Future Clauses
Diunggah oleh
Carolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Future Clauses
Diunggah oleh
Carolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
What do FUTURE TIME CLAUSES, HYPOTHETICAL SUBJUNCTIVES
and WISH have in common?
The verb tense they all use is a step back in time because
what is being communicated is either uncertain,
hypothetical, unreal, unrealistic, improbable, imaginary,
or cannot be collocated on the future time line in a
specific place.
TIME LINE
past present future
By using a verb tense which is a step back in time to the real
time collocation we communicate that what we are saying is not,
in fact, true or real; or cannot be associated with a specific
future time.
Example: Will you call me when you arrive? (FTC your arrival time
is uncertain and unspecified)
If you studied harder, you would get higher marks.
(Hypothetical subjunctive in a II conditional in reality you are not
studying hard enough)
I wish I had a new car. (I would like things to be the opposite
of what they are in reality wishful thinking)
I will/am going to do my homework when I get back
home.
(I cannot, or do not want to specify an exact time, but I am certainly
talking about some time in the future so the simple present is used
instead of a future tense in the time clause).
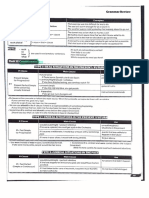
FUTURE TIME CLAUSES
These use the following conjunctions + simple present form of
verb whilst the main clause uses a future tense or a modal
verb form.
When I finish my homework I will/am going to go to the cinema.
Before you go out with your friends you must finish your
homework.
What will you/are you going to do after you finish your
homework?
As soon as I finish my homework Ill/Im going(to go)to the
cinema.
Until/Till you finish your homework you wont be given
permission to go to the cinema. (future passive voice in main clause)
If you finish your homework will you be able to come to the
cinema with me?
Tomorrow you will clean the kitchen and I will clean the
bathroom. ======
Youll clean the kitchen while Im cleaning the bathroom.
You will need an umbrella. Take mine. ======
Whenever you need an umbrella you can take mine.
Should you need an umbrella, take mine. (type I conditional.
Indicates that the action, though possible, is not very likely).
The future perfect simple or continuous take a step back in
time when a conjunction is used and become the present perfect
simple or continuous.
I will have finished my homework in five minutes. Then Ill
call John.
When I have finished my homework (no specific time is given), Ill
call John.
John will have stopped playing tennis by tea-time. He will
have a shower before he comes in for tea.
John will have a shower as soon as he has stopped playing
tennis.
Time expressions such as the minute, the moment, when referring
to the future also step back to the present tense.
I will see John sometime today. I will tell him the good news.
The minute I see John I will tell him the good news.
If you arent careful you will drop the egg, and it will break.
The moment you drop the egg it will break.
HYPOTHETICAL SUBJUNCTIVE
One of the uses of the subjunctive is to communicate a
hypothesis that is highly unlikely to occur in the future or
simply was not true in the past.
Unlike many other languages the subjunctive mood in English is
falling into disuse and is infrequent nowadays, as forms using
a modal such as might, could or should are now more common.
We recommend that each student study (not studies)two hours
after school.
Students should study two hours after school.
Students do, however, encounter the use of the subjunctive in
conditionals and fixed expressions such as God save the
Queen, Come what may, So be it.
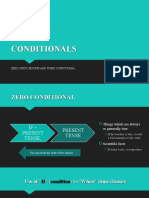
If or
time
When in claus condition result typ
time e e
S
Simple present imple present
Always
0 Scientific truth
you heat ice it melts.
Refers If/ Personal truth
to when I always win.
anywhere I play tennis with
in time. John
I always take an
it rains umbrella with me.
It never rains but it pours.
meaning: When troubles come they come General truth
together.
Will/going to/modal
Simple present + base form of main
verb
future If 1 Probable
you dont leave
I will/am going to
If it rains call the police.
I wont/might not
Unless it rains play tennis
tomorrow. the
Shoul event will take
d it rain
place.
The event wont
take place.
Simple past Modal (usually Improbable
(subjunctive) would) + base verb
.
If I had time I would call Mary. At the moment
future 2 the opposite is
If John were/was here he would help us. true: I dont
have time and
The English Channel you could walk to John is not
If here.
froze France.
.
I went to London This is
I would/could visit
If improbable.
the Tate Gallery.
