Chart of Hormones
Diunggah oleh
springdingDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chart of Hormones
Diunggah oleh
springdingHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Secreted By Secretion Action Stimulus for Secretion
Hypothalamus GRH -secretion of GH, sleep induction -sleep rhythm, stress, exercise
CRH -stimulates ACTH production (circadian rhy) -time set pt, stress, low gluc.
Cortisol
GnRH -release of LH and FSH for gametogenesis
Pulsatile secretion, if continuous LH, FSH
TRH -release of TSH -High temp, stress
-stimulates prolactin T4/T3
Adenohypophysis LH thecaandrogensOVULATION -E2 is inhibitory but then
Leydig testosterone stimulatory at ovulation
-T & inhibin
FSH granulosa aromatase to make E2 -P is stimulatory at mid cycle
Sertoli cells ABP + inhibin but inhibitory during luteal
For Spermatogenesis and maturation -T & inhibin
Prolactin milk synthesis and differention of milk cells -TRH, Sleep
pulsatile GnRH (contraceptive) -PRL Inhib. Factor
Too much prob. w/mensturl cycle
TSH thyroid T4/T3 -TRH, or low T4/T3
ACTH adrenal cortex cortisol /androgens Cortisol
-permissive for adrenarche
Neurohypophysis Oxytocin -contraction of uterine muscle (parturition) -partruition, suckling, coitus
(just stored) -and breast myoepi cells (milk letdown)
ADH - water absorption in the kidney -blood volume, osmolality
-pain/fear
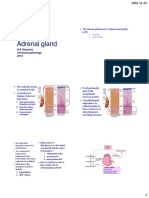
Adrenal Cortex Aldosterone (ZG) Na reabsorption and thus H2O at CCT -AngiotensinII,
(released after syn) -No P450 c17 (BP, or Na JGcells
-11B-OH steroid DH reninangIACEangII binds
to get rid of cortisol in MC- A1r PLC [Ca]
responsive cells SCC/P450c17Asaldosterone)
-Hyperkalemia
Thru DP and Ca channels
ACTH
Weak, cortisol similar activity
Cortisol (ZF) -insulin antagonist(glucose/glycogen syn) (hypo)CRH(pit)ACTH
17a Hydroxylase activity By breaking down protein, fat, etc appetite -pulsatile secretion
-maintains BP and myocardial performance
By allowing vasoconstriction
-anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive
By PLA2, M, IL-1 etc..
-Stimulates bone absorption
-cushings syndrome (HP, diabetes, obesity)
DHEA (ZR) -androgen production needs
17-20 lyase activity Cytochrome b5, Sult2A1
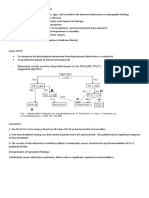
Synthesis: Cholesterol TO IMM (StAR) 21C=Progenolone [enzyme: SCC] RLS many different paths leading to above
Adrenal Medulla Dopamine -Flight or Flight Mechanism -anger, injury, pain, cold,
excerise, hypoglycemia
-AcH
-ACTH, Cortisol
Enzymes
-tyrosine hydroxylase + AA
decarboxylase
Norepinephrine - + Dopamine B-hydroxylase
Epinephrine* -+ PMNT
Parathyroid PTH Ca in serum, PO4 -decrease in Ca turns off th Ca
(from chief cells) -by PO4 uptake from PT (internalize NaP2) - sensor thus allowing
If too high - Ca uptake from DT/CD by HPopen transcription of PTH
EcaCCa entry (prevents IP3/PKC mediated
osteoperosis
-bone resorption: release of internal Ca)
osteoblastspg +Il-6osteoclastsresorb
*doesnt increase body supplies of calcium*
Thyroid Calcitonin Ca in serum - Ca or gastrin mediated
(c-cells) -TAL: reabsorption by el. driving force anticipation
-DT: entry by increasing intracellular Ca -low magnesium
-Bone: osteoclasts by cCAMP
Use to treat pagets disease
Thyroxin [T4] -Iodide, but too much
-made by organification Too little goiter
and coupling by TPO -TSH ( in hypothyroidism)
-Estrogen bound but not free
and active T4, T3
Triiodothyronine [T3]* -->activates some genes
(deioidinated T4 at GH for growth
target tissue) LDL r. in liver to (derease cholesterol)
a-myosin ATPase to increase CO
CNS devt/calorigenesis?
