunfa100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Firmware Manual ACS800 Standard Control Program 7.xDokumen284 halamanFirmware Manual ACS800 Standard Control Program 7.xjunfa100% (1)
- En 600 DSU Um 3Dokumen62 halamanEn 600 DSU Um 3boba78Belum ada peringkat
- En 600 DSU Um 3Dokumen62 halamanEn 600 DSU Um 3boba78Belum ada peringkat
- Discrepancy Switches Control Discrepancy Switches 3sv4 5Dokumen4 halamanDiscrepancy Switches Control Discrepancy Switches 3sv4 5KnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Brakes For Cranes and HoistsDokumen3 halamanBrakes For Cranes and HoistsKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Discrepancy Switches ControlDokumen11 halamanDiscrepancy Switches ControlKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- 1654B Fluke PDFDokumen65 halaman1654B Fluke PDFKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines Relay SettingDokumen468 halamanGuidelines Relay Setting1453h100% (5)
- ABB Control SystemDokumen36 halamanABB Control Systemhagh_mostafa2787Belum ada peringkat
- Afc4 - Landing GearDokumen303 halamanAfc4 - Landing GearEjigayehu Lemma100% (2)
- 4165 CLGDokumen2 halaman4165 CLGဆားပုလင္းႏွင္းေမာင္Belum ada peringkat
- Automotive Vehicles - Brakes and Braking Systems: Indian StandardDokumen13 halamanAutomotive Vehicles - Brakes and Braking Systems: Indian Standardyogesh shindeBelum ada peringkat
- Scania Retarder 2Dokumen27 halamanScania Retarder 2neilevcvr85% (20)
- 1 - BPW AxlesDokumen12 halaman1 - BPW AxlesAhmed Abo ElkomsanBelum ada peringkat
- Hyster 221YDokumen20 halamanHyster 221YHELYBelum ada peringkat
- C6 Manual de Bolsillo PDFDokumen223 halamanC6 Manual de Bolsillo PDFgume pesaBelum ada peringkat
- Hz30477 Machu Picchu Smt2022 - LiftDokumen2 halamanHz30477 Machu Picchu Smt2022 - LiftAbel Valderrama PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Land Cruiser 70 ManualDokumen99 halamanLand Cruiser 70 Manualcybervinni75% (8)
- Radial Piston Motor MCRDokumen56 halamanRadial Piston Motor MCRjuanchis650100% (1)
- Bournemouth Tram Crash 1908Dokumen10 halamanBournemouth Tram Crash 1908droshkyBelum ada peringkat
- Crane Calculation Report Bull Hoists and The Lifting Appliance ConsideredDokumen13 halamanCrane Calculation Report Bull Hoists and The Lifting Appliance ConsideredenterlogBelum ada peringkat
- VX 40-55 Bro ENDokumen20 halamanVX 40-55 Bro ENIonut GrozaBelum ada peringkat
- 1999 Jeep TJ Wrangler Service Manual - 05. BrakesDokumen38 halaman1999 Jeep TJ Wrangler Service Manual - 05. Brakesbfranklin33100% (1)
- Israel Railways LTD.: Railway Buffer Stops Planning GuidelinesDokumen40 halamanIsrael Railways LTD.: Railway Buffer Stops Planning GuidelinesShahryarBelum ada peringkat
- WorkshopManual Indica PDFDokumen888 halamanWorkshopManual Indica PDFPhillip van Dalen100% (7)
- RT600E Pressure Setting ProcedureDokumen10 halamanRT600E Pressure Setting ProcedureQike FlowersBelum ada peringkat
- Manual - Buggy RCM Kapton PDFDokumen34 halamanManual - Buggy RCM Kapton PDFCookie PandaBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic Swing Drive: Service and Maintenance ManualDokumen16 halamanHydraulic Swing Drive: Service and Maintenance ManualmasakpBelum ada peringkat
- Baja SAE Tech Inspection Sheet 2014-2015Dokumen12 halamanBaja SAE Tech Inspection Sheet 2014-2015FoureyeddjBelum ada peringkat
- Braking System PartsDokumen4 halamanBraking System PartsCadeco ZamoraBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 13 - ClutchesDokumen81 halamanPertemuan 13 - Clutchesanonim 1178Belum ada peringkat
- Beeaar HyundaiDokumen34 halamanBeeaar HyundaiAakash RajBelum ada peringkat
- CatalogDokumen19 halamanCatalogHamis ShekibulaBelum ada peringkat
- H 100Dokumen8 halamanH 100api-199203074Belum ada peringkat
- AAR Manual of Standards and Recommended Practices Brakes and Brake EquipmentDokumen38 halamanAAR Manual of Standards and Recommended Practices Brakes and Brake EquipmentCory BallardBelum ada peringkat
- TP 122 03 - TagDokumen117 halamanTP 122 03 - TagJUANBelum ada peringkat
- Friction Material Codes PDFDokumen1 halamanFriction Material Codes PDFAtendra SinghBelum ada peringkat
- XXXX Volvo d11 Brochure r3Dokumen6 halamanXXXX Volvo d11 Brochure r3Muhammad rizkiBelum ada peringkat
- Crane ControlDokumen81 halamanCrane ControlKnjigescribdBelum ada peringkat
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsDari EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeDari EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (9)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialDari EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionDari EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (15)
- Electronics All-in-One For Dummies, 3rd EditionDari EverandElectronics All-in-One For Dummies, 3rd EditionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesDari EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosDari EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tDari EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (27)