Chemistry Unit 3 Edexcel As LEVEL Notes
Diunggah oleh
Books0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
477 tayangan1 halamanThis document provides information on various chemistry concepts and laboratory techniques:
1. It describes flame tests for different metal ions and chemical tests to identify common gases and anions such as sulfate, sulfite, ammonium, and carbonate.
2. Precipitation reactions and displacement reactions are explained along with observations of reaction products.
3. Laboratory techniques like distillation, reflux, titration, and determining melting points are outlined to purify and analyze organic compounds and solutions. Safety precautions are also noted.
Deskripsi Asli:
notes
Judul Asli
266236284 Chemistry Unit 3 Edexcel as LEVEL Notes
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document provides information on various chemistry concepts and laboratory techniques:
1. It describes flame tests for different metal ions and chemical tests to identify common gases and anions such as sulfate, sulfite, ammonium, and carbonate.
2. Precipitation reactions and displacement reactions are explained along with observations of reaction products.
3. Laboratory techniques like distillation, reflux, titration, and determining melting points are outlined to purify and analyze organic compounds and solutions. Safety precautions are also noted.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
477 tayangan1 halamanChemistry Unit 3 Edexcel As LEVEL Notes
Diunggah oleh
BooksThis document provides information on various chemistry concepts and laboratory techniques:
1. It describes flame tests for different metal ions and chemical tests to identify common gases and anions such as sulfate, sulfite, ammonium, and carbonate.
2. Precipitation reactions and displacement reactions are explained along with observations of reaction products.
3. Laboratory techniques like distillation, reflux, titration, and determining melting points are outlined to purify and analyze organic compounds and solutions. Safety precautions are also noted.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
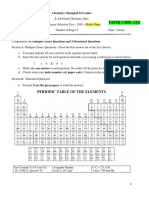
USEFUL CHARGES
CHEMISTRY UNIT 3 REVISION
Ag+ MNO4- CO32-
Zn 2+
HCO3 -
SO42-
FLAME TESTS HYDROGEN - burning splint; squeaky pop Al 3+
NO3 -
SO32-
(1) Add HCl to solid sample; this forms a OXYGEN - burnt splint; relights NH4+ OH- CR2O72-
salt CO2 - pass thru limewater; goes milky white O 2-
S 2-
PO43-
(2) Dip nichrome wire into sample with HCl NITROGEN DIOXIDE - brown gas evolved; blue litmus > red HALOGENOALKANE - AQ ALKALI
(3) Hold wire/salt into bunsen flame SULPHATE - add HCl and BaCl2; forms white ppt. of BaSO4 - react w/ aqueous alkali (e.g.
SULPHITE - add HCL/H2SO4 - sulphur dioxide produced
NaOH)
SULPHUR DIOXIDE - add K2Cr2O7; goes orange -> green
PRECIPITATION REACTIONS AMMONIA - turns blue litmus red (remember; its toxic - use fume - halogen substituted by OH
(1) Add nitric acid; remove impurities/neut. cup) - forms alcohol
OH AMMONIUM (NH4+) - add NaOh; turns blue litmus red (forms NH3)
(2) Add AgNO3; makes silver halide (AgX) - called hydrolysis/nucleophilic sub.
HCl - steamy fumes produced; ammonia on glass rod - white smoke
(3) Add NH3 (Ammonia) Solution CHLORINE - bleaches litmus; KBr red > brown (Br2 made) - fluoro least reactive; high bond
(4) Sunlight + 2AgX; darkens to make 2Ag & BROMINE - add to KI; goes from colourless > red/brown (I2) H
IODINE - starch indicator; turns dark blue (if iodine present) HALOGENOALKANE - AMMONIA
WATER - copper cobalt paper blue > pink - reacts w ammonia to make amine
HALIDE SALTS & SULPHURIC ACID C=C BOND - bromine water; turns brown > colourless
- in all reactions; forms HX (hydrogen halide) - amine is -NH2/-NH/-N-group
NITRATE - add NaOH and Devardas Alloy; makes NH3 (red lit >
- observation: steamy fumes (NH3:white blue)
- is example of nucleophilic sub.