other genes (TRH in hyp/TSH in pit)
Liver, sun, 1a25(OH2)D3 Ca, PO4, CaPO4 (body stores) - Ca, high PTH, LowCT
liver, kidney (works through dimerizing -Duo: CaT1 + calbindin D9
RXRVDRE via Zn binding -CCD/DCD: ECaC + calbindin D28
domaintranscription) -SI/PT: NaPiIIb (apical PO4 channel)
Mutation rickets -Bone: type I colland alkaline phosphatase
BOUND/Nuclear Receptors= thyroid and steroid
FREE = amines & polypeptide hormones
Example of +ve Feedback: Pituitary LHoocygteestradiol Pituitary
-ve Feedback: Pituitary TSH Thyroid TH
REPRO
Testis Testosterone
Inhibin
Ovary Estradiol
Androgens
Pancreatic Islets Insulin
Glucagon
Somatostatin
Placenta hCG
hPL
Estradiol
Progesterone
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Internal Medicine Study GuideDokumen71 halamanInternal Medicine Study GuideMedicine4theMasses95% (19)
- Chemical Coordination and Integration PDFDokumen12 halamanChemical Coordination and Integration PDFSanjana SubramaniamBelum ada peringkat
- MI40-X - Supplement GuideDokumen22 halamanMI40-X - Supplement GuideBhimsen Budhathoki95% (20)
- Body CavitiesDokumen22 halamanBody Cavitiesapi-421876553Belum ada peringkat
- Naturalpath Intake Form - ADULTDokumen5 halamanNaturalpath Intake Form - ADULTcms_gcoles100% (1)
- Pituitary Disorders - Adrenal Disorders - Thyroid DiseasesDokumen207 halamanPituitary Disorders - Adrenal Disorders - Thyroid Diseasesnurliah armandBelum ada peringkat
- IMMUNOCAL Projected To Become #1Dokumen2 halamanIMMUNOCAL Projected To Become #1m_wfulton3815Belum ada peringkat
- Pituitary Gland: The Master GlandDokumen15 halamanPituitary Gland: The Master GlandMohammed ShahanewzBelum ada peringkat
- Niacin and NAD+ DeficiencyDokumen19 halamanNiacin and NAD+ DeficiencykatzrayBelum ada peringkat
- Components of The Blood & ImmunityDokumen47 halamanComponents of The Blood & ImmunityKafara EllisBelum ada peringkat
- For Best Viewing:: Open in Slide Show Mode Click On IconDokumen32 halamanFor Best Viewing:: Open in Slide Show Mode Click On IconSutapa PawarBelum ada peringkat
- Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDokumen3 halamanRenin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDivya Ranasaria100% (1)
- Endocrinology NotesDokumen24 halamanEndocrinology NotesEmily Dong100% (1)
- Pass 2010 ScheduleDokumen1 halamanPass 2010 SchedulewldcrdBelum ada peringkat
- Adrenocortical HyperfunctionDokumen132 halamanAdrenocortical Hyperfunctionshobharamkrishna100% (2)
- A New Theory and Case Report - David B. Miller D.D.S PDFDokumen11 halamanA New Theory and Case Report - David B. Miller D.D.S PDFdrgayen60420% (1)
- Topics For ExaminationDokumen1 halamanTopics For ExaminationBobet ReñaBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetic Food List To Eat PDFDokumen2 halamanDiabetic Food List To Eat PDFSandeepNairBelum ada peringkat
- Attia General Surgery Review ManualDokumen158 halamanAttia General Surgery Review Manualbphage100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Nursing Lecture Notes PDF - CompressDokumen43 halamanFundamentals of Nursing Lecture Notes PDF - CompressFelyn DavideBelum ada peringkat
- S1 Hippocratic Oath Seminar and Reading NotesDokumen7 halamanS1 Hippocratic Oath Seminar and Reading NotesTaraSubba1995Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 3: Control and Regulation: Physiological HomeostasisDokumen16 halamanUnit 3: Control and Regulation: Physiological HomeostasisaclumutBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotic DosingDokumen2 halamanAntibiotic Dosingscohen1Belum ada peringkat
- Case Study - Seizuring DogDokumen8 halamanCase Study - Seizuring Dogapi-301746262Belum ada peringkat
- Heparin Drip - PortfolioDokumen20 halamanHeparin Drip - Portfolioapi-306657745100% (1)
- GlaucomaDokumen5 halamanGlaucomaspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen12 halamanEndocrine SystemMa. Ellah Patricia M. Gutierrez100% (2)
- Adrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseDokumen8 halamanAdrenal Insufficiency and Addison's DiseaseyancefinceBelum ada peringkat
- MUST To KNOW in Parasitology PDFDokumen22 halamanMUST To KNOW in Parasitology PDFvillajanellaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac Arrest and CardiopulmonaryDokumen14 halamanCardiac Arrest and CardiopulmonaryCarlos UrquijoBelum ada peringkat
- Let The Saints Be JoyfulDokumen1 halamanLet The Saints Be JoyfulspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- MUST To KNOW in Medical Technology Laws EthicsDokumen12 halamanMUST To KNOW in Medical Technology Laws EthicsRona Salando100% (3)
- Hypotension: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDokumen4 halamanHypotension: Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factorsclubsanatate100% (1)
- Anaerobic BacteriaDokumen16 halamanAnaerobic BacteriaPriti Go0% (1)
- Anaerobic BacteriaDokumen16 halamanAnaerobic BacteriaPriti Go0% (1)
- Full Download Ebook PDF Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues 8th Edition PDFDokumen41 halamanFull Download Ebook PDF Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues 8th Edition PDFwilliam.decosta187100% (35)
- Anticancer Drugs PharmacologyDokumen19 halamanAnticancer Drugs PharmacologyZainBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis Treatment of Back Pain MedicationsDokumen41 halamanDiagnosis Treatment of Back Pain Medicationsrabin1994Belum ada peringkat
- Head To Toe AssessmentDokumen7 halamanHead To Toe AssessmentShine TorricerBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Anti HistaminesDokumen5 halamanNatural Anti Histamineskethan2212Belum ada peringkat
- Blood Pressure Range ChartDokumen5 halamanBlood Pressure Range Chartagdeshpande09Belum ada peringkat
- Prostitution in Five Countries: Violence and Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderDokumen22 halamanProstitution in Five Countries: Violence and Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderMMMMMMMMMMBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Interpretation of EcgsDokumen41 halamanRapid Interpretation of EcgsAdela abboudBelum ada peringkat
- Job Shadowing Thank You LetterDokumen1 halamanJob Shadowing Thank You Lettertml8397Belum ada peringkat
- Hypo Thyroid Is MDokumen3 halamanHypo Thyroid Is MjhBelum ada peringkat
- Jehovah's Witness and Blood Transfusions.Dokumen13 halamanJehovah's Witness and Blood Transfusions.MeddebateBelum ada peringkat
- West Visayas State University: Nursing ProcessDokumen4 halamanWest Visayas State University: Nursing ProcessPhylum Chordata100% (1)
- Diabetic and Endocrine EmergenciesDokumen21 halamanDiabetic and Endocrine Emergenciesjoko5157Belum ada peringkat
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDokumen49 halamanFluids and ElectrolytesvanessaBelum ada peringkat
- Primary Care Guidelines VertigoDokumen1 halamanPrimary Care Guidelines VertigoSyahidatul Kautsar NajibBelum ada peringkat
- IaemspcrDokumen5 halamanIaemspcrPrecious Ann Gonzales Reyes100% (1)
- Drugs and Defibrillation: Department of Anesthesiology & Reanimation General Hospital TasikmalayaDokumen20 halamanDrugs and Defibrillation: Department of Anesthesiology & Reanimation General Hospital TasikmalayaAfrida Sahestina100% (1)
- GI NotesDokumen19 halamanGI NotesBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Emergency MnemonicDokumen5 halamanEmergency Mnemonicanon_549623261Belum ada peringkat
- Hypertensive CrisisDokumen1 halamanHypertensive Crisisapi-495201002Belum ada peringkat
- Name: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859Dokumen12 halamanName: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859drng48Belum ada peringkat
- Obama CareDokumen13 halamanObama Careapi-24287846550% (2)
- DigoxinDokumen6 halamanDigoxinZiedTrikiBelum ada peringkat
- Cystic Fibrosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers May 2015Dokumen20 halamanCystic Fibrosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers May 2015Tapan AnkleshwariaBelum ada peringkat
- Psoriatic ArthritisDokumen12 halamanPsoriatic ArthritisSelvia RosadiBelum ada peringkat
- Improvement in Lactation With Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Herbal Medicine A Case StudyDokumen6 halamanImprovement in Lactation With Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Herbal Medicine A Case StudyCarleta Stan100% (1)
- Hypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid AxisDokumen15 halamanHypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid AxisEdmari Joy Pojas MontilBelum ada peringkat
- Quizlet EndoDokumen17 halamanQuizlet EndoemmaBelum ada peringkat
- Uterine FibroidsDokumen7 halamanUterine FibroidsGretchen TanBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily Value BiotinDokumen6 halamanVitamins: Vitamin What It Does Where Is It Found Daily Value BiotinissaiahnicolleBelum ada peringkat
- Barbiturate PoisoningDokumen17 halamanBarbiturate PoisoningRaymond ManjengwaBelum ada peringkat
- Hormone Therapy in The Postmenopausal Years - Considering Benefits and Risks in Clinical PracticDokumen36 halamanHormone Therapy in The Postmenopausal Years - Considering Benefits and Risks in Clinical PracticPaloma PeñaBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis Unknown EbookDokumen252 halamanDiagnosis Unknown Ebookapi-3738852Belum ada peringkat
- Patient Care SkillsDokumen15 halamanPatient Care SkillsIts John100% (1)
- Patho Exam 3Dokumen7 halamanPatho Exam 3menickel3Belum ada peringkat
- L ArginineDokumen1 halamanL ArginineNner G AsarBelum ada peringkat
- CPM16TH Intrapartum and Immediate Postpartum CareDokumen25 halamanCPM16TH Intrapartum and Immediate Postpartum CarespringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Airway MGTDokumen8 halamanAirway MGTspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFDokumen140 halamanPhilippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Wound ManagementDokumen19 halamanWound ManagementspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Femur 151205075833 Lva1 App6891Dokumen14 halamanFemur 151205075833 Lva1 App6891springdingBelum ada peringkat
- Airway MGTDokumen8 halamanAirway MGTspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Intracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsDokumen2 halamanIntracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- MJ Legal FundamentalsDokumen2 halamanMJ Legal FundamentalsspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Pedia Gi NotesDokumen34 halamanPedia Gi NotesspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Spirometry IntrepretationDokumen1 halamanSpirometry IntrepretationspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Intracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsDokumen2 halamanIntracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Zako HematologyDokumen35 halamanZako Hematologydoctormehmeteren8292Belum ada peringkat
- RNA VirusesDokumen11 halamanRNA VirusesKate Alyssa CatonBelum ada peringkat
- ShapesDokumen10 halamanShapesRosalind GohBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Secondhand SmokeDokumen3 halamanWhat Is Secondhand SmokespringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Indirect Inguinal Hernias Are The Most Common Groin Hernias in Men and WomenDokumen2 halamanIndirect Inguinal Hernias Are The Most Common Groin Hernias in Men and WomenspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Spirometry IntrepretationDokumen1 halamanSpirometry IntrepretationspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Glycogen Metabolism Index CardDokumen3 halamanGlycogen Metabolism Index CardspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Cancer in The Philippines Vol. IV Part 1 PDFDokumen78 halamanCancer in The Philippines Vol. IV Part 1 PDFspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Digging Up The Bones - MicrobiologyDokumen31 halamanDigging Up The Bones - MicrobiologyMossa Di Base100% (1)
- Neeraj's Notes Plan A Trip: USMLE CS: Step-1: Arrange The DocumentsDokumen0 halamanNeeraj's Notes Plan A Trip: USMLE CS: Step-1: Arrange The DocumentsvarrakeshBelum ada peringkat
- FIGOCEDokumen11 halamanFIGOCEAldwin TanuwijayaBelum ada peringkat
- 07 - Memorial AcclamationDokumen1 halaman07 - Memorial AcclamationspringdingBelum ada peringkat
- Polygraphy Module NewDokumen85 halamanPolygraphy Module NewFranco Angelo Reyes100% (1)
- LL INDIA January 6th 2002 MD/MS Entrance Examination Questions With Suggested AnswersDokumen26 halamanLL INDIA January 6th 2002 MD/MS Entrance Examination Questions With Suggested AnswersAnil KumarBelum ada peringkat
- PHEOCHROMOCYTOMADokumen37 halamanPHEOCHROMOCYTOMAYosi OktarinaBelum ada peringkat
- SON y SON-IDO - Origen Del Sonido ArticuladoDokumen214 halamanSON y SON-IDO - Origen Del Sonido ArticuladoDaniel Medvedov - ELKENOS ABEBelum ada peringkat
- SCI10 - Q3 - M3 - The Nervous SystemDokumen20 halamanSCI10 - Q3 - M3 - The Nervous SystemChristine Faith DimoBelum ada peringkat
- (2017) Toxicological Effects of Glycyrrhiza Glabra (Licorice) A ReviewDokumen16 halaman(2017) Toxicological Effects of Glycyrrhiza Glabra (Licorice) A ReviewicaBelum ada peringkat
- Geriatric Physiology by Dr. Leandro D. Vila and Dr. Edmee Y. MartinezDokumen72 halamanGeriatric Physiology by Dr. Leandro D. Vila and Dr. Edmee Y. MartinezMelissa SalayogBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Reproduksi Pria IkrDokumen141 halamanSistem Reproduksi Pria IkrNidiyamilhaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology-Endocrine SystemDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and Physiology-Endocrine SystemEixid Enna YeLikBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry Week 8 - LipidsDokumen7 halamanBiochemistry Week 8 - LipidsMicah JadeBelum ada peringkat
- IP-Worksheet-4-Endocrine System Response To Stress (Estomagulang)Dokumen2 halamanIP-Worksheet-4-Endocrine System Response To Stress (Estomagulang)Filmae EstomagulangBelum ada peringkat
- The Thymus Gland (Thymus) Aspects in Children (Review of Literature)Dokumen8 halamanThe Thymus Gland (Thymus) Aspects in Children (Review of Literature)Central Asian StudiesBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDokumen34 halaman10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieBelum ada peringkat
- A Study of The Relationship Between Stress and Psychosomatic DisordersDokumen4 halamanA Study of The Relationship Between Stress and Psychosomatic DisordersRubab shah Rubab shahBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Nutrition and Human Metabolism 7th Edition Gropper Solutions ManualDokumen9 halamanAdvanced Nutrition and Human Metabolism 7th Edition Gropper Solutions Manualjuliemooreowsgjmqaxc100% (20)
- Adrenal GlandDokumen9 halamanAdrenal GlandUhuebor DavidBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 9 Endocrine HormonesDokumen18 halamanLecture 9 Endocrine HormonesKC PalattaoBelum ada peringkat
- KVPY (SA) - Test-6 - Online Mock Test (Soln.Dokumen9 halamanKVPY (SA) - Test-6 - Online Mock Test (Soln.Subham AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- SOCIETY For ENDOCRINOLOGY ENDOCRINE EMERGENCY GUIDANCE - Emergency Management of Acute Adrenal Insufficiency (Adrenal Crisis) in Adult PatientsDokumen3 halamanSOCIETY For ENDOCRINOLOGY ENDOCRINE EMERGENCY GUIDANCE - Emergency Management of Acute Adrenal Insufficiency (Adrenal Crisis) in Adult PatientsMuhammad ReyhanBelum ada peringkat
- Biology and Behavior PDFDokumen62 halamanBiology and Behavior PDFsalvadorBelum ada peringkat
- Psychology GeneralDokumen73 halamanPsychology GeneralJessmirah LandinginBelum ada peringkat
- Med 12th Feb (1med)Dokumen39 halamanMed 12th Feb (1med)Naeem AminBelum ada peringkat
- Eating For Supercompensation (Ideal post-MI40X!)Dokumen3 halamanEating For Supercompensation (Ideal post-MI40X!)GJONES80Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12Dokumen24 halamanChapter 12MaskManBelum ada peringkat