First Is First: Hull Profile Hull. Hull Profile, Final Final
Diunggah oleh
shahjada0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
3 tayangan1 halamanship resistance
Judul Asli
p118
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniship resistance
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
3 tayangan1 halamanFirst Is First: Hull Profile Hull. Hull Profile, Final Final
Diunggah oleh
shahjadaship resistance
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
near the keel).
The first approximation to the equivalent linearized
hull is thus found. Hence, using linearized wavemaking source theory,
an approximation to the hull wave profile can be calculated, first for
the equivalent linearized hull and then transformed back to the real
hull. The original double-model distributions of pressure and flow
direction over the hull surface are then altered to become more
consistent with this hull wave profile, a new set of isobars is found,
and the process is repeated a sufficient number of times to give a
converged final solution.
The final solution for the pressure distribution over the hull enables
the sinkage and trim to be calculated. The program contains an option
to re-calculate the flow round the hull with its offsets modified to
represent the hull when sinkage and trim have taken place.
3. Rankine source method
The method is still fundamentally the same as that described in ref 2.
The hull and its double model reflection in the free surface are
divided into panels, and further panels are situated in the region
surrounding the hull in the plane of the undisturbed free surface.
Rankine sources are distributed on each panel and the source strengths
found so that the hull surface boundary condition is met and a non
linear form of the free surface condition is also satisfied.
In principle the free surface panel distribution should extend over
the entire region where there are significant waves. In practice the
region of free surface panels has to be severely limited in extent.
The neglect of the source distribution outside of this truncated
region in the former computations was liable to cause appreciable errors.
In the present modified method these difficulties are partially
surmounted as follows. The number of "active" free surface panels is
118
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 2009 - Adaptive Grid Refinement For Unsteady Ship Flow and Ship Motion Simulation - Nutts09 - Wackers Et Al. 1Dokumen6 halaman2009 - Adaptive Grid Refinement For Unsteady Ship Flow and Ship Motion Simulation - Nutts09 - Wackers Et Al. 1tsaipeterBelum ada peringkat
- FLD 3890Dokumen21 halamanFLD 3890Rhu DynzBelum ada peringkat
- An Improved Shape For Hermetic Compressor HousingsDokumen7 halamanAn Improved Shape For Hermetic Compressor HousingsMohammed Naim UddinBelum ada peringkat
- EpplerDokumen5 halamanEpplersumon1314Belum ada peringkat
- Predict Distillation Tray Efficiency: Reactions and SeparationsDokumen7 halamanPredict Distillation Tray Efficiency: Reactions and SeparationsJohn AnthoniBelum ada peringkat
- Lee-Kim2006 Article OptimizationOfMassBleedControlDokumen7 halamanLee-Kim2006 Article OptimizationOfMassBleedControlnanocardosoBelum ada peringkat
- B Bits, B Bytes. Log: FieldDokumen15 halamanB Bits, B Bytes. Log: FieldLuis SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Equivalent Plane Strain Modeling of Vertical Drains in Soft Ground Under Embankment Combined With Vacuum PreloadingDokumen18 halamanEquivalent Plane Strain Modeling of Vertical Drains in Soft Ground Under Embankment Combined With Vacuum PreloadingFarid Maruf0% (1)
- Part 1 RANS Solution Using A Medium Resolution MeshDokumen15 halamanPart 1 RANS Solution Using A Medium Resolution Meshmorris gichuhiBelum ada peringkat
- An Improved Finite-Difference Calculation of Downhole Dynamometer Cards For Sucker-Rod Pumps PDFDokumen7 halamanAn Improved Finite-Difference Calculation of Downhole Dynamometer Cards For Sucker-Rod Pumps PDFlord azraelBelum ada peringkat
- SPE 104581 Transient Behavior of Multilateral Wells in Numerical Models: A Hybrid Analytical-Numerical ApproachDokumen14 halamanSPE 104581 Transient Behavior of Multilateral Wells in Numerical Models: A Hybrid Analytical-Numerical ApproachhusseinhshBelum ada peringkat
