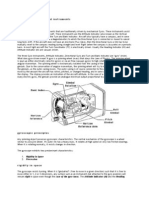
Instuments 1
Diunggah oleh
Pravin HandeJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Instuments 1
Diunggah oleh
Pravin HandeHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1.
When the spin axis of gyro becomes coincident with one or other axis of freedom the condition known as
a. Gimble lock
b. Gimble error
c. both (a) and (b)
d. apparent drift
2. Property of gyroscope is rigidity and precession. A Gyro has
a. gimble system for providing freedom about the desired axis.
b. rotor with weight concentrated around the rim to obtain high value of angular momentum
c. bearing with very low friction and rotor rotates at a very high speed
d. all above are correct
3. MTCS
a. An earth gyro is different from space gyro. The earth gyro is reference to the earth.
b. a gyro can have a pneumatic drive mechanism or electric drive mechanism
c. a and b are correct
d. A gyro need not have any erection mechanism and a space gyro is very useful in aircraft control.
4. MTCS:
a. A mercury switch in gyro horizon erection system operates by level sense by force of gravity.
b. a gyro cannot be moved immediately after switching off as moving a gyro will cause high precession forces and will
cause internal damage
c. both a and b correct
d. a is correct and b is wrong
5. Freedom about horizontal axis X and Y is known as
a. pitch and roll freedom
b. yaw freedom
c. employed in gyro horizon
d. a and c are correct
6. The purpose of erection device in gyro horizon is
a. to increase the speed of rotor
b. increase the mass of gyroscope
c. a and b are correct
d. to maintain gyro in vertical position during operation
7. The property of a Gyro is rigidity and precision
a. in Gyro Horizon property of rigidity is used to obtain stabilized horizon indication
b. in directional gyro property of precession is used to obtain heading information by slaving to magnetic heading.
c. the property of rigidity is used to obtain rate of turn indication
d. the property of precession is not used for any purpose in Gyro Horizon.
8. An Artificial Horizon employs:
a. A tied gyro.
b. An earth gyro.
c. A rate gyro.
9. One characteristic that a properly functioning gyro depends upon for operation is the:
a. Resistance to deflection of the gyro rotor.
b. Ability to resist precession at 90 degrees to an applied force.
c. Position of the gyro axis relative to the Earths axis.
10. The principle of rigidity is used for the operation of the following gyroscopic instruments:
a. Directional Gyro and Artificial Horizon.
b. Directional Gyro and turn indicator.
c. Artificial horizon and turn indicator.
d. Directional Gyro, Artificial Horizon and turn and slip indicator.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Asp 2020Dokumen197 halamanAsp 2020Pravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- CLASS TEST 01 Module 13Dokumen1 halamanCLASS TEST 01 Module 13Pravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- PN-ATPL Oral Exam1st Session of 2020Dokumen1 halamanPN-ATPL Oral Exam1st Session of 2020Pravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Radio Navigation Question RN MCQDokumen188 halamanRadio Navigation Question RN MCQPravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Module 13.8 Module 13Dokumen1 halamanModule 13.8 Module 13Pravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Government of India Technical Centre, Opp Safdurjung Airport, New DelhiDokumen3 halamanGovernment of India Technical Centre, Opp Safdurjung Airport, New DelhiPravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Series L PDFDokumen4 halamanSeries L PDFPravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- DGCA Module-3 QuesDokumen7 halamanDGCA Module-3 QuesPravin Hande100% (1)
- Surveillance Procedure ManualDokumen67 halamanSurveillance Procedure ManualPravin Hande100% (1)
