Improve Textile Dye Fastness with Non-Formaldehyde Fixing Agents
Diunggah oleh
MaggieWoodsDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Improve Textile Dye Fastness with Non-Formaldehyde Fixing Agents
Diunggah oleh
MaggieWoodsHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
D y e i n g F i n i s h i n g P r i n t i n g C o a t i n g
<Technical Briefing> Dye Fixing
Fix the Dye Fixing Problem
<Technical Briefing>
on Textile Substrates
By Dr Naresh M. Saraf, of Sarex, India
Introduction
Dye-fixing agents are of considerable interest in
the art of textile coloration. Dyed and printed
fabrics often have unsatisfactory wet fastness,
especially washing and water fastness. This
is found with dyeings carried out using direct
dyestuffs, acid dyestuffs and, to a lesser extent,
reactive dyestuffs.
All direct dyestuffs are regarded as being
substantive to cellulosic materials, whereas
reactive dyes are considered substantive as
well as reactive. Direct dyes are normally 27
applied from an aqueous dyebath containing
an electrolyte. They impart moderate to good
light fastness but moderate to poor washing
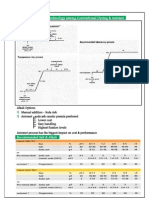
Figure 2: Dye-fixing agents for polyamide:
fastness. acid dyestuffs
Although the dyeing process with direct
dyes is simple, it lacks in the wet-fastness
properties. In the case of all reactive dyestuffs,
part of the dyestuff will react chemically with a
hydroxyl group on the cellulosic fibre and part
of the dyestuff will react with the water present
in the dyebath to form hydrolysed dye. The
un-reacted and hydrolysed dye may be removed Figure1: Dye-fixing agents for cotton: reactive and direct dyestuffs
by repeated washing; however, the washing-off
process is more costly and time consuming than
the dye-fixing process. by the electrostatic force. The ionic bonding or In order to improve the fastness of dyed
In industry, cationic dye-fixing agents electrostatic force are relatively weak and can materials, an aftertreatment dye-fixing agent
are used to overcome the problem of poor lead to the problem of wash fastness. is typically applied to the dyed material. Due to
wet-fastness properties with direct and reactive A variety of fixing agents are known for the non-eco-friendliness of formaldehyde-based
dyeing on cellulosic fabric. Figures 1 and 2 show application to polyamide fabric to improve wash dye-fixing agents, the demand for
the type of dye-fixing agents available for cotton fastness. These agents, termed syntans, are non-formaldehyde-based fixing-agents has
and polyamide fabrics. low-molecular-weight polymers with anionic increased.
Most anionic dyes are members of the groups which can associate with the nitrogen-
well-known class of acid dyes. Another type of containing groups of the polyamide polymer Properties of a good fixing agent include:
anionic dyes is pre-metallised or metal-complex and form a surface layer that reduces diffusion Good capability with cross-linking agents
dyes, which are the reaction products of of the dye out of the treated fibre. Syntans are Good levelling and migration properties
chromium or cobalt and selected dyes. Most condensation products of aromatic sulphonic No effect on the shade
popularly, acid or metal-complex dyes are used acids and formaldehyde derivatives. Syntans are Good affinity for the fibre
for dyeing and printing of nylon fabrics. The acid unstable to shear forces and hence not suitable Stable to steaming and dry heat
dye is held on polyamide by an ionic bond or in jet dyeing machine. Improving overall fastness properties
ISSUE 3 2015
P 27 - 29 Dye Fixing.indd 27 27/03/2015 13:42
D y e i n g F i n i s h i n g P r i n t i n g C o a t i n g
<Technical Briefing> Dye Fixing
It is undesirable that dyestuffs exhibit a lack Application of Fixanol (Conc) and Saradye-FN on cotton fabric
<Technical Briefing>
of wet fastness since the removed dyestuff
may be absorbed by undyed textile material
being washed in the same washing operation
and, in addition, the dyed substrate does not
retain its original shade. Textiles are sometimes
treated after dyeing with a dye-fixing agent in
order to improve the wet fastness of the dyed
substrates.
