Weebly Pedagogy Map
Diunggah oleh
api-351196801Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Weebly Pedagogy Map
Diunggah oleh
api-351196801Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
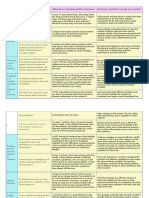
A/C General Key Ideas Low end pedagogy High end pedagogy Links to pedagogy ICT connections
Capabilities
Literacy Students should Explicitly teaching Provide opportunities Deep understanding: Students should use digital tools
understand the and communicating for students to learn students research and apply to help communicate with
language and the use with students to and build from other information relating to teachers, students, family and in
of literacy skills to model language use. student responses. knowledge to respond to the community. An example, of
communicate and Having students health-related issues and using ICTs in a HPE classroom
connect respectfully provide a summary of questions would be through the use of
with other people, key points of the computers. Individually or in
plus describing own lesson. Deep knowledge: students groups students answer
health and require advanced questions that are displayed on
information. They knowledge, understanding the students laptops. This
develop skills that and skills to actively engage digital tool teaches students
enhances students to with health issues and apply language, grammar, vocab and
access, analyse, new information to new understanding.
interpret, evaluate and ideas/questions
challenge the
changing evolution. Higher-order thinking:
students have ability to
selectively access and
critically analyse
information, health-related
from multiple sources to
help promote health and
wellbeing
Connectedness to the world:
students develop brochures
or other information sources
to help with promoting
health and wellbeing of
others.
Numeracy Students are provided Modelling data Students analyse and Higher-order thinking: Students learn to apply their
with opportunities to analyses using an elevate graphs, table students critically analyse learning to the real world.
use estimation and array of graphs with and data on particular graphs, reports, statistics etc. Students will also explore the
measurement to make an variety of topics. Then using to develop greater use of biomechanics through
sense of information measurements. data to support their understanding of health programs such as Coachs eye
related to various Providing examples conclusion information. which allows a variety of
skills. Eg. Nutrition and of reports, measurements and skills to be
outdoor navigation. advertisements and Knowledge integration: applied.
Using statistical media sources that students carry knowledge
reasoning and use statistical into other subjects, for
identifying patterns, information and example science.
students will be able data.
to consider trends, Connectedness to the world:
make predications and students learn about the
draw conclusions importance of time, speed,
through interpreting distance etc. for real-life
and analysing health relation and future
and physical activity assistance.
information.
Problem-based curriculum:
students calculate problems
that will be used in real-life
situations. Eg maps
Ethical Students discuss and Students model Students assist others Deep understanding: Students will understand the
Understanding elaborate on the interaction with and become aware of students elaborate with importance of privacy and
importance of respect, other students to different points of others to create new ideas settings when using multiple
fairness and share/discuss ideas views and prepare and form learning digital tools and social media
compassion, integrity around particular themselves to express discussions resources. They will develop
and valuing equality topics, issues or their own opinions. storing, acquiring and validating
and diversity for all. problems. Flexibility with the Knowledge integration: qualitive and quantitative data
Ethical principles are allowance of students discuss different from an array of sources.
examined through contributing at times aspects relating to the topic
different contexts and places or on the sporting field
including at home, at appropriate for them.
school, in Background knowledges:
relationships, in the students research and
community, in the discover diverse
environment, on the backgrounds and the
sporting field, and importance of inclusion
when using social
media. Cultural knowledges:
students consider
activities/sporting games
that best represent and
develop communication
amongst different cultural
groups
ICTs Students use ICTs for Students engage Students work to solve Higher-order thinking: Students learn about an array of
collaborating, with core knowledge real-life or life-like students create and publish digital tools and how they can
communicating, and skills enhanced problem or challenges their work to sites and be used in the real world. They
seeking help, by digital technology related to the subject. services to manage health will also investigate, analyse,
accessing information with a structured Students use a range and wellbeing. define, explore, design,
and analysing activity teacher modelling of traditional and/or implement, create through the
in health and physical and delivering. digital tools to create Deep understanding: different tools to develop
education. ICTs are and publish their students create videos, understanding.