I were you I would study
If harder. Probability/poss
ibility
Were I you
I would study
In reality I am
harder. not you.
Past perfect Modal (usually Impossible to
(continuous) WOULD) + perfect change a past
subjunctive infinitive fact/situation
If
past Id known about your I would have come.
If party.
We hadnt eaten so we wouldnt have 3
If much been so ill. Unfortunately,
I would/could have I didnt go.
If I had gone to London visited the Tate. Ability not
we could have saved performed.
If we had found him him. This
earlier we might have saved possibility
If him. did not occur.
we had found him I would/could/might
earlier have been seriously
I hadnt been injured in the
wearing a seat belt. accident.
If I wouldnt have
been crying when But the truth
John had told me the you saw me. is he lied and
truth I was crying.
WISH
We use the modals would and could to talk about wishes for
the future when we are not satisfied with the present
situation/reality.
I dont like living in England. I wish I could live in
Italy. My husband wishes he could live in Italy too.
What an awful noise. I wish John would stop practicing
the violin.
I wish the phone would ring.
We step back in time and use a past tense (subjunctive)form to
talk about wishes for the present time:
I dont like this place. I wish I lived somewhere more
interesting.
These second-class carriages are very dirty. I wish we
were travelling first class.
I wish it werent/wasnt so hot.
Wish you were here!
We use the past perfect (subjunctive) form to express the
desire that something different had happened, or express regret
for what happened in the past.
Im very tired. I wish I had gone (not went) to bed earlier
last night.
I wish (now) I had studied harder when I was at school.
Harry wishes he had listened more carefully to the
instructions he was given.
When John saw the results of the exam. He wished (when he
saw the results)that he had studied harder.
If only can be used with the same significance/ verb
constructions as wish
I wish I were/was rich.
If only I were/was rich.
I wish I had seen that green dress before I bought
the red one.
If only I had seen that green dress before I bought the
red one.
I cant sing well!
I wish I could sing.
If only I could sing.
We wish he didnt smoke.
If only he didnt smoke. (It is such a bad habit)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Conditional SentencesDokumen4 halamanConditional Sentencesminhquan20112006Belum ada peringkat
- Conditional SampleDokumen10 halamanConditional SampleJennifer R. JuatcoBelum ada peringkat
- Use real conditionals to discuss possible future situationsDokumen1 halamanUse real conditionals to discuss possible future situationsJuanCamiloAcunaBelum ada peringkat
- The Zero and First Conditional For SharingDokumen7 halamanThe Zero and First Conditional For SharingabielgtgBelum ada peringkat
- ConditionalulDokumen3 halamanConditionalulsimina antonBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Language Practice- ConditionalsDokumen8 halamanAdvanced Language Practice- ConditionalsJay Be-ElBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals If Clauses Classroom Posters CLT Communicative Language Teach - 84188Dokumen1 halamanConditionals If Clauses Classroom Posters CLT Communicative Language Teach - 84188Lore DanaBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals If Clauses Classroom Posters CLT Communicative Language Teach - 84188Dokumen1 halamanConditionals If Clauses Classroom Posters CLT Communicative Language Teach - 84188Felipe Alberto Ramírez LozanoBelum ada peringkat
- Conditional Sentences: and Other Expressions of ConditionsDokumen12 halamanConditional Sentences: and Other Expressions of ConditionsHannia GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Green & Orange Conditionals PresentationDokumen12 halamanGreen & Orange Conditionals PresentationИбрагимова МахинурBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 2Dokumen15 halamanLesson 2martaa.levytskaaBelum ada peringkat
- Conditional (If Clause)Dokumen8 halamanConditional (If Clause)Meiri NadiaBelum ada peringkat
- CONDITIONALSDokumen3 halamanCONDITIONALSMellBelum ada peringkat
- Modal Verbs LessonDokumen5 halamanModal Verbs LessonSilviaJerez96Belum ada peringkat