- Government of India Office of The Director General of Civil AviationDokumen30 halamanGovernment of India Office of The Director General of Civil AviationPravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Airframe and Aircraft Components PDFDokumen168 halamanAirframe and Aircraft Components PDFPravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- APM - Part 2 Chapter 9 PDFDokumen256 halamanAPM - Part 2 Chapter 9 PDFPravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Government of India Technical Centre, Opp Safdurjung Airport, New DelhiDokumen3 halamanGovernment of India Technical Centre, Opp Safdurjung Airport, New DelhiPravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Car D2T-T2Dokumen10 halamanCar D2T-T2Pravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Wave Ratio Meter (SWR) : StandingDokumen2 halamanWave Ratio Meter (SWR) : StandingPravin HandeBelum ada peringkat
- Car 66 QuestionsDokumen1 halamanCar 66 QuestionsPravin Hande100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1091)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Instrument Rating QuestionsDokumen88 halamanInstrument Rating Questionskhushal bansalBelum ada peringkat
- 1303 FT (Retest)Dokumen6 halaman1303 FT (Retest)Akshay MaheshwariBelum ada peringkat
- The ARC Navomatic 300A Autopilot: Please Note Its Operation Highlighted in "Blue" BelowDokumen14 halamanThe ARC Navomatic 300A Autopilot: Please Note Its Operation Highlighted in "Blue" BelowJoão AlmeidaBelum ada peringkat
- Ex 6 - Straight and Level FlightDokumen15 halamanEx 6 - Straight and Level FlightMrunali MhatreBelum ada peringkat
- Hal Report LkoDokumen49 halamanHal Report Lkohina patelBelum ada peringkat
- ATPL Inst 2.5 PDFDokumen12 halamanATPL Inst 2.5 PDFKoustubh VadalkarBelum ada peringkat
- Pilot Aptitude Battery Test (PABT)Dokumen8 halamanPilot Aptitude Battery Test (PABT)Chandan BugaliaBelum ada peringkat
- 3300 Series Directional Gyro PDFDokumen12 halaman3300 Series Directional Gyro PDFHanh Trung Nguyen DucBelum ada peringkat
- Gyroscopic InstrumentDokumen67 halamanGyroscopic InstrumentMohamed Omar IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Gyroscopic Systems and InstrumentsDokumen3 halamanGyroscopic Systems and InstrumentsBookMaggotBelum ada peringkat
- C172RG Ground Training OutlineDokumen20 halamanC172RG Ground Training OutlineLeonel Fernandez100% (1)
- 02 - Basic - AhrsDokumen40 halaman02 - Basic - AhrsGazi JayedBelum ada peringkat
- 022 Instrumentation (922 Soru)Dokumen151 halaman022 Instrumentation (922 Soru)Barış Çiçek80% (5)
- General Nav - 2020: Scanned With CamscannerDokumen138 halamanGeneral Nav - 2020: Scanned With CamscannerDhruv VijayBelum ada peringkat
- Aviation English ExercisesDokumen57 halamanAviation English ExercisesLeila Hannane100% (7)
- Gyroscopic InstrumentsDokumen23 halamanGyroscopic Instrumentsvinay100% (1)
- Flight InstrumentsDokumen65 halamanFlight InstrumentsShirat Mohsin100% (1)
- 01 - PA-44-180 SystemsDokumen24 halaman01 - PA-44-180 SystemsMike AguirreBelum ada peringkat
- Training Report On Aircraft Instrument SystemsDokumen33 halamanTraining Report On Aircraft Instrument Systemsrohit2rBelum ada peringkat
- Instrumentations QBDokumen78 halamanInstrumentations QBSong Hiep100% (4)
- Flight InstrumentsDokumen8 halamanFlight InstrumentsBarnister OngaroBelum ada peringkat
- Instrument CourseDokumen320 halamanInstrument CourseabnzsaBelum ada peringkat
- Easa Instrument SysDokumen6 halamanEasa Instrument Sysadityarana531Belum ada peringkat
- CompassDokumen54 halamanCompasspasha.tenrani5034Belum ada peringkat
- RADIONAVDokumen29 halamanRADIONAVKer KigenBelum ada peringkat
- GyroscopesDokumen14 halamanGyroscopesEknoor BatraBelum ada peringkat
- ST180 Slaved Compass SystemDokumen32 halamanST180 Slaved Compass Systemsparkyoshida100% (1)
- Compass QuestionsDokumen26 halamanCompass QuestionsAMIYA SHANKAR PANDA75% (4)
- (56q en 1h30) : Air Data InstrumentsDokumen17 halaman(56q en 1h30) : Air Data InstrumentsNicolas Cuvelier100% (2)