used to develop plans, learning to state-wide podcasts etc. to collate their
for instance nutrition or national audience concepts and ideas
and physical activity through educational
participation. sites. Connectedness to the world:
students critically evaluate
technologies that are used
currently by students and
understanding the positive
and negative effects of the
actions in the community
Student direction: students
make their own decision on
how they want to
communicate their ideas
Active citizenship: students
communicate on other work
to create relationships and
create new learning for
others
Critical & Students learn their Students solve Provide opportunities Student direction: students Students will critically and
Creative critical and creative unfamiliar real world for students to develop and create creatively explore digital tools
Thinking skills through the problems and are integrate logic, reason, questions for themselves and design their own work to be
development of aware of the many imagination and and others published.
learning experiences possibilities. innovations to class
that encourage them activities. Connectedness to the world:
to question and seek students are able to make
solutions to health- their own decisions and have
related issues by an open mind in relation to
creating strategies to health-related topics
promote wellbeing.
Creative thinking is Substantive classroom:
supported through students and teacher have
game creation, class discussion that lead to
technique refinement open-minded opinions and
and dance making. ideas
Deep understanding:
students critically learn
through the invention of
own outcomes and open-
ended questions
Personal & Students progress on Explicit teaching Students are provided Active citizenship: students Students define real-world
Social their interpersonal when students are with opportunities to actively participate and problems and take into account
Capability skills, negotiation, working practice interpersonal communicate with others to the functional and non-
communication and collaboratively to skills as their skills will create understanding and functional requirements. They
appreciation of diverse practice be applied in an array appreciation of those with also will identify personal and
perspectives. They communication, of social situations in diverse needs social needs through
learn about validating, negotiation, time their lives. exploration of multiple sources
understanding, management and Cultural knowledge: students
analysing, and how to conflict resolution. critically evaluate different
respond to their own cultures to understand the
and others strengths, types and differences
emotions and values.
Knowledge integration:
students learn through an
array of theory or practical
based health and physical
activity components
Intercultural Similar to ethical Students build Provide opportunities Cultural knowledge: students Students would learn about the
Understanding understanding, knowledge on for students to understand the differences cultural groups through media
students also access histories and construct, create and in the array of cultural sources, like news articles
concepts and languages. communicate groups through research and online and also videos.
consequences of fair knowledge with other discussion
play, empathy and students
respect, equitable Connectedness to the world:
participation, plus students actively
develop skills on communicate and develop
making ethical skills to create respect
decisions and
understanding Knowledge integration:
consequences of their students develop skills that
actions. are integrated onto a
sporting field and off
Substantive conversation:
students collaborate in the
class to share opinions and
create additional knowledge
on cultures
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- BAERD GEN-007 Rev CDokumen27 halamanBAERD GEN-007 Rev CPaulBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Presentation DIP5000 enDokumen31 halamanPresentation DIP5000 enNeelakandan MasilamaniBelum ada peringkat