Against this background Sarex has developed
various dye-fixing agents, viz: Fixanol (Conc)
and Saradye-FN for cotton; Nylofix-993 and
Application of Nylofix-993 and Sarafix-NEW on nylon fabric
Sarafix-NEW for polyamides. Below are the
unique features of the mentioned dye-fixing
agents, which meet the requirements of
customers for improved fastness properties.
Unique features of Fixanol (Conc)/Saradye-FN:
Fixanol (Conc) is concentrated and
Saradye-FN is a ready-to-use dye-fixing
agent
Formaldehyde-free
Improves washing fastness and water
contact
Does not affect the light fastness Improves wet-fastness properties Reactive Red 141 (4% shade)
No effect on the shade of treated Prevents cross-staining during Lanaset Bordeaux 4B (3% shade)
material washing-off of printed goods TJ4 Scarlet Red (3% shade)
Can be applied by exhaust as well as pad No effect on shade or light fastness of
28 dyeing Experimental
Unique features of Nylofix-993/Sarafix-NEW: Low-foaming formulation, hence can be Dyeing of cotton fabric was carried out
Nylofix-993 is a powder while used in soft-flow machine separately with 6% Drimaren Navy X-RBL and
Sarafix-NEW is a liquid dye-fixing agent 4% Reactive Red 141, whereas dyeing of nylon
for polyamide and its blends Materials and Methods fabric was carried out separately with 3% Lanaset
Materials: Cotton fabric; nylon fabric Bordeaux 4B and 3% TJ4 Scarlet Red. After the
Chemicals: Fixanol (Conc), Saradye-FN, completion of dyeing process, the fabrics were
Nylofix-993, Sarafix-NEW subjected to dye-fixation treatment.
Dyestuff: Below are the recipes followed for dye fixing
Drimaren Navy X-RBL (6% shade) on cotton and dye fixing on nylon fabric. To
Figure 3: 6% Drimaren Navy X-RBL dyed cotton fabric Figure 4: 4% Reactive Red 141 dyed cotton fabric dye fixed with Saradye-FN
dye fixed with Fixanol (Conc)
INTERNATIONAL DYER
P 27 - 29 Dye Fixing.indd 28 27/03/2015 13:42
D y e i n g F i n i s h i n g P r i n t i n g C o a t i n g
study the efficiency of dye-fixing agents, the analysed according to the test methods set out Results and Discussion
treated fabrics were subjected to washing in the following standards: The results obtained are shown in Figures
fastness tests. ISO 105 C03: Colour fastness to washing 3 6. Fabrics dye fixed with Fixanol (Conc),
ISO 105 E01: Colour fastness to water Saradye-FN, Nylofix-993 and Sarafix-NEW
Evaluation of Fastness Properties ISO 105 C06 : C2S 60oC: Colour fastness showed very slight staining on multifibre
The efficiency of the dye-fixing agents was to domestic and commercial laundering strip depending on the dosages used. None
of the dye-fixed fabrics showed any shade
change irrespective of the class of dye and
concentration of dye-fixing agent used.
Conclusions
Fixanol (Conc) and Saradye-FN are
non-formaldehyde based cationic dye-fixing
agents for reactive and direct dyes. Nylofix-993
and Sarafix-NEW are novel dye-fixing agents
for dyed and printed polyamide fabric.
After-treatment with dye-fixing agents improves
the washing fastness of the dyed fabrics. Cotton
dyed fabrics treated with 0.25-1% Fixanol
(Conc) and 1-2% Saradye-FN and Nylon dyed
fabric treated with 0.5-1.5% Sarafix-NEW and
0.4-0.8% Nylofix-993 show very slight staining
on the multifibre, thus signifying their utility
in meeting the needs of the textile coloration
market.