- Conditionals 0 1 2 3Dokumen2 halamanConditionals 0 1 2 3gocan12-1Belum ada peringkat
- Conditional Sentences and Wishes ExplainedDokumen13 halamanConditional Sentences and Wishes Explainedyola harmilaBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals Definition: Types of Conditional Sentences ExplainedDokumen6 halamanConditionals Definition: Types of Conditional Sentences Explainedlarisa jamiesonBelum ada peringkat
- Other ConditionalsDokumen6 halamanOther ConditionalsNamahoro JanvierBelum ada peringkat
- Zero and Type Conditionals ExplainedDokumen4 halamanZero and Type Conditionals ExplainedInes RuedaBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals: Zero, 1st, 2ndDokumen26 halamanConditionals: Zero, 1st, 2ndMarcela FernándezBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Present/Continuous Simple Present: (Certainty) (Probability) (Possibility)Dokumen1 halamanSimple Present/Continuous Simple Present: (Certainty) (Probability) (Possibility)GAME REPAIRBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals in EnglishDokumen1 halamanConditionals in EnglishTamaraBelum ada peringkat
- Learn the Four English ConditionalsDokumen5 halamanLearn the Four English ConditionalsPianistasenderistaBelum ada peringkat
- ConditionalsDokumen3 halamanConditionalsdanijelapjBelum ada peringkat
- Zero, first, second, third conditionalsDokumen7 halamanZero, first, second, third conditionalsablanncoBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals Type Use If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result) Zero Present Simple Present SimpleDokumen13 halamanConditionals Type Use If Clause (Condition) Main Clause (Result) Zero Present Simple Present SimpleAurelia Mihaela SoleaBelum ada peringkat
- How to Use Conditionals in EnglishDokumen11 halamanHow to Use Conditionals in EnglishNohelia Rodriguez OrozcoBelum ada peringkat
- BODY Time Firts and Zero Conditional2022Dokumen46 halamanBODY Time Firts and Zero Conditional2022Lucila CarrilloBelum ada peringkat
- Verbe 2Dokumen2 halamanVerbe 2Natalia SBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Activity - 8 Conditional Sentences: When, As Soon As, Until, Before, Unless, and So On, May Take Place of IfDokumen8 halamanLearning Activity - 8 Conditional Sentences: When, As Soon As, Until, Before, Unless, and So On, May Take Place of IfSulistya Ningsih Pratiwi AzzahBelum ada peringkat
- IT1 Lecture 3 - Technical English-IIDokumen14 halamanIT1 Lecture 3 - Technical English-II오뚜기Belum ada peringkat
- Conditional If 2nd Year 2019 What Is A ConditionalDokumen9 halamanConditional If 2nd Year 2019 What Is A Conditionalenglish teachersBelum ada peringkat
- IF CLAUSE RULESDokumen5 halamanIF CLAUSE RULESDiana GonzaliBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals SummaryDokumen2 halamanConditionals SummaryAnca ȘtefănescuBelum ada peringkat
- ConditionalsDokumen12 halamanConditionalsMothBelum ada peringkat
- Conditional SentencesDokumen12 halamanConditional SentencesJEJIE FLORESBelum ada peringkat
- Conditional Clauses - Grammar PDFDokumen2 halamanConditional Clauses - Grammar PDFAdrián Gutiérrez SanzBelum ada peringkat
- Conidtional SentencesDokumen5 halamanConidtional SentencesAijamal SartaevaBelum ada peringkat
- Conditional SentenceDokumen10 halamanConditional Sentencemedia kreasiBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar partsDokumen8 halamanGrammar partsfirewyimer921Belum ada peringkat
- If I were rulesDokumen13 halamanIf I were rulesVanessa PoulainBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals Zsófi MódraDokumen3 halamanConditionals Zsófi MódraBácskay Balázsné ZsófiaBelum ada peringkat
- First Conditional: When You Visit, We Might Go To The ParkDokumen6 halamanFirst Conditional: When You Visit, We Might Go To The ParkRaquel CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals PDFDokumen10 halamanConditionals PDFMARBelum ada peringkat
- ConditionalsDokumen23 halamanConditionalsCarmen BugnarBelum ada peringkat