- Panel MethodsDokumen94 halamanPanel MethodsGoutam Kumar SahaBelum ada peringkat
- Top 5 Methods of Estimation of Peak FlowDokumen10 halamanTop 5 Methods of Estimation of Peak Flowchetan powerBelum ada peringkat
- Laminar Boundary Layer On Oscillating Plates and CylindersDokumen14 halamanLaminar Boundary Layer On Oscillating Plates and CylindersSafaa Hameed Al NaseryBelum ada peringkat
- 17 PDFDokumen3 halaman17 PDFJPYadavBelum ada peringkat
- Applications and Limitations of Potential Flow Codes For The Wave Making ProblemDokumen18 halamanApplications and Limitations of Potential Flow Codes For The Wave Making ProblemRita Morice GómezBelum ada peringkat
- Y. F. Yao and N. D. Sandham - Direct Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Trailing-Edge Flow With Base Flow ControlDokumen9 halamanY. F. Yao and N. D. Sandham - Direct Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Trailing-Edge Flow With Base Flow ControlWhiteLighteBelum ada peringkat
- 2016 Improvement of The Acoustic Black Hole Effect by Using Energy Transfer Due To Geometric NonlinearityDokumen12 halaman2016 Improvement of The Acoustic Black Hole Effect by Using Energy Transfer Due To Geometric Nonlinearitydhiraj.biswasBelum ada peringkat
- Optimization of Non-Hydrostatic Euler Model For Water Waves: A, B A, B, B, CDokumen17 halamanOptimization of Non-Hydrostatic Euler Model For Water Waves: A, B A, B, B, CCesar Lines GuardapucllaBelum ada peringkat
- Documents null-Design+DischargeDokumen12 halamanDocuments null-Design+DischargeMaitri Gwyneth Zoe PetalloBelum ada peringkat
- J9 Microfluidics HaikDokumen9 halamanJ9 Microfluidics Haikmkilani77Belum ada peringkat
- Mechanisms of Foam Flow in Porous Media: Apparent Viscosity in Smooth CapillariesDokumen15 halamanMechanisms of Foam Flow in Porous Media: Apparent Viscosity in Smooth CapillariesfylypeBelum ada peringkat
- Transient Response of Nonhomogeneous Aquifers: Member Aime Standard Oil California San FranciscoDokumen11 halamanTransient Response of Nonhomogeneous Aquifers: Member Aime Standard Oil California San Franciscotomk2220Belum ada peringkat
- Computational Aerodynamics: Name:Akhil Raj - Awale ROLL NO:17951A2105Dokumen15 halamanComputational Aerodynamics: Name:Akhil Raj - Awale ROLL NO:17951A2105Jaikar Jaikar RahulBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen21 halamanChapter 4Cris MastrodomenicoBelum ada peringkat
- Embrechts Und Billon - 2011 - Theoretical Determination of The Random-IncidenceDokumen11 halamanEmbrechts Und Billon - 2011 - Theoretical Determination of The Random-IncidenceTrojanBelum ada peringkat
- SPE 81043 Exact Solution of Two Layer Reservoir With Crossflow Under Constant Pressure ConditionDokumen6 halamanSPE 81043 Exact Solution of Two Layer Reservoir With Crossflow Under Constant Pressure ConditionWaleed Barakat MariaBelum ada peringkat
- RPN01 - Optimal Parabolic - IWWADokumen6 halamanRPN01 - Optimal Parabolic - IWWAJ.R. EnginnerBelum ada peringkat
- FM 3e SI Chap09 LectureDokumen111 halamanFM 3e SI Chap09 LectureRuben SegarBelum ada peringkat
- Far Field Boundary Conditions For Compressible FlowsDokumen18 halamanFar Field Boundary Conditions For Compressible FlowsmicBelum ada peringkat
- Vibroseis Deconvolution: A Comparison of Cross-Correlation and Frequency-Domain Sweep DeconvolutionDokumen12 halamanVibroseis Deconvolution: A Comparison of Cross-Correlation and Frequency-Domain Sweep DeconvolutionRoger WaLtersBelum ada peringkat
- Spe 98035 MS PDokumen9 halamanSpe 98035 MS PJose Gregorio Fariñas GagoBelum ada peringkat
- Bölüm 4 TümüDokumen32 halamanBölüm 4 Tümüramazanvank40Belum ada peringkat
- SPE 114591 Rate Transient Analysis in Naturally Fractured Shale Gas ReservoirsDokumen17 halamanSPE 114591 Rate Transient Analysis in Naturally Fractured Shale Gas ReservoirsIbrahim ElsawyBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation of The Flow Around The Surface Combatant DTMB Model 5415 atDokumen9 halamanSimulation of The Flow Around The Surface Combatant DTMB Model 5415 atFatwa AzamBelum ada peringkat