smoke CARBONATE - add HCl; releases CO2 // or heat; decomp; HALOGENOALKANE -
KF + H2SO4 > KHSO4 + HF SAFETY and PRECAUTIONS
ALCOHOLIC
oxide/CO2
KCl + H2SO4 > KHSO4 + HCl REFLUX: organic compounds vapor condense back to reaction Toxic - use gloves & fume cupboard
vessel Flammable - use water bath, no
F/Cl n/a 4 > KHSO4 + steamy
KBr + H2SO HBr fumes (HCl) - r.o.r for organic compounds slow; reflux heats without losing flame
2HBr + H2SO4 > SO2 + Br2 +2H2O product Harmful gases - use fume cupboard
Br reduces to SO2 steamy fumes (HBr) +
- round bottom flask; reflux condenser with open tap; H20 in at Corrosive
brown gas (Br2) MELTING -POINT
wear googles and
bottom
DETERMINATION
I reduces to S and purple vapour (I2) + - use electric heater as ethanol/vapour can be flammable
- ensure H2O is in at bottom; ensure full condenser w/ no air bubbles - sharp bp. over small range - pure
YIELDS NEVER 100%
DISTILLATION - used to separate desired product from mixture
- transfer losses [loss during
- round bottomed flask, still head w thermometer (head at opposite -
purifc.]
end of condenser), reflux condenser and heater (electric)
DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS - vapour that is 2 from b.p. is condensed + collected in beaker - competing reactions
- more reactive halogen displaces less - cool flask in H2O; so flammable liquid doesn't escape + vig. carbon dioxide dissolves
-MAKE in H2O
UP 100CM3 OF SOLUTION
reaction
reactive halide ion from their compound
- NaHCO3; used to neutralize acid; shake in a separating funnel - discard rinsings; make up to mark
- Cl>Br>I - in separating funnel; open tap and run off bottom/top layers after - shake/mix/invert
FEHLINGS/BENEDICTS
- changes clear w/ organic solvent (2 layers - magnesium sulfate/calcium chloride are drying agents; remove SOLUTION
Cl2 + KBr (solution) = orange solution (Br2) H2O
+H (bond breaking) vs -H (bond making) - blue -> red w/ aldehyde (blue,
TITRATIONS - use to fnd the conc. of unknown solution; one known ket.)
- rinse pipette with solution and discard rinsings; use fller to fll to
CARBONATE/NITRATE THERMAL
mark - deep blue Cu2+ complex, reduced
STABILITY
- discharge pipette into conical flask; touch end of pipette onto to red Cu2O
- thermal stability increases down a group; surface TOLLENTS REAGENT
MAKING SALT SOLUTION
group 2 is less thermally stable than group - rinse burette w/ other solution & discard rinsings; funnel to fll
HALOGENOALKANES - add NaOH (aq), nitric acid and AgNO3 - add salt to water until it doesn't
1
1o ALCOHOL - distillation to ALDEHYDE +[O], reflux to CARB. ACID dissolve
- larger cations (more shielding/shells) 2o ALCOHOL - same as above, forms KETONES TYPES OF REAGENTS
- add salt in excess
- therefore, less polarising effect/distortion 3o ALCOHOL - cannot be oxidized therefore remains same Nucleophiles
!!!! 3o HALOGENOALKANES react fastest; due to SN1 vs SN2 - heat and allow to cool afterwards
- therefore more stable - electron pair donators
[g1 nitrate] - attack +ve ion or + with lone pair
decomp. to nitrite
ENTHALPY CHANCENO2)CALCULATIONS
& oxygen (O2) Electrophile
[g2 q=mc
(1) nitrate]
t (kJ) (2) fnd n (mol) (3) H=q/n - species (+) that accepts
decomp.
- be suretotooxide, nitrite
include sign&and
oxygen (incl. g1
unit (kJmol -1 Li)
) electrons
[g1 carbonate]
Common Errors - attracted to electron rich area
- heat loss due to apparatus; no lid/insulation TYPES OF REACTIONS aldehyde - cho (c=c)
- incomplete combustion (soot); less energy Addition - join two or more molecules to form one single
carb. acid large
- cooh Free Radicals
(100AE) ketone - =o
- beaker absorbs heat/alcohol evap; less nrg - highly reactive single atoms (-)
Polymerisation - join many simple monomer units to make polymer
with and unpaired electron.