- Substitution TaskDokumen1 halamanSubstitution Taskapi-351196801Belum ada peringkat
- Substitutio 2Dokumen1 halamanSubstitutio 2api-351196801Belum ada peringkat
- Substitutio 1Dokumen1 halamanSubstitutio 1api-351196801Belum ada peringkat
- SubstitutionDokumen1 halamanSubstitutionapi-351196801Belum ada peringkat
- Embedded Task 1 Samr ModelDokumen1 halamanEmbedded Task 1 Samr Modelapi-351196801Belum ada peringkat
- Substitutio 1Dokumen1 halamanSubstitutio 1api-351196801Belum ada peringkat
- SubstitutionDokumen1 halamanSubstitutionapi-351196801Belum ada peringkat
- Reflection 2 - IctsDokumen3 halamanReflection 2 - Ictsapi-351196801Belum ada peringkat
- Introducing Maf and Mef Frameworks: Exploring Managed Addin FrameworkDokumen9 halamanIntroducing Maf and Mef Frameworks: Exploring Managed Addin Frameworkkris2tmgBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Compressed Air SystemDokumen23 halamanIntroduction To Compressed Air SystemMohd Zulhairi Mohd NoorBelum ada peringkat
- Vessel Maneuverability Guide E-Feb17Dokumen111 halamanVessel Maneuverability Guide E-Feb17KURNIAWAN100% (1)
- Heinzmann ControlsDokumen4 halamanHeinzmann ControlsShahzad AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- PS User Security SetupDokumen30 halamanPS User Security Setupabhi10augBelum ada peringkat
- Characterisation of Soil ESCI 16-2-2012Dokumen102 halamanCharacterisation of Soil ESCI 16-2-2012Divya Tadepalli100% (1)
- Manual de Serviço PDFDokumen394 halamanManual de Serviço PDFMarcos Antonio de Souza JuniorBelum ada peringkat
- Multilin 369Dokumen5 halamanMultilin 369Edo RossBelum ada peringkat
- Orkot® TLM & TXM Marine Bearings: Trelleborg Se Aling SolutionsDokumen7 halamanOrkot® TLM & TXM Marine Bearings: Trelleborg Se Aling Solutionsprodn123Belum ada peringkat
- Ooad Question BankDokumen5 halamanOoad Question Bankkhusboo_bhattBelum ada peringkat
- REVIEWDokumen12 halamanREVIEWGoka Agbesi GokaBelum ada peringkat
- MIS Officer Job Description and Person SpecificationDokumen3 halamanMIS Officer Job Description and Person SpecificationviewpawanBelum ada peringkat
- Project Reoprt On JSW SteelsDokumen30 halamanProject Reoprt On JSW SteelsSakthi Krishnan100% (1)
- All C PG and CPP Service ManualDokumen60 halamanAll C PG and CPP Service Manualhurantia100% (1)
- Mohiuddin Ahmad and Rafiqul Tarefder Department of Civil Engineering, University of New MexicoDokumen1 halamanMohiuddin Ahmad and Rafiqul Tarefder Department of Civil Engineering, University of New MexicoMohiuddin AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Design Checklist-9 USACE AngineeringDokumen15 halamanDesign Checklist-9 USACE AngineeringSankar CdmBelum ada peringkat
- North Museum Science & Engineering Fair 2015 WinnersDokumen9 halamanNorth Museum Science & Engineering Fair 2015 WinnersKarenShueyBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Microscopy Simplifi Ed: Bx53M/BxfmDokumen28 halamanAdvanced Microscopy Simplifi Ed: Bx53M/BxfmRepresentaciones y Distribuciones FALBelum ada peringkat
- Roland Mdx-650 Milling TutorialDokumen28 halamanRoland Mdx-650 Milling TutorialRavelly TelloBelum ada peringkat
- RRLDokumen3 halamanRRLNeil RosalesBelum ada peringkat
- Paul Ryan ResumeDokumen3 halamanPaul Ryan ResumePaul RyanBelum ada peringkat
- Pioneer PDP-501MX Plasma DisplayDokumen96 halamanPioneer PDP-501MX Plasma DisplayJavier RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Reckitt Benkiser (Case Study) For SCMDokumen13 halamanReckitt Benkiser (Case Study) For SCMDiptiman GuhaBelum ada peringkat
- Tolerance RingsDokumen13 halamanTolerance Ringspai mjrBelum ada peringkat
- Filtration 2Dokumen5 halamanFiltration 2Ramon Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Nyuszi SzabásmintaDokumen3 halamanNyuszi SzabásmintaKata Mihályfi100% (1)
- West Zone: South-West Zone: South Zone: Central Zone: North Zone: North West Zone: East ZoneDokumen6 halamanWest Zone: South-West Zone: South Zone: Central Zone: North Zone: North West Zone: East ZoneKanupriyamBelum ada peringkat