- One-Dimensional Compressible Flow: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesDari EverandOne-Dimensional Compressible Flow: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesBelum ada peringkat
- NE of The Most Important Applications Of: Generalized Plane Wave Horn TheoryDokumen13 halamanNE of The Most Important Applications Of: Generalized Plane Wave Horn TheoryBob BeduneauBelum ada peringkat
- Effective Recombination Velocity of Textured Surfaces: Kanglin Xiong Shulong Lu Desheng Jiang Jianrong Dong Hui YangDokumen4 halamanEffective Recombination Velocity of Textured Surfaces: Kanglin Xiong Shulong Lu Desheng Jiang Jianrong Dong Hui YangRajeev PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Cinco Ley - PVP - YNF PDFDokumen4 halamanCinco Ley - PVP - YNF PDFMiguel Angel Vidal ArangoBelum ada peringkat
- Methods For Streambed Mobility/ Stability AnalysisDokumen34 halamanMethods For Streambed Mobility/ Stability AnalysisVera FerreiraBelum ada peringkat
- Launch Vehicle - HeatFlux - ASET2012 - VSSC - TrivandrumDokumen5 halamanLaunch Vehicle - HeatFlux - ASET2012 - VSSC - Trivandrumअभिषेक जैनBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of Reservoir Heterogeneity On Performance: S F IETYDokumen11 halamanEffects of Reservoir Heterogeneity On Performance: S F IETYmartin ferrerBelum ada peringkat
- ICAS2022 0630 PaperDokumen7 halamanICAS2022 0630 PaperRahul jwsBelum ada peringkat
- 96 GT 039 DeMeulenaereDokumen11 halaman96 GT 039 DeMeulenaereBhaskar NandiBelum ada peringkat
- International Journal of Marine Energy: D.S. Coles, L.S. Blunden, A.S. BahajDokumen19 halamanInternational Journal of Marine Energy: D.S. Coles, L.S. Blunden, A.S. BahajNasteho DjamaBelum ada peringkat
- Evolving Sub-Grid Turbulence For Smoke AnimationDokumen7 halamanEvolving Sub-Grid Turbulence For Smoke AnimationMadi ShimizuBelum ada peringkat
- Flood 2007 DasDokumen8 halamanFlood 2007 DaselsaBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Well Control On Constrained Sparse Spike Seismic InversionDokumen9 halamanEffect of Well Control On Constrained Sparse Spike Seismic InversionCerón Niño SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- SPE 77951 Multirate Test in Horizontal Wells: SurcolombianaDokumen12 halamanSPE 77951 Multirate Test in Horizontal Wells: SurcolombianaJorge RochaBelum ada peringkat
- Simulations of Flow Around A Confined Oscillating Circular Cylinder Using A Virtual Boundary Method - LazarkovDokumen10 halamanSimulations of Flow Around A Confined Oscillating Circular Cylinder Using A Virtual Boundary Method - LazarkovSabir GojayevBelum ada peringkat
- Fully Nonlinear Properties of Periodic Waves Shoaling Over SlopesDokumen14 halamanFully Nonlinear Properties of Periodic Waves Shoaling Over SlopesMed Ali MaatougBelum ada peringkat
- Spe 1236 PaDokumen11 halamanSpe 1236 Papetra wattimuryBelum ada peringkat
- Active Control of Jet MixingDokumen10 halamanActive Control of Jet MixingJINU CHANDRANBelum ada peringkat
- Ain Shams Engineering Journal: Dilshad A. HaleemDokumen5 halamanAin Shams Engineering Journal: Dilshad A. HaleemDilshad A. HaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Materi 7 - DST - Maxsurf MotionDokumen14 halamanMateri 7 - DST - Maxsurf MotionIlmia HamzahBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Data Processing SequenceDokumen15 halamanBasic Data Processing SequenceMuhammed TarekBelum ada peringkat
- Stochastic Methods for Flow in Porous Media: Coping with UncertaintiesDari EverandStochastic Methods for Flow in Porous Media: Coping with UncertaintiesBelum ada peringkat
- Blade Area Ratio Defined: A Hydrocomp Technical ReportDokumen2 halamanBlade Area Ratio Defined: A Hydrocomp Technical ReportshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- NAME 591 Final Report Ice Princess - AppendicesDokumen54 halamanNAME 591 Final Report Ice Princess - AppendicesshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- CFD Simulation of A Planing Hull: International Journal For Traffic and Transport Engineering (IJTTE) September 2019Dokumen7 halamanCFD Simulation of A Planing Hull: International Journal For Traffic and Transport Engineering (IJTTE) September 2019shahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- PROBABILISTIC DAMAGE STABILITY: Knowledge and UnderstandingDokumen24 halamanPROBABILISTIC DAMAGE STABILITY: Knowledge and UnderstandingshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Best Practices For Marine Propeller Design - Metalphoto of CincinnatiDokumen7 halaman5 Best Practices For Marine Propeller Design - Metalphoto of CincinnatishahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Vessel Performance: Technical Solutions For Operational ChallengesDokumen8 halamanVessel Performance: Technical Solutions For Operational Challengesshahjada100% (1)