- assumption of density/s.h.c of water Elimination - when a small group of atoms breaks from larger
Improvements BOND FISSION
molecule
Heterolytic
- add lid to beaker or cup Substitution - when one species replaced by another
Hydrolysis - split molecule into 2 new molecules (add H+ and OH-) - bond breaks unevenly;
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Mass Spectrometry: Fragmentation: Ethers & Sulfides ! ! ! !Dokumen57 halamanMass Spectrometry: Fragmentation: Ethers & Sulfides ! ! ! !sharifah sakinah syed soffianBelum ada peringkat
- A2 Test 11 Notes - Transition ElementsDokumen11 halamanA2 Test 11 Notes - Transition Elementswill bellBelum ada peringkat
- Dependent Variables - Time Taken For The Metal Carbonate To Decompose To ProduceDokumen3 halamanDependent Variables - Time Taken For The Metal Carbonate To Decompose To ProduceZou JunyiBelum ada peringkat
- NMR Booklet QuestionsDokumen21 halamanNMR Booklet QuestionsSumaira AliBelum ada peringkat
- 4.8 Further Organic Chemistry PDFDokumen11 halaman4.8 Further Organic Chemistry PDFMohamed ZaidhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chemsheets AS 1087 IR SpectrosDokumen67 halamanChemsheets AS 1087 IR SpectrosjnfjngsdjBelum ada peringkat
- Olympiad Model Paper 2018Dokumen9 halamanOlympiad Model Paper 2018deeyamullaBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristicDokumen8 halamanOrganic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristictasneemBelum ada peringkat
- Chemsheets As 049 (Dodgy Mechanisms)Dokumen2 halamanChemsheets As 049 (Dodgy Mechanisms)Arjuna50% (2)
- Chemistry Answers John Green and Sadru Damji Third Edition Ibid 2008Dokumen129 halamanChemistry Answers John Green and Sadru Damji Third Edition Ibid 2008bnkjaya-1100% (1)
- Answers To Eocqs: Cambridge International A Level ChemistryDokumen2 halamanAnswers To Eocqs: Cambridge International A Level ChemistryCarissa Tabina RiandaBelum ada peringkat
- Redox ReactionsDokumen29 halamanRedox ReactionsSoniaAlexBelum ada peringkat
- 2011 H2 Chem SRJC Prelim Paper 2 Suggested AnswersDokumen15 halaman2011 H2 Chem SRJC Prelim Paper 2 Suggested AnswersonnoezBelum ada peringkat
- Prescribed Practicals Lab Manual 2016Dokumen28 halamanPrescribed Practicals Lab Manual 2016rbgrossBelum ada peringkat
- A and As Level Physics Syllabus 2010Dokumen72 halamanA and As Level Physics Syllabus 2010amachqBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Unit 4 Notes: 4.1 Rates of ReactionsDokumen36 halamanChemistry Unit 4 Notes: 4.1 Rates of ReactionssarawongBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Qs With First Part of Answers PDFDokumen17 halamanThermodynamics Qs With First Part of Answers PDFAkyl AkanovBelum ada peringkat
- GCSE Quantitative Chemistry Home Learning SheetsDokumen30 halamanGCSE Quantitative Chemistry Home Learning SheetsShaheer HashmiBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Book AnswersDokumen37 halamanEdexcel IGCSE Chemistry Book AnswersFATIN NOORBelum ada peringkat
- ELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Dokumen33 halamanELECTROLYSIS o Level 2Tom TommmaBelum ada peringkat
- H2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)Dokumen12 halamanH2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)iuhihzBelum ada peringkat
- Collated Acids AnswersDokumen9 halamanCollated Acids AnswersmadonnaBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Electrode PotentialsDokumen26 halamanDetermination of Electrode PotentialsGliezl ImperialBelum ada peringkat
- SNAB Biology - Mark Scheme June 09Dokumen72 halamanSNAB Biology - Mark Scheme June 09Izzat Azmeer Ahmad0% (1)
- A Brief Review Article Various Synthesis and Therapeutic Importance of 1, 2, 4-Triazole and Its Derivatives.Dokumen18 halamanA Brief Review Article Various Synthesis and Therapeutic Importance of 1, 2, 4-Triazole and Its Derivatives.Dr Ali Malani100% (1)
- Chemsheets A2 1102 Amino Acids 2Dokumen1 halamanChemsheets A2 1102 Amino Acids 2Ebtihal AlharthiBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Skills User GuideDokumen28 halamanPractical Skills User GuideTharindu Dissanayake100% (1)
- 3-2 MSDokumen60 halaman3-2 MSputriBelum ada peringkat
- AQA Chemistry Data BookletDokumen2 halamanAQA Chemistry Data BookletRuby ChongBelum ada peringkat
- EOCQ Ans 30 PDFDokumen2 halamanEOCQ Ans 30 PDFSyed Hamza TariqBelum ada peringkat
- Born-Haber CycleDokumen5 halamanBorn-Haber CycleShahnaz AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6Dokumen148 halamanEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 6AbdulRahman MustafaBelum ada peringkat
- All Contents MergedDokumen154 halamanAll Contents MergedBAHAAHAHABelum ada peringkat
- Reaction List v002Dokumen5 halamanReaction List v002cecil3414Belum ada peringkat
- Reaction KineticsDokumen37 halamanReaction KineticsDaisyBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneDokumen30 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Transition Metals TestDokumen12 halamanTransition Metals Testpaulcampbell37Belum ada peringkat
- Edexcel IAS Bonding 1Dokumen14 halamanEdexcel IAS Bonding 1mostafa barakatBelum ada peringkat
- 9647 H2 Chemistry PlanningDokumen3 halaman9647 H2 Chemistry PlanningNicholas Ow100% (1)
- 14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture NotesDokumen22 halaman14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture Notesgeoboom12100% (4)
- Electrolysis ExerciseDokumen1 halamanElectrolysis ExerciseSeptina R Nurhalimah100% (1)
- IB Questionbank With ANSWERSDokumen6 halamanIB Questionbank With ANSWERSRaunak ChawlaBelum ada peringkat
- IAL Chemistry SB2 Answers Topic17Dokumen6 halamanIAL Chemistry SB2 Answers Topic17salmaBelum ada peringkat
- Aqueous Ion Colors: AP Chemistry: Colors Flame Test ColorsDokumen1 halamanAqueous Ion Colors: AP Chemistry: Colors Flame Test ColorsZhi ZhingBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 1 Section B Question-Answer Book BDokumen20 halamanPaper 1 Section B Question-Answer Book BKathy WongBelum ada peringkat
- AQA AS Level Chemistry Data SheetDokumen4 halamanAQA AS Level Chemistry Data SheetA100% (1)
- Gravimetric Analysis of Iron PDFDokumen3 halamanGravimetric Analysis of Iron PDFEmrico Luiz PerezBelum ada peringkat
- I A Extended Essay Ideas For Ib ChemistryDokumen3 halamanI A Extended Essay Ideas For Ib ChemistryAaliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Formulae and Equations Part 2Dokumen18 halamanChemical Formulae and Equations Part 2Mohd NorihwanBelum ada peringkat
- Equilibria (With Solution)Dokumen49 halamanEquilibria (With Solution)Nidhi SisodiaBelum ada peringkat
- A2 Further Practical SkillsDokumen8 halamanA2 Further Practical SkillsFiaz medico0% (1)
- Chemistry Unit 3 Edexcel (AS LEVEL) NotesDokumen1 halamanChemistry Unit 3 Edexcel (AS LEVEL) Notes--------29% (7)
- Csec Identification of Cations and AnionsDokumen6 halamanCsec Identification of Cations and AnionsDarrion BruceBelum ada peringkat
- Qualitative Analysis Summary Chart 1 - FLOW CHART FOR QUICK IDENTIFICATION OF CATIONS A) Using Sodium HydroxideDokumen5 halamanQualitative Analysis Summary Chart 1 - FLOW CHART FOR QUICK IDENTIFICATION OF CATIONS A) Using Sodium HydroxideJeremy TehBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Dokumen7 halamanEdexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Ibrahim BtBelum ada peringkat
- Data Sheet Revision PDFDokumen2 halamanData Sheet Revision PDFShifa RizwanBelum ada peringkat