- Meeting 3 - ConditionalDokumen7 halamanMeeting 3 - ConditionalIkram Wahyu PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals: Zero, First, Second and Third ConditionalDokumen8 halamanConditionals: Zero, First, Second and Third ConditionalIsabel María Castellano MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- PORTFOLIO - 1st and 2nd partial-AVEGNO MENDOZADokumen26 halamanPORTFOLIO - 1st and 2nd partial-AVEGNO MENDOZASolange RiofrioBelum ada peringkat
- ConditionalsDokumen12 halamanConditionalsSvetlana SvetlichnayaBelum ada peringkat
- CONDITIONALSDokumen1 halamanCONDITIONALSClaradelolmoBelum ada peringkat
- ConditionalsDokumen22 halamanConditionalshappyindriyono2402100% (1)
- Grammar 7Dokumen8 halamanGrammar 7tomyBelum ada peringkat
- Conditionals & WishesDokumen5 halamanConditionals & WishesCong ChinhBelum ada peringkat
- The Category of Mood in English. Some Theoretical NotesDokumen7 halamanThe Category of Mood in English. Some Theoretical NotesMonica AndreeaBelum ada peringkat
- Four main types of conditional sentences in EnglishDokumen25 halamanFour main types of conditional sentences in EnglishVasilachi-CerchezSvetlanaBelum ada peringkat
- ConditionalsDokumen13 halamanConditionalsCande LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Conditional Type 0Dokumen16 halamanConditional Type 0marore100% (1)
- (Lecture - 7) Conditional SentencesDokumen21 halaman(Lecture - 7) Conditional SentencesN. W. FlannelBelum ada peringkat
- GR ConmixedDokumen20 halamanGR ConmixedJason WBelum ada peringkat
- No Mistakes Grammar, Volume III, More Misused WordsDari EverandNo Mistakes Grammar, Volume III, More Misused WordsBelum ada peringkat
- Phrasal VerbsDokumen2 halamanPhrasal VerbsCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Past Tens Test: 1. Go 2. Come 3. Buy 4. Have 5. DoDokumen3 halamanPast Tens Test: 1. Go 2. Come 3. Buy 4. Have 5. DoCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- A Typical DayDokumen1 halamanA Typical DayCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Days of The WeekDokumen2 halamanDays of The WeekCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Present PerfectDokumen2 halamanPresent PerfectCarolina Andrea Muñoz Aravena40% (5)
- Final ExamDokumen2 halamanFinal ExamCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Review Final Test GrammarDokumen4 halamanReview Final Test GrammarCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Connectors Adverbs and ConjunctionsDokumen3 halamanConnectors Adverbs and ConjunctionsCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- 419 Genitive CaseDokumen1 halaman419 Genitive Casesarah gaia ruoccoBelum ada peringkat
- Trip To The DoctorDokumen2 halamanTrip To The DoctorCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Cover LetterDokumen1 halamanCover LetterCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Possessive Adjectives and Possessive PronounsDokumen2 halamanPossessive Adjectives and Possessive PronounsCarolina Andrea Muñoz Aravena100% (1)
- Adverbs of Frequency GuideDokumen5 halamanAdverbs of Frequency GuideCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Irregular Verbs Memory Card Game 1 3Dokumen1 halamanIrregular Verbs Memory Card Game 1 3Carolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Fanboys PictureDokumen1 halamanFanboys PictureCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Past SimpleDokumen2 halamanPast SimpleCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Correlative Conjunctions WorksheetDokumen1 halamanCorrelative Conjunctions WorksheetCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Verb To Be Reading ActivityDokumen2 halamanVerb To Be Reading ActivityCarolina Andrea Muñoz Aravena100% (1)
- The Verb "To Have" - Beginners LevelDokumen5 halamanThe Verb "To Have" - Beginners LevelCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Verb To Be Have Got RevisonDokumen11 halamanVerb To Be Have Got RevisonCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Verb To Be First StepsDokumen1 halamanVerb To Be First StepsCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- The Use of ArticlesDokumen14 halamanThe Use of ArticlesCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Family Members Family MembersDokumen7 halamanFamily Members Family MembersCarolina Andrea Muñoz Aravena100% (1)