Figure 5: 3% Lanaset Bordeaux 4B dyed nylon fabric dye Figure 6: 3% TJ4 Scarlet Red dyed nylon fabric dye fixed
fixed with Sarafix-NEW with Nylofix-993
29
ISSUE 3 2015
P 27 - 29 Dye Fixing.indd 29 27/03/2015 13:42
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Reactive Dye and Disperse DyeDokumen44 halamanReactive Dye and Disperse DyeNguyễn Huy Cường100% (1)
- Dyeing of Acrylic FibresDokumen19 halamanDyeing of Acrylic FibresHugo Eduardo Ipiales Mesa100% (1)
- Levelling Agent For Dyeing Polyester FabricsDokumen4 halamanLevelling Agent For Dyeing Polyester Fabricssusheel deora0% (2)
- Sulphur Dyeing in Exhaust ApplicationDokumen5 halamanSulphur Dyeing in Exhaust ApplicationRezaul Karim TutulBelum ada peringkat
- Green Chemistry DyeingDokumen6 halamanGreen Chemistry DyeingRajdeep SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Wrinkle Free Finishing: by Dr. Pintu Pandit Asst. Professor, NIFT PatnaDokumen18 halamanWrinkle Free Finishing: by Dr. Pintu Pandit Asst. Professor, NIFT PatnaARYAN RATHOREBelum ada peringkat
- Reports On Soaping Agent& Fixing AgentDokumen59 halamanReports On Soaping Agent& Fixing AgentRashed Hasan100% (4)
- Migration Inhibitors Effect On Fabric PropertiesDokumen61 halamanMigration Inhibitors Effect On Fabric PropertiesAsad Jamil Rana100% (6)
- Cotton DyeingDokumen9 halamanCotton DyeingJamal HossenBelum ada peringkat
- OBA Uses in TextilesDokumen2 halamanOBA Uses in TextilesNasir SarwarBelum ada peringkat
- Disperse PrintingDokumen20 halamanDisperse PrintingCamila Suarez100% (1)
- Blend Dyeing (NEW BOOK) (Upload 28-06 - 2007)Dokumen232 halamanBlend Dyeing (NEW BOOK) (Upload 28-06 - 2007)ibayraktar775208100% (1)
- Quality & Process Control in Textile ProcessingDokumen56 halamanQuality & Process Control in Textile ProcessingKeshav Dhawan100% (3)
- Test For The Suitability of Thickener in The Print Paste Formulation and Other ConcepttestDokumen21 halamanTest For The Suitability of Thickener in The Print Paste Formulation and Other ConcepttestGaurav DhawanBelum ada peringkat
- BEN-BLEACH Desizing, Scouring and Bleaching MachineDokumen16 halamanBEN-BLEACH Desizing, Scouring and Bleaching MachinearjmandquestBelum ada peringkat
- Dye Fixing AgentDokumen2 halamanDye Fixing AgentSachin Patil100% (1)
- RFT in Reactive DyeingDokumen24 halamanRFT in Reactive DyeingRezaul Karim Tutul100% (9)
- Pigment Dyeing - ExhausionDokumen12 halamanPigment Dyeing - Exhausionviathung02Belum ada peringkat
- Analyzing Electrolytes for Reactive Cotton DyeingDokumen6 halamanAnalyzing Electrolytes for Reactive Cotton DyeingRajeev MehraBelum ada peringkat
- Exhaust Dyeing Polyester with Disperse DyesDokumen16 halamanExhaust Dyeing Polyester with Disperse DyesBurak EmekliogluBelum ada peringkat
- Product SurveyDokumen26 halamanProduct SurveyAdnan PervaizBelum ada peringkat
- Reactive DyeingDokumen23 halamanReactive Dyeingshivkalia8757100% (2)
- Dyeing of Polyester - Cotton BlendsDokumen2 halamanDyeing of Polyester - Cotton Blendstkr163Belum ada peringkat
- Textile Warp SizingDokumen19 halamanTextile Warp SizingAmir YasinBelum ada peringkat
- Dyefix-CF - Dye Fixing Agent With Excellent Fastness To Chlorine.Dokumen10 halamanDyefix-CF - Dye Fixing Agent With Excellent Fastness To Chlorine.L.N.CHEMICAL INDUSTRYBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Testing For FabricDokumen24 halamanChemical Testing For FabricParth Dev Verma100% (3)
- 90 Questions of Garments Washing & Dyeing.Dokumen26 halaman90 Questions of Garments Washing & Dyeing.Ferdous Khan RubelBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE CIT Textile Chemical Processing-XII Text PDFDokumen124 halamanCBSE CIT Textile Chemical Processing-XII Text PDFJacob Kalloor100% (2)