- Seakeeping and Maneuvering Prof. Dr. S. Beji 2Dokumen17 halamanSeakeeping and Maneuvering Prof. Dr. S. Beji 2shahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Ocean Engineering: Michael D. Woodward, Martijn Van Rijsbergen, Keith W. Hutchinson, Andrew ScottDokumen8 halamanOcean Engineering: Michael D. Woodward, Martijn Van Rijsbergen, Keith W. Hutchinson, Andrew ScottshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Ks 0179 1 Procedure For Inclining Test and Determination of Lightship Displace EngDokumen15 halamanKs 0179 1 Procedure For Inclining Test and Determination of Lightship Displace EngshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Vessel Performance - KONGSBERG DIGITALDokumen6 halamanVessel Performance - KONGSBERG DIGITALshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Another Blow On The Torn Down Wall-The Inclining Experiment: Selahattin Ozsayan Metin TaylanDokumen19 halamanAnother Blow On The Torn Down Wall-The Inclining Experiment: Selahattin Ozsayan Metin TaylanshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Marine Survey Practice - Surveyor Guide Notes For Ship Stability, Inclining Test ProcedureDokumen11 halamanMarine Survey Practice - Surveyor Guide Notes For Ship Stability, Inclining Test ProcedureshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Tank Capacity TableDokumen3 halamanTank Capacity TableshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Computation of Total Resistance of Ships PDFDokumen20 halamanComputation of Total Resistance of Ships PDFshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Longitudinal Ship Launching: Daniel Žgomba Anton Turk Marko Hadjina Dijana Pražić Ivan MargićDokumen12 halamanLongitudinal Ship Launching: Daniel Žgomba Anton Turk Marko Hadjina Dijana Pražić Ivan MargićshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Technical and Cost Model For Slipway DevelopmentDokumen36 halamanTechnical and Cost Model For Slipway DevelopmentshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- KCS Resistance Calculation: Click To Edit Master Title StyleDokumen57 halamanKCS Resistance Calculation: Click To Edit Master Title StyleshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On Hydrodynamic Coefficients Estimation ofDokumen8 halamanA Study On Hydrodynamic Coefficients Estimation ofshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Shallow Water Resistance Charts For Preliminary Vessel DesignDokumen18 halamanShallow Water Resistance Charts For Preliminary Vessel DesignshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Application of RANSE Based Simulations FDokumen4 halamanApplication of RANSE Based Simulations FshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To Railway Drydocks and Transfer SystemsDokumen9 halamanAn Introduction To Railway Drydocks and Transfer SystemsshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Slipway DesignsDokumen30 halamanAnalysis of Slipway DesignsshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
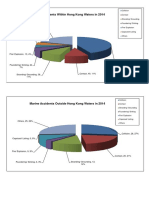
- Marine Accidents Within Hong Kong Waters in 2014Dokumen1 halamanMarine Accidents Within Hong Kong Waters in 2014shahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- An Empirical Survey On The Role of Human Error in Marine IncidentsDokumen5 halamanAn Empirical Survey On The Role of Human Error in Marine IncidentsshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- 2011 Mullai PaulssonDokumen14 halaman2011 Mullai PaulssonshahjadaBelum ada peringkat
- Bernoulli Effect Accidents ShipsDokumen14 halamanBernoulli Effect Accidents ShipsshahjadaBelum ada peringkat