- Countries and Nationalities ExplainedDokumen2 halamanCountries and Nationalities ExplainedCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Linking Words PracticeDokumen2 halamanLinking Words PracticeCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Present and Past ContinuosDokumen13 halamanPresent and Past ContinuosCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Past Tense Was WereDokumen1 halamanPast Tense Was WereCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- At On in EjercDokumen1 halamanAt On in EjercCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Prepositions of Place and PositionDokumen7 halamanPrepositions of Place and PositionCarolina Andrea Muñoz AravenaBelum ada peringkat
- Reflective Paper Assignment 2 Professional Practice Level 2Dokumen3 halamanReflective Paper Assignment 2 Professional Practice Level 2api-350779667Belum ada peringkat
- String Harmonics in Ravel's Orchestral WorksDokumen97 halamanString Harmonics in Ravel's Orchestral WorksYork R83% (6)
- MKTG10001Dokumen38 halamanMKTG10001Jessica KokBelum ada peringkat
- Comparison of Treadmill Based and Track Based Rockport 1 Mile Walk Test For Estimating Aerobic Capacity in Healthy Adults Ages 30-50 YearsDokumen4 halamanComparison of Treadmill Based and Track Based Rockport 1 Mile Walk Test For Estimating Aerobic Capacity in Healthy Adults Ages 30-50 Yearsmanjula dangeBelum ada peringkat
- Somatic Symptom DisorderDokumen26 halamanSomatic Symptom DisorderGAYATHRI NARAYANAN100% (1)
- QP ScriptDokumen57 halamanQP ScriptRitesh SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Explain Mod 4Dokumen20 halamanExplain Mod 4Gab IgnacioBelum ada peringkat
- RUN ON SENTENCES AND FRAGMENTS GUIDEDokumen17 halamanRUN ON SENTENCES AND FRAGMENTS GUIDEWAHEED-UL -ISLAMBelum ada peringkat
- FortiEDR Product Overview TrainingDokumen16 halamanFortiEDR Product Overview TrainingRafael Steven Soto del CampoBelum ada peringkat
- Sic 789 ADokumen19 halamanSic 789 AFlorinMacoveiBelum ada peringkat
- Myasthenia Gravis Presentation and Treatment Variations: A Case Study ApproachDokumen5 halamanMyasthenia Gravis Presentation and Treatment Variations: A Case Study ApproachLiyasariBelum ada peringkat
- Systematic Risk of Select Banking ScriptsDokumen70 halamanSystematic Risk of Select Banking ScriptsHassim KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Practical 1Dokumen3 halamanPractical 1Paulus DorlenBelum ada peringkat
- Ds Mini ProjectDokumen12 halamanDs Mini ProjectHarsh VartakBelum ada peringkat
- KYLE DE VERA BSA-3A (Auditing & Assurance in SPCL Industries MT Exam) AnswersDokumen3 halamanKYLE DE VERA BSA-3A (Auditing & Assurance in SPCL Industries MT Exam) AnswersKyree Vlade100% (1)
- Touw 1982 Roses MedievalDokumen14 halamanTouw 1982 Roses MedievalВладан СтанковићBelum ada peringkat
- Sidak 2008 FAQsDokumen3 halamanSidak 2008 FAQssikhswimBelum ada peringkat
- English (Step Ahead)Dokumen33 halamanEnglish (Step Ahead)ry4nek4100% (1)
- Outlook Business The Boss July 2015Dokumen14 halamanOutlook Business The Boss July 2015Nibedita MahatoBelum ada peringkat
- 20764C ENU Companion PDFDokumen192 halaman20764C ENU Companion PDFAllan InurretaBelum ada peringkat
- A480 PDFDokumen95 halamanA480 PDFIrma OsmanovićBelum ada peringkat
- MERLINDA CIPRIANO MONTAÑES v. LOURDES TAJOLOSA CIPRIANODokumen1 halamanMERLINDA CIPRIANO MONTAÑES v. LOURDES TAJOLOSA CIPRIANOKaiserBelum ada peringkat
- Woodman Et Al 1993Dokumen30 halamanWoodman Et Al 1993Azim MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Fitch CLOs and Corporate CDOsRating Criteria PDFDokumen57 halamanFitch CLOs and Corporate CDOsRating Criteria PDFantonyBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 7 RC Time ConstantDokumen8 halamanLab 7 RC Time ConstantMalith Madushan100% (1)
- Pilar Fradin ResumeDokumen3 halamanPilar Fradin Resumeapi-307965130Belum ada peringkat
- 15 Tips To Get Fair Skin Naturally PDFDokumen2 halaman15 Tips To Get Fair Skin Naturally PDFLatha SivakumarBelum ada peringkat
- MOH Formulary Drug List 2014Dokumen115 halamanMOH Formulary Drug List 2014mahmud000Belum ada peringkat
- 1 Prepositions With AnswersDokumen6 halaman1 Prepositions With AnswersManal El ShafieBelum ada peringkat
- The General RetiresDokumen17 halamanThe General Retiresfo100% (1)