- MercerizationDokumen7 halamanMercerizationRahadian Noor MadanyBelum ada peringkat
- Continuous Bleaching RangeDokumen8 halamanContinuous Bleaching RangeKhandakar Nayem100% (1)
- Pigment Printing of CottonDokumen14 halamanPigment Printing of Cottonrbchavan100% (1)
- Disperse DyesDokumen6 halamanDisperse Dyescoolsiash44Belum ada peringkat
- Clariant NewDyestuffWorldDokumen12 halamanClariant NewDyestuffWorldNaeem Shehzad50% (2)
- Bleaching of WoolDokumen5 halamanBleaching of Woolahmer adnanBelum ada peringkat
- Eco-friendly textiles: reducing environmental impacts across the production chainDokumen17 halamanEco-friendly textiles: reducing environmental impacts across the production chainMehedi Hassan EvanBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions For Polyester DyeingDokumen9 halamanSolutions For Polyester DyeingSandeep Behl50% (2)
- Dyeing ProblemsDokumen12 halamanDyeing ProblemsShivam Bajpai100% (1)
- University of Management and Technology: Textile Labs Wet Processing Lab Manual TX-232Dokumen16 halamanUniversity of Management and Technology: Textile Labs Wet Processing Lab Manual TX-232Safdar ZafarBelum ada peringkat
- Automat Process For Reactive DyeingDokumen3 halamanAutomat Process For Reactive DyeingRezaul Karim Tutul100% (1)
- Thermefix 338 Continuous Dyeing RangeDokumen48 halamanThermefix 338 Continuous Dyeing RangeImran Malik100% (1)
- Identification&Class DyesDokumen38 halamanIdentification&Class DyesAmit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Solving - KnitsDokumen17 halamanProblem Solving - KnitsBhaskar Mitra100% (1)
- Classification of Dyes: Natural, Synthetic, and by ChromophoreDokumen12 halamanClassification of Dyes: Natural, Synthetic, and by ChromophoreSabeeh Ul HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Dyeing-Pad Batch AssignmentDokumen22 halamanDyeing-Pad Batch AssignmentTooba Anum100% (1)
- Polyester ProcessingDokumen16 halamanPolyester ProcessingSoumen Bag100% (3)
- Chemical Used in TextileDokumen24 halamanChemical Used in TextileFeroz Alam0% (1)
- Dye ClassesDokumen13 halamanDye ClassesGayatrimoneBelum ada peringkat
- Dekol Disperse SNS MSDSDokumen11 halamanDekol Disperse SNS MSDSMuhammad Aasim HassanBelum ada peringkat
- DyeingDokumen21 halamanDyeingTanavi KhandpurBelum ada peringkat
- Cold Pad BatchDokumen5 halamanCold Pad BatchCarlos Ernesto Aguilar López100% (2)
- Dyeing AND Printing: Assignment-2Dokumen21 halamanDyeing AND Printing: Assignment-2Kumar GauravBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Wet ProcessingDokumen84 halamanIntroduction To Wet Processingzynab123Belum ada peringkat
- Intro, Classification & Functions of Auxiliaries .PPTX Lecture 123Dokumen16 halamanIntro, Classification & Functions of Auxiliaries .PPTX Lecture 123nida0% (1)
- Textile Dyeing Process ExplainedDokumen10 halamanTextile Dyeing Process ExplainedMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Terasil Standard Dyeing MethodDokumen1 halamanTerasil Standard Dyeing MethodKhandaker Sakib FarhadBelum ada peringkat
- The Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes V6: Reactive DyesDari EverandThe Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes V6: Reactive DyesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Mcquillan Rissa Nen Roberts 2013Dokumen11 halamanMcquillan Rissa Nen Roberts 2013MaggieWoodsBelum ada peringkat
- Free Cutting Julian RobertsDokumen129 halamanFree Cutting Julian RobertsalbabrazoBelum ada peringkat
- Free Cutting Julian RobertsDokumen129 halamanFree Cutting Julian RobertsalbabrazoBelum ada peringkat
- Fashion of Early 20th Century Part2Dokumen38 halamanFashion of Early 20th Century Part2MaggieWoods100% (2)
