Doppler Effect
Diunggah oleh
Syed TanveerHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Doppler Effect
Diunggah oleh
Syed TanveerHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
DOPPLER EFFECT
Pitch is defined as the sensation that sound produces in the ear of a listener. It depend upon the
frequency of sound. The greater the frequency, greater the pitch and lower the frequency, lower
the pitch of the sound produced by source. If the frequency is greater, sound will be shrill. If
frequency is lower, sound will be grave.
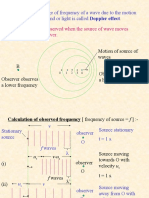
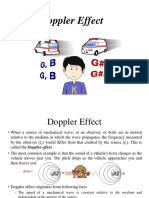
The apparent change in the pitch of sound waves due to relative motion of source of sound and
the listener is known as Dopplers Effect.
Dopplers Effect can be explained by considering three possibilities:
1. When the listener is moving and the source of sound is at rest.
2. When the source is moving and the listener is at rest.
3. When both the source of sound and listener are moving.
Case 01(a)
When the listener moves towards a stationary source.
Consider a stationary source of sound emitting waves of frequency and of wavelength . If V
V
be the speed of sound waves then: = ----- eq (1)
If the listener is moving towards the source with
speed Vo, the sound waves approaches him with
a speed of V + Vo. Since the relative velocity of
sound waves changes, as a result frequency of
sound will also change. Therefore the apparent
frequency (`) heard by the moving listener will be:
V + Vo
` =
Putting the value of from eq (1)
V + Vo
` = V
V + Vo
` = ( )
V
Above equation shows that apparent frequency (`) heard by the listener moving away from the
source will be greater than the frequency () emitted by the source. Hence, pitch of the sound
increases.
Case 01(b)
When the listener moves away from a stationary source.
If the listener is moving away from the source with
speed Vo, the sound waves approaches him with
a speed of V Vo. Since the relative velocity of
sound waves changes, as a result frequency of
sound will also change. Therefore the apparent
frequency (`) heard by the moving listener will be:
V Vo
` =
Putting the value of from eq (1)
V - Vo
` = V
Engr. Syed M. Tanveer Page 1 of 3
V Vo
` = ( )
V
Above equation shows that apparent frequency (`) heard by the listener moving away from the
source will be less than the frequency () emitted by the source. Hence, pitch of the sound
decreases.
Case 2(a)
When the source moves towards a stationary listener
If a source of sound approaches a stationary listener with a speed Vs then the sound waves present
between the listener and the source are compressed. Therefore, the wavelength of the waves
received by the listener decreases and it is given by:
V Vs
= ----- eq (2)
As the wavelength decreases, frequency
increases. If ` be the apparent frequency
then it is given by:
V
` =
'
Putting the value of from eq (2), we have
V
` = V Vs
V
` = ( )
V Vs
Above equation indicates that apparent frequency (`) increases due to which its pitch also
increases.
Case 2(b)
When the source moves away from a stationary listener
If a source of sound moves away from a stationary listener with velocity Vs, then the wavelength
of sound waves received by the listener increases and is given by:
V Vs
= ----- eq (2)
As the wavelength increases, frequency
decreases. If ` be the apparent
frequency then it is given by:
V
` =
'
Putting the value of from eq (2), we
have
V
` = V + Vs
(
)
V
` = ( )
V + Vs
Above equation indicates that apparent frequency (`) decreases due to which its pitch also
decreases.
Engr. Syed M. Tanveer Page 2 of 3
Case 3 (a)
When both source of sound and listener are moving towards each other
If the listener is moving with velocity Vo towards the source of sound then frequency changes from
to ` and is given by:
V + Vo
` = ( )
V
If the source of sound is also moving towards
the listener with velocity Vs then frequency
further changes from ` to `` and is given
by:
V
`` = ( ) `
V Vs
Putting the value of ` from above equation,
we have
V V + Vo
`` = ( )( )
V Vs V
V + Vo
`` = ( )
V Vs
In this case, frequency heard by the listener will be greater than the frequency emitted by the
source. Hence pitch of the sound increases.
Case 3(b)
When both source of sound and listener are moving away from each other
If the listener is moving with velocity Vo away from the source of sound then frequency changes
from to ` and is given by:
V Vo
` = ( )
V
If the source of sound is also moving
away from the listener with velocity Vs
then frequency further changes from
` to `` and is given by:
V
`` = ( ) `
V + Vs
Putting the value of ` from above
equation, we have
V Vo V
`` = ( )( )
V V + Vs
V Vo
`` = ( )
V + Vs
In this case, frequency heard by the listener will be lesser than the frequency emitted by the source.
Hence, pitch of the sound decreases.
Engr. Syed M. Tanveer Page 3 of 3
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Intensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleDari EverandIntensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleBelum ada peringkat
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsDari EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsBelum ada peringkat
- EXERCISEDokumen7 halamanEXERCISEvenkyBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture19 Physics of SoundDokumen2 halamanLecture19 Physics of SoundhuzaifaalyanhfBelum ada peringkat
- Lab ManualDokumen8 halamanLab ManualDavinder KakkarBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler EffectDokumen7 halamanDoppler EffectYugandhar VeeramachaneniBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Waves: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyDokumen15 halamanMechanical Waves: Exercise - I Exercise - Ii Exercise - Iii Answer KeyRoNBelum ada peringkat
- The Observed Change of Frequency of A Wave Due To The Motion of The Source of Sound or Light Is Called Doppler EffectDokumen8 halamanThe Observed Change of Frequency of A Wave Due To The Motion of The Source of Sound or Light Is Called Doppler Effectnorhazli ibrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Useful Concepts Wave TheoryDokumen4 halamanUseful Concepts Wave TheoryAli AsgerovBelum ada peringkat
- Genius PHYSICS: Doppler EffectDokumen4 halamanGenius PHYSICS: Doppler EffectAman BhuttaBelum ada peringkat
- The Doppler Effect (Or The Doppler Shift) Is The: Page 1 of 27Dokumen27 halamanThe Doppler Effect (Or The Doppler Shift) Is The: Page 1 of 27Mohamed Aswir AswirBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture21 - Doppler (Harvard)Dokumen7 halamanLecture21 - Doppler (Harvard)adityaBelum ada peringkat
- Acfrogdzj H0zar4vvglvjpkthv0adygcporwkzbktzoozc0dgpn 16cyq1jadd28wuetcftt7mtl6a5x9f34ib Vn8wsxxmmf95 4mutixnbxjykuf 6j3rqaqrzvj81uwv28hhygrdwvyj WWMDokumen3 halamanAcfrogdzj H0zar4vvglvjpkthv0adygcporwkzbktzoozc0dgpn 16cyq1jadd28wuetcftt7mtl6a5x9f34ib Vn8wsxxmmf95 4mutixnbxjykuf 6j3rqaqrzvj81uwv28hhygrdwvyj WWMmalanga.bangaBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler Effect (Theory) .PDF Module-3Dokumen8 halamanDoppler Effect (Theory) .PDF Module-3Raju SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Bansal Mechanical Waves PDFDokumen32 halamanBansal Mechanical Waves PDFAshish Ranjan33% (3)
- Geophysics Lec4Dokumen19 halamanGeophysics Lec4R P SrivastavBelum ada peringkat
- Sience PGDokumen8 halamanSience PGastridBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler Effect Problem Solving: DR Spencer Wheaton Dept. of Physics University of Cape TownDokumen29 halamanDoppler Effect Problem Solving: DR Spencer Wheaton Dept. of Physics University of Cape TownEthelbert Davitson100% (1)
- Linear AlgebraDokumen18 halamanLinear AlgebraT BlackBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler Effect:: (I) Observer (Detector) Moving, Source at RestDokumen3 halamanDoppler Effect:: (I) Observer (Detector) Moving, Source at RestMishkat Ahmed NaoshadBelum ada peringkat
- Unit I Quantum Mechanics-1Dokumen23 halamanUnit I Quantum Mechanics-1uttamshetty27Belum ada peringkat
- CH 26Dokumen21 halamanCH 26aBelum ada peringkat
- Classnote 524d3998cef81 PDFDokumen39 halamanClassnote 524d3998cef81 PDFNiravParekhBelum ada peringkat
- WavesDokumen34 halamanWavessridevi73Belum ada peringkat
- Doppler'S Effect Derivation IDokumen11 halamanDoppler'S Effect Derivation IRamesh Chand sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Amplitude Intensity SoundwavesDokumen23 halamanAmplitude Intensity SoundwavesJason LuBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler EffectDokumen38 halamanDoppler EffectIhtisham Ahmad ButtBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler EffectDokumen11 halamanDoppler Effect5G (15) Chuang Hui Hua VeraBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 02-Lecture 03Dokumen6 halamanUnit 02-Lecture 03Harshan SBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Physics Revision Notes Chapter 4Dokumen15 halaman12 Physics Revision Notes Chapter 4johana benjaminBelum ada peringkat
- Special Theory of Relativity 3Dokumen31 halamanSpecial Theory of Relativity 3msn3bscBelum ada peringkat
- Sound Waves: AccousticsDokumen10 halamanSound Waves: AccousticsDiyar KhoshnawBelum ada peringkat
- NEET UG Physics Ocsillations and Waves MCQs PDFDokumen59 halamanNEET UG Physics Ocsillations and Waves MCQs PDFMaqsood 9682619146Belum ada peringkat
- Ch15c11marks1and2ques SolutionDokumen16 halamanCh15c11marks1and2ques SolutionVikrant Shivajirao SambheraoBelum ada peringkat
- Specital Notes:: 2w B N VDokumen1 halamanSpecital Notes:: 2w B N VKunalKaushikBelum ada peringkat
- DopplerEffect PDFDokumen5 halamanDopplerEffect PDFNeelam KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- NEET UG Physics Ocsillations and Waves MCQs PDFDokumen48 halamanNEET UG Physics Ocsillations and Waves MCQs PDFTrilok AkhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Noise in Analog Circuits: DF F V VDokumen17 halamanNoise in Analog Circuits: DF F V VSarthak RautBelum ada peringkat
- Sound Waves:: Doppler EffectDokumen7 halamanSound Waves:: Doppler EffectDadan HamdaniBelum ada peringkat
- Real Analysis by BartleDokumen59 halamanReal Analysis by BartleabhishekBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Motion and Sound-1 PDFDokumen26 halamanWave Motion and Sound-1 PDFPriyanshu SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Waveopticsnotes 6903Dokumen14 halamanWaveopticsnotes 6903ammonish08Belum ada peringkat
- Part1 - NEET UG Physics Ocsillations and Waves MCQs PDFDokumen24 halamanPart1 - NEET UG Physics Ocsillations and Waves MCQs PDFTrilok AkhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Physics IADokumen15 halamanPhysics IAManishBelum ada peringkat
- Lec# 4Dokumen4 halamanLec# 4Batool MurtazaBelum ada peringkat
- Waves - II: Dr. Tariq Al-AbdullahDokumen37 halamanWaves - II: Dr. Tariq Al-AbdullahSlayer 45073Belum ada peringkat
- PH-107 (2018) Tutorial Sheet 10: V E. 0), For Which The ProbabilityDokumen3 halamanPH-107 (2018) Tutorial Sheet 10: V E. 0), For Which The ProbabilityVangala PorusBelum ada peringkat
- String WavesDokumen19 halamanString WavesRakesh Singh kushwahaBelum ada peringkat
- S.6 Physics WavesDokumen20 halamanS.6 Physics WavesSABAKAKI JOHNBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler Effect - OkDokumen66 halamanDoppler Effect - OkAntonioBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter # 20. Sound Version 1Dokumen5 halamanChapter # 20. Sound Version 1Daniel EmmanuelBelum ada peringkat
- (L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Waves - 11th NovemberDokumen77 halaman(L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Waves - 11th Novemberashish goelBelum ada peringkat
- Topic403 (Doppler Effect)Dokumen14 halamanTopic403 (Doppler Effect)Jeffry RamonidaBelum ada peringkat
- Affine CombinationDokumen3 halamanAffine CombinationRaul TevezBelum ada peringkat
- Doppler Effect: Roy D. Tipones, EceDokumen20 halamanDoppler Effect: Roy D. Tipones, EceErica May ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Wavesas21 023204Dokumen5 halamanWavesas21 023204kartik lakraBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Phenomenon: By: Nessy Marina (06101011014) Fresty Rianty (06101011034)Dokumen26 halamanWave Phenomenon: By: Nessy Marina (06101011014) Fresty Rianty (06101011034)Nessy Binti HosriBelum ada peringkat
- Topic4 Euclidean N-SpaceDokumen34 halamanTopic4 Euclidean N-SpaceFilipus Boby Setiawan BudimanBelum ada peringkat
- Sound WavesDokumen25 halamanSound WavesEng Bile LastroBelum ada peringkat
- PC360 Course Notes7Dokumen19 halamanPC360 Course Notes7Saied Aly SalamahBelum ada peringkat
- A Mathematical Model of Snowball MeltingDokumen5 halamanA Mathematical Model of Snowball MeltingJohnBelum ada peringkat
- 5 1doneDokumen3 halaman5 1doneeperlaBelum ada peringkat
- Universiti Malaysia Perlis: EQT 102 Engineering Mathematics II (Matematik Kejuruteraan II)Dokumen7 halamanUniversiti Malaysia Perlis: EQT 102 Engineering Mathematics II (Matematik Kejuruteraan II)lailarry321Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 - Free EnergyDokumen16 halamanLecture 4 - Free EnergyyudhiprasetyoBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Malaysian Matriculation Semester 1 Notes CompleteDokumen474 halamanPhysics Malaysian Matriculation Semester 1 Notes CompleteJay Bee96% (68)
- Notes On 2nd Physics by Asif RasheedDokumen7 halamanNotes On 2nd Physics by Asif RasheedAsif Rasheed RajputBelum ada peringkat
- Syrian Seismic Building Code - 2004Dokumen12 halamanSyrian Seismic Building Code - 2004Timur UzunogluBelum ada peringkat
- 21041.heat Transfer Thermal Management of ElectronicsDokumen526 halaman21041.heat Transfer Thermal Management of ElectronicsAli Adnan100% (3)
- 107D Iv Feg 05a 00012Dokumen68 halaman107D Iv Feg 05a 00012vinayak jadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus of Vector Valued FunctionsDokumen18 halamanCalculus of Vector Valued FunctionsDilo Tan100% (1)
- Task 1 - Esneyder QuevedoDokumen11 halamanTask 1 - Esneyder QuevedoEsneyder QuevedoBelum ada peringkat
- MH CET 2024 Sample PaperDokumen135 halamanMH CET 2024 Sample PaperRishi ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Failure Theories PDFDokumen2 halamanFailure Theories PDFBenBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion - Part I: Instructor Name: Dr. Kallol Mondal Institute: IIT KanpurDokumen2 halamanCorrosion - Part I: Instructor Name: Dr. Kallol Mondal Institute: IIT KanpurHareeshBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Mannual-Stewart and Gee's-2Dokumen17 halamanLab Mannual-Stewart and Gee's-2Sitaramaraju VengalarajuBelum ada peringkat
- Phuong Phap Tinh Tai Theo Phan Mem MistralDokumen8 halamanPhuong Phap Tinh Tai Theo Phan Mem Mistralntt_121987Belum ada peringkat
- Geiger Muller CounterDokumen27 halamanGeiger Muller CounterMuhammadSajidBelum ada peringkat
- Diffusion DefinitionDokumen7 halamanDiffusion DefinitionTechnical UmairjiBelum ada peringkat
- Degrees of FreedomDokumen9 halamanDegrees of FreedomReyner LozaBelum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Physics - Mind Map - Lakshya NEET 2024Dokumen1 halamanNuclear Physics - Mind Map - Lakshya NEET 2024aanyakaurchonaBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Field Pattern Due To A Circular Loop (Or Circular Wire) Carrying Current - Edusaint CoursesDokumen3 halamanMagnetic Field Pattern Due To A Circular Loop (Or Circular Wire) Carrying Current - Edusaint CoursesNitin BeniwalBelum ada peringkat
- Ph8151 Py1 Iq RejinpaulDokumen2 halamanPh8151 Py1 Iq RejinpaulriyaBelum ada peringkat
- An EMTP - RV Based Analysis of The Line SurgeDokumen6 halamanAn EMTP - RV Based Analysis of The Line SurgeEleazar Sierra EspinozaBelum ada peringkat
- Inflow Performance Relationships: Flowing Bottomhole Pressure (PWFDokumen6 halamanInflow Performance Relationships: Flowing Bottomhole Pressure (PWFashraff09Belum ada peringkat
- Must Know-Physics (NMAT)Dokumen18 halamanMust Know-Physics (NMAT)iya100% (2)
- Pre Foundation For Class IX by Career Point KotaDokumen8 halamanPre Foundation For Class IX by Career Point KotaLoveSahilSharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 02 - The 1st Law of ThermodynamicsDokumen24 halamanLecture 02 - The 1st Law of ThermodynamicsArc ZeroBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 Springer Nature Fully Open Access JournalsDokumen36 halaman2022 Springer Nature Fully Open Access JournalsEntertainment HubBelum ada peringkat
- Meteodyn Complex Terrain Modeling CFD Software Bolund Hill Round Robin TestDokumen18 halamanMeteodyn Complex Terrain Modeling CFD Software Bolund Hill Round Robin TestMeteodyn_UrbawindBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic PropertiesDokumen50 halamanPeriodic PropertiesVholts Villa Vitug100% (1)