Definition of Terms
Diunggah oleh
nysea0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
14 tayangan2 halamanAphasia - inability to express oneself or to understand language. Aneurysm - a weakening or bulge in an arterial wall. Ataxia - impaired ability to coordinate movement, often seen as a staggering gait or postural imbalance.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniAphasia - inability to express oneself or to understand language. Aneurysm - a weakening or bulge in an arterial wall. Ataxia - impaired ability to coordinate movement, often seen as a staggering gait or postural imbalance.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
14 tayangan2 halamanDefinition of Terms
Diunggah oleh
nyseaAphasia - inability to express oneself or to understand language. Aneurysm - a weakening or bulge in an arterial wall. Ataxia - impaired ability to coordinate movement, often seen as a staggering gait or postural imbalance.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Definition of Terms
• Agnosia - failure to recognize familiar objects perceived by the senses.
• Agnosia- failure to recognize familiar objects perceived by the senses.
• Aneurysm – a weakening or bulge in an arterial wall.
• Aphasia – inability to express oneself or to understand language.
• Apraxia – inability to perform previously learned purposeful motor acts on a
voluntary basis.
• Apraxia- inability to perform previously learned purposeful motor acts on a
voluntary basis.
• Ataxia – impaired ability to coordinate movement, often seen as a staggering
gait or postural imbalance.
• Atherosclerosis- is the build up of a waxy plaque on the inside of blood vessels.
• Cardiomegaly - abnormal enlargement of the heart.
• Cholesterol - a eukaryotic sterol that in higher animals is the precursor of bile
acids and steroid hormones and a key constituent of cell membranes.
• Dysarthria – defects of articulation due to neurologic causes.
• Dyslexia- disorder involving difficulty in learning to read wordsw, letters, and
other symbols.
• Embolic Stroke- is a stroke caused by an embolus
• Enzymes: Proteins that act as catalysts in mediating and speeding a specific
chemical reaction.
• Expressive aphasia – inability to express oneself; often associated with
damage to the left frontal lobe area.
• Hemianopsia – blindness of half of the field of vision in one or both eyes.
• Hemianopsia- blindness of half of the field of vision in one or both eyes.
• Hemiplegia/ hemiparesis – weakness/ paralysis of one side of the body, or
part or it, due to an injury to the motor areas of the brain.
• Hemiplegia/Hemiparesis- weakness/paralysis of one side of the body, or
part of it.
• Hemorrhagic Stroke- bleeding within or around the brain.
• Horner’s syndrome- paralysis of nerves to the eye.
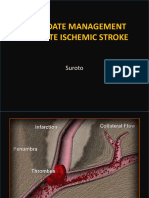
• Infarction – a zone of tissue deprived of blood supply.
• Ischemic stroke- is cause by a thrombotic or embolic blockage of blood flow
in the brain.
• Korsakoff’s syndrome – personality disorder characterized by psychosis,
disorientation, delirium, insomnia, and hallucinations.
• Penumbra syndrome – area of low cerebral blood flow.
• Perseveration – continued and automatic repetition of an activity or word or
phrase that is no longer appropriate.
• Receptive aphasia – inability to understand what someone else is saying;
often associated with damage to the temporal lobe area.
• Somatostatin: A hormone widely distributed throughout the body, especially
in the hypothalamus and pancreas that acts as an important regulator of
endocrine and nervous system function by inhibiting the secretion of several
other hormones such as growth hormone, insulin, and gastrin.
• Thrombotic stroke- is a stroke that is caused by a thrombus.
• Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs)- reversible episodes of neurologic
dysfunction caused by temporary, focal cerebral ischemia, and is also
called ‘’intermittent cerebrovascular insufficiency’’.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CalcI IntegralsDokumen90 halamanCalcI IntegralsnyseaBelum ada peringkat
- High Advanced Analogies 4Dokumen2 halamanHigh Advanced Analogies 4nyseaBelum ada peringkat
- High Advanced Analogies 1Dokumen2 halamanHigh Advanced Analogies 1nyseaBelum ada peringkat
- Introducing Leadership in Development: AnuaryDokumen14 halamanIntroducing Leadership in Development: AnuarynyseaBelum ada peringkat
- Cervical Cancer Is A Disease in Which Malignant (Cancer) Cells Form in The Tissues of The CervixDokumen21 halamanCervical Cancer Is A Disease in Which Malignant (Cancer) Cells Form in The Tissues of The CervixnyseaBelum ada peringkat
- Cervical Cancer OverviewDokumen22 halamanCervical Cancer OverviewnyseaBelum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- SSP HandbookDokumen246 halamanSSP Handbookacgarci83% (58)
- Mayo Medical ManualDokumen1.079 halamanMayo Medical Manualmakmad100% (7)
- Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers - UpToDateDokumen40 halamanManagement of Diabetic Foot Ulcers - UpToDatePriscillaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacological Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS) and Acute Limb Ischemia (ALI)Dokumen44 halamanPharmacological Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS) and Acute Limb Ischemia (ALI)hendratj90Belum ada peringkat
- Guia Aha Asa Stroke PDFDokumen77 halamanGuia Aha Asa Stroke PDFAndrea Cayufilo CarmonaBelum ada peringkat
- The Society For Vascular Surgery Clinical Practice Guidelines On Popliteal Artery AneurysmsDokumen12 halamanThe Society For Vascular Surgery Clinical Practice Guidelines On Popliteal Artery AneurysmsGhaithBelum ada peringkat
- Carotid Artery Disease FlyerDokumen2 halamanCarotid Artery Disease Flyerdinh son myBelum ada peringkat
- Blueprints - SurgeryDokumen164 halamanBlueprints - SurgeryKhalid Labadi50% (4)
- Libro Medicina NuclearDokumen46 halamanLibro Medicina NuclearGabriel PaucarBelum ada peringkat
- Rilantono, Lily L. 5 Rahasia Penyakit Kardiovaskular (PKV) - Jakarta: Badan Penerbit Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia 2012. p.279-287Dokumen1 halamanRilantono, Lily L. 5 Rahasia Penyakit Kardiovaskular (PKV) - Jakarta: Badan Penerbit Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia 2012. p.279-287Tegar DharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Bahir Dar University College of Medicine and Other Health ScienceDokumen61 halamanBahir Dar University College of Medicine and Other Health ScienceGizachew AsimareBelum ada peringkat
- An Update Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: SurotoDokumen36 halamanAn Update Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: SurotoShinta DianBelum ada peringkat
- Caso Clinico Electivas 3Dokumen9 halamanCaso Clinico Electivas 3MARIANGEL LAFONTBelum ada peringkat
- Health Psychology 8th Edition Taylor Test BankDokumen26 halamanHealth Psychology 8th Edition Taylor Test BankJosephMartinezwgrin100% (12)
- SARIDokumen138 halamanSARIohalu781391Belum ada peringkat
- Bok:978 3 642 40717 8Dokumen741 halamanBok:978 3 642 40717 8Ruben I. Garcia GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Perinatal Stroke in Fetuses, Preterm and Term Infants: R. Srivastava, J. Mailo, and M. DunbarDokumen14 halamanPerinatal Stroke in Fetuses, Preterm and Term Infants: R. Srivastava, J. Mailo, and M. Dunbarender izaguirreBelum ada peringkat
- ACLS Pocket CardDokumen6 halamanACLS Pocket Cardno_spam_mang80% (5)
- Altered Cerebral PerfusionDokumen3 halamanAltered Cerebral PerfusionRoseben SomidoBelum ada peringkat
- Defining Hemodynamic InstabilityDokumen9 halamanDefining Hemodynamic InstabilitynadyajondriBelum ada peringkat
- An StrokeDokumen22 halamanAn Strokejuanc0518Belum ada peringkat
- The Diabetes and The BrainDokumen26 halamanThe Diabetes and The BrainPrecious SantayanaBelum ada peringkat
- Neurological DiseasesDokumen91 halamanNeurological Diseasesrabia khalidBelum ada peringkat
- HBOT and Stroke - TBIDokumen24 halamanHBOT and Stroke - TBIStemCellMDBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology Short NotesDokumen10 halamanPathology Short NotesMr. PhorBelum ada peringkat
- Biopsychology, 6/E: ISBN: 0-205-42651-4Dokumen30 halamanBiopsychology, 6/E: ISBN: 0-205-42651-4Gînțăgan Denisa GabrielaBelum ada peringkat
- Vascular EmergencyDokumen324 halamanVascular EmergencyAhmed Aboud100% (1)
- 11-THROMBOLYTIC Drugs-Ishfaq 2016Dokumen34 halaman11-THROMBOLYTIC Drugs-Ishfaq 2016Eni Purwaeni100% (2)
- Postoperative Blindness After Spine Surgery in The Prone PositionDokumen17 halamanPostoperative Blindness After Spine Surgery in The Prone Positionwidget_13Belum ada peringkat