- Fashion of Early 20th Century Part1Dokumen38 halamanFashion of Early 20th Century Part1MaggieWoods100% (7)
- Epoxy Coating GuideDokumen8 halamanEpoxy Coating GuideAzlan Othman100% (1)
- Module 1 - ElectrochemistryDokumen31 halamanModule 1 - ElectrochemistryjeniferBelum ada peringkat
- IJBE-9-3-2021 Bahrami Guillot 13 30Dokumen18 halamanIJBE-9-3-2021 Bahrami Guillot 13 30Elina EsfandiariBelum ada peringkat
- TRUEDokumen50 halamanTRUECLARISSA TAGUBABelum ada peringkat
- Spring Manufacturing ProcessDokumen4 halamanSpring Manufacturing ProcessUzma sijratBelum ada peringkat
- 1-S2.0-S0360128515300149-Main Imp PDFDokumen40 halaman1-S2.0-S0360128515300149-Main Imp PDFSuresh ChinniBelum ada peringkat
- Closed Book API RP 577 Practice QuestionsDokumen10 halamanClosed Book API RP 577 Practice QuestionsIslam Fawzy100% (1)
- 16 - SEC Nickel Cadmium Pocket Plate - I O Manual May 2008Dokumen75 halaman16 - SEC Nickel Cadmium Pocket Plate - I O Manual May 2008PrashantKumarBelum ada peringkat
- Capítulo J - Diseño de Conexiones AISCDokumen36 halamanCapítulo J - Diseño de Conexiones AISCArgentina EspinozaBelum ada peringkat
- Project On Soil TestingDokumen33 halamanProject On Soil TestingVinayPawar67% (3)
- Sustainable StationeryDokumen34 halamanSustainable StationeryMonica Cortina72Belum ada peringkat
- Effects of PVC Pipes on the EnvironmentDokumen9 halamanEffects of PVC Pipes on the EnvironmentNeeraj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Que BankDokumen26 halamanSteel Que BankyawaleapurvastBelum ada peringkat
- CRC Handbook KivonatDokumen12 halamanCRC Handbook KivonatPresslly Gebol LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Deck Institute Diaphragm Design Manual Second EditionDokumen279 halamanSteel Deck Institute Diaphragm Design Manual Second EditionGeoffre14Belum ada peringkat
- A Powerpoint Presentaion On Ready-Mix ConcreteDokumen22 halamanA Powerpoint Presentaion On Ready-Mix ConcreteGowriSenthilBelum ada peringkat
- Commitment To Sustainability: Parson Adhesives' Environmental ResponsibilityDokumen1 halamanCommitment To Sustainability: Parson Adhesives' Environmental ResponsibilityParson AdhesivesBelum ada peringkat
- Guide For The Gas Shielded Arc Welding of Aluminum and Aluminum Alloy PipeDokumen38 halamanGuide For The Gas Shielded Arc Welding of Aluminum and Aluminum Alloy PipeCGRRBelum ada peringkat
- B4 Fracture and Size EffectDokumen7 halamanB4 Fracture and Size EffectClaudio Masjid MaktubBelum ada peringkat
- A574m PDFDokumen7 halamanA574m PDFLeonardo GomideBelum ada peringkat
- Cumene: Process Features Process BenefitsDokumen2 halamanCumene: Process Features Process BenefitsGerman Arrieta ZapaBelum ada peringkat
- Partial cement replacement with rice husk ashDokumen12 halamanPartial cement replacement with rice husk ashGbenge JoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- محاظرة 4Dokumen10 halamanمحاظرة 4iiHaiderBelum ada peringkat
- ChemicalDokumen1 halamanChemicalTimothy John IgnacioBelum ada peringkat
- Geotechnics With GeosyntheticsDokumen24 halamanGeotechnics With GeosyntheticsAnonymous VeDNBhBelum ada peringkat
- Saep 1145Dokumen20 halamanSaep 1145Amit shah100% (1)
- Conservado SP: Water-Repellent For Facades With A High Protective PowerDokumen2 halamanConservado SP: Water-Repellent For Facades With A High Protective PoweracarisimovicBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen ProbeDokumen4 halamanHydrogen ProbemahiengBelum ada peringkat
- HaloalkaneDokumen20 halamanHaloalkaneHediarta Widiana PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Metallurgy - Chapter (5) - Steels and Cast IronsDokumen79 halamanMetallurgy - Chapter (5) - Steels and Cast IronsKarim Mamdouh100% (1)