- Our Common Future: Report of The World Commission On Environment and DevelopmentDokumen300 halamanOur Common Future: Report of The World Commission On Environment and DevelopmentRobert PollardBelum ada peringkat
- SDGs Guide To Interactions PDFDokumen239 halamanSDGs Guide To Interactions PDFMiguel PachioniBelum ada peringkat
- 5 +Pre-Production+ChecklistDokumen2 halaman5 +Pre-Production+ChecklistBooksBelum ada peringkat
- SDGs Guide To Interactions PDFDokumen239 halamanSDGs Guide To Interactions PDFMiguel PachioniBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Abroad Country ChartDokumen11 halamanTeaching Abroad Country ChartMZeeshanAkramBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - 2020 GKS-G Application Guidelines (English)Dokumen46 halaman4 - 2020 GKS-G Application Guidelines (English)stella wijaBelum ada peringkat
- Table 3 - : The 2019 SDG IndexDokumen2 halamanTable 3 - : The 2019 SDG IndexNoor ChahalBelum ada peringkat
- New As Biology Teaching SchemeDokumen18 halamanNew As Biology Teaching Schemeaby251188Belum ada peringkat
- 4area SectorDokumen7 halaman4area SectorBooksBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation of Errors: DefinitionsDokumen6 halamanCalculation of Errors: DefinitionsBooksBelum ada peringkat
- Calculations WorkbookDokumen113 halamanCalculations WorkbookAliAlbaker100% (1)
- CIE Resources: Educ - ICTDokumen7 halamanCIE Resources: Educ - ICTflowerkm44% (9)
- Solutions To Exercise 12 Carbohydrates: B.Sc. Applied Biology - Summer Semester 2021Dokumen4 halamanSolutions To Exercise 12 Carbohydrates: B.Sc. Applied Biology - Summer Semester 2021BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Scheme - A2 ConceptDokumen7 halamanTeaching Scheme - A2 Conceptaby251188Belum ada peringkat
- 54.1 Arenes Benzene Chemistry Ial Edexcel Chemistry QPDokumen19 halaman54.1 Arenes Benzene Chemistry Ial Edexcel Chemistry QPBooksBelum ada peringkat
- 0510 s16 RP 51Dokumen20 halaman0510 s16 RP 51BooksBelum ada peringkat
- 54.1 Arenes Benzene Chemistry Ial Edexcel Chemistry QPDokumen19 halaman54.1 Arenes Benzene Chemistry Ial Edexcel Chemistry QPBooksBelum ada peringkat
- SemicolonDokumen3 halamanSemicolonBooksBelum ada peringkat
- SalerioDokumen28 halamanSalerioRizqaFebrilianyBelum ada peringkat
- Core Practical Notes 1Dokumen14 halamanCore Practical Notes 1Books100% (1)
- 6403 LISTA NYAKUDYA Provisional Acceptance LetterDokumen3 halaman6403 LISTA NYAKUDYA Provisional Acceptance LetterBooksBelum ada peringkat
- History Revision IGCSEDokumen2 halamanHistory Revision IGCSEAndrea Gulli100% (1)
- C34 Formula SheetDokumen19 halamanC34 Formula SheetAmeerHamzaaBelum ada peringkat
- Vanilla Eclairs - Home Cooking AdventureDokumen2 halamanVanilla Eclairs - Home Cooking AdventureBooksBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Organic FlowchartsDokumen3 halamanChemistry Organic FlowchartsLouisefleming0% (1)
- Questions CompleteDokumen100 halamanQuestions CompleteBooks100% (1)
- Edexcel - IAL - Biology - Unit - 5 - (WBI05 - 01) - June-2018-scientific-article-Teacher-packDokumen10 halamanEdexcel - IAL - Biology - Unit - 5 - (WBI05 - 01) - June-2018-scientific-article-Teacher-packBooks100% (3)
- Carbonyl ChemistryDokumen17 halamanCarbonyl ChemistryBooksBelum ada peringkat
- 4325 2HDokumen28 halaman4325 2HBooksBelum ada peringkat
- 4.5 Equilibria PDFDokumen6 halaman4.5 Equilibria PDFNyak PereraBelum ada peringkat
- Sulfuric Acid PlantDokumen9 halamanSulfuric Acid PlantArriane JadeBelum ada peringkat
- Fda 10051Dokumen5 halamanFda 10051Ugodilinwa Nnaemeka La SonBelum ada peringkat
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers - MTG.Self-Assessment - QnsDokumen3 halamanAlcohols Phenols and Ethers - MTG.Self-Assessment - QnsVeankatapathy 613 Xl group BBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Estimation of Fe2 by KMnO4Dokumen3 halaman4 Estimation of Fe2 by KMnO4Shyamapada Shit100% (2)
- Inorganic Chem 2Dokumen68 halamanInorganic Chem 2yvg95100% (1)
- Energetic Materials - Inorganic Azides (OCRed)Dokumen33 halamanEnergetic Materials - Inorganic Azides (OCRed)alex100% (2)
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Topics Course Question Document SolutionDokumen64 halaman2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Topics Course Question Document Solutionalaamoalla02Belum ada peringkat
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 1 (E)Dokumen8 halamanIT Chem F5 Topical Test 1 (E)Norzawati NoordinBelum ada peringkat
- Essay On StalinDokumen8 halamanEssay On Stalinfz6zke9m100% (2)
- D128 PDFDokumen11 halamanD128 PDFJuan Diego ArizabalBelum ada peringkat
- Synthesis and Evaluation of Some Amine Compounds HDokumen8 halamanSynthesis and Evaluation of Some Amine Compounds HMaximiliano MackeviciusBelum ada peringkat
- SukanyaDokumen2 halamanSukanyaSrijaBelum ada peringkat
- Acid Bases Salts WorksheetDokumen5 halamanAcid Bases Salts WorksheetAvani AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry I (D. Pharm 1st Year)Dokumen35 halamanPharmaceutical Chemistry I (D. Pharm 1st Year)PrathiBelum ada peringkat
- Volumetric Determination of NitrateDokumen3 halamanVolumetric Determination of NitrateRuchita PoilkarBelum ada peringkat
- Solubility and Thermodynamic Functions For A 3-2 Salt, Samarium Sulfate, in Water and Sulfuric Acid Solutions at Temperatures To 350°cDokumen6 halamanSolubility and Thermodynamic Functions For A 3-2 Salt, Samarium Sulfate, in Water and Sulfuric Acid Solutions at Temperatures To 350°cWalter Sperandio SampaioBelum ada peringkat
- US4922043 Methyl ChlorideDokumen7 halamanUS4922043 Methyl ChlorideRizal EffendiBelum ada peringkat
- Silver Magflow MetersDokumen10 halamanSilver Magflow Metersgreggles69Belum ada peringkat
- Model Questions For The Final ExamDokumen17 halamanModel Questions For The Final ExamMohammad KhBelum ada peringkat
- MV Agusta f4 750 Engine ManualDokumen416 halamanMV Agusta f4 750 Engine ManualJoe deSanutsBelum ada peringkat
- Total Costs of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers With Concentric Helical Tube CoilsDokumen19 halamanTotal Costs of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers With Concentric Helical Tube CoilsJenni ArdiferraBelum ada peringkat
- Test For IonsDokumen4 halamanTest For Ionsdkbose3Belum ada peringkat
- JP16 General Tests PDFDokumen288 halamanJP16 General Tests PDFGopalaKrishnan SivaramanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen5 halamanChapter 1Nur AqilahBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 20483 2013 (E) - Character PDF DocumentDokumen18 halamanISO 20483 2013 (E) - Character PDF DocumentLorena Rafael TaipeBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/63Dokumen12 halamanCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/63krishav shuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Sip TemplateDokumen60 halamanSip TemplateJhun Lerry TayanBelum ada peringkat
- Zinc Dust Pigment For Paints - Specification: Indian StandardDokumen16 halamanZinc Dust Pigment For Paints - Specification: Indian StandardDevesh Kumar PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Analysis of Cuprous Oxide and Copper Pigments: Standard Test Methods ForDokumen5 halamanChemical Analysis of Cuprous Oxide and Copper Pigments: Standard Test Methods ForMadhavanBelum ada peringkat
- GR 7 Term 2 2020 Ns Resource PackDokumen26 halamanGR 7 Term 2 2020 Ns Resource PackLorraine NoloBelum